Background
Fostering change through the alterations of the organizational culture is a necessary step toward improving the overall service quality and rising customer loyalty and satisfaction levels. Moreover, the importance of the consistent communication must be borne in mind. Therefore, the introduction of a coherent strategic corporate management (SCM) tool should be viewed as necessary.
The phenomenon of SCM is not new and has several definitions; however, by far the most accurate one has been provided by Komer (2014). According to the latter, the phenomenon of SCM can be viewed from several angles and, therefore, can be identified as either the process of assisting an organization in building its capacities and values, or creating a framework that would shed light on the nature of internal and external processes within a firm, or studying the choices made and actions taken by the company’s staff so that a better understanding of by what factors the decision-making process in the firm is driven (Komer 2014).
Therefore, a more detailed analysis of the SCM framework adopted by an organization will allow exploring the nature thereof and the mechanisms of its operation in the context of the target market’s economic environment. One might argue that the process of exploring the strategic management framework used by a firm does not necessarily imply that the outcomes should be contextualized by defining their effects in a specific market. However, it could also be claimed that the development of a particular SCM framework is guided by the need to design the system that will provide flawless functioning in the realm of the target environment. Therefore, the choices of the SCM tools are likely to hinge on the specifics of the external environment as well. Herein lies the importance of studying the National Bank of Abu Dhabi (NBAD) from the perspective of the global market and the challenges that it poses to organizations.
When considering the factors that compelled the members of NBAD to reconsider the existing tools for managing the organizational processes within the context of the firm and alter the relationships between the staff members and managers toward fostering talents and encouraging development, one should mention the fact that NBAD has been suffering from high staff turnover rates (National Bank of Abu Dhabi 2016). Because of low satisfaction rates among the members of the organization, the turnover process was becoming increasingly more intense, which affected the quality of the company’s services to a considerable extent. Indeed, with the regular introduction of new staff members to the context of the company’s environment, there was the need to wait until the adjustment process finishes and the newly recruited participants are fully aware of the company’s goals, as well as capable of meeting the set performance standards. Therefore, delays and the failure to meet the quality standards set by NBAD an expected from it by its customers became glaring. The drop in performance levels and the subsequent reduction of the firm’s profit margins were the primary threats that NBAD was trying to avoid, and the promotion of the strategic corporate management system that would hold the company together was viewed as a viable solution.
The case of NBAD shows that investing in staff members and their further professional development is a critical step for any organization, and especially those that operate in the realm of the global economy. Because of the necessity to develop multicultural ties and cater to the needs of an increasingly diverse population, companies such as NBAD need to introduce the principles of talent management into their framework. Thus, the premises for the further rise in loyalty levels among employees, an increase in their motivation, and the enhancement of the corporate performance can be expected.
Considering the unique system for enhancing the strategic corporate management processes, in general, and the redesign of the principles of cross-cultural communication, in particular, along with a significant change in the approaches to information sharing within the system of NBAD, therefore, makes the case under analysis a rather peculiar one to consider. By taking a closer look at some of the challenges faced by the organization, the methods designed to address the specified impediments, the concept of talent management as it was interpreted by NBAD, and the alterations that had to be made to reconcile the UAE culture and the contemporary requirements for carrying out key business processes, one will be able to shed more light on how to promote the active organizational change.
Multinational Talent Management Framework: Review
The focus on the active use of the merit-driven reward as the foundational principle for implementing strategic corporate management is what sets the National Bank of Abu Dhabi (NBAD) apart from other UAE organizations (McCoy 2014). The company must be credited for its focus on the active fostering of essential qualities and values in its staff members, as well as searching for their hidden talents and creating the environment in which these latent abilities can evolve. As a result, NBAD has built a reputation of one of the most innovative and progressive companies in the environment of the UAE economy (National Bank of Abu Dhabi 2015). As shown in Figure 1 below, the framework is rather basic, yet it contributes to the active promotion of staff’s progress and, therefore, a rapid improvement of service quality.
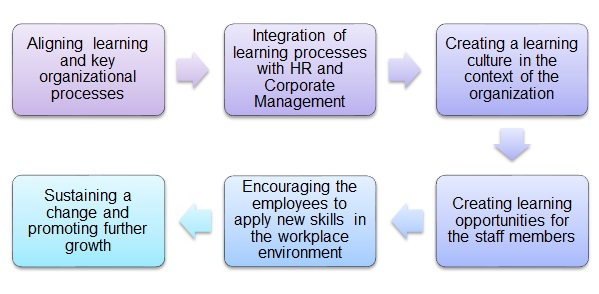
The specified approach allows NBAD to create premises for the consistent improvement of its services. Indeed, by investing in its staff members, the firm contributes to its rapid development and the active promotion of positive change in its environment. Furthermore, the emphasis on the multinational cooperation helps enhance the process of cross-cultural communication. For instance, the conflicts and misunderstandings that may occur in the process can be addressed successfully.
Furthermore, the introduction of a multinational approach to human resource management (HRM) is likely to lead to the further enhancement of the interdisciplinary approach toward corporate communication. To be more accurate, the process of active information and experience sharing is likely to transcend the environment of a single department and grow into the open communication process between all employees working an NBD. Consequently, the foundation for the active learning of new information and skills will be built. Furthermore, apart from encouraging the staff to engage in the consistent process of sharing information, one is likely to remove the boundaries between different elements of the corporate environment and, thus, create the platform for an uninhibited dialogue between all company members. In other words, along with the active exchange of information, corporate transparency of the key organizational processes is introduced into the framework of the firm’s operations.
Herein lies the significance of the multinational framework promoted at NBAD. The suggested approach contributes to the enhancement of the key corporate processes extensively through the reconsideration of the current data management framework. As a result, the premises for a consistent improvement in the company’s performance are created (McCoy 2014).
The application of the multinational talent management framework as the means of galvanizing the company’s performance and improving NBAD’s record should also be viewed through the prism of managing the company’s resources, in general, and its people, in particular. The human resource management (HRM) strategy that the NBAD organization deploys is based on the idea of encouraging the staff members to focus on exploring their talents and addressing their weaknesses so that the premise for a consistent professional growth could be built. The creation of the environment in which employees feel enticed about the idea of the unceasing personal and professional growth must be regarded as NBAD’s key success.
A closer look at the success of the strategy and the factors that contribute to it will reveal that NBAD has designed an elaborate approach toward making its organizational culture, the cultural values and traditions of Middle East, and the unique characteristics of its staff members compatible.
National Bank of Abu Dhabi: Narrative
The NBAD was founded in 1968 by Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan (McCoy 2014). It quickly grew into one of the most influential organizations in the UAE. At present, the company is considering an expansion into the global market (McCoy 2014). In retrospect, NBAD partially owes its framework for multinational talent management and the success thereof to Towers Watson, a firm with which it collaborated prior to the reconsideration of its organizational design. Towers Watson influenced massively the way in which NBAD managed its HRM framework and the design of the organizational behavior management, taking a huge step in advancing the relationships between NBAD’s employees and managers. Particularly, the partnership between NBAD and Tower Watson has led to a total reconsideration of the former’s approach toward career advancement of its staff, especially as far as the grading structure was concerned, the transfer from a 16-star to a 5-star assessment of the employees provided an opportunity to simplify the assessment, at the same time retaining its essential elements intact; as a result, the outcomes of the evaluation still informed the choices made by HR managers, yet the process of determining the employees’ progress and assets became considerably less convoluted (Buchanan & Ahmad 2014).
The collaboration with Towers Watson, thus, can be deemed as the essential milestone in the development of NBAD and its SCM. However, apart from the advantages that shared experience provided, NBAD also had to utilize a significant amount of its resources to sustain its technological progress and support the newly introduced changes with the IT tools that it had at its disposal at the time. In retrospect, the importance of using IT innovations as the methods of encouraging change and convincing the staff members to accept it was paramount. By incorporating IT resources into the set of tools used for managing the changes in the organizational context, the managers at NBAD managed to institutionalize the identified alterations and convince the staff members to accept the latter, thus, addressing possible resistance issues. Indeed, a closer look at the effects that the application of the stated technologies has had on the organizational change will reveal that the identified tools contributed significantly to the improvement of information management, particularly, the process of analyzing the feedback received from the staff. As a result, the employees’ voices were heard, and the appropriate steps were taken to make sure that the staff members’ loyalty levels should remain high.
One must also give the developers of the framework credit for putting an impressive effort into the development thereof. After a scrutiny of the current strategic corporate management approach, one will have to admit that it must have taken the company a lot of patience to make sure that the innovative approach toward fostering the active growth of the staff members and the support of their discovery is their hidden assets and talents should coincide with the long-lasting traditions and values of the UAE society, which have perpetuated themselves in the UAE business world as well (Institute of Developing Economies 2015). The integration of the developmental program aimed at fostering the consistent professional development among the members of the NBAD within the existing system of values and standards can be viewed as one of the key accomplishments of the organization (Ahmed 2016). The result was achieved by locating a compromise between the traditional UAE values such as the adherence to traditions and the careful and steady promotion of innovative thinking within the context of the NBAD organizational environment.
Difficulties: Performance Data, Corporate Strategies, and Value Creation
Even though NBAD has managed to introduce the principles of talent management into its organizational structure successfully, claiming that the process of making a change to the environment of NBAD was completely flawless and did not imply dealing with any hindrances would be quite a stretch. For instance, the creation of the environment in which the staff members could feel secure and, therefore, be willing to stay and grow professionally, was an admittedly difficult task. As stressed above, high turnover rates in the organization were caused by the lack of the value system that could keep the organization together and introduce its members to the idea of corporate loyalty. The NBAD leaders managed to locate a rather elegant solution to the specified concern.
By navigating between the active enhancement of the policy that implies investing in the employees’ development extensively and the traditional values that lauded the qualities such as loyalty and trust, the company managed to build relationships with its staff members from scratch, therefore, reinventing the employees’ attitude toward the company and its philosophy. The identified approach allowed altering the target audience’s perspective without facing a significant amount of resistance from it. Indeed, the emphasis on the provision of assistance to staff members in their attempts to explore and fulfill their potential seems to have a tangibly positive effect on the employees’ attitudes toward the organization. The lack of trust that defined the previous increasing high turnover rates seems to have been replaced with a steady growth in corporate loyalty levels (Cherian & Farouq 2013).
Furthermore, the issue of the unwillingness to accept the responsibilities that the new values and principles of corporate relationships implied should be listed among the primary areas of concern that NBAD had to face. The introduction of opportunities for the staff members to acquire new skills and knowledge served as a powerful impetus for the personnel at NBAD to follow the suggested behavior models and focus on exploring and fulfilling their potential. The resistance levels among the members of NBAD were minor, which allowed handling them efficiently. Because of the evident advantages that the people accepting the provided system of SCM received, the implementation of the talent-oriented HR framework and the further enhancement of the corporate policies based on the established behavior standards became comparatively easy for NBAD.
Finally, the issues associated with the quality of the end product had to be addressed so that NBAD could continue working in the same intensity mode as it used to before the introduction of talent management principles as the foundation for the SCM framework. There is no need to stress that the shift toward an entirely new system of values and corporate standards is likely to lead to a major disruption in the company’s key processes, as well as cause some of its members feel comparatively disoriented. The specified issues may affect the success of the decision-making processes, as well as the management of routine tasks (Sidani & Ariss 2014).
Herein lies the significance of setting quality standards and introducing an efficient framework for keeping the emphasis on the corporate priorities and the relevant values. NBAD’s leaders were smart enough to introduce a multiculturalism-oriented system of values prior to the reinforcement of the quality standards and resetting the requirements for the communication process. As a result, when facing the need to transfer to a more complex and challenging mode of conversing with customers, the employees at NBAD managed to retain their enthusiasm and even inspire them to engage in a continuous process of improving their professional skills, as well as acquiring new information and shaping their values to adjust to the principles of multicultural communication (Collings 2014).
Recommendations
By reconsidering the current concept of the communication process and investing in the professional growth of its staff member, NBAD has built the foundation for a rapid enhancement of its performance in the context of the global economy. Because of the necessity to establish intercultural ties and engage in a multicultural communication, at the same time avoiding possible misunderstandings and ensuing conflicts, NBAD had to focus on reinventing the current framework of SCM. In other words, the value system, principles of cooperation, essentials of information management, and other crucial aspects of the company’s operation in the target market had to be altered.
Because of the rigid standards that the organization set from the very start as the principal ideas by which its planning and decision-making was defined, NBAD restricted its opportunities considerably. Herein lies the problem regarding the high staff turnover rates; unable to handle the increasingly large number of responsibilities and tasks, as well as However, the incorporation of talent management and the focus on the enhancement of communication between employees, managers, and customers can be deemed as an essential step in the right direction. By investing in its personnel, NBAD built the platform for fostering its values and the principles of Corporate Social Responsibility to the target audience. As a result, a gradual increase in the motivation levels among the staff and, therefore, the overall quality of the company’s performance can be expected.
It is also advised that NBAD should consider implementing the principles of a top-down approach so that the specifics of relationships within the organization could be explored in detail. Indeed, while providing employees with specific guidelines concerning the application of the relevant standards and values is bound to shape their perception of their roles and responsibilities, as well as the methods of building relationships within the company, indoctrinating the specified principles of communication is barely a possibility since the staff members already have their own concepts of establishing a connection with their peers. Therefore, studying the characteristics of the interpersonal dialogue in the context of a company is a crucial step toward designing the tools that will help supervise and control the changes in the interaction between the staff members. The tow-down framework, in turn, will allow shedding light on the patterns according to which the relationships between the employees are built in the workplace. Furthermore, the target audience’s concepts of decision-making, task management, information transfer, and problem-solving can be determined, and the gaps in people’s knowledge of the subject matter can be identified. As a result, the HRM team will receive essential data about the tools that can be utilized to enhance the performance of the team, as well as the areas that will need further improvements and, therefore, should be viewed as the focus of the further training.
Creating the environment in which staff members will feel enthusiastic about further changes is a complicated yet attainable task. As the recent experience of NBAD has shown, the approach based on appealing to people’s culture and the associated needs is bound to lead to success. Particularly, the identified strategy will contribute extensively to spurring the process of developing international ties through the enhancement of the communication process. By preventing the instances of cross-cultural conflicts from occurring and engaging its staff members in the process of continuous self-directed education, NBAD will shape its corporate environment so that the threats of cross-cultural conflicts will be minimized, and the occurring misconceptions will be used to reduce the threat of cultural confrontations to an even greater degree. As a result, NBAD will be able to build strong international ties and cement its position in the global market.
Reference List
Ahmed, NOA 2016, ‘Impact of human resource management practices on organizational citizenship behavior: an empirical investigation from banking sector of Sudan’, International Review of Management and Marketing, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 964-973.
Buchanan, FR & Ahmad, SZ 2014, ‘Business in developing countries: globalization of a large emerging market bank’, Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1-16.
Cherian, J & Farouq, S 2013, ‘Does effective leadership style drive financial performance of banks? Analysis in the context of UAE banking sector’, International Journal of Economics and Finance, vol. 5, no. 7, pp. 105-114.
Collings, DG 2014, ‘Integrating global mobility and global talent management: exploring the challenges and strategic opportunities’, Journal of World Business, 49, no. 2, pp. 253–261.
Institute of Developing Economies 2015, Boards of directors and bank performance in United Arab Emirates, Web.
Komer, F 2014, Conceptualizing processes of strategic change. the contribution of an attention-based view to strategy formulation, GRIV Verlag, New York, NY.
McCoy, L 2014, United Arab Emirates, Simon and Schuster, New York, NY.
National Bank of Abu Dhabi 2015, Towers Watson, Dubai, UAE.
National Bank of Abu Dhabi 2016, Consolidated financial statements, Web.
Sidani, Y & Ariss, A 2014, ‘Institutional and corporate drivers of global talent management: evidence from the Arab Gulf region’, Journal of World Business, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 215-224.