Prince Henry the Navigator
Prince Henry the Navigator is known to have contributed to the history of America by playing a significant role in the development of slave trade routes.
Even though he was not a sailor who explored the world, he discovered and financed several sea routes from North and West Africa to the Indies.
He was the son of the King of Portugal in addition to being a devoted Christian. One of his first ever success was when he discovered some of the islands in the West Indies.
The positions of the islands could be calculated from the harbor, and as Prince Henry sent his young men, they were able to return.
In essence, the routes which were used in these navigations became important for the development of trade and commerce. Also, the routes were also used for the development of the slave trade.
The Columbian exchange
In the late 15th century, Christopher Columbus came to America, particularly the Caribbean region. The arrival was met with an exchange of various items, diseases, and ideas.
As he made the voyage to the Americas, he met Native Indians who had occupied most of the land within the region (Davidson, 102).
The most noteworthy change that took place during this time was the displacement of the locals from their land. The Native were dispossessed of their land and were made to still hang around and watch as others make good use of the land.
Five other tangible things have also been described by historians to be the major exchanges that took place during this period. They include sugar, disease, horse, potato, and corn.
The intangible items that were exchanged include ecology, corporate structure, and liberty. These ideas have had a lasting impact which is still witnessed up to today. Globalization can be attributed to the exchange of ideas that took place during the Columbian exchange.
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés was a Spaniard who assisted in the conquest for what is today known as Latin America. During the early 16th century, he sailed to the Dominican Republic and to Cuba, where he reinforced the effort of the Spaniards to conquer the two areas.
He was very courageous in his pursuit. Through the conquest, the region was able to become civilized. He later became the governor of the New Spain after conquering Mexico and some of the Latin American colonies.
Before the beginning of the 16th century, the Americas were predominantly occupied by indigenous Americans. These groups practiced hunting and gathering. It is believed that they got into America through this practice of hunting and gathering.
They were able to enter Alaska using the land bridge that connected Siberia and Alaska. It is believed that during that time, the region was filled with ice and it was easy to navigate through.
However, later when the ice melted, the connected regions were separated. As a result, those who remained in Alaska were also separated from the rest.
Later on, they began to move down to the central plains, and as the ice caps continued to melt down, the region around Alaska and the North became habitable for living things. The Native Americans continued with their life style of hunting and gathering.
By 2500 BC, the natives began venturing into different lifestyles. They started cultivating crops in addition to hunting and gathering. Evidence of these activities was found in the area around present-day Mexico.
The farming methods did not depend on planting seeds because the land could not be easily plowed. Technological development and innovation in agriculture remained unexplored. The crop species were planted individually.
The community that settled in present South America was engaged in the cultivation of crops such as cotton, chili, and corn. Out of the cotton, they were able to make some weaves to cover themselves.
Civilization was not a strange thing to the region because, by 1000 BC, the Gulf of Mexico experienced some development. The development is attributed to the efforts made by the Olmec community.
The beginning of civilization in America is evident in the culture of the Olmec community. They set the pace for development as other communities also followed suit. The pattern of civilization set in the south and Central American regions influenced other regions.
However, when the Spaniards conquered the region, they were shocked by the development. They decided to destroy everything they saw and impose their civilization and development.
There is no doubt that the native communities had differences and similarities in their cultures. Some practiced agriculture while others remain hunters and gathers.
Civilization was first seen in the communities around Central America while the others remained uncivilized. The differences in culture can arguably be a result of the need to adapt to their local environment.
With regards to cultural similarities, the various communities were organized in clans. The clans had an individual figure that can be used to trace their descent. The communities also had leaders, some of whom were elected while others inherited their leadership position.
In addition to the clans, the communities spoke the same language. They were all religious and spiritual. They believed in the power of spiritual beings existing in nature.
As a result, there was a need to have peace with nature by protecting and conserving it. The spiritual leaders could consult the nature spirit for almost anything in life.
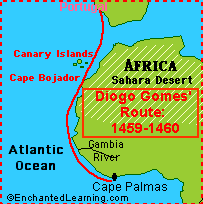
Figure 1: trade routes discovered by Prince Henry
The image above indicates one of the routes discovered and funded by Prince Henry the Navigator. The route shown in the image is called the Diogo Gomes route which connected Portugal to the Canary Islands, Cape Verde, and Western African regions.
As earlier mentioned, Henry played a significant role in the development of trade between various regions in the world.
Even though he was not a sea sailor, he managed to provide financial resources that led to the discovery of trade routes. From the routes he discovered, the slave trade was initiated.

Figure 2: Columbian exchange
The image above illustrates some of the activities that used to take place during the Columbian exchange. The exchange was between North America and three different continents including Europe, Africa, and Asia.
The three continents were considered the old world, while North America was considered the new world. Tangible and intangible items were exchanged between the old and the new world. People from the old world began to settle in the new world and interacted with the natives.
They exchanged cultures and ideas. Some of the ideas that were developed during the period are believed to have had a lasting impact.
At the same time, the commodities that were exchanged were completely new for each world. For instance, Europe had never used tomatoes and potatoes before. As the commodities were traded to Europe, they took time before gaining acceptance.

Figure 3: Hernan Cortes’ expedition
The image above shows one of the expeditions that were led by Hernan Cortes in the conquest of regions in Latin America. The Aztec community in Central America contributed to the civilization of the region and had even formed an empire.
Upon the arrival of Hernan Cortes in the region, the conquest by Spaniards began. He was able to bring down the empire and subject the region under the rule of the Spanish King.
His bravery led to the expansion of Spanish rule in the region. He is considered to be among the pioneers of Spanish colonization in Central America.
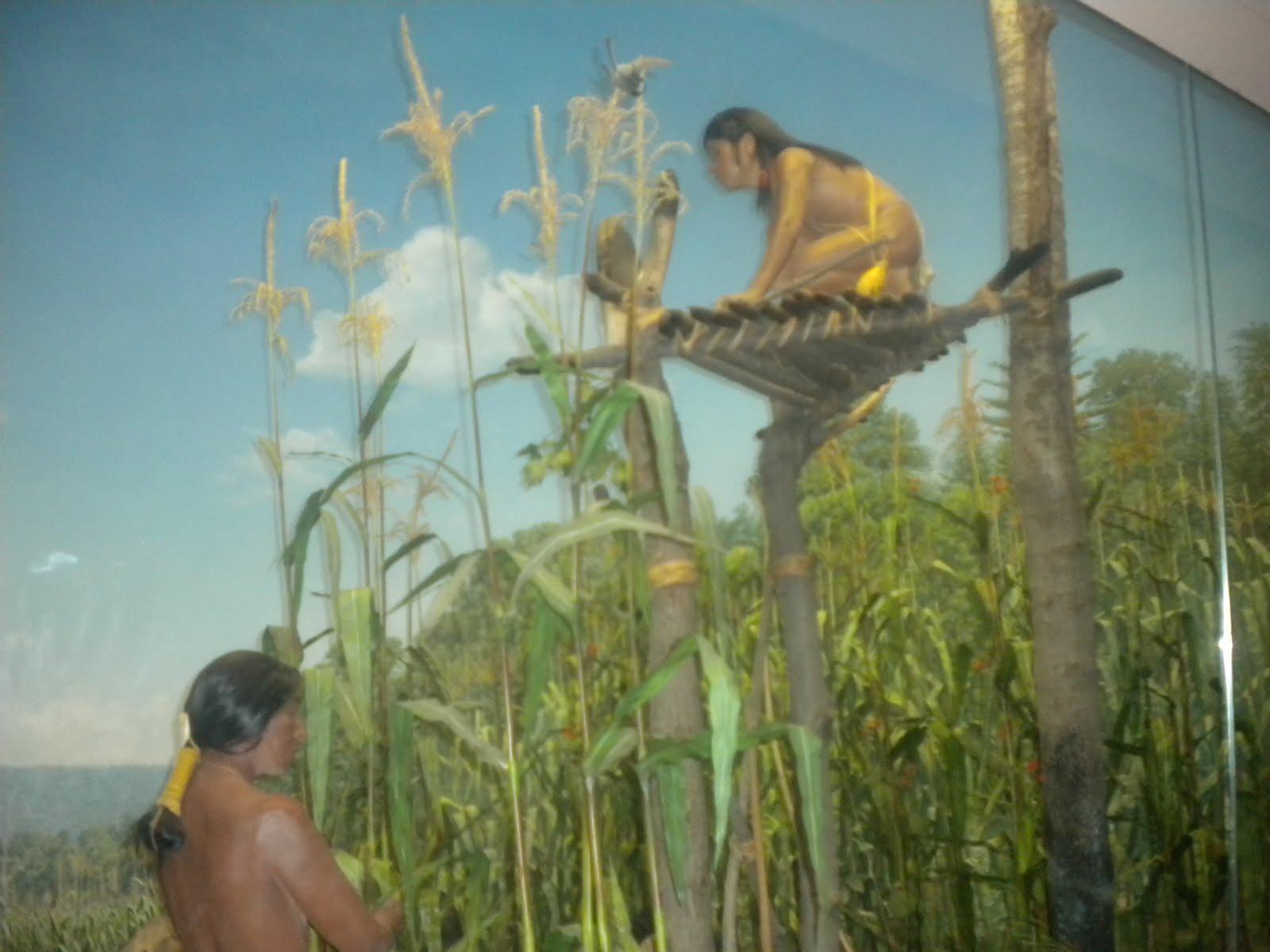

Figure 4: Native culture
The image above illustrates the farming activities that the natives practiced before the start of the 16th century. The native Indians were diverse in their economic and cultural practices. This was because they settled in different geographical locations across the Americas.
They adapted differently to their surrounding environments. Some of them were forced into cultivation of crops because that was the easiest way to survive while others continued with their traditional practice of hunting. Civilization also took place during their time.
There is evidence of development especially with the communities that occupied Central America. Despite the differences, there were numerous similarities in their cultures.
The similarities ranged from their cultural organizations to their belief systems. For instance, as it was mentioned earlier, they used to organize themselves in clans, and they believed in spirits that existed in nature.
Works Cited
Davidson, James West. US: A Narrative History, Volume 1: To 1877. New York: McGraw Hill, 2008. Print.