Abstract
There is a significant interdependent relationship between the Office of Strategic Services (O.S.S) operational groups and the effectiveness of governance structure. The primary purpose of establishing an O.S.S functional group encompassed gathering intelligence from rival countries and using the information during decision-making. The strategy demonstrated core effectiveness by distributing the power and enhancing dominance against Germany.
This study explores dynamic concepts steered by the development of the O.S.S operational group and relativity to governance approach. The research methodology involves analyzing secondary sources under the gradient of national interests and measuring the effectiveness scale. The outcome affirms the thesis statement regarding the profound influence of the O.S.S operations towards promoting the incorporation of functional international relations and peaceful coexistence across the global community.
Introduction
Significance of the Study
World War II optimally influenced international relations due to the variate consideration of dominance in the intelligence framework. One of the factors that highly affects military performance and attack strategy enshrines acquiring crucial information regarding the enemies. In this case, the countries involved in the battle proficiently used spies and global networks to attain vital insights concerning the rivals as a formative aspect of decision-making.
The Office of Strategic Services (O.S.S) operational groups are an outcome of the American government’s strategic combat initiatives. Despite using spies to acquire vital details, the administration assigned different teams dynamic tasks encompassing attacking villages in a short span and retrieving to the home country. Therefore, the core factor engulfed maximizing surprise assaults in the dissentient nations. The aspect fostered gathering of intelligence based on the weaknesses and strengths of rivalries across the various regions attributing in the decision-making among the executive military personnel.
The study of the importance of O.S.S operational groups is attributed to the attainment of crucial insight concerning information during wrangles. Different countries uphold distinct practices and strategies during battles (Deterding, 2020). However, the efficiency optimally relies on attained intellect regarding the rivalries. The lack of adequate details risks poor decision-making and dysfunctional policies.
Therefore, it is the responsibility of key stakeholders to coordinate in the governance of a nation and distribution of power to alleviate bias and contrasts on philosophical foundations. The derived overview intensifies the evaluation of crucial variables that impact international relations and the implementation process within the academic scholarly domain. In a different spectrum, the interdependent relationship exploration contributes to the pool of ideologies concerning strategic management mainframes for administrators.
O.S.S operational groups is an initiative aptly used during World War II to influence dominance based on decisions made by the government officials and policies implemented for counterattacks.
Research Objectives
- To investigate the impact of O.S.S operational group strategy during World War II.
- To assess the impact of international relations on alleviating World Wars.
- To determine the significance of intelligence to policy development and implementation.
- To establish the interdependent relationship between dynamic philosophies and governance structure.
Research Questions
- What was the impact of O.S.S operational group strategy during World War II?
- What was the contribution of international relations to World Wars?
- What is the significant relationship between intelligence and policy development and implementation?
- How do dynamic philosophies affect the governance structure of a country?
Reviewed Sources
America faced a profound challenge after the Second World War due to the proficient spread of communism against the preferable capitalism philosophy. One of the emergent social and economic consequences involved the Vietnam conflict and the increased inflation rate (Maddox, 2018). Establishing the integral approach of effective recovery is crucial to alleviating the imminent problem. The loss of soldiers and property destruction derailed the aspect’s convalescence, highly influencing the trade relations and the trickle-down effect of the accrual benefits.
World War II contributed to a significant loss of American lives and the destruction of property. Apart from the damage, the government prompted investing in weaponry to win the combat, compromising the economic growth and development index. Researchers argue that capitalism leads to competition despite the adverse effect on the population (Maddox, 2018). It is one of the factors that contributed to the conflicts as a means of profitability at the expense of the soldiers’ lives and the parsimony’s performance outlier. The primary responsibility of all stakeholders encompasses enhancing the advancement of standards to justify the framework and the interdependent variables. In this case, the mainframe attributed to a dynamic impact towards the burgeoning contrary to Russia’s recovery in the short run due to the coordinative efforts.
The emergence of World War II highly affected countries that engaged during World War I due to the adept impact on the socio-cultural and economic foundations. During the industrialization era, the European nations attained profound developmental initiatives such as technological advancement (Kumari & Tiwari, 2022). It is a condition that cultivated tension across countries due to the differences in achievements and power status. An excellent example of the impact of development is the essence of imperialism and alliance justified by militarism. The short-term and long-term causes of the battles are a consequence of the notable blooming; hence nations focused on establishing their worldwide position.
One of the significant differences between the two world wars is the short-term cause of the conflicts. At the onset of the first combat, although there was tension among nations, Archduke Franz Ferdinand’s assassination, was heir to the Austro-Hungarian leadership. He was murdered by a Serbian nationalist known as Gavrilo Princip. The two countries were rivals; therefore, assassinating an influential person in one of the parties triggered the clash (Kumari & Tiwari, 2022). The provocation of the second military confrontation engulfed the disagreements and arrogance between the American and Japanese governments.
The U.S administration received news of Nanjing’s rape and the Manchurian crisis that led to its decision to establish sanctions against Japan (Huddlestone, 2021). These sanctions included the exportation of oil, iron, and essential supplies. It is an initiative that significantly affected the economic growth in Japan hence the promptness to foster an attack at Pearl Harbour, thus triggering the tussle. Therefore, while the incite for the first strife was politically inclined, the spark for the second battle was socio-economically inclined.
The establishment of different O.S.S operational groups significantly elevated the attainment of the critical objective. Research by Moon (2018) indicates that the development of the strategy encompassed empowering the military force of countries against the German policy during World War II. In this case, different countries incorporated policies enhancing the incorporation of distinctive O.S.S operational groups. The teams included the American Office of Strategic Services, British Special Operations Executive (S.O.E.), and the French Bureau Central de Renseignements et d-Action. The institutions significantly contributed to gathering intelligence concerning German military operations and action plans to develop countermeasures. Notably, the collection of vital information aptly influenced the objective overview of promoting peaceful endeavors by avoiding biased international relational frameworks.
Evaluation Methods
This study analyzes insights based on relativity to the national interests in a different spectrum. Different countries uphold dynamic socio-cultural, economic, and political philosophies. According to Neuchterlein (2001) cited in Graham (2001), there are four categories of national interests. The frameworks encompass defense, economic, world order, and ideological interests. The distinction in the variables contributes to the objective overview regarding the effectiveness and accomplishment of functional governance structure.
The development of the O.S.S operational group is an outcome based on the intersection of world order and ideological mainframes. As a result, the measure of O.S.S operational groups’ success and failure relies on a distinction between the purpose entailing gathering of intelligence to accomplish the core objective of peace and harmony. Domestic and global relations depend on the decision-making approach among the distinctive administrative entities, hence prioritizing objectivity as the orienting gradient for the practice.
Dependent and Independent Variables
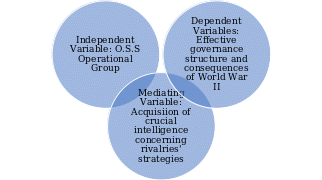
The study focuses on exploring the impact of O.S.S operational groups during World War II. There is a significant interdependent relationship between the dynamic variables due to the attributable factors. On the one hand, the independent variable encompasses O.S.S functional groups. On the other hand, the dependent variables enshrine the consequences of World War II to America’s sociocultural, economic, and political structures. Different countries involved in World War II engaged in the tactical strategy to elevate dominance and win against the opponents. The O.S.S operational group’s primary purpose is to gather intelligence from enemy countries and use the insights to strategize counterattacks. Therefore, the mediating factor to the relationship is the acquisition of intelligence.
Literature Review
Introduction
The First and Second World Wars emanated from similar long-term causes that encapsulated the effect of industrialization on the global territories. Technological advancement is an entity that empowered countries and the necessity to test the limits of power dynamism worldwide. In this case, America and other European states focused on competing for recognition and martial dominance, a concept that enhanced the tension among rivalries (Wilson et al., 2022). Societies with similar philosophies formed alliances to establish an influential baseline while the margin intensified.
The significant frameworks spearheaded the conflicts, and the motivation involved imperialism, nationalism, and militarism. There is a significant difference and similarity between the causes of the two world wars. On the one hand, the long-term triggers of the confrontations involved nationalism, imperialism, industrialization, and militarism. On the other hand, different short-term factors led to the emergence of tussles. While the incitement for the first combat was politically inclined, the instigation for the second clash was socio-economically motivated. The evolution of the global society rendered a significant imbalance among communities to determine the power position internationally.
Influence of O.S.S Operations during World War II
Different scholars establish dynamic effects of the Office of Strategic Services’ dynamic effects on the American military practice. Ames (2020) articulates that the O.S.S emerged as an essential element contributing to the effective gathering of information from rivalries. During World War II, the core value for the battle enshrined the use of strategic initiatives to win the wrangle. Therefore, the central role of the combat groups encompassed infiltrating the hostile nations, stealing crucial details, and returning to the home country. The government exploited the gathered intelligence to make policy decisions and determine essential domains of optimal performance.
Over the decades, the central economic policy that contributed to the significant growth index in America is capitalism. The approach enshrines the personal ownership of property and wealth hence imposing the importance of business competition for optimal profitability margin. The concept rendered a proficient effect to the marginalization of poor communities from the elite social group. However, the American government encountered the challenge due to the philosophy after the Second World War. The core reason for the problem involved the demand for togetherness and cooperation among all stakeholders in rebuilding the country for better living conditions (Maddox, 2018). The aftermath of World War II attributed to the justification of communism and the spread across the highly affected nations globally and a trickle-down effect to the U.S.
The Significance of International Relations
Asia-Pacific
Over the decades, one of the prevalent issues affecting the global society is the competition among the superpower nations towards attaining individual objectives. On the one hand, the U.S seeks to maintain the international order and the ideal security and superpower state globally. On the other hand, China aims to regain its leading influential position within the current global order (Nordin & Graham, 2018). Before colonization, China was one of the leading nations globally in producing goods and trading activities. However, the political influence fostered the derail of Chinese economic growth and maintenance of the top position. An excellent example is the communist ideology and abounds policies that led to the imbalanced distribution of wealth across the Chinese population. The contrasting American and Chinese convergent goals reflect a duel encompassing both parties striving to attain the core objective of power and global influence based on individual principles.
The American socio-economic policy encompasses capitalism, while China’s socio-economic policy is communism. The contrasting policies foster the distinctive differences between the countries. In this case, it becomes hard for the American government to convince China to regain its leading position. According to Nordin and Graham (2018), a significant percentage of the Asia-Pacific region is China’s territories. It is essential to establish the war between U.S and China as a duel of two wrestlers in a ring to battle and determine the winner for the title.
On the one hand, the American motivating factors as a global superpower nation are interest and fear. On the other hand, China’s motivating factors in regaining trading power and influence are honor and fear. Although America attempts to develop a close relationship with China, its fear includes the Chinese winning the economic leadership and altering the international order and global nations’ convergent goals (He & Mingjiang, 2020). Further, China is a major exporter of goods to the American economic entities. Therefore, poor relations between the two countries threaten Americans’ economic and social integrity.
China features the highest population ratio globally, hence the adequate labor workforce and productivity provision. Apart from the vast population, the Chinese territories mark a significant percentage proportionate to the people. Therefore, the country easily accesses the resources and labor workforce to boost productivity. On the other hand, the U.S is a superpower nation and enjoys certain security privileges based on international treaties hence the government’s concern to maintain international order.
Over the decades, Americans have sought to ensure peace and capitalist influence globally to elevate economic growth and development. In this case, there is the fear of the unknown from the American government due to contrasting communist policies (Johnston, 2019). The central communist policy focuses on the equal distribution of wealth. It is an initiative that hinders competence in the business environment. However, the Chinese government seeks to retain the honor and eradicate the fears of the unknown based on the communist policies.
Russia’s International Relations’ Philosophy
Stalin is considered one of the historic mass murderers mainly because of his policies implemented in Russia. The leader considered the ultimate solution of resistance as terror. The first approach to promote development engulfed the exploitation of collectivism among the small farmers. Although the agricultural worker fostered optimal produce, Stalin imposed socialism as the solution in elevating productivity among the kulak (Rozenas & Zhukov, 2019). Nevertheless, the statesman geared violence among the peasants to agree and amalgamate farmlands. The use of intimidation and fear is a high cost that led to the loss of Russian lives to enhance economic development and supremacy on a global scale.
As a political leader, Stalin spearheaded communism in Russia, and the transition incurred a high cost of Russian lives. Between 1933 and 1934, the country experienced famine, and at least four million residents died due to hunger (Rozenas & Zhukov, 2019). The idealist argued that despite the decline in productivity, economic development was a prominent issue over the lives of the workers and the peasants. In this case, Stalin emerged as one of the greatest mass murderers because of his vision to lead the nation to greatness through industrialization. Apart from the famine that led to the deaths of inhabitants and laborers, terror as the primary motivational element caused a significant loss of lives.
Stalin led the Russian economy to communism based on strict policies that cost a significant percentage of workers’ and peasants’ lives. The politician and idealist focused on empowering the nation to avoid being colonized by other developed countries. As a result, Stalin enhanced industrialization based on the essence of boosting communism and economic competence globally (Maddox, 2018). However, the initiative negatively affected the residents and mainly the peasants. The lucrative impact of the concept nurtured its widespread adoption across different nations as a reconstructive philosophy to the negative effect of World War II.
Communism significantly affected the U.S economic growth and development because of the interplay of dynamic values. As a capitalist, the American government faced a profound problem after the Second World War due to the demand for labor and resources to reconstruct the socio-economic system (Maddox, 2018). However, other nations utilized bolshevism to establish the efficient rebuilding of the structures despite gender and ethnic disparity. It is contrary to America’s philosophy on private ownership of factors of production alleviating the inherent challenges of dependence and poverty.
After the combat, tension intensified between the U.S and Russia due to the distinct economic frameworks. It is an initiative that attributed the emergence of the Vietnam conflict and other South American nations with the American administration adopting Russia’s perspective. In the short run, socialism was necessary to enhance the residents’ unity and cooperation. Nevertheless, it was a threat to the enterprise’s profitability in the long run. As a result, the American government focused on enhancing a proficient influential value across a broader scope of the global realms, elevating commercialism.
The Significance of Information to Policy Development and Implementation
The two world wars played a vital role in transforming different states’ socio-cultural, economic, and political domains. One of the key factors contributing to the significant impact from the wrangles involved the media’s role in promoting distinct propaganda. The broadcasting industry focused on monetizing news to acquire market and attain relevance (Jones, 2018). In this case, the news agencies aptly violated the journalism spectrum’s ethos, pathos, and logos ideologies. An excellent example encompassed the lack of advocating for peaceful agreements among states and encouraging youths to enroll in the army to boost defense. The ethical obligation among the professionals enshrines promoting socialization and international relations based on the relayed insights. Despite divergent opinions, the press’s mandate is to advocate for harmonized and sustainable living under the spectrum of propagandas.
The news agency utilizes different forms of advertising and relaying information to the public. A significant percentage of journalists focus on outlets that render a considerable number of audiences for marketability. In this case, researchers establish that one of the factors attributed to intensified war among nations entailed the essence of capitalism (Mehrpouya & Marie-Laure, 2019). The key stakeholders in the industry prioritized profit maximization, hence amplifying the benefits of winning the war while minimally addressing the repercussions of the violence to the international community.
War is an event that poses significant repercussions to the participants and non-partisans due to the optimal destruction. Different societies uphold distinct socio-cultural, economic, and political overviews concerning governance and relationship-building inbound and outbound. Human behavior mainly depends on the rules within a region. An excellent example of an outcome due to the conflict of interests is the emergence of the Great War, also known as World War I. The combat attributed to a profound loss of lives and the wreckage of costly properties.
The survivors encountered prominent health effects due to the horrific experiences and existing wrangles. The lack of agreement among nations risks confrontations that significantly affect residents due to the displacement from their settlements, rise in insecurity, and loss of relatives (Hall & Ross, 2019). Primarily, the psychological consequence among people after World War I encompassed the survivor’s guilt and post-traumatic stress disorder.
One of the factors that led to World War II encompassed the influence of industrialization on the European and American nations. In this case, leaders rendered the initiative to utilize effective and highly graded tools for the bombing, shooting, and facilitating counterattacks against enemies. During World War I, the Americans cooperated with the French armies to fight against the Germans in Arbonne (Cooper, 2021). Although the unity fostered the increase in the number of battalions, it is a situation that caused the loss of a significant number of soldiers due to the lack of strategies for attacks and counterattacks. Although weaponization empowered the armies with an additional support system, the issue lay in the traumatic experiences of hunger, thirst, and loss of colleagues.
The contrast in economic ideologies significantly affected international relations between the capitalists and communists. It is an initiative that attributed the emergence of the Vietnam conflict and other South American nations with the U.S administration adopting Russia’s perspective. In the short run, socialism was necessary to enhance the residents’ unity and cooperation (Sampson, 2019). Nevertheless, it threatened the enterprise’s profitability in the long run. As a result, the U.S government focused on enhancing a proficient influential value across a broader scope of the global realms, elevating commercialism. There was a prominent effect among the Chinese due to opening up the economy to international organizations. Despite extending the Chinese market to other countries through World Trade Organization, the government encountered hindrances on subsistence.
Capitalism is a concept that proficiently influenced international relations between the U.S and other regions through treaties and agreements. The approach enshrines the personal ownership of property and wealth hence imposing the importance of business competition for optimal profitability margin. The concept rendered a proficient effect to the marginalization of poor communities from the elite social group. However, the U.S government encountered the challenge due to the philosophy after the Second World War.
The core reason for the problem involved the demand for togetherness and cooperation among all stakeholders in rebuilding the country for better living conditions (Liczbińska, 2018). The aftermath of World War II attributed to the justification of communism and the spread across the highly affected nations globally and a trickle-down effect to the US. Ideally capitalism is the foundation of the U.S budget akin to China’s communist domain as the pillar of its economy.
The global political economy is a framework that entails the optimal interdependent relationship between private and public power-sharing initiatives. The researcher interprets the international political economy as a foundation for the globalization effect through dynamic theoretical frameworks (Shapiro, 2019). In this case, neoliberalism, Marxism, and realism play a crucial role in developing an international political economy (Shapiro, 2019).
Primarily, the context focuses on the various mainframes that attribute to the globalization effect based on the influence of individual state decisions to the globally-based socio-cultural and economic standards (Froese et al., 2019). China faces difficulty adapting to globalization through its accession to World Trade Organization. The resolution poses a central problem due to contrasting economic ideologies to domestic economic practices. As a result, it is the responsibility of the World Trade Organization executive team to establish clarity regarding the individual interests between China and the World Trade Organization member states based on the established trade pacts.
World War II fostered optimal disparities among countries based on the philosophical ideologies. An excellent example is international companies operating in China. The diversity on economic policies across nations fosters significant effect to the success of a business due to the contrast on integral values of ethical practices. Chinese firms utilize the communist aspect during the implementation of an action plan to enhance adherence to domestic entrepreneurial culture (Froese et al., 2019). However, the development of O.S.S operational groups enhanced attainment of crucial insights among dynamic stakeholders regarding the economic conceptual frameworks through the acquired intelligence. Therefore, investors aligned enterprise goals based on the formative structures of socio-cultural, economic, and political structures across various nations.
In a different spectrum, the O.S.S operational groups significantly contributed to the acquisition of crucial insights concerning the functional neoliberalism concept. According to Saad-Filho and Lecio (2018), there is a significant difference between neoliberalism and democratic notions. Neoliberalism encompasses the integration free will and capitalism to enhance economic growth and development. On the other hand, democracy entails the focus on promoting equality despite the need for elevating economic sect in the country. Stiglitz (2019) articulates that after the neoliberal concept implemented after World War I, government agencies used intelligence concerning the spread of communism to intensify the balance between democracy and neoliberalism. Therefore, the O.S.S operational groups aptly contributed in the acquisition of crucial details regarding the efficacy indicators on governance and business practice.
Research Methodology
Introduction
This chapter focuses on the description of dynamic research methodology in analyzing primary and secondary sources. Therefore, the framework presents the design, evaluation technique, and analysis approach. The illustration fosters an objective overview and attainment of the core objective to understand the failure and success level of the O.S.S operational group strategy utilized by the American government during World War II. International relation is a multidimensional phenomenon that influences the socio-cultural, economic, and political domains. Therefore, it is vital to assess the productivity of the interdependent relationship between O.S.S operational groups and effective governance structure.
Research Design
This study optimizes on exploratory research design based on the in-depth overview regarding the efficiency scale of developing O.S.S operational groups to the American government. According to Meharg (2009), the critical approach to achieving the main goal based on the core assessment mainframe involves measuring the effectiveness. The researcher indicates that despite the subjective consideration of efficiency, the primary entity during practice involves articulating relativity between the outcome and the objective. In this case, this research focuses on measuring the relationship between results from gathering intelligence and the initial intention rendering the intervention.
Analysis Approach
This study uses a descriptive analysis approach based on the comparative essence of the secondary sources. The comparison fosters optimal understanding concerning the topical issue. On the one hand, the research aligns its objectives under the gradient of America’s national interests during World War II. On the other hand, the study steers its assessment criteria under the spectral view of measuring effectiveness to determine the success and failure prominence from the process. Notably, World War II involved the determination of superiority within the construct of socio-cultural and economic foundations. The evolution of the global society rendered a significant imbalance among communities to determine the power position internationally. As a result, the use of O.S.S operational groups was a guideline towards attaining dominance and power based on the acquired crucial intelligence regarding the enemies.
Discussion
Introduction
There is a significant interdependent relationship between the establishment of O.S.S operational groups and the effective governance initiative. This section focuses on the analysis of attained information under two key frameworks: national interest objective and measure of effectiveness. Primarily, implementing the strategy to intensify gathering intelligence is an initiative that faces adept controversies due to the violation of a nation’s sovereignty and privacy essence. Therefore, the significance of the discussion is the indication of core values attained from the exploration of crucial details concerning O.S.S operational groups and the attribution during World War II.
Analysis Based on National Interest
Globalization is a multidimensional phenomenon that profoundly affects the structuring of the social frameworks within a region and internationally. The significant issues associated with the globalization effect include inequity, migration, and the exploitation of laborers. A considerable percentage of entrepreneurs focus on increasing profit margins, relying on capitalist ideology regarding the personal acquisition of wealth over equality (Otero, 2021). In this case, globalization fosters the surplus in wealth accumulation and expands the poverty margin across different social classes. In a different aspect, the international political economy enhances the migration among people from one region to another for better living conditions and employment opportunities. The mainframe triggers the establishment of border deals that accommodate free movement and the market. As a result, individuals and families seek alternatives for an enhanced living quotient based on the available data regarding economic performance.
Another factor that attributes to the international political economy is the hegemony status of the U.S across the scope to intensify its influential power. The paradigm shift through technological advancement empowers other nations to emerge as powerful entities in the decision-making forum. An excellent example is China and Russia’s upcoming major global economic players while the globalization effect persists (Plehwe et al., 2020). Therefore, the significant parties in the international economy must cooperate towards implementing effective initiatives. The centralization of the global political economy within one state risks a proficient effect during an economic crisis such as the recession that caused increased bankruptcy and loss of jobs among people worldwide (Froese et al., 2019). Globalization involves redefining international relations as a foundation of adequate growth and developmental index.
The establishment of different O.S.S operational groups significantly elevated the attainment of the critical objective. Research by Moon (2018) indicates that the development of the strategy encompassed empowering the military force of countries against the German policy during World War II. In this case, different countries incorporated policies enhancing the incorporation of distinctive O.S.S operational groups. The teams included the American Office of Strategic Services, British Special Operations Executive (S.O.E.), and French Bureau Central de Renseignements et d-Action (Gregory, 2021). The institutions significantly contributed to gathering intelligence concerning German military operations and action plans to develop countermeasures. Notably, the collection of vital information aptly influenced the objective overview of promoting peaceful endeavors by avoiding biased international relational frameworks.
Analysis Based on Effectiveness Scale
The establishment of the O.S.S operational group encompassed determining the core value of the outcome to the nation and the international community. Despite its evolution to Central Intelligence Agency (C.I.A.), the O.S.S significantly contributed to attaining optimal dominance against the rivalries (Nelson, 2021). The lack of coordination among states risks the rise in tension and misunderstandings concerning particular ideologies.
An excellent example is the establishment of distinctive trade treaties and agreements. O.S.S operational group was a success due to the proficient collection of information within enemy regions, that is, Germany (Royack, 2018). In this case, researchers indicate that the military action fostered the acquisition of vital insights used in strategizing for counterattacks (Schachtner, 2018). The primary goal encompassed exploiting the details to defeat Germany. However, the mainframe contributed to the enlightenment of vital approaches within the international relations domain. One of the significant outcomes to the European nations engulfed the development of the European Union.
The development of the strategy involving British S.O.E., O.S.S operational group, and French Bureau Central de Renseigne ments et d-Action contributed to the emergence of the European Union. Therefore, the establishment of the European Union features as a success indicator of the initiative’s goal to enhance peaceful coexistence (Van Voorst & Ellen, 2017). The European Union regulations address two main functional groups across the member states: the government and the firms. Further, the legislation distributes the power based on the duties and responsibilities. However, the European Union faces one profound limitation.
The critical shortcoming is the poor coordination between the commission and the citizens in enforcing the regulations (Garrett, 2018). The European Union Council, Court, and the Commission must implement policies that promote the participation of all member states encompassing the citizens. Sustainability spearheads the equitable distribution of resources (Crespo, 2020). In this case, it is the responsibility of the commission to participate in all litigations of infringement despite the marginal status of either losing or winning. As a result, the commission’s engagement in all case proceedings reduces the marginalization impact and empowers the functional decentralization pact of law enforcement.
Effective international treaties such as the European Union constructs heavily rely on the compliance ability of the governments in the member states. In most cases, administrations join and agree to treaties that align with the nation’s interests, such as the merging of the European member states to boost the economic function (Gould, 2018). Ideally, the lack of compliance is an issue rendered by the crash in the interests of a government with the welfare of the regional treaty, namely, the European Union treaty (Riccardi et al., 2020). Some of the major causes of the compliance issues include reputation and reciprocity, the credibility of the commitments, cultural and social norms, and the domestic support system (Soffer et al., 2020). The implementation of the compliance issue, that is, either centralized or decentralized, significantly affects the level of compliance of governments to the European Union treaty.
The establishment of the O.S.S operational groups aptly contributed to achieving the main objective involving intensifying international relations objectively. Under the spectrum of enhancing networks among nations, the alleviation of bias enshrined determining the dynamic variables (Do, 2020). In this case, the O.S.S operational groups significantly influenced the balance and distribution of power by neutralizing the rivalry countries, mainly Germany, leading to its defeat and the end of an era (de Wit, 2021). World War II profoundly negatively affected the global economy, socio-cultural, and political structures. Therefore, intelligence gathering empowered American government agencies with decision-making and policy development knowledge.
The significance of a policy encompasses the demonstration of critical values fostered through certain practices. In this case, the O.S.S operational group contributes to establishing functional guidelines steering domestic and international relations (Kilcullen, 2019). The administration’s mandate is to develop approaches that enhance protection among the citizens and the advancement of the local and global economy (Scherer, 2018). However, it is challenging for countries to coordinate advocacy for unity across regions based on limited knowledge resources.
As a result, the O.S.S significantly attributed the necessity of power and dominance by attaining crucial details concerning the rivalry territories (Spitaletta, 2021). Notably, the critical indicator of O.S.S’s effectiveness lies in implementing strategies that elevated coordination among the states involved in World War II (Rose, 2020). One of the profound outcomes featuring the apt efficacy is the development of the United Nations. The O.S.S operational group represents vital tenets of World War II consequences and strategies.
Conclusion
There is a significant interdependent relationship between the establishment of O.S.S operational groups and the efficiency in the governance structure. The team’s primary role encapsulated intelligence gathering to empower American executive officials with crucial insights during decision-making. Implementing different policies during military actions boosted strategic combat missions against the rivalries. Economic growth and development eventually depend on the intersectionality of public and private power-sharing and the inherent strategic management initiatives. In this case, Germany lost during World War II due to the lack of information concerning the counterparts’ mainframes.
Apart from ending the war, the prioritization of knowledge fostered an understanding of the significance of functional international relations pillars. The evolution of the global society rendered a significant imbalance among communities to determine the power position internationally. It is the responsibility of government leaders to adhere to the bounds of networking across the distinctive regions despite the difference in economic and political philosophies. The frameworks significantly contribute to the advancement of essential values on ethical and moral pillars.
References
Ames, J. Agriole. 2020. Spy Combat Tenets of WWII. Lulu.com.
Cooper, Malcolm. 2021. The Birth of Independent Air Power: British Air Policy in the First World War. Routledge.
Crespo, Ricardo. 2020. “Currency warfare and just war: The ethics of targeting currencies in war.” Journal of Military Ethics 19 (1): 2-19.
Deterding, Bailey. 2020. “The Rise of U.S. Army Special Forces in the 20th and 21st Centuries.” The University of Wyoming. Libraries.
de Wit, Daniel. 2021. “Fake News for the Resistance: The O.S.S. and the nexus of psychological warfare and resistance operations in World War II.” Journal of Advanced Military Studies 12 (1): 34-56.
Do, Phuong Thuy. 2020. “The O.S.S. in Vietnam during the Second World War.”
Froese, Fabian Jintae, Dylan Sutherland, Jeoung Yul Lee, Yipeng Liu, and Yuan Pan. 2019. “Challenges for foreign companies in China: Implications for research and practice.” Asian Business & Management 18 (4): 249-262.
Garrett, Tanner C. 2018. Mission Command Principles Applied to Paramilitary Forces in Europe During the Second World War. Army command and general staff college Fort leavenworth ks fort leavenworth United States.
Graham, Ross. 2001. “Canada’s Vital Interests.” Canadian Forces College, NSSC 3: 2.
Gregory, Derwin. 2021. The global infrastructure of the special operations executive. Routledge.
Gould, Jonathan S. 2018. German Anti-Nazi Espionage in the Second World War: The O.S.S. and the Men of the TOOL Missions. Routledge.
Hall, Todd H., and Ross, Andrew. 2019. “Rethinking affective experience and popular emotion: World War I and the construction of group emotion in international relations.” Political Psychology 40 (6): 1357-1372.
He, Kai, and Mingjiang Li. 2020. “Understanding the dynamics of the Indo-Pacific: US-China strategic competition, regional actors, and beyond.” International Affairs 96 (1): 1-7.
Huddleston, R. Joseph. 2021. “Causes of War.”
Johnston, Alastair Iain. 2019. “China in a world of orders: Rethinking compliance and challenge in Beijing’s international relations.” International Security 44 (2): 9-60.
Jones, Matthew L. 2018. “How we became instrumentalists (again) data positivism since World War II.” Historical Studies in the Natural Sciences 48 (5): 673-684.
Kilcullen, David. 2019. “The evolution of unconventional warfare.” Scandinavian Journal of Military Studies 2, no. 1.
Kumari, Pushpalata, and Nishikant Tiwari. 2022. “Analyzing the causes of the First World War.” Journal of Studies in Social Sciences 21.
Liczbińska, Grażyna, Zbigniew Czapla, Janusz Piontek, and Robert M. Malina. 2018. “Age at menarche in Polish University students born before, during and after World War II: Economic effects.” Economics & Human Biology 28: 23-28.
Maddox, Robert James. 2018. The United States and World War II. Routledge.
Meharg, Sarah Jane. 2009. Measuring Effectiveness in Complex Operations: What is Good Enough. Canadian Defence & Foreign Affairs Institute.
Mehrpouya, Afshin, and Marie-Laure Salles-Djelic. 2019. “Seeing like the market; exploring the mutual rise of transparency and accounting in transnational economic and market governance.” Accounting, Organizations, and Society 76: 12-31.
Moon, Millard E. 2018. “Secret operations of World War II.”
Nelson, Taylor. 2021. “North Africa and the making of American psychological warfare and propaganda, 1942-1945.”
Nordin, Astrid HM, and Graham M. Smith. 2018. “Reintroducing friendship to international relations: relational ontologies from China to the West.” International Relations of the Asia-Pacific 18 (3): 369-396.
Otero, Gerardo. 2021. “The neoliberal diet.” In Handbook of Critical Agrarian Studies. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Plehwe, Dieter, Quinn Slobodian, and Philip Mirowski, eds. 2020. Nine lives of neoliberalism. Verso Books.
Riccardi, Mark T., John P. Dolan, and Robert W. Redding. 2020. “O.S.S. operations in occupied Yugoslavia: Enduring principles.” Special Operations Journal 6 (1): 55-69.
Rose, Matthew A. 2020. “Commanding America’s Military Spies.” In Intelligence Relations in the 21st Century, pp. 123-155. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Royack, Christopher J. 2018. “The Creation of the O.S.S. and Anglo-American Intelligence Cooperation in Yugoslavia: A Case Study in Diverging Agendas.” PhD diss., University of Massachusetts Boston.
Rozenas, Arturas, and Yuri M. Zhukov. 2019. “Mass repression and political loyalty: Evidence from Stalin’s ‘terror by hunger’.” American Political Science Review 113 (2): 569-583.
Saad-Filho, Alfredo, and Lecio Morais. 2018. Brazil: Neoliberalism versus democracy. London: Pluto Press.
Schachtner, Alan J. 2018. Military Intelligence in the Gray Zone: The Strategic Role of Intelligence in Unconventional Warfare. U.S. Army Command and General Staff College Fort Leavenworth United States.
Scherer, David A. 2018. “The secret war in the Far East: American espionage in China and the establishment of AGFRTS.”
Shapiro, Carl. 2019. “Protecting competition in the American economy: Merger control, tech titans, labor markets.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 33 (3): 69-93.
Soffer, Sarah, Carter Matherly, and Robert Stelmack. 2020. “Psychology as a warfighting domain.” Global Security & Intelligence Studies 5 (1): 27828.
Spitaletta, Jason A. 2021. Operational Cyberpsychology: Adapting a Special Operations Model for Cyber Operations. Johns Hopkins University-Applied Physics Laboratory.
Stiglitz, Joseph. E. 2019. “After neoliberalism.” Project Syndicate, 30.
Van Voorst, Stijn, and Ellen Mastenbroek. 2017. “Enforcement tool or strategic instrument? The initiation of ex-post legislative evaluations by the European Commission.” European Union Politics 18 (4): 640-657.
Wilson, Sandra, Michael Sturma, Arjun Subrahmanyan, Dean Aszkielowicz, and J. Charles Schencking. 2022. The U.S. and the War in the Pacific, 1941–45. Routledge.