Introduction
A debit card is a plastic card similar to a credit card and contains a magnetic strip that contains the account information of the cardholder. The major difference between a credit card and a debit card is that debit card transactions are reflected directly in the bank account unlike credit card where transactions are reflected after the customers pays for the purchases.
Debit cards involve two main transactions: point-of-sale (POS) transactions and ATM transactions. With an ATM, debit cardholders can withdraw cash or enquire about the account information. Point-of-sale transactions are of two types: those authorized by PIN numbers and those authorized by a signature.
Debit card is the preferred non-cash payment method in the United States. The Debit card industry is one of the biggest engines that drive the profits of banks and point-of purchase sales. It has redefined the traditional payment methods both in business and the government sector, for instance in payroll and food stamps.
The debit card industry has gone through a significant growth over the past few decades to become the most commonly used payment method in the United States. According to a study conducted in 2010 by the Federal Reserve, approximately 38 billion debit card transactions were performed in 2009.
This represented about 35% of all the non-cash payments performed in the united states in that year. This study reviewed that the debit card industry grew by 18% per year between 2000 and 2009. During this period, checks declined substantially as people opted for debit card for non-cash payments instead of the checks. The interchange rates averaged $0.44 in 2009 (Wyman, 2010).
This contributed a total earning of $16.2 BN to the banking industry. In the large retail banks in the United States, debit card constitute a major line of business. Bank of America issues the biggest number of debit cards followed by wells Fargo and JP Morgan.
Most of the banks that issue debit cards generate approximately 20% billion every year from the issue of these cards. This paper gives an industrial analysis of the debit card industry in the United States. The first part of the paper looks at the external environment affecting the industry. Social issues are discussed at length. These are the issues affecting the industry from society or its consumers.
Technological issues are also discussed because this is an industry that is highly affected by changes in technology on a daily based. On top of these, economic, environment, and political issues pertaining the industry are discussed. The second part of the paper looks at the strengths, weaknesses and threats (SWOT) facing the debit card industry.
It is necessary to conduct the SWOT analysis so as determine the current state of the industry as well as the opportunities that the industry can venture into in order to expand both locally and internationally. The third part looks at the debit card market. This is done by analysis the five forces of competition as discussed by Porter.
These forces are: buyers’ bargaining power, sellers’ bargaining power, threat of new entrants, competitive rivalry, and threat of substitutes. The fourth and the final part gives some of the recommendations that should be adopted by the debt card industry to make more attractive and concludes the major point discussed in the paper.
STEEP analysis
STEEP analysis is a management tool that assists in making informed decision about the influence that the debit card industry is going to get from the outside environments as the technology and other variables change. Its analysis is applicable in start-ups and ongoing business (Brannan, 1995).
The debit card industry in the United States is highly competitive and this calls for strategic strategies.
Social
- Consumer’s attitudes towards convenience.
- Level of income.
- Years of Education.
- Age (under 35 years).
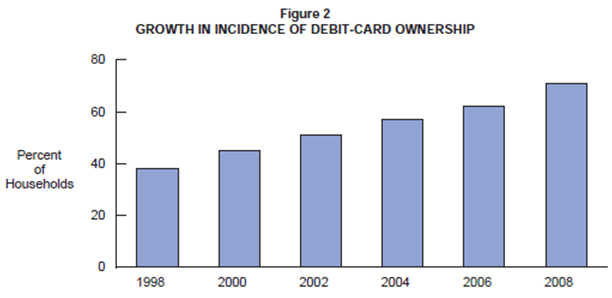
Lifestyle trends and consumer preferences affects the business’s performance. Customers demand for services that are most convenient to them. Debit cards provide this convenience because customers do not have to carry cash wherever they go and can be able to purchase with these cards. With the increase in the level of convenience, the number of households holding debit cards has increased substantially since 1998 as shown by the chart below:
The level of income determines the volume of transactions performed using a debit card. A study conducted in the US in 2004 reviewed that individuals who earn less than $25, 000 per year are less likely to use a debit card than individuals who earn more than $50, 000 (Hayashi & Klee, 2003). The years of education also determines the number of consumers holding debit cards.
Individuals who have the knowledge of how to use the internet and who are conversant with technology use debit cards than individuals who do not know how to use the internet. Younger adults below the age of 35 years hold more transactions using debit cards than older adults.
Political
- government regulation on the banking services,
- taxation policies,
- technical standards,
- competition regulation,
- the Durbin amendment.
The United States has legislation laws that a firm must comply with if it has to undertake business in the country. Companies have to follow the companies’ laws and acts of the international business as well as domestic business. While working on the global level, the industry has to consider three types of the legal systems including common law, civil law, and theocratic law.
The industry is faced with increased laws since there is need for health laws compliance. The non-compliance with such laws creates critical legal issues for the industry which has an adverse impact on the business performance as well as corporate image of the industry. Competition regulation as well as the requirement of certain technological standards results in a raise in the operation costs.
There is a likelihood of appearance of international pressure groups which might force the industry to reconsider its pricing strategy. The Federal Reserve Board has proposed a new rule called the Durbin Amendment which is to be implemented on all electronic card transactions. This rule is to be effected on July 21, 2011 and this is going to affect the debit card industry.
The new proposal has set standards to determine whether the interchange fee received by the issuer is realistic and relative to the cost incurred. If this goes into law, the interchange fees are likely to go down and the industry has to do a lot of administrative work trying to verify that the fees are reasonable and proportional to costs incurred (Wyman, 2010).
Economical
- Household wealth and personal preferences.
- Transactions-specific factors for instance dollar size, and online or offline locations availability of appropriate payment infrastructure.
- Can be used to control spending.
- Expansion in real consumer expenditure.
- Cost savings.
- Benefits three main parties; the issuing bank, the network, and the merchant acquirer.
Household wealth determines the volume of transactions. Low income individuals hold very minimal transactions with their debit cards as compared to high income earners. As a matter of fact, a very small number of the low income earners actually hold a debit card. There has been an upward trend in the number and volume of debit card transactions since 2000.
One of the key drivers of this great expansion has been the proliferation of point-of-sale terminals and ATMs in many parts of the country. Competition in this industry is mainly based on the quality of the services. Other factors that determine competition level include availability of POS terminals and ATMs, interest rate, interchange rates, and take taken to complete one transaction.
Over the years, the banking sector has been undergoing a considerable change (Hayashi & Klee, 2003). This has been as a result of the increase in competition internationally and the change toward global supply sequence. The end users play a major task in terms of choice of suppliers and in decision making of products which is changing from being operational to being strategic (Brannan, 1995).
Through research it has been found that a 10% increase in the share of electronic payments result in approximately 0.5% increase in real consumer expenditure. There is a direct link between GDP and consumer spending, therefore as real consumer spending expands, GDP increases.
The increase in debit card transactions results in macroeconomic benefits such as cost savings. The utilization of electronic payment is more cost effective relative to checks. Costs that are saved relate to overhead costs, for instance the maintenance of networks, clerks, among others. It also results in reduction of paper work and other administrative duties.
A debit card transaction benefits three parties: the issuing bank that gets approximately 2% of the transaction fee, the network (debt card operates in two main networks, MasterCard and Visa) get about 0.10%, and the merchant acquirer that keeps the rest of the fee. The merchant acquirer derives most of his revenue (about 1.8%) from the small business transactions and only 0.06% from large businesses.
This is because his markup on large business transactions is very small compared to the small businesses. However, issuing banks retain the same percentage regardless of the size of the business.
Environmental
The industry operates in an environment with people who have different cultures, way of doing things, economic and cultural beliefs. A combination of these forms a Social environment. It is important for business coordination be in harmony with the social function of the larger society. There should be coordination between the values of the industry as well as the community.
Social norms are considered essential by the business organizations as the purchasing behavior of the customers living in a particular society is dominantly affected by these norms. In the case of debit card industry services offered should be in line with the expectations of the community. In this case ethics should be upheld at all time.
Political environment includes the government systems and judiciary systems, which influence the business of the international organizations. The political way may determine things such as where the roads are going to be made, who maintains them among other factors. Due to this, the industry is required to work according to the government regulations of the United States.
Concerns about taking care of a country’s environment are in the forefront in almost all countries. Directly the debit card industry is dependent on the serenity of environment since it depends on how well the environment is maintained for its success. The ecological environment affects the business in a broader way than individuals.
At present, the businesses of the industry are affecting the natural ecology through use of energy sources in an excess amount. All these come under the corporate social responsibility of the business. This is the major consideration to be followed by the business organizations (Anon, 2009).
Technological
- Consumers who employ new technologies are more likely to use debit cards.
- Physical characteristics of the POS.
- Improved infrastructure.
- Rapid growth of electronic payment transactions.
- Use of advanced networks such as Visa and MasterCard.
The use of debit cards is dependent on technology. They are used by consumers who are able and willing to adapt changes in technology. The introduction of ATMs and POS terminals has facilitated growth in the industry and this is expected to continue as long as consumers are willing to adapt changes in technology.
Physical characteristics of POS also determines the growth and expansion of the industry; as more and more POS are being introduced in different areas all over the country, the volume of debit card transactions are on the increase. Improvement in infrastructure and development of buildings has played a very vital role in the growth of the industry (Hayashi & Klee, 2003).
The United States has continued to develop its road networks and new buildings are being built. This creates opportunities for growth and expansion of the industry in the years to come (Pearce & Robinson, 2009). Recent studies has shown that with recent growth of electronic payment, operating efficiency has increased resulting in a reduction of the operating costs incurred by banks.
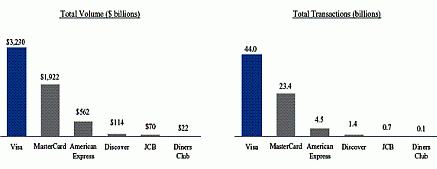
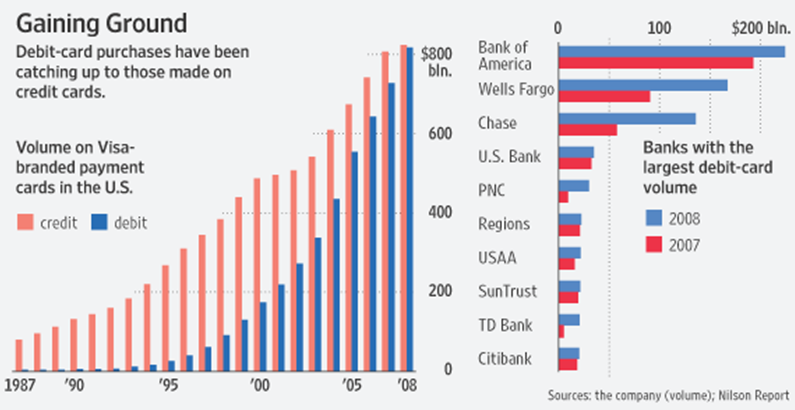
Visa is the largest processor of debit card transactions in the United States. It accounts for over 60% of the volume of transactions followed by MasterCard. The chart below shows the total volume and total transactions processed by different networks.
SWOT analysis
The SWOT analysis contains clear indicators of the key determinants of success in the segment being focused on. It, in effect, encapsulates the perception of the marketplace; summarize what the management is trying to do; and point out required future actions (Pahl & Ritchter, 2009). If pursued aggressively, this approach will make competitors into followers.
Strengths
- Low interest charges.
- Online use of debit cards.
- Wide geographical coverage.
- Ease transfer of funds from the bearer’s bank account.
- Instant cash withdrawal.
- ATMs withdrawals with no extra charge.
- Reduced number of chargeback.
Debit cards are associated with low interest charges compared to credit cards. This is one of the strengths for the industry because it is assured of a high number of consumers. The introduction of online debit cards has resulted in a significant growth of the industry over the last decade.
With online debit cards, consumers can purchase goods from other countries with very minimal charges. This ensures that the industry is able to penetrate into international markets thereby increasing its geographical coverage. With debt cards, funds are transferred easier from the bearer’s bank account unlike with credit cards where transfer has to be authorized by users.
Debit cards allow users to acquire instant cash from ATM or POS with no extra charge (Hayashi & Klee, 2003). The number of transactions doubted by cardholders, mainly because of fraud is very small compared to the total number of transactions. This ranges from 0.015% to 0.025% of total volume of transaction
Weaknesses
- Increased fraud.
- Impulse buying.
- Some cards are only acceptable within a particular country.
- Low profit margins due to competition.
Debit cards give a lot of personal information thereby increasing the case of fraud. They also result in impulse buying on the side of consumers. Statistics taken in 2009 reviewed that, more than 507 million debit cards were in circulation in America.
People starts using debit cards as early as 20 years and an individual can own up to 3 different debit cards (Wyman, 2010). However, some of these cards are used to buy many goods that are not necessarily important and ignore the basic things such as food and clothing. Other people like impulse buying and will buy anything that attracts them so long as they are not removing cash from their pockets.
They end up paying high charges in terms of fees and interest rates for the debit cards which they would have been avoided if they did not have the debit card. Statistics taken in 2004 reviews that, more than 84% African-American and 54% white-American carried debit card debt. With debit cards, Americans tend to eat a lot only to be surprised at the end of the month when they are asked to pay huge bills for the expenses.
Currently the world is going through a recession period, there is need to cut down on expenses and the only feasible way to do this is to reduce the reliance on debit cards (Wyman, 2010). There is intense competition in the industry especially because of the use of credit cards and checks which remain to be favored payment methods by a large number of people.
Opportunities
- Increase of POS.
- Online bill payment.
- International business expansion.
- Increasing technological advancements.
- Rise in leisure activities.
- Increased economy development.
- Rise in per capital income.
- Increasing technology advancements.
- An unfulfilled customer need.
If the debit card industry increases the POS terminals then transactions are expected to increase even further. It is estimated that an average cardholder in the US uses the debit card for about 52 times every year (Hayashi & Klee, 2003). This is an indication that, there is still room for growth for POS terminals.
Another significant opportunity for the debt card industry is the facility to carry out online bill payments. Presently, online bills are paid using credit cards or using online banking. The debit card industry can utilize this opportunity and link with utility websites and in that way it will be able to facilitate online payment of bills. This opportunity will create an opportunity that allows consumers to visit utility websites where they enter their debt card information.
Given the rate at which the debit card industry is growing at, there is a likelihood that it is going to surpass the growth of other non-cash payment options such as credit cards. This creates a good opportunity for the industry to expand its operations both locally and internationally.
The industry can also venture into the less developed areas as well as introduce other products and services that are going to boast the industry. Apart from that, technology is advancing at a very high rate and this making the transactions even easier. A group number of people have been able to embrace technology and this call for technologically advanced products such as debit cards.
With the rise in leisure activities, the industry can take advantage and introduce mechanisms where customers do not have to use cash when accessing leisure activities such as tourism but instead use the debit cards. Household income has increased substantial with the government raising the level of minimum wages and this creates a good opportunity for the industry to expand its operations.
On top of this, the US economy has been on a positive growth rate with many developments taking place. If the industry takes advantage of this, it is going to enjoy a big market share as well as retain its competitive advantage (Pearce & Robinson, 2009).
Threats
- Time.
- Availability of services.
- Emergence of offline debit card.
- security.
- Overdraft charges.
- Low levels of protection offered in some countries.
- Rejection of some transactions by banks.
- Global competition.
- Intense rivalry.
- Reduction in interchange rates.
One of the biggest threats to the growth of the industry is the time taken to make payments at many of the retail centers as well as the availability of services in some of the remote areas. Some of the retail establishments are still using outdated payment terminals thereby increasing the time spent in completing a single transaction.
The interchange rate for a debit card is much higher than for a credit card this creates a hurdle in the growth of the industry in future. An average customer conducts transactions worth $384 on credit cards while average debit card holders spend about $2, 757 every year. This means that if the industry does not reduce its charges, the credit card industry will remain as its major competitor (Hayashi & Klee, 2003).
Another threat to the industry and to its future growth is related to the emergence of offline debit cards. These cards have resulted in a reduction in the number of transaction done on online debit cards. The advantage of using online debit cards is that they provide immediate payment at the merchant terminals. Offline debit cards use different physical components, such as POS terminals, computers, and telecommunication connection.
These cards are being promoted by commercial banks by giving incentives because they are associated with a higher interchange fees as compared to online debt cards. Consumers prefer offline cards to online cards because of their convenience; offline cards can be accepted in terminals where credit cards are accepted. However, online cards offer more security and can be used in overseas markets.
Debit card transactions are performed directly on the bearer’s bank account. This may lead to overdrafts because some banks do not have a minimum threshold to limit debit card transactions. Also in some countries, the level of protection offered to debit card holders is very low and this poses a major threat in the future development of the industry.
Some banks do not accept debit cards and therefore they reject transactions using these cards. This limits the development of the industry and exposes it to its competitors. The US debit card industry faces the threat of global competition especially because of the increase in the number of non-cash payment options.
For many years, consumers have been relying on the use of checks to make payments but with the advancement in technology, other options have come up, for instance debit cards and credit cards. Most of these services are operated over the internet thereby increasing competition from other industries in other parts of the world. There is also the threat of intense rivalry within the industry as companies try to outshine one another.
This has resulted in a decrease in interchange rates which is expected to reduce even further. It has been suggested that, the debit card fees be reduced by almost 73% (Wyman, 2010). If this is agreed upon, banks will be hurt significantly. The banks that are expected to lose substantially from such a reduction are the top three issuers (Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and JP Morgan).
However, this reduction will be a benefit to big retailers such as Wal-mart and Target since they will be required to pay less to banks for the processing of their debit card. There remains a big question which is yet to be answered, senators, such as Senator Durbin, wonder if consumers will benefit from the reduction.
Porter’s five forces analysis
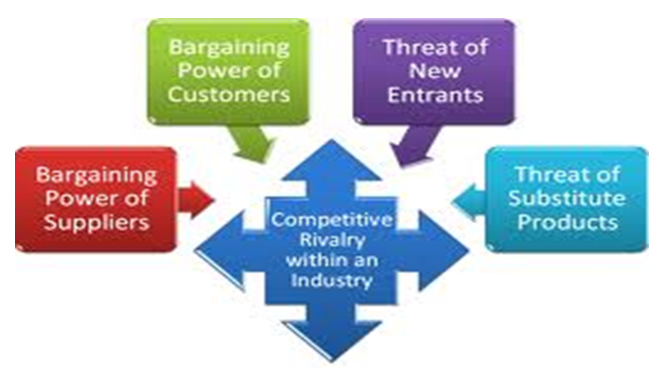
Porter developed a structure for analyzing the nature and extent of competition within an industry. His argument was that, in every industry, there are at least five competitive forces which establish the nature of competition within that industry. These five forces are discussed below:
Threat of entry
The US debit card industry enjoys the largest market share in the banking sector; this does not mean though that there are no threats to its operations. The industry takes advantage of the barriers that exist in relation to entry into the market. The threat of new entrants to an industry such as the debit card industry depends on the number of entry barriers available. The higher the entry barriers, the fewer the number of competitors will be in the industry.
In the US debit card industry, there is:
- Strong economies of scale.
- Brand loyalty of customers.
- Consumer convenience.
- Legal constraints.
The debit card industry stands to win over the threat of entry in the market because; the government has put strong entry barriers (Wyman, 2010).
Threat of substitutes
A product is termed as a substitute if it meets the same needs as those met by a product from the same industry. Credit cards and checks are some of the substitute products for the debit card industry in the United States. The industry is competing internationally and thus there is the threat that some people may decide to use another country’s debit cards instead of those of the industry (Pearce & Robinson, 2009).
The extent of the threat from credit cards depends upon two factors; namely, willingness of consumers to accept new technology and the degree to which the value and performance of the credit cards competes with the debt cards. Debit cards are more advanced than credit card and stand to win over credit cards. Most consumers in the US now prefer the debit cards because their transactions are faster and the services are available at many establishments.
Buyer’s bargaining power
The success of a business is dependent on the buyers. They are the customers of a business. They shape the kind of products that a business makes. Buyers have the ability to determine which products will move first and which will not. It is through buyers that an industry realizes its competitive advantage in the market.
In the debit card industry, consumers are concerned with the security of the services, charges, and availability of the service. The demand for this service has been facilitated by increased awareness of the industry as well as advancement in technology.
Supplies’ bargaining power
- industry’s request flexibility
- Offered price and volume
- concentrated suppliers
- high (switching) cost
The suppliers (bargaining) power is seen as weak (over the buyers) and could constantly lower their prices to ensure a share of the buyers’ (prospective) profits. If the debit card industry wants to retain its competitive advantage and still attract a big number of consumers, it has to lower its interchange fees.
Competitive rivalry in the industry
Within an industry, there are businesses which compete with one another for the available market share. These businesses either specialize in the production of similar products or differentiated products. In the debit card industry, there are businesses which compete with each other for the available market share. These businesses are the banks, retail establishments, among others.
These businesses either specialize in the production of similar products or differentiated products. Banks offer incentives to their consumers who make many transactions with their debt cards as a way of encouraging them to continue using the service. This is because they are assured of a high interest rates. They compete with one another on the basis of:
Space matrix
The space matrix is an instrument used to determine whether aggressive, defensive, competitive or conservative techniques are appropriate for the industry. In this case, SPACE matrix is used to determine the appropriate strategy that the debit card industry should adopt for its growth and development. It helps the industry to favorably compete with other companies within the industry.
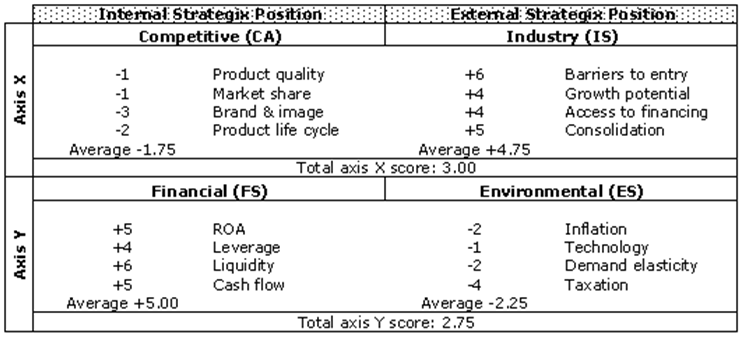
For the debit card industry, it is important that aggressive strategy be adopted. By adopting the aggressive strategy, the industry will be seeking to catch up and probably outweigh its major competitors. The strategy will be used in new acquisition of assets which are necessary for the industry’s expansion to other foreign countries and other regions where it has the potential of creating more market opportunities.
Furthermore, the strategy is very appropriate in terms of attracting more clients. With the large number of operators in the industry and the potential entrance of new players, aggressive strategy is most appropriate in grabbing customers and even establishing loyal clients.
Conclusion and recommendations
Since the debit card industry is growing fast and at the same time facing challenges, it is important that certain recommendations be proposed. The recommendations should be adopted with the sole reason of advancing the industry’s global operations. To achieve this, the following recommendations are important;
- Restructure marketing techniques: the industry is facing stiff international competition and is likely to lose out in case it remains with the same old marketing strategies; the industry should consider drawing new market communication strategies that will reposition its products in the market. In addition, the industry should re-brand its products through careful and skillful innovation in order to attract new customers.
- To ensure that the operations of the industry are successful, it is important that the industry defines its operation principles of internal control. Moreover, the industry should also establish ways of monitoring and evaluating the internal controls.
- The industry should establish proper criteria according to which the process of risk management will be taking place. The criteria should be in such a way that potential risks are identified early enough and appropriate actions taken promptly.
- Financial strength is one of the most important core businesses of the industry. To ensure that the industry’s financial resource are well managed and utilized, it is recommended that the industry gives a clear description on how the internal audit should function to avoid any form of Fraud or misappropriation of financial resource
- It will also be important for the industry to enhance the flow of information from the top level to bottom level. The flow of information on crucial and sensitive matters should be effective and efficient. This should utilize the most current communication technology.
- The strengths and weaknesses of the industry should be evaluated on a periodic basis in order to identify potential challenges that can affect the normal operations of the industry. It is important to note that new challenges arise and can contribute to the industry’s already existing weaknesses. Again, the industry is likely to gain more strength in areas which, if well utilized, can help enhance the competitive advantage of the industry. A definite period should therefore be set to be used in monitoring and evaluating the internal weaknesses and strengths of the industry.
References
Anon. 2009, SLEPT analysis with example, the Times Web.
Brannan, T., 1995, A practical guide to integrated marketing communications marketing in action series Kogan Page Publishers.
Hayashi, F, & Klee, E, 2003, “Technology Adoption and Consumer payments: Evidence from survey Data,” Review of Network Economics, Vol. 2, pp.175-190.
Pahl, N. & Ritchter, A, 2009, SWOT Analysis – Idea, Methodology and a Practical Approach Akademische Schriftenreih. GRIN Verlag.
Pearce, J. A. & Robinson, R. B, 2009, Strategic Management: Formulation, Implementation, and Control (11th ed.). New York, McGraw-Hill.
Wyman, O, 2010, The US debit card market and the Durbin Amendment: Worse than the worst-case scenario. What banks need to do now. Print.