Calculating WACC is simple when a company has one source of capital. The components of WACC are more when there are many sources of financing. Debts and equity are its components when companies use them as the only sources of finance. In such cases, the firms’ analysts express the total cost of capital as a sum cost of debt and cost of equity (Moore, 2016). As shown in figure 1, those who calculate the cost of debts must know the interest payments and the principal amounts.
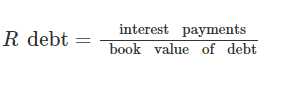
Analysts use the equation in figure 2 to obtain the cost of debt after tax.
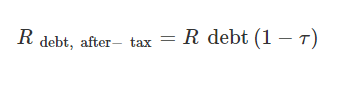
Figure 3 shows that cost of equity is a ratio of cash flows to equity’s market value.
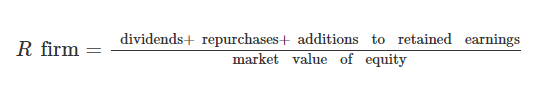
Firms and investors utilize the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) to make crucial decisions. Moore (2016) suggested that firms use WACC to make project decisions while investors use it in valuation judgments. The cost of capital rises when WACC is high because investors demand more returns on their investment. For instance, when a firm has volatile stock, its WACC is high. Thus, investors must demand more returns because their confidence in the company is low. Similarly, the firm must analyze investment projects to determine whether they will generate profits that exceed the cost of capital. If the losses are more than the returns, the company will seek other projects.
References
Moore, D. J. (2016). A look at the actual cost of capital of US firms.Cogent Economics & Finance, 4(1), 1233628.