Project Overview
The aim of the project is to develop the plan of the student campus within the frames of public private partnership – private finance initiative.
Client: Abu Dhabi Education Council (ADEC)
Developer: AlHikma Development Company (subsidiary of Mubadala development company) BOOT (Build Own Operate and Transfer)
Size: 290,000m2 , 19,000 students. Capital expenses $ 410 million
Planned duration: construction duration – 4 years
Concession duration – 28 years. This involves creation of a complementary, reliable project for long-term use, stable and endurable infrastructure, that will involve communications, motorways, and facilities for comfort and security
Funding and Payments
Type of funding: Total bank funding Dept package
Method of Payment: Service payment over 28 years (From Client via Availability Fees)
Contractors: Oger Abu Dhabi, AlFuttaim Carillion, AlSaleem Group,
The selected type of funding is featured with the increase reliability and suitability for this type of project with the given duration. It is stated that dept packages funding principles are mainly selected by educational establishments for the governmental support and insurance (Glennerster 56). Additionally, the payment method is regarded as a reasonable alternative for long-term financial projects, and the properly controlled cash flows will help to derive maximal effectiveness from the given type of funding. As it is stated by Forrer, Kee, and Zhang (43) Dept package funding as the closest type to grants that are generally used for financial educational projects. The key difference is in the emission reducing equipment costs that may be up to 100% in dept packaging, while grants do not overwhelm 75%.
Risk Assessment
The risks of the project are associated with several spheres. These are financial risks (private finance sector), construction risks, environmental risks, as well as managerial risks associated with long duration of the project. Financial risks involve inflation, depreciation values of the equipment, materials, salaries, and debts. In accordance with the research by Simkins (115), the private finance initiative is featured with transaction risks especially if financial resources are transferred from other sectors. Construction risks may be linked with the quality of materials, environmental and climatic factors, as well as experience of the construction personnel. Environmental risks are minimal, as construction will not violate natural animal populations, and environment friendly materials will be used.
Financial risks should be mitigated by creating control accounts that will monitor all the financial flows and expenses. This is also required for ensuring financial resources that will be transferred from other sectors to private initiative, and as Ychang (231) offers, these risks will involve debt creation, however, the debts will be compensated by the control account creation.
Construction risks mitigation is closely linked with the values of team experience, and quality of the materials. Therefore, quality control team should be created that will monitor the terms of storage, experience of the construction teams, and technical condition of the construction equipment.
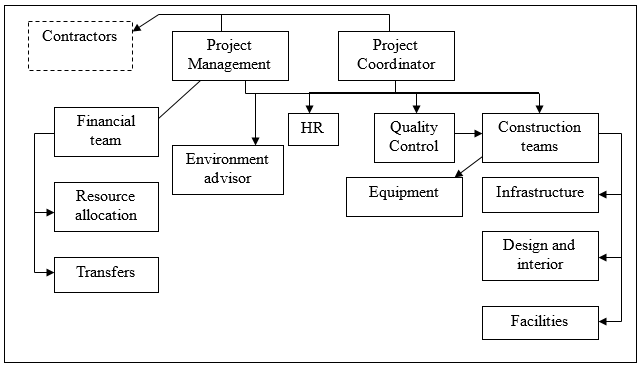
Organizational Strategy
Organizational strategy of the project represents the relations among the entire project team then involves project coordination efforts and managerial connections. Therefore, all the departments are subjected to project management and coordinator. HR, Quality control, and environment advisor issue decisions and recommendations, the value of which is defined by the coordinator. Contractors control the entire implementation process.
The Reasons for Project Selection
Education is a problem which touches everybody, as people understand that to get a good job, it is important to study well. The United Arab Emirates University has about 16 campuses in different parts of the city (“The New Campus Project” n.p.). Students have to spend much time on getting from one campus to another. The New Campus Project will allow the University to offer students an opportunity to remain in one and the same building. There are a lot of different reasons why we have chosen this specific project for discussion. It is obvious that education is important for us, so the problem of building a new campus can touch us along with other students. It is always exciting to watch at the creation of something new, but the building of such powerful project is twice interesting.
The project we have chose as a focus for our discussion is an example of centre of learning experience. The knowledge is going to be centred in one building. It is important to understand that this is not just a building which is going to comprise all students. It is a building which going to represent the grandeur of UAE as a whole. This building is going to be the reflection of UAEU unique characterizes. High attention to the details and the process of building this specific building is of high interest for us as deep research of this topic may allow us to be among of the first ones who can be aware of the new campus characteristics.
We would like to note that among the reasons of our attention to this specific building became its uniqueness and magnificence in the predicted space. Middle East becomes a part of the world where unique projects are realised. The choice of Qatar as the place for World Cup 2022 is one of the best events. The projects of the stadiums which are going to be built there are incredible. When we got to know that the New Campus is going to be built, we understood that this is the project we should dwell upon. The construction of this project, the attention its details may be very useful for us in the future.
The choice of the Middle East as the place for the championship shows that we become interesting for the world. Deep consideration of such magnificent projects as the New Campus may give us much experience. Having considered the main details of the project, its duration, different financial questions along with the risks, we will have a theoretical experience in how such huge projects are carried out. The experience in assessing different kinds of risks, the prediction of the project duration and calculation of costs and funding will be helpful in the future when we have to apply the theoretical knowledge we have got into practice.
Project Key Features, Personal View on Project Risks, and Success
Dwelling upon key features of a project, it is necessary to mention that all the studying facilities are going to be located in one and the same place, like laboratories, libraries, computer classes, etc. All sport facilities, swimming pool, and other opportunities will also be located in the campus. The possibility for students to have single rooms and in the easy reach is also a key feature of the New Campus along with other advantages (“The New Campus Project” n.p.).
The key feature of the project is that it is a PPP project, a private-public partnership, where a private company works for the benefit of a public-sector. Building a New Campus for the University, the private company is responsible for the risks, but the whole society is going to benefit from this project. In other words, building of a New Campus can be characterised as “a contractual relationships where a private party takes responsibility for all or part of a government’s (departments) functions” (Akintoye, Beck and Hardcastle 31). Thus, the building of a New Campus makes a private company to bear most of the responsibilities, including financial ones.
Considering this problem from the personal point of view, it can be stated that there are a lot of options which may help reduce the level of risk to the private company and share the responsibilities. It is rather difficult for a private company to raise long-term debt which covers the whole amount of financial responsibility. The government should become a guarantee in this case and “act as one of the long-term lenders to a project but still benefit from the discipline of having private sector at risk of performance” (Farquharson, Yescombe, Mastle, and Encinas 65).
Being funded mostly by the private sector, it bears most of the risks and it may create a conflict of interests. The project is public, and the mismatch of public and private interests is a big risk in the situation. The transfer of risks is a strategy which may be helpful in this case as it may allow the private sector to deliver some part of risks on other organization and share the outcomes of the affair (Pretorius, McInnes, Lejot, Chung-Hsu, and Arner 335). The organization takes risks, but in case of the successful outcome the profit is going to be on the highest level as well.
Considering the risks of the venture, the environmental issues should be considered. All kinds of building influence environment, still, the campus is going to be built in such a way that the plan presupposes the availability of the nature park which is going to cover the harm acted in the relation to the environment while building the campus. Pointing to the project success, it should be mentioned that being constructed in 4 years, the company will have to pay debts for 24 years more, still, the profit is going to be received earlier.
Issues Arising from PPP / PFI Schemes
PPP / PFI Schemes that are used for the project implementation are not risky, and the key risks that are common for these financing principles are linked with transactions only. This fact is crucial for understanding the issues that arise from the Public Private Partnership financial scheme, as considering the importance of the transaction safety, the Private Finance Initiative scheme involves using the set of control accounts that minimize all the possible risks associated with transactions. On the other hand, it should be stated the selected schemes are closely linked with the values of infrastructural funding that is originated from the public sector financing.
In accordance with the research by Simkins (118), the maintenance services offered by PFI schemes are intended for achieving the necessary security level. Additionally, the private sector financial transactions that are common for the initial stages of project funding are maintained by the public sector staff, and conclusion of the employment agreements. These measures help to mitigate the possible employment risks, hence, also insuring financial risks associated with improper HR allocation. Therefore, every PFI scheme is aimed at dealing with the particular characteristics that are defined by the negotiation process between contractors and coordinators.
Another issue that is associated with the PPP / PFI financial schemes is the governmental commissioning. On the one hand, the private sector does not require this commissioning, as this may harm the smooth nature of public and private sector cooperation, on the other hand, governmental bodies need to control these projects, as most of them are of an important nature. Therefore, the government is able to undertake the financial control, and regulate financial transfers to the private sector. On the one hand this will help to manage financial risks, on the other hand, if governmental regulation principles change, this will inevitably cause the necessity to restructure the entire financial management strategies.
As it is stated by Glennerster (45), if the design, finance and support schemes of the project are provided, the governmental bodies control the private sector financial transactions, and ensure that the project will be financed for the required period. When the contract expires, the ownership of the project is returned to private sector, and project procurement is no longer performed in accordance with the PPP / PFI schemes, as most PFIs are effective for new construction projects only (“A Private Initiative. A Global Partnership 72).
As for the service provision, the given scheme is effective for creating control schemes and quality assurance teams for the project implementation, as there are numerous spheres that should be controlled and maintained. Therefore, as it is stated in the organizational chart, environment control, quality control, financial control, as well as construction and equipment monitoring will be required for proper project implementation. These control measures are easily regulated by the employment practices available for PPP / PFI schemes.
Works Cited
Akintoye, Akintola, Beck, Matthias and Cliff Hardcastle. Public-private partnerships: managing risks and opportunities. New York: Wiley-Blackwell, 2003. Print.
“A Private Initiative. A Global Partnership.” UN Chronicle Fall 2005: 72.
Farquharson, Edward, Yescombe, E. R., Mastle, Clemencia Torres, and Javier Encinas. How to engage with the private sector in public-private partnerships in emerging markets. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications, 2011. Print.
Forrer, John, James Edwin Kee, and Zhibin Zhang. “Private Finance Initiative: A Better Public-Private Partnership?.” The Public Manager 31.2 (2002): 43. Print.
Glennerster, Howard. Understanding the Finance of Welfare: What Welfare Costs and How to Pay for It. Bristol, England: Policy Press, 2003. Print.
Pretorius, Frederik, McInnes, Arthur, Lejot, Paul, Chung-Hsu, Berry-Fong and Douglas Arner. Project finance for construction & infrastructure: principles & case studies. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2008. Print.
Simkins, Betty. “Enterprise Risk Management: Current Initiatives and Issues Journal of Applied Finance Roundtable.” Journal of Applied Finance 18.1 (2008): 115. Print.
“The New Campus Project.” United Arabian Emirates University. 2011. Web.
Vries, Piet de. “The Taxpayer-shareholder Fallacy and Private Finance Initiatives.” Journal of Public Budgeting, Accounting & Financial Management 19.3 (2007): 273. Print.
Ychang, Ike, et al. Use of Public-Private Partnerships. Santa Monica, CA: Rand, 2002. Print.