Introduction
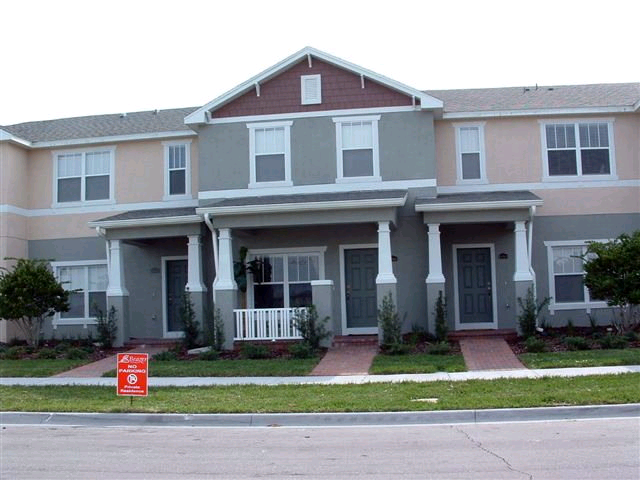

The project description is associated with the analysis of dwelling functions; construction materials used in the building process, installation system, and house building elements. The component parts and service of the building will be presented with photos and functional requirements description.
The domestic house project is based on the construction analysis of a two-store dwelling. This is a traditional two-story house having brick and cavity dwelling. The house was reconstructed 5 years ago with the insertion of additional design and building elements. The paper will be focused on the construction detail description on the basis of its building elements and internal service installation. (Best, and Valence, 2002)
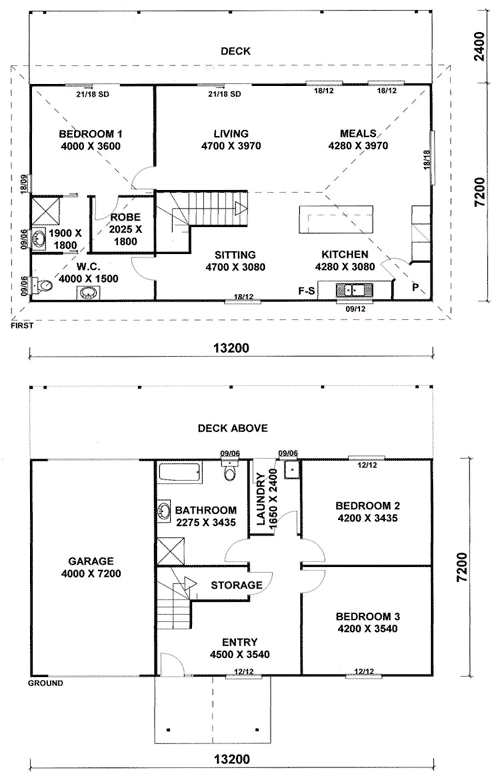
The house is located in UK, Poole, Dorset. It is necessary to underline the fact, that the house façade is considered to be a combination of country-style elements. The first floor of the house leads to the big living room; the house has French doors underlining the style of European architecture. At the end of the central hall on the first floor one can see the door leading to the kitchen; here is a family room with having fireplace and cathedral ceiling. It is necessary to note that these rooms form a complete flowing area that is aimed at the rear lawn and the deck overlooking. (MacCollum, 2005) The second floor of the house is open through the main staircase having an open balustrade; the hall of the second floor is quite large and light comprising enough furniture for making the space comfortable for living. According to the house plan, the end of the second-floor hall is open to three bedrooms, having one generous bath. The other end of the hall has a master suite; the bathroom, which has a platform tube, glass shower, and dual vanities, is separated from the bedroom by a dressing area built with walk-in closets.
Domestic Dwelling Specifications.
Elements of the Construction
Roof Structure

The roof structure has a double-pitched structure having a symmetrical shape; it is laid with brick to the edges. It is important to stress that the roof has a traditional form, is characterized by practical and reliable nature. The roof serves as the waterproof membrane which is performed in a traditional modernized design.
The roof of the house uses trusses for its framing that is triangulated wooden structures supporting the roof; the frame of the roof is 2x10s. This allows characterizing the house roof through its principal advantages, such as:
- strength of the trusses adds reliability to the roof;
- the truss serves to transmit the weight to the walls;
- the interior walls are considered to be load-bearing.
The left-hand side of the roof creates a cathedral-like ceiling in the house living room. The front room uses scissors trusses and one can observe M trusses over the garage. Then three rooflines are ended with gable trusses.

Cavity walls
My dwelling’s cavity walls
The house cavity walls are considered to be effective characteristics keeping the warmth in the house. They function as an effective means for saving temperature. The cavity of the house walls is introduced for more reliability and strengths. External wall construction is developed in accordance with the balancing of materials quality and characteristics making the building being adapted to the environmental changes. The walls provide thermal mass service in the house responding to slight temperature changes.
Cavity walls are built with nonferrous ties 60 mm wide; the ties are placed 900 mm horizontally and 455 mm vertically. At the openings, the ties are placed with one tie with a height of 300 mm and 225 mm within the opening. The wall ties have a twisted kink allowing the water to form on this part and not run uphill.
DPC
The walls of the house are built on the basis of Damp Proof Course (DPC); the construction of the external wall has the cavity walls form, being built from the outer brick leaf and inner blockwork leaf. It is necessary to underline the fact that the outer walls up to DPC are considered to be made of four blockwork layers below around bricks layers. DPC is considered to be the part of outer and inner walls; 200mm is the outer wall of the house. Under the structure of timber floor, the construction has inner walls DPC. This system gives an opportunity to protect the dwelling from rapid environmental changes, making the construction to be strong.
Water supply
Water supply service
The system of water supply is appropriately developed; water is provided to all the bathrooms, kitchen, and boiler rooms require no water supply. Garages and workshops are considered to be without water supply either, as initially, it was not presupposed by the project.
The water meter is located close to the curb in front of the house; the pipe draining system equalizes the pressure of draining water. Pipes of the house lead to the bathroom sink, kitchen sink, and shower; the pressure of the water supply is considered to be 100 pounds per square inch. Pipework was built of the following components: flanges, gaskets, pipes, bolts, strainers, supports, valves, flexibilities, and joints. Steel was selected as the material for the pipework; it is necessary to stress that it is mostly adapted to the temperature changes.
Hot and cold water can be easily regulated; in case one does not want to use hot water, there is a mounted flash heater which is above the shower in the bathroom on the second floor. All the installation service is made in accordance with the initial house planning.
Internal Service installation: Materials
Material house characteristics are to be concentrated on building materials used in house projecting. This dwelling has brick veneer walls and a timber floor. It is necessary to stress that brick veneer walls used in house building comprise a single external brickwork layer and an inside lined stud frame. The thermal mass ability of the house wall is characterized by the heat storage level; it gives an opportunity to store the daytime warmth in winter releasing it at night. In summer this service allows to keep the house cooler during the hot day; the initial aim of the architecture selecting the housing material was directed at making the night air cooling the home mass in order to provide further comfortable conditions. (Building Materials. 2009)
The house has sub-floor ventilation contributing to construction installation; excessive humidity which can be observed in the under-floor area is liquidated through the cross-ventilation. It is necessary to discuss the material reinforcement; this method is used for providing extra strength to the construction. The reinforcement is directed at building structures and components encompassing covering walls, beams, slabs, mats, columns, and frames. It is necessary to stress that concrete reinforcement is based on the merging of two materials together; it combines concrete with high compressive strength and steel bars to introduce more tensile strength. (Kurt, 2007) The house design is made in light colors which are used for sun heat-reflecting; the light decking material helps to keep the house cooler during the outside summer heat. The system of thermo mass has been taken into account in the process of building materials selection and construction design. (Ambrose, 2005) The Colonial form with the classic elements conveys the elegance of the house style; the second floor has several extra rooms which can be used for entertaining. The total floor area of the house is considered to be 2,866; it covers the porch area which is 32, the basement area being 1,680, and the garage area 497. The house deck area makes 220.
The system for concrete quality control is considered to be of great importance in the constructing process, as this is the key structural building material. It is necessary to underline the fact that the method of concrete quality monitoring is concentrated on the maturity of the material or its temperature history. It should be stressed that present invention in this sphere is concentrated on the key embodiments or applications to be taken into account; they are Improved maturity (the system and method curing concrete strength determination on the basis of maturity calculations); Enhanced maturity (it is focused on the method of maturity calibration through the accounting of air content, the ratio of water-to-cementitious-materials, and concrete gross unit weight); SPC maturity (it is based on the method of coupling the calculations and maturity measurements with the methods of Statistical Process Control, which give an opportunity to recognize the concrete mix changes between its principle components); Moisture-loss (the method of time determination of concrete moisture-loss protection and structures termination); and Loggers and Software (the method allowing to represent the applications for simplifying and automating the implementations of all other quality control methods). (Merritt, 2002)
Conclusion
The usage of the house planning can be used for the development of personal specifications in the design and material selection; thus, one can expand the number of baths and bedrooms, and kitchen layouts, and upgraded master baths. Besides, the design of the building can be changed and raised to nine feet with a lengthening of the main house to four feet. The place of the door can be changed taking into account the placement of the garage. Besides, in the building planning, one can use brick, stucco, clapboard, and shingles; the design transformations can be observed in roof style, porch, and gables. (Choi, 2004)
The house project analyzed above is considered to be based on the material characteristics, design approach, and planning of the structure. Taking into account the plan of the existing building, one can develop the personal design and expand the opportunities, both inside and outside. It was shown that the selection of building materials is of great importance in the building process. (Original Home Plans. 2009)
References
Ambrose, J. 2005. Building construction: service systems. Springer.
Best, R. and Valence, G. 2002. Design and construction: building in value. Butterworth-Heinemann.
Building Materials. 2009. Government of Western Australia. Web.
Choi, Y. 2004. Principles of applied civil engineering design. ASCE Publications.
House Planning. 2009. Web.
Kurt, H. 2007. Dimension stone use in building construction. ASTM International.
Levy, S. 2006. Design-build project delivery: managing the building process from proposal through construction. McGraw-Hill Professional.
MacCollum, D. 2005. Building Design and Construction Hazards. Lawyers & Judges Publishing Company.
Merritt, F. 2002. Building design and construction handbook. 6th Edition. McGraw-Hill Professional.
Original Home Plans. 2009. Web.
Trost, S. and Fox, M. 2008. Method and System for Concrete Quality Control Based on the Concrete’s Maturity. Dunlap Codding. Oklahoma City.