This essay would consider human resources and knowledge management of the US Army as these are mostly interrelated with the management functions.
Human Resources
Assessment of the effectiveness of organizing functions of managing human resources of the US Army has accepted the Army Leadership Program (ALP) long ago. In recent times, policy and standards of HRM (Human Resource Management) are integrated to structure personnel management and administration individually. Hypothetically, HRM conveyed a sequence of integrated decisions to define the employment relationship status, whether it influenced the effectiveness and efficiency of personnel and the organization. Conversely, in accordance with US Army, HRM operations are core dynamics of military HRM that conceived through a supportive role of SHCM (Strategic Human Capital Management).
In assessing organizing function of management bodies of US Army, the paper has identified that existing challenge of US Army suffered from a crisis of required decisions to work on diversified functions (Force Structure Requirements, Recruiting & Retention Programs, Well-Being Programs, & Personnel Readiness from Both Individual & Unit Perspectives). To rescue from the dilemma, US Army HRM leaders are obligatorily assigned to possess specialized multidimensional skills and, additionally, should involve managing HRM Life Cycle Model (LCM). From the US Army viewpoint, LCM is the most forceful dynamic that has key proficiency in time management, effective and efficient military service to serve Federal civilian.
Moreover, the HR community of the US Army discovered through eight functions of HRM LCM to structure development programs, acquire personnel, distribute efficient logistic support and recruit, organize and compensate sustainable personnel. Alternatively, US Army attached with the intensified framework, development strategies (Acquiring Personnel, Efficiently Distributing Management Support Solutions Personnel, Developing Personnel, Deploying Personnel, Compensating Personnel, Sustaining Personnel & Transitioning Personnel), networking, training, and allocation of responsibilities through HRIM (Human Resource Information Management) to stimulate their self-development initiatives and well-being of their family as well. In a specific form, the following are significant LCM components –
Table 2. Source: Self-generated.
Knowledge Management
Evaluation of organizing functions of US Army management, the term knowledge is treated under AKM (Army Knowledge Management), which is a complete package of strategies to network-centric as well as knowledge base transformation. Alternatively, the AKM strategy is attributed to numerous significant goals and objectives to specify accomplished tasks and potential progress of decision dominance of the entire tactical commanders. Moreover, the key concentration of AKM goals and objectives are to manage and administration IT (Information Technology) infrastructure to attach with the GIG (Global Information Grid).
Meanwhile, AKM functions are involved in reducing unnecessary resource and equipment volume as well as restrict ubiquitous accessibility into the heart of the knowledge portal with applicable network services. Conversely, the best utilization of governance practices along with prioritizing innovative HCM (Human Capital Management) strategies is also an indispensable ingredient of AKM goals. More specifically, AKM goals, objectives, and strategies are proficiently transforming intellectual human capital (Individual, Team & Enterprise Knowledge, Systems & Services & Workforce) through a change of catalysts to foster functional decision flow.
On the other hand, infrastructure (Computers, Software, Architecture, Security, Communications, Programs & Facilities) is an ingredient of IT, obligatory for managing and supporting network centric Army. In the meantime, change of catalysts involved in assigning policy constructing, aggregate resource management, and exploring the entire Army to acclimatize with network centric atmosphere. In other words, the AKM is providing an entire strategy of the US Army to investigate and recommend how to develop AKM and, additionally, network centric implementation approach globally.
For instance, to foster overseas integration, US Army employs CIO/G–6, whereas C4/IM is proficient in providing knowledge management solutions. Furthermore, the CIO/G–6 is a functional proponent whilst structuring Army resource policies like the E−Business Model, potential governance structure, integration of new technologies, and a knowledge-centered workforce. In executing functional tasks, US Army goals are outlined in parallel to maximize the workforce as well as network atmosphere transformability. For more clarification, the following are sequential goals and objectives of US AKM followed by a comprehensive AKM figure (Department of the Army, 2009, p.574-581) –
Table 3: goals and objectives of the US Army Knowledge Management. Source: Self-generated.
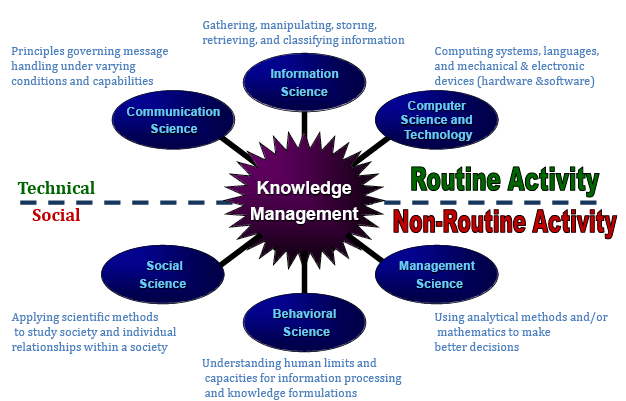
In light of the previously mentioned discussion on HRM and AKM of the US Army, the paper has addressed that the HRM division of the organization has suffered from the integration of diversified task where as knowledge management frequently has in a crisis of conveying pioneer outsourcing role. Taking into account these two issues, the US Army should pay core concentration on integrating HRM with AKM though existing AKM organizing functions have recently outlined a parallel network-centric atmosphere to maximize the entire workforce.
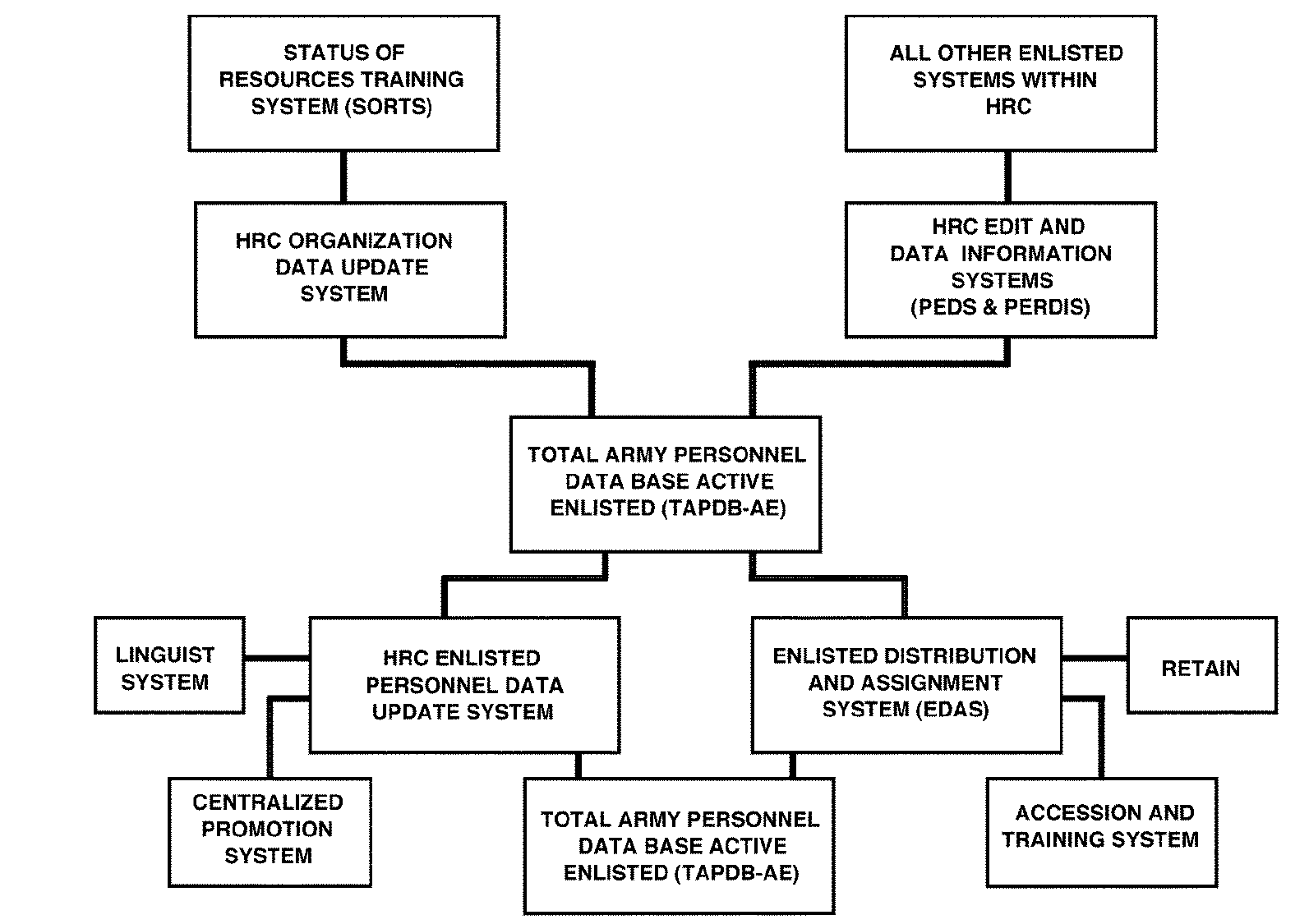
This policy does not guarantee enough efficiency to optimize organizational resources effectively. To rescue from these dilemmas, the following is the most modern outline of integrating HRM and AKM of the US Army through automation, where TAPDB−AE is the heart of the process. More specifically, the automation of HRM and AKM of the US Army should consist of three logical components in accordance with the following figure, namely, containing personnel data of every recruited staff, requisition, and then organizing gathered data where HRC is proficient to upgrade gathered data as well as AKM.
Finally, EDAS worked for reducing the time limit to upgrade, integrate, and deliver required data to superior personnel and, consequently, involved to assign new personnel as well as integrate diversified tasks of the Army personnel considering AKM functions.
Reference List
Department of Defence. (2009). Knowledge Management in the DoD. Web.
Department of the Army. (2004). Soldier’s Manual and Trainer’s Guide. Web.
Department of the Army. (2009). How the Army Runs. Web.
Serco. (2006). Strategic Human Capital Management: Managing, and maintaining the human capital needed to maximize government performance and ensure its accountability. Web.