Change Model: Overview
The proposed model – The Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice (JHNEBP).
Benefits:
- The approach is proposed due to its simplicity and efficiency.
- It offers consistent guidelines for a step-by-step implementation.
- It is targeted at the successful incorporation of the research findings into clinical practice (Center for Evidence-Based Practice, n.d.).

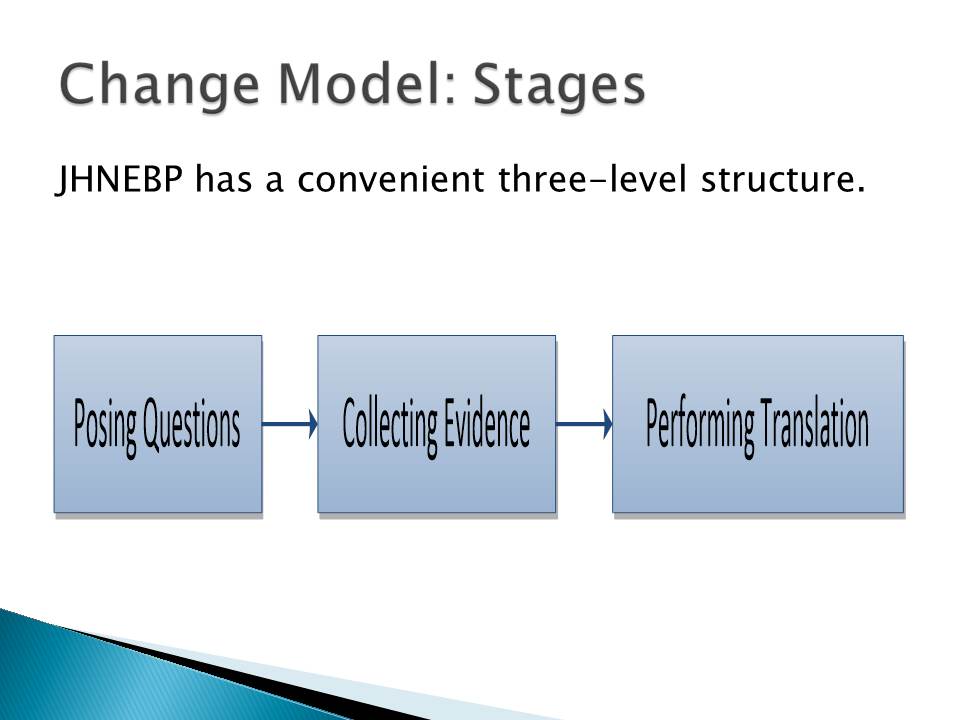
Change Model: Stages
JHNEBP has a convenient three-level structure:
- Posing questions;
- Collecting evidence;
- Performing translation.
PICO Question
- Population: elderly patients exposed to falls;
- Intervention: a complex approach to falls prevention;
- Comparison: a complex approach that considers both intrinsic and extrinsic factors opposite to narrow-focused methods;
- Outcomes: reducing the risks of falls and the number of fall-related injuries.
The pivot question resides in whether a complex approach that considers intrinsic and extrinsic factors can be more effective than the narrow-focused methods (ex. the frequent rounding technique).
The targeted population is composed of elderly patients that prove to be particularly exposed to the risks of falls.
The proposed intervention is a well-structured prevention program that addresses both intrinsic and extrinsic factors and targets at eliminating all the key problems that make a patient more exposed to falls.
The proposed complex approach is compared to the narrow-focused techniques. In other words, those techniques that suggest concentrating on a particular aspect: supporting equipment, psychological prerequisites, etc.
The expected outcome is eliminating the risk of falls, reducing the number of falls, and preventing the falls-related injuries.

Scope of the Question
According to official statistics:
- Every fifth fall leads to broken bones, hip fractures, head and brain injuries;
- 2.5 millions of elderly people are treated for fall injuries annually;
- More than 700,000 patients are hospitalized due to a fall injury annually (Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2016).

Stakeholders
The key stakeholders:
- A fall prevention team;
- Elderly patients;
- Healthcare organizations.
It is proposed that a fall prevention team is composed of a falls consultant, a charge nurse, a nurse specialist and a psychologist. Another group of stakeholder is the elderly patients that need to participate actively in the program activities. Lastly, health care organizations comprise another stakeholder group – they will need to provide the facilities necessary for implementing the program.

Empirical Evidence: Findings
The main findings:
- There is a significant literature gap in the field of fall prevention (Lea et al., 2012);
- A team-based approach needs to be adopted to perform a successful intervention (Healey, 2010);
- Narrow-focused programs are less effective than a complex approach (Schwendimann, Bühler, De Geest, & Milisen, 2006);
- Considering both intrinsic and extrinsic factors elevates the efficiency of a fall prevention activity (Graham, 2012).

Empirical Evidence: Implications
The main implications:
- Further research needs to be carried out to fill in the existing literature gap;
- A fall prevention team comprising different specialists needs to be formed;
- It is essential to take into account both intrinsic and extrinsic factors while planning the fall prevention activity.

Action Plan
The proposed action plan includes the following stages:
- Target a group;
- Evaluate the frequency of falls;
- Implement a pilot program;
- Evaluate the frequency of falls;
- Evaluate the outcomes.

Targeting a Group
- Size: 20-30 patients;
- Age: elderly;
- Prerequisites: willing to prevent falls.

Evaluating the Frequency of Falls
- 1st: before the program is implemented;
- 2nd (supplementary): in the course of the program;
- 3rd: upon the program’s completion.

Implementing a Pilot Program
- Exercises;
- Psychological seminars;
- Supporting technologies.
The program comprises varied activities. Hence, one of the core elements is daily exercises that are supposed to improve the patient’s legerity and slenderness. The psychological seminars, in their turn, are expected to assist in eliminating the mental difficulties: low self-esteem, fears, etc. during these seminars, the participants will be welcomed to share their experience and discuss their concerns in a tense-free atmosphere. The introduction of the supporting technologies implies getting the participants acquainted with such mechanisms as bed alarms.

Evaluating the Outcomes
- Compare the registered frequency of falls;
- Collect the relevant feedback;
- Eliminate the existing drawbacks.

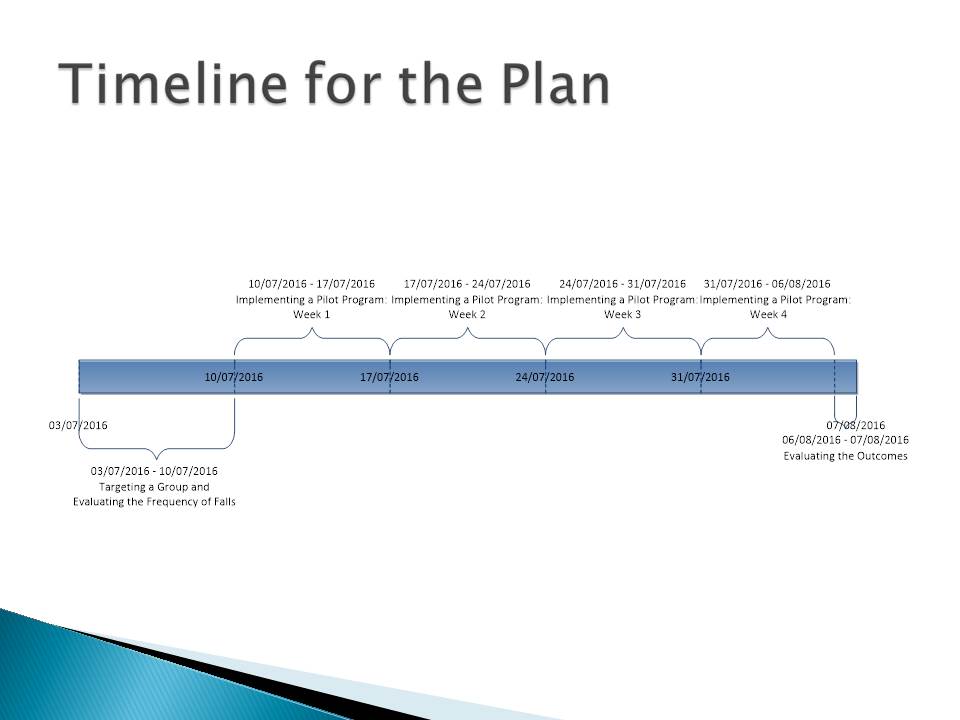
Timeline for the Plan
The program’s implementation is targeted at five weeks: the first week is a preparation stage. The last stage is devoted to the evaluation of the outcomes. It is expected that the falls among elderly patients reduce at least by 25%. As long as the program is successfully implemented, the experience might be adopted in other health care centers. The health care community should be informed about the positive results of the proposed change through web platforms.
The Nurses’ Role and Responsibility in the Pilot Program
- Collect the relevant empirical evidence;
- Analyze the findings and generate an effective program;
- Communicate the change to the relevant health care organizations;
- Prepare the organization for the change;
- Assist the participants in completing the program;
- Evaluate the program’s efficiency and target the further activity.

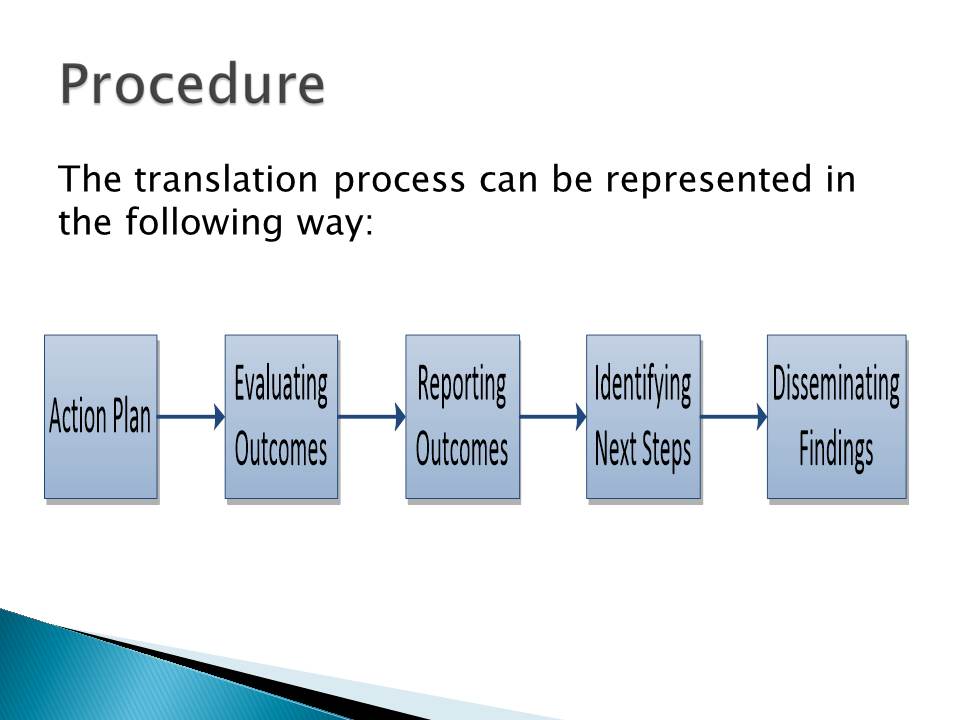
Procedure
The translation process can be represented in the following way:
- Action plan;
- Evaluating outcomes;
- Reporting outcomes;
- Identifying next steps;
- Disseminating findings.
Resources Available to the Staff
The staff can use the following resources:
- scientific journals;
- the materials provided by American Nursing Association;
- social networks.
Scientific journals are necessary to collect more information relevant to the problem. American Nursing Association provides valuable data regarding the latest programs, statistics, etc. Social networks can be employed in order to communicate the problem to the relevant stakeholders and raise money for the pilot implementation.

Summary
- The proposed change: a fall prevention program;
- Targeted population: elderly patients;
- Specificity: a complex approach considering both intrinsic and extrinsic factors;
- Length: one month;
- Expected outcomes: the reduction of falls and fall-relating injuries.

References
Center for Evidence-Based Practice. (n.d.). Johns Hopkins Nursing Evidence-Based Practice Model. Web.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016.). Important Facts about Falls. Web.
Graham, B.C. (2012). Examining evidence-based interventions to prevent inpatient falls. Medsurg Nursing, 21(5), 267-270.
Healey, F. (2010). A Guide on How to Prevent Fall and Injury In the Hospitals, Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. Nursing Older People, 22(9), 1896-1905.
Lea, E., Andrews, S., Hill, K., Haines, T., Nitz, J., & Haralambous, B. (2012). Beyond the ‘tick and ‘: Facilitating best practice fall prevention through an action research approach. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 21(13-14), 1896-1905.
Schwendimann, S, Bühler, H., De Geest, S., & Milisen, K. (2006). Falls and consequent injuries in hospitalized patients: effects of an interdisciplinary falls prevention program. Web.