A brief introduction of Virgin Atlantic Airline
Virgin Atlantic Airlines (VAA) was established in 1984 in the UK under the initiative of Richard Branson, and it is headquartered at Crawley in England. The airline is focused to developing a strong foundation in its operations, which is evidenced by its mission statement, which according to Virgin Atlantic (2014a, par.1) seeks ‘to embrace the human spirit and let it fly.’
One of the areas that the firm has focused on continuously relates to customer service. VAA has been committed to achieving a high competitive advantage by procuring new aircraft and expanding its route network. Subsequently, VAA has been in a position to break new grounds, hence increasing the level of customer satisfaction.
Purpose of the VAA and reasons for its existence
VAA is a profit-making entity unlike the Red Cross and the UK Fire Services department, which are not-for-profit-making entities, and thus, the firm’s objectives are not profit-oriented. The operations of the UK Red Cross and Fire Services departments receive funding from the UK government. Subsequently, they obtain budgetary allocation from the government.
Furthermore, these institutions are established to provide services that cannot be provided by profit-making entities. The core motive for the establishment of these institutions is to assist the government in disaster management.
The operation of airline companies is similar to firms operating in a competitive market. Subsequently, airline companies have an overall fiduciary duty to maximize the shareholders’ wealth. One of the ways through which a firm can maximize its shareholders’ wealth is by improving the stream of its future profits. The UK airline industry has become very competitive over the past few decades.
Some of the factors that have increased the intensity of competition include the optimal position of UK airports in the European region. The firm’s ability to achieve its profit maximization objective is enhanced by the recent liberalization of the airline sector in the European region. However, the extent to which VAA achieves its profit maximization objectives will depend on its competitive nature.
VAA’s responsibilities to its key and how it addresses these responsibilities
Business managers have a responsibility for formulating and implementing effective strategies and decisions. However, decisions made must take into account the various stakeholders. Seliet (2000) defines stakeholders as the various individuals or groups that have some interests in an organization.
Internal stakeholders
Employees- VAA has an obligation to ensure that employees are satisfied. Subsequently, the firm’s HR manager should ensure that the organization has implemented effective HR management practices. In its quest to nurture a high level of employee satisfaction, VAA has implemented good working conditions. The firm ensures that employees are compensated fairly and equitably. The airline has implemented a comprehensive reward management system, which is comprised of both monetary and non-monetary benefits.
Virgin Atlantic recognizes the role of employees in attaining its objectives. Subsequently, the firm has integrated a continuous employee-training program, which enables employees to progress through their career in addition to providing customers with high-quality services.
Some of the areas in which the firm trains its employees to relate to engineering technical training, cabin safety, wine training, and customer service training (Virgin Atlantic 2014b). With regard to non-monetary benefits, the Airline offers its employees seven flights every year.
Connected stakeholders
Shareholders – this group of stakeholders cover the owners of a particular company. Subsequently, shareholders are concerned with high profits, long-term organizational growth, and development of a positive corporate image. Virgin Atlantic Airways is committed to maximizing the shareholders’ wealth.
Subsequently, the airline has ensured that its customers achieve a high level of profitability. In an effort to achieve long-term organizational growth, the airline has integrated joint venture as one of its corporate strategies. For example, in 2013, the airline announced its intention to enhance its profitability and growth by establishing a joint venture with Delta Air Lines (CAPA Centre for Aviation 2014).
The joint venture will enable VAA to increase its profitability by exploiting the American market. Furthermore, the joint venture will increase the firm’s profitability by providing the UK customers with diverse destinations, which will arise from the effectiveness with which the firm will exploit the Delta Airlines network. The firm is committed to maximizing its profitability by incorporating fuel-efficient aircrafts such as Boeing 787 within its fleet (Parker 2013).
The joint venture will enable the airline to restore its operating profits from the negative trend, as illustrated in the graph below. In 2013, the airline experienced a pre-tax loss of £ 93 million, which is relatively high as compared to a loss of £ 99 in 2012 (CAPA Centre for Aviation 2014).
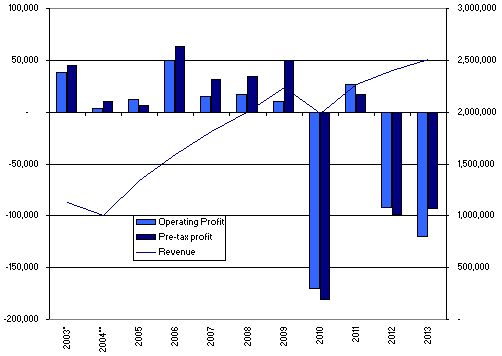
Customers and society – the airline have an obligation to ensure that customers and the general society achieve a high level of satisfaction. Seliet (2000) argues that the level of satisfaction amongst customers and the society influences the effectiveness with which an organization achieves sustainability in its operations.
In an effort to increase its customer base, Virgin Atlantic Airways has integrated price as competitive elements. Moreover, the firm has improved its in-flight services over the years in an effort to nurture a unique customer experience.
With regard to society, the airline is committed to protecting the society within which it operates. The airline has incorporated corporate social responsibility as one of its core strategies. It ensures that its operations do not affect society negatively. For example, the airline ensures that its operations do not increase climate change through carbon emissions.
In a bid to achieve this goal, the airline has integrated fuel-efficient technologies such as bio-fuel technologies. This move has remarkably reduced the firm’s carbon footprint (Virgin Atlantic 2014b). Additionally, the airline has integrated a comprehensive code of ethics, which has led to the establishment of ethical behaviors.
The government – in an effort to minimize interference from the government, VAA is committed to ensuring that its operations comply with the set rules and regulations. Firms in the UK airline industry are required to ensure a high level of customer safety and desist from practices that amount to exploitation of employees and customers.
Fiscal and monetary policy; effect of expansionary monetary and fiscal policy on VAA
The UK economy has experienced a wave of economic challenges over the past few years. The economy was adversely affected by the 2008 global economic recession. The recession led to a significant decline in the level of demand within the economy. Furthermore, the UK economy slipped into recession in 2012, hence affecting its economic growth (Thomson 2012).
The prevailing economic fluctuations have adversely affected the performance of firms in different economic sectors. For example, the manufacturing sector experienced a 1.8% decline in the volume of its output between 2008 and 2009. Moreover, companies implemented downsizing strategies, hence increasing the rate of unemployment to 8.1%. Subsequently, firms such as British Airways experienced poor financial performance (Bank of England, 2014).
In an effort to stimulate growth, the government adjusted its economic policies by implementing expansionary monetary and fiscal policies. The government’s objective in implementing the fiscal and monetary policies was to minimize the deflationary gap and stimulate aggregate demand. One of the expansionary fiscal policies that the UK government implemented entailed increasing the level of government spending by 3.5% (Seager 2009). The budget increment was utilized in diverse projects such as the construction of new roads and airports.
Other fiscal policies that the UK government implemented include a £ 145 tax cut amongst consumers whose income is £34,800 per annum, £ 20 billion funds to small enterprise-loan guarantee scheme, £ 3 billion in investment spending, and a 2.5% reduction in sales tax. The UK government is committed to stimulating economic growth by increasing the volume of the money supply. For example, the government allocated £ 375 billion in its Asset Purchase Facility (Bank of England, 2014). Subsequently, the government was in a position to increase the amount of money available in the economy.
The aforementioned policies will remarkably improve the performance of VAA. For example, a reduction in the VAT rate and a decline in the rate of interest will improve the consumers’ purchasing power. Subsequently, consumers will be in a position to purchase goods and services, which were considered as luxuries during the recession.
Assessment of the impact of EU/ UK competitive policies on the activities of British Airways
Competition is a critical element in the success of organizations in different economic sectors. Through fair competition, consumers can access diverse products and services at relatively low prices. Furthermore, the implementation of competition a policy promotes efficiency. The UK government and the European Union have instituted a number of competition policies, which are based on four main pillars that include antitrust and cartels, state aid control, market liberalization, and merger control.
The establishment of the Office of Fair Trade [OFT] in 1973 has played a remarkable role in enhancing fair competition amongst firms in the UK. Prasad (2009, p.8) notes that the office ‘prohibits businesses from engaging in unfair trade practices such as the establishment of cartels and swindles.’ Failure to comply with the set competition laws can affect the competitiveness of a business adversely.
In 2007, the UK government, through the OFT penalized British Airways £ 121.5 million for engaging in unfair trade practices (Office of Fair Trading 2007). British Airways had engaged in collusion with Virgin Atlantic in setting the price of its long-haul passengers by adopting price surcharges. This aspect led to a significant rise in the prices of jet fuel prices. During this period, the price of a ticket in British Airways and Virgin Atlantic Airways increased by a margin of £5 and £60 (Office of Fair Trading 2007).
Effect of increase /decrease in demand/supply of VAA tickets on pricing and sales decisions
VAA operates in a free market, which is characterized by fair competition and lack of government control with regard to prices. Subsequently, the VAA’s ability to maximize its profits will be subject to market forces of demand and supply. The prevailing demand and supply for VAA tickets will influence the firm’s pricing decision.
During high seasons, the demand for VAA tickets will be higher than the supply. Subsequently, the firm will be required to increase the price of the tickets in order to maximize its profit. On the other hand, the firm will be forced to lower the price of tickets during low seasons, as the demand will be lower as compared to the supply. Therefore, one can assert that the elasticity of VAA’s tickets will be subject to market forces.
Impact of cultural, political, economic, social, technological and legal factors on VAA
Businesses are operating in the international market face numerous challenges, one of which relates to the existence of culture shock. Schuler and Jackson (2001) argue that a culture shock arises from the existence of differences between corporate culture and national culture. According to Schuler, Jackson, and Luo (2004), national culture affects the operations of multinational companies such as VAA in a number of ways.
First, the existence of culture shocks may hinder the effectiveness with which VAA creates market awareness in the host country. For example, the advertising campaign adopted by VAA may be offending in some cultures. Subsequently, the firm might experience a challenge in its efforts to penetrate its target foreign market.
The existence of cultural differences may affect the firm’s productivity in the international market adversely due to differences regarding the employees’ attitude towards work. For example, Russian managers do not attach much value to reward management. This aspect may affect the employees’ productivity adversely, hence the firm’s long-term performance. Additionally, cultural differences may affect a firm’s ability to achieve its growth objectives through formation of mergers and acquisitions because of cultural differences.
A study conducted by Schuler, Jackson, and Luo (2004) shows that cultural differences increase the rate of employee turnover. Furthermore, it leads to a 15% decline in the employees’ level of productivity. The rate of employee turnover is mainly experienced by executives. Cultural differences also increase the likelihood of conflict amongst employees.
For example, employees may not possess similar values, norms, beliefs, and attitudes towards their job and the organization. Therefore, the ability of the firm to achieve its growth objective may be hindered (Carleton & Lineberry 2004).
Pestle analysis
Political, economic, technological, and legal forces may adversely affect the VAA’s operations as illustrated herein.
Benefits of international trade to VAA
As a profit-making entity, VAA should be concerned with how to maximize its profit. The firm can achieve its profit maximization objective by adopting internationalization as one of its business-level strategies. Moreover, the firm should target emerging markets in its internationalization processes. Some of the markets that the firm should consider include the Gulf region countries.
International expansion will enable the airline company to establish new routes, hence increasing the number of passengers carried within a given financial year. Moreover, venturing into the international market will also present the firm with an opportunity to understand how best it can serve the international market. Subsequently, the firm will be in a position to maximize the level of its profitability.
Effect of global factors [emerging markets, enlargement of EU, customs unions, WTO, NAFTA, and other PESTEL] on VAA
The establishment of diverse trade agreements such as the WTO, NAFTA, and the European Union will greatly influence the firm’s success in the international market. First, the trade agreements such as the formation of the European Union will lead to an increment in the firm’s market share. This arises from the fact that the trade agreements aid in eliminating trade barriers, hence providing the firm with an opportunity to venture into markets of the member state countries at a relatively low cost.
Consequently, the firm’s profitability will increase (Prasad, 2009). On the other hand, the business environment will be influenced by political, legal, economic, social, and technological changes. In order to survive in the long term, VAA will be required to adjust its operational strategies in line with the macro-environmental changes.
Impact of EU policies on VAA [customs union, harmonization of technical safety standards]
Virgin Atlantic operates in a number of EU countries. Subsequently, the firm has been greatly affected by the economic policies adopted by the member states such as the harmonization of technical safety standards and custom unions. First, the firm is required to ensure that it adheres to the safety standards as stipulated by the EU.
This requires the firm to adjust its operations management in order to ensure a high level of safety to its customers. Additionally, the firm is required to develop a comprehensive database and to work in collaboration with the respective customs union in order to enhance the level of security of its customers and other stakeholders.
Conclusion and recommendations
The above analysis identifies VAA as a profit-making entity. Subsequently, the firms’ operations aim at maximizing the shareholders’ wealth. However, the firm’s long-term success will be subject to the extent to which it takes into account the internal, the connected, and external stakeholders.
In a bid to survive in the long term, VAA should assess how macro-environmental forces will influence its operations. Additionally, it is also important for the firm to exploit the market benefits presented by the high rate of globalization through internationalization.
Reference List
Bank of England: Asset purchase facility results from 2014. Web.
CAPA Centre for Aviation: Virgin Atlantic airways track record for losses; partnerships should help cutting cost 2013. Web.
Carleton, R. & Line berry, C. 2004, Achieving post-merger success: a stakeholder’s guide to cultural due diligence, assessment, and integration, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Office of Fair Trading: British Airways to pay record 121.5 million pound penalty in price-fixing investigation 2007. Web.
Parker, 2013, Chief of Virgin Atlantic fuels hope in the joint venture. Web.
Prasad, E. 2009, Assessing the G-20 stimulus plans; a deeper look. Web.
Schuler, R. & Jackson, S. 2001, Cultural diversity in cross border alliances, Cengage, New York.
Schuler, R., Jackson, S. & Luo, Y. 2004, Managing human resources in cross border alliances, Routledge, New York.
Seager, 2009, Budget 2009; UK economy to shrink 3.5% this year. Web.
Select, H. 2000, Business, Heinemann, London.
Thomson, 2012, UK economy to fall into recession, the government should ease fiscal policy. Web.
Virgin Atlantic: Exceptional services require exceptional training 2014a. Web.
Virgin Atlantic: What is Virgin Atlantic doing to combat climate change? Can you give specific details? 2014b. Web.