Abstract
The core objective of this research paper is to examine water scarcity and its effects to the environment. This research paper will lean towards a descriptive approach. Several causes of water scarcity will be reviewed in this research and subsequently suggest solutions to the problems will be discussed.
In conclusion, this research paper will make a number of recommendations to ensure significant strides are achieved in curbing water scarcity. Besides, after reviewing the recommendations applied, this paper will determine ways in which the research results can be dispersed. Introduction
Introduction
This report will assess the increased demand for water resources as a result of its unavailability. Besides, the paper will also consider the solutions and recommendations for supplying water to all. Water is a valuable resource to humans and the world as a whole.
If water resources continue to diminish, the environment will continue to experience the struggle of surviving since the environment, and forests particularly depend on water resources. Huge industrial demand for water, increased populations and agricultural demands for water increase the scarcity of water. Australia, for instance, is estimated to maintain its domestic water needs rise to 70 percent in the near future. Water Scarcity
Water scarcity is a problem that is experienced all over the world. It is estimated that over a billion people are annually hit by water scarcity. The U.S. department of state puts a figure of 1.1 billion people who lack safe drinking water while 2.4 billion cannot access basic sanitation. Interestingly, “water scarcity also occurs in regions that contain freshwater and sufficient amounts rainfall” (Postel 85).
This is because sufficiency of water supply depends on water conservation methods, distribution channels available in the community and the quality of water as stated by Postel (192). Besides, meeting the demand for household water use, farms, industry and the environment requires substantial conservation methods and timely distribution methods. It is estimated that one out of every three people on each continent of the globe is affected by water scarcity.
As the world population grows the need for more water also increases. Besides, more urban cities are coming up, and urbanization increases the household and industrial consumption. 1.2 billion people across the globe live in areas where water is not present or is physically not available. This is a fifth of the world’s population.

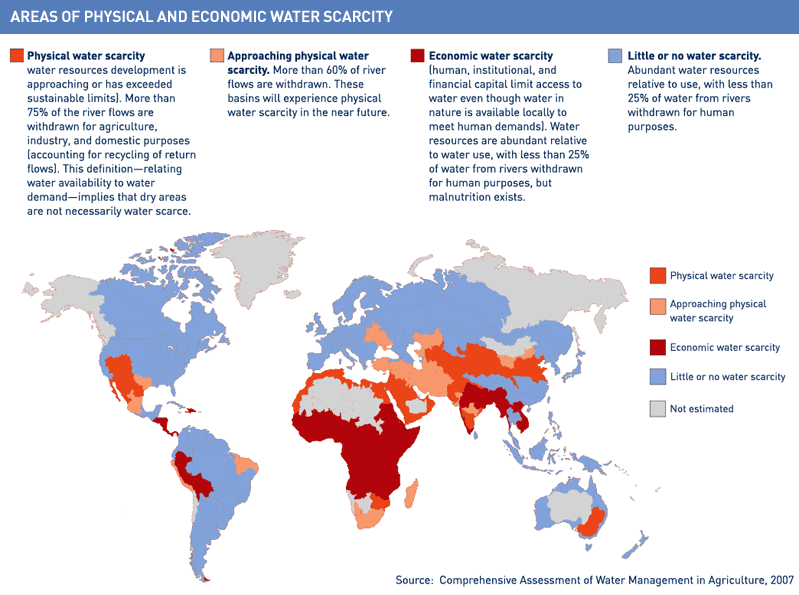
As shown by the above figure, water scarcity is fast becoming a major challenge in developing countries where a quarter of the world population lives. This is due to “lack of proper technique of supplying water from sources such as rivers and aquifers to where it is needed most” (Berk 190). In places where water shortage is experienced, communities are forced to use unsafe drinking water for drinking and washing their clothes.
Unsafe drinking water increases the chances of water borne diseases such as dysentery, cholera and typhoid fever being transmitted to humans. Furthermore, “water scarcity can lead to other diseases including trachoma, which is an eye infection that leads to blindness, plague and typhus” (Pereira and Lacovides 299). When people are faced with water scarcity, they institute measures to store water in their home. These measures can include using water tanks or sinking wells.
This method leads to a breeding ground for mosquitoes – which are known carriers of malaria and dengue fever among others. In the face of all this problems associated with water scarcity, there arises a need to address the issue of water scarcity before it gets out of hand. Better water management policies ensure safety of the communities relying on the water as breeding grounds for insects are eliminated, hence a reduction in water borne diseases like the schistosomiasis which is a devastating illness.
According to Sherbinin (26) the shortage of water and agricultural production in poor urban settings utilizes waste water. More than 10% of the world’s population consumes foods that have been grown using waste water.
These irrigated foods can contain harmful chemicals or disease-causing organisms. It may almost seem ironical to note that the world has enough water for everyone. However, the problem that leads to water shortage is poor distribution. “Water scarcity is a natural occurrence in some areas. However, in others areas it is a man-made phenomenon” (Sherbinin 26).
Similarly, the world is endowed with sufficient water resource to cater for approximately 6 billion people. According to Pereira and Lacovidae 302) scarcity has contributed to uneven distribution channels, wastage. This is because of poor harvest and utilization strategies. Poor methods of handling the water resource have led to water Pollution. Hence, this has created a big challenge that threatening the ecosystem and human population.
Types of Water Scarcity
Physical Scarcity
Physical scarcity of water is prevalent across the world. As the name suggests, access to water sources is physically limited. This happens when the demand for water surpasses the land’s capacity to provide the much-needed water. This form of deficiency is primarily associated with the dry parts of the world, including arid regions of the globe as clearly illustrated by the figure below.
The northern part of Africa and some parts in Asia and Australia are the worst hit by this physical scarcity. However, we have some regions in the world which do not fall in the dry land category but have man-made physical scarcity. For instance, the Colorado River basin has been “over used causing physical water scarcity downstream” (Pereira and Lacovides 299). Thus, scarcity can also be attributed to over management of the river resources.
Below is Figure 1.3 showing water scarcity distribution around the globe (BBC NEWS)
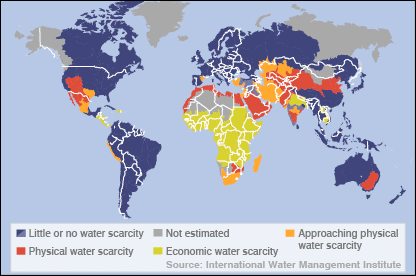
Economic Scarcity
The most problematic type of water scarcity is economic water scarcity. This happens when no concrete measures are taken to ensure water availability. This situation persists largely due to lack of good governance, and lack of good will to change the situation. Therefore, economic scarcity is demonstrating the lack of resources in terms of funds or monetary benefit to utilize available sources of water.
The sub-Saharan Africa falls under this model of economic water scarcity. Unequal water resource distribution is generally experienced in the Sub-Saharan due to several reasons. These reasons are tied to political and ethnic conflicts, which are a common occurrence in this part of the world.
As shown in Fig 1.2 much of sub-Saharan Africa falls under economic water scarcity. However, Odgaard explains that in the presence of good governance mechanisms, this situation is manageable (140). In most cases, access to clean and safe water can be as simple as constructing small dams for communities to harvest rain water. Besides, the principal objective should be to provide relief for the already suffering communities.
To ensure clean water is available to world population, water harvesting techniques should be developed. These need not be complicated as it may mean rain water collection from roof tops and construction of water storage tanks. Without question, this situation can be tackled with the construction effort from the local community, availability of funds and engineering.
Water Scarcity in the U.S
As highlighted earlier in this research paper, water shortage is a global concern that is affecting communities and the environment and threatens to affect many others if substantial measures are not taken to tackle the scarcity.
However, it is difficult to compare the struggle of an African woman walking long distances in search of fresh water with water scarcity as experienced in the United States. The Colorado River is beginning to run dry in some places; this sounds almost impossible considering the size of the river. Huge water bodies like Lake Mead found in Arizona may become obsolete.
These are some of the dramatic changes that are facing the United States with regard to water scarcity. With this realization, more and more people are starting to connect with situations in dry regions of the globe. More so, the effects of water mismanagement are starting to be felt. Research indicates that Lake Mead may run dry by the year 2012. This is a serious issue considering the lake currently supplies up to 22 million people with water.

This is proof enough that water scarcity is not just a problem of people who never had water but rather a problem for all. Demand for more water and problems associated with pollution is contributing factor to water shortages. The daily demand for water means that the availability of the same will be affected in the future. Many people may thirst in the future if the current trend of wasteful toilet flushes and showerheads are not minimized.
Key Causes of Water Scarcity
Water scarcity has been caused by increased demand. These demands can be categorized into five major contributors to water shortage. Firstly, industrial water consumption enhances their production has created a strain on water resources. Most industries require having sufficient water supplies in order to perform optimally and produce goods or services.
Besides, most mining and oil industries use water in their operations. Thus, water scarcity makes these industries to be more susceptible to water shortages. Secondly, agricultural water needs for farms where there is unreliable rainfall create a huge demand for water, thus exerting more pressure on the already strained water resources.
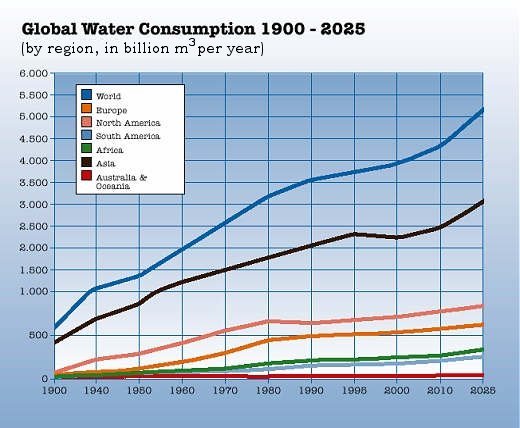
As the world population grows, more demand for water is experienced as illustrated by fig 1.4. The world population recently hit 7 billion, and the figure could only mean that pressure to supply water for all is expected to rise. Consumer demand is closely linked to population growth as more and more households require water to maintain their households.
Economic growth is a positive step towards improving the lives of people in a given community, but calls for the need to supply resources to fuel it. One of it is water; hence as more economic growth is experienced more demand for water is created.
Suggested Solutions to Water Scarcity
Environmentalists maintain that immediate solutions have to be devised. Low cost solutions come in handy. In China for instance, farmers are already making use of these inexpensive water conservation methods with great results (FFTC). However, “low cost solutions, for example, creating still water conservation may harm the population downstream” (Berk 190). Therefore, it is important for the conservation efforts to involve everyone to provide an amicable solution for all.
Conclusion
In order to ensure water scarcity is effectively tackled, total commitment to set targets and solutions is required. Figure 1.5 clearly indicates that the demand for water is rising, and as a matter of urgency, conservation efforts will bear fruit if every one of us realizes that they have a role to play.
Constant assessment of the strategies governing water bodies and their utilization will ensure that positive progress is achieved. Though much effort has been focused on water conservation, its use and proper management should be emphasized as it will ensure clean water service delivery for us and generations to come. Moreover, focus on climate changes and environmental degradation should also be improved, and a positive environmental culture encouraged.
Works Cited
BBC NEWS. Map Details, Global Water Stress. 2006. Web.
Berk, Richard. Water Shortage: Lessons in Conservation from the Great California Drought. Halifax: Abt Books, 1981. Print.
FFTC. Irrigation Management in Rice-Based Cropping Systems: Issues and Challenges in Southeast Asia.” 1998. Web.
KTAR. As Lake Meads Drops, Water Concerns Rise. 2010. Web.
Links between Population and Fresh Water. Population Growth and Water. 1996. Web.
Odgaard, Rie. Conflicts over land & water in Africa. Michigan: MSU Press, 2007. Print.
Pereira, Cordery and Lacovides. Coping With Water Scarcity, Addressing the Challenges. New York: Springer, 2009. Print.
Postel, Sandra. The Last Oasis: Facing Water Scarcity. Oxford: Earthscan, 1992. Print.
Sherbinin, Alex. Water and Population Dynamics: Local Approaches to a Global Challenge. Montreal: IUCN, 2009. Print.
Tag Archive for ‘Water Scarcity’. “Hydro-diplomacy” Needed to Avert Arab Water Wars. 2011. Web.
Umwelt Bundes Amt. Exhibitions from the Umwelt bundes amt (Federal Environment Agency). 2010. Web.