Project introduction
The chosen company for this project analysis is Wells Fargo. This analysis of the company will be focused on online ticketing and receipting system’s planning, design, and implementation. Wells Fargo, which is in the finance and security industry, has various affiliate branches across the United States of America. This American company is a multinational one that offers various financial services across the globe.
It is one company that has assets in securities, stocks, and property in the United States. In addition, it has the biggest market capitalization in America (Wells Fargo, 2012). This project will focus on designing an online ticketing theatre box since Wells Fargo has been experiencing difficulty in its receipting process. This has come as a result of growing number of customers and users (Peltier, 2010).
Project description-Business Case
Wells Fargo has been chosen as the firm that needs the implementation of a new information system. This company has been in the business since 1852, when the Wells Fargo securities were started with the aim of incorporating the company’s new capital market. The market capitalization of the company currently stands at $175.32 billion.
The company was initially started as a small business venture under the ownership of Henry Wells and William G. Fargo. Currently, the company has grown its business operations, among both the insurance companies and banks. Wells Fargo Company provides banking services, mortgage loans, and security services.
Its competitors include Citigroup and JP Morgan Chase. Bank of America is the other closest rival of the company in both the banking and insurance industries (Wells Fargo, 2012).
The corporate Mission and vision statements of the Wells Fargo Company are as follows:
“We want to satisfy all our customers’ financial needs and help them succeed financially. Our vision of financially satisfied, successful customers is based on a simple, time-tested premise. We believe our customers can save more time and money if — after carefully shopping around and comparing choices — they bring all their financial services to one trusted provider” (Wells Fargo, 2012).
This company uses UML-based business modeling, which includes, but is not limited to online business ticketing. In addition, the project to be designed and implemented in this system analysis will be geared towards solving various problems, such as the need for the new sales channel.
In addition, it will help in finding solutions to falling market share. Poor internal communication and poor receipting and payment systems are also going to be managed by the system.
Role of the systems analyst
The systems analyst involved in the Wells Fargo Company plays the role of planning, designing, and implementing the information systems that help in solving the problems discussed earlier. This systems analyst acts as external consultants who have sound knowledge regarding business and operations of the company.
They acted on a middle level management since they relied on the company’s management to provide them with the necessary information. Though they are independent, their authority is limited to their scope of work, by following the procedures and guides of the company.
The systems analyst engaged in the project would help in meeting time, quality, risk constraints, costs, and scope through proper planning and budgeting for the company’s human resources and the financial capital.
The systems analyst would get support from the IT management in order to develop a good system for the organization. There are on-staff developers, but some will be outsourced to provide some technical backups because of shortages. The outsourcing will help in providing diversity in knowledge and quality results. The system analysts have independent authority over the project and its final product.
However, the ownership and the project would be passed on the company’s IT management, once the completion stage has been reached. The responsibility of the systems analysts on the project installation would be partially passed to the IT management team after the completion process has been realized.
Though, the systems analysts developers would still have some vested authority and responsibility over the entire system. In fact, about 70 percent crossover would be necessary on the role of the project manager. This will impact directly on my role as an assistant IT analyst. Crossover involves the act of incorporating a different role into one’s current role in the project design and implementation (Larman & Basili, 2006).
Feasibility analysis
The proposed system is going to be 80 percent economically feasible to the Wells Fargo Company since it can help in improving both the receipting and payment processes. The organizational factors such the level of cooperation among the employees of the company would help or hinder the design and implementation of the project.
The employees of the company need to cooperate fully with the project manager and the systems analyst. This is due to the fact that the project manager and the systems analysts requiring some information about the processes and operations of the company, and the employees could be in the best positions to give the needed information.
It is also important to note that when proper budgeting is not carried out, it is likely that the shortages of software, hardware, and networking will be experienced during the project design and implementation (Wells Fargo, 2012).
The type of budget to be used during the project design would be done at quarterly intervals of a financial year that incorporates the costs of the hardware, networking, software, and consultation fees. However, the maintenance fees for the system would be incorporated in the budget after the implementation stage.
At the implementation stage, the project is rolled out to the entire company. The timeframe for this budget would be nine months since the costs were to be reported in the financial reports for that particular accounting period.
The highlighted factors affect the implementation of the new information system due to the fact that human resources and financial constraints are crucial in both the design and the implementation of the project. For instance, if the financial resources are inadequate, then materials such as software, hardware, and networking cannot be purchased. This means that the whole project cannot proceed to completion.
The inadequate financial resource means that the project coordinators cannot pay their contracted employees. On the other hand, it is crucial for the company’s employees to produce the necessary and sufficient information to the systems analysts about the operation procedures and processes of the company.
Elements such as the departmental politics also play some significant roles in the project design, implementation, and development. For instance, the finance department might fail to provide the IT department with the necessary information that would facilitate the design and implementation of the system.
Such resistance can be overcome through attractive bonus pay that motivates the employees to adopt the system, with little opposition. Another way to minimize the resistance among the departmental employees about the new system would be through the adoption of training programs.
Moreover, the new online ticketing system will have several benefits since the automated payment process can help in facilitating both the ticketing and receipting procedures. This system will help in facilitating online ticketing and receipting. In fact, the project is expected to yield 25 percent return at the end of the five years. The costs on the project can be significantly reduced so as to make it feasible.
It is quite unfortunate to note that scaling down the application of the system will reduce its potential effects on the company’s technical operations since not all the areas of payment processes, such as great plain reconciliation will covered.
In essence, the need for the new sales channel, the falling market share, poor internal communication, and poor receipting and payment systems will not be covered sufficiently. Therefore, the scope of the entire online ticketing reporting and information system should be detailed and exhaustive (Larman & Basili, 2006).
User requirement gathering
The users can be engaged through online interviews and questionnaires to gather the information on the requirements of the new system. The methodologies to be used are the interviews, and the data gathered would be documented through both the qualitative and the statistical tools of analysis. The users of the system would play very crucial roles in the design and implementation of the system.
These groups of users will help in testing the functionality and the suitability of the entire project on the information system. Notably, it is important to engage them at very early stages so that they can be in the position to detect errors in the new system before it is finally rolled out for use by the entire company. Such early detections would facilitate the corrections and the amendments to be carried out on the entire project.
Indeed, the users can help in preventing the design mistakes by detecting the errors in the new system before it is finally rolled out. Such mistakes can be dealt with at the earliest stages of the development since they are costly in the long term. For instance, if the new system is designed and finally implemented with a lot of mistakes, it will fail to function and perform as expected.
Another discrepancy that might be realized is the fact that a system with many mistakes is very costly to maintain. This can be prevented by frequently engaging the users at the initial stages. These project lifecycle mistakes are very costly to the company in the long run. Therefore, the user interface is very essential and should be integrated in the entire system of the project.
Importantly, the characteristic of the successful user interface should serve the demands of all the users who rely on the system. It should be fast, and deliver quality output within the expected time frame.
The useable interface increases the chances of the successful user adoption of the new system by making sure that there is less resistance, as evidenced in Peltier’s case (2010). In addition, the new system will be easy to understand and use.
Systems planning and design
Here, a data flow diagram, an objected-oriented class diagram, an entity relationship diagram are designed and incorporated in this analysis. Envisioned components in this analysis are the data tables, primary, and foreign key (Gane & Sarson, 2007). The data are saved in the files and the databases after every stage of the project design. The types of data tables envisioned in the systems designs are the relations table and the object tables.
Moreover, the primary and foreign key relationships can be regarded as that of referential constraints. This is due to the fact that the foreign key from a given table acts as the reference to the primary key, which is from a different table. The UML process model is the object-based class to be employed in this analysis.
This would be incorporated on the proposed online theatre ticketing box to facilitate the users’ receipting and ticketing process. The properties and methods of this object-based class are the information contained in the objects.
The relationships between the properties on an object and its method are witnessed on the sets of the object entity as well as the object-context. In fact, instances of the object would be necessary for the system to run routinely (Peltier, 2010).
Overview of the proposed system
Use of three generic strategies enables the organization, through its operational processes and the people to demand creative designs that employ the complete applicability of the value chain to facilitate the achievement of organizational information capabilities. Such information system capability will ensure that the organization is capable of looking beyond the physical walls of the company.
Further, in this section, the system developers provide reliable and researched e-commerce strategies that any organization can employ to enable the required information system capability aimed at facilitating the attainment of the overall organizational goals.
It is suggested that mass customization and personalization are one of the key e-commerce strategies that any organization seeking to survive in the contemporary competitive environment must utilize to guarantee the achievement of the desired competitive advantage. The other e-commerce strategies that companies could employ include the disintermediation strategic approach and the global reach strategic approach.
In this section, the analysis seeks to provide the technical and managerial approaches available in managing information resource in this business organization. In order, to effectively manage receipting process, which has been a major problem for Wells Fargo, system developers begin by exploring the importance of developing and managing the business intelligence resource.
In this regard, the system developers suggest that the organization needs to maintain the relational database model to enable the efficient and sufficient provision and availability of the necessary data that form the core of business intelligence.
The system developers observe that the relational database model should be developed on a clear framework that ensures the collection of sufficiently relevant information which is created with logical structures and logical ties among the information. The relational database model also utilizes the built-in constraints within the collected information that works to ensure the security of the information intelligence agency.
The section goes further to evaluate the database management system tools together with the data houses and data mining basics. Moreover, the system developers suggest the pertinent information relevant for the derivation of sufficiently managed information resource in any organization (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008).
Here, Haag, Cummings and McCubbrey employ an interactive approach to examine the relationship between the organizational decision and the various decision support systems, collaboration systems including the geographical information systems (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008).
In this regard, the system developers explored the various types of decision that the business manager will always be facing during the operational management of the organization. The system developers also examined the various components of the decision support system as well as the reliable domains of collaboration system in facilitating and influencing the capability of the business manager to make organizational decisions.
Further, the system developers assessed the constituting components of artificial intelligence and how such components influence the decision process within the organization. As such, the system developers went further to discuss the contribution of the various intelligent agents including buyers, users, monitoring-and-surveillance, and data mining agents (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008).
As a way of exploring further into the component make-up of online ticketing system, the project developers used this section to examine the tangible growth prospects of this new venture.
Following this approach and in a bid to emphasize the importance of online theatre ticketing box in facilitating receipting processes, the system developers evaluated the resulting merits of this proposed project to Wells Fargo through an in-depth analysis of the constituting success to its users.
Further, the system developers examined the business to business e-commerce model and how it influences the transactional relationship between the main players in the given business environment. Additionally, the system analysts provided sufficient discussion on the significant role that government play in facilitating e-commerce models.
In concluding this section, the system developers explored the various e-commerce payment systems including credit and smart cards and their influence on the company’s information capability that facilitates increased generation of financial benefits.
The system developers introduce this section by emphasizing on the significant influence of the process of developing an information system on the resulting information capabilities (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008). In the following parts, the systems analyst expound on the necessary seven phases involved in system development including planning, analysis, designing, development, testing, implementation and maintenance.
The system developers also describe knowledge workers and the significant role that they play in system development life cycle. In this regard, it was also important that the system developers evaluate the possible failures of the information system under investigation. Why systems fail provide the possible failure loops that undermine the capability of any information system.
The system developers further explored the prospects of self sourcing, outsourcing ,and prototyping types of system development. In a bid to further explore the strategic components of the organization, the system developers employed an analytical approach to examine how the business-driven technology helps the organization to achieve the desired performance levels.
The system developers provide topical discussion in regards to the contribution of business-driven technology in increasing employee productivity, enhancing decision making, improving team collaboration, creating business partnerships and alliances, enabling global reach, and thereby facilitating organizational transformation.
In concluding this section, the system developers employ a realistic approach in examining the role of information technology infrastructures in influencing the occurrences in the real world (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008).
Information protection is primal in ensuring the proper brand management within any business venture. Business managers must ensure that the organizational information is kept safe from the public indulgence except for the reasons that the industry demands. Therefore, in light of the above propositions, Haagthe systems analysts explore the ethical perspectives of the internet age.
The system developers deeply examined the two factors that determine how business owners and the other managers as well as the employees decide ethical issues. It is on this basis that the system developers provide guidelines for ethical computer system use as intellectual property.
Additionally, the system developers provide sufficient discussion on privacy issues relating to the use of information technology in any given organization. By employing an evaluative approach the systems developers evaluate the privacy relationship between the business owner and other stakeholders of the organization.
In addition to the privacy issues, the system developers provided an analytical approach in assessing the significant importance of information as raw material and financial capital to the organization. Finally, the system developers examine the security-related issues involved in the development and maintenance of efficiently sustainable information system (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008).
The emergence of the global market has made it possible for the free flow of information within and without any organization set-up. In this section the systems developers discuss the emerging trends and technologies in terms of the need for information filtering.
This is due to the fact that the organizations need to employ push technologies that encourage competent and fruitful interaction between the organization and the customers as well as between the organization and the employees.
The system developers also examined the contemporary organizational movement from the basic computing to intellectual-driven computing that underpin the operational capabilities of many economies today. The changing psychological interaction has also taken center stage in this section since the system developers evaluate the expected possible information automation approaches.
Further, the system developers have also noted the increasing portability and mobility of information system devices including free internet phone calls, wearable computers and micro-payments, and financial cybermediaries. In the digital domain the system developers provide the readers with sufficient discussion of the emerging digital cash and implant chips (Haag & McCubbrey, 2008).
Information system outsourcing at Wells Fargo Company involved a contract, which specified business/technical service that the organization required to deliver. Wells Fargo Company used the total outsourcing approach where the platform for small scale material management planning system was maintained at organization’s side.
The main aim of the outsourcing strategy was to help the Wells Fargo Company to reduce its operational costs. The outsourcing strategy enabled Wells Fargo Company to enjoy from the removal of the burden of information technology, thus reducing information technology risks since the firm had synopsis to blame for system failures.
Like most of the information systems, customer relationship management system will subject the staff to management training in order to be able to execute the requirements of the strategic information management efficiently.
This implies that the company will incur training costs to enable its employees to acquire the necessary knowledge base for the system to be successful. In addition, the company will have to incur installation and maintenance costs, which were not incurred when the material resourcing planning system was resourced.
Analysis of the proposed system
Insurance and banking are the fast growing industries that need proper methods of managing clients’ transactions. In order to serve the customers better, the management can decide to put in place a ticket booking system. The ticketing system will be responsible for handling various ticket purchasing requests, which are generated from ticket vending machines, point-of-sale (POS) at box offices, and web based applications.
The business logic used to handle the booking request includes a number of steps. First, once a booking request is received, the booking service processes the ticket-information first. The process involves checking the availability of the ticket; if the ticket is available or when it is held for the customer.
Alternatively, the customer can be given some options, such as applying appropriate promotion and calculating the total amounts involved (dollar amount). In the second step, the booking service is in charge of the client using the payment information that is incorporated in the booking-request (Martin, 2006).
Finally, the booking service sends a confirmation to the client using the contact information, which is included in the transaction request (Oatman, 2007).
A logical data model represents an abstract structure of domain of a ticket booking system information. The diagrammatic logical data models are used in the business process that seeks to capture the necessary data on the ticket booking system and its relationship with the insurance and banking’s box office system. The logical data model is based on the structures which are identified in the earlier conceptual data-model.
The conceptual models describe semantic information of the ticket booking system. A business process model represents the activities of the ticket booking system (the insurance and banking’ box office system) the analysis of the current system and the proposed improvements. The business process modeling is performed to improve the quality and efficiency of the ticketing processes.
Though the use of information technology is essential in the improvement of business process, it is not always a requirement. Generally, a business is a framework that is used to create social, economic and other forms of value.
The term is thus used represent various core and functional aspects of the business, which include, but not limited to purpose, strategies, organizational structure, operational processes, trading activities, and business policies.
Essentially, the business model facilitates the ticketing process in insurance and banking services, and through which the organization can sustain itself. The model shows how the organization can increase its revenue through the increased sales of tickets. A process design includes the organization and evaluation of tasks that the receipting process is composed of.
Designing the ticket booking system that improves the efficiency of the current ticketing is a challenging task that requires a variety of inputs, such as the strategies of the organization, information technology capabilities, goals, and constraints. The process modeling is one of the areas that are widely researched aspect of the ticket booking system, and the entire business process cycle.
It forms the important pre-requisite of the business process design. However, it is important to put into account that the most important process in the improvement of the ticket booking system is one that adds value to the entire process lifecycle. Arguably, process design has received little research as compared to the process modeling.
Limited academic contribution on the process design has forced the practical improvements, for example, the ticket booking processes, to rely entirely on personal experiences, tacit knowledge, and inspirations without guidance on the most appropriate approaches to use in the design process.
The situation leads to inconsistent results, which undermine the real potential of a business process management in the insurance and banking industry (Peltier, 2010). For example, below is an object modeling diagram of online ticketing of a business process design.
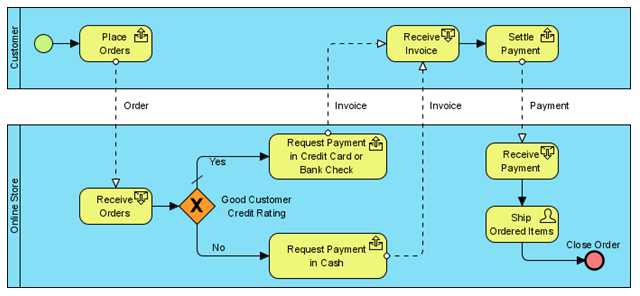
There are number of things that need to be organized for the business process to run effectively. These include; venue management, proper layout of the accounting procedures, seat booking, and publicity in promoting the entire insurance and banking business. Seat booking for the insurance and banking involves counter booking and telephone booking options which are available to the customers.
Once a payment (using cash or credit card) is made the tick booking system prints a ticket for collection by a customer. The other processes involved are cancellation and build mailing lists. The former is applied upon a customer’s request, and when the transaction is erroneous. Venue management of the insurance and banking composed of booking, cancellation and payment.
Details of the venue and book venue are entered in the booking functionality. On the other hand, the accounting is made of the ticket sales and venue hiring charges. In the latter, the details of the hirer are entered, invoice the hirer, process payment, and chase after the clients for payments.
Finally, the publicity advertises the performance of the insurance and banking, which might include, but not limited to uploading information and receiving e-mails (Oatman, 2007).
The structural modeling diagram below shows the map out of the entire insurance and banking (Huddersfield Playhouse) business process.
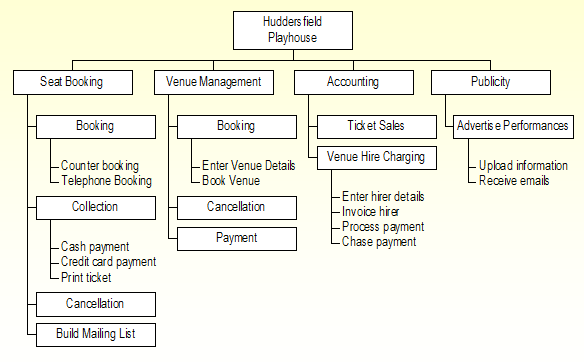
To understand the business process, it is important to review some of the stakeholders involved in the business, such as the insurance and banking manager and booking clerk.
For example, the booking manager is in charge of the entire ticketing processes, which include the venue management, seat booking, accounting, and publicity. On the other hand, the booking clerk is responsible for recording all the ticketing transactions. Notably, the insurance and banking manager and the booking clerk are happy with the new ticket booking system designed.
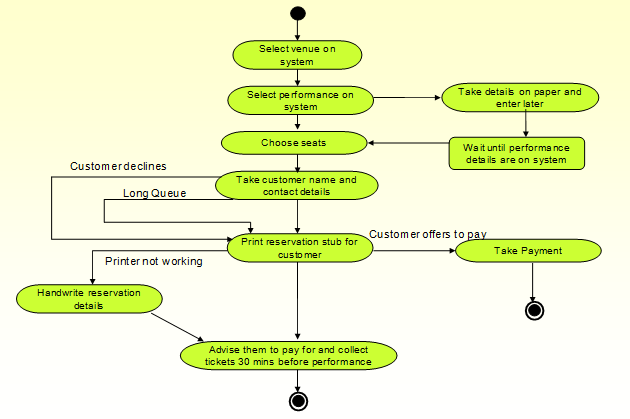
The data for instance need to store the whole activities involved in the counter booking process. The new system designed initially, incorporated in the counter booking process, various activities. The activities are outlined as follows:
- Select venue on the system.
- Select performance on the system.
- Choose seats.
- Take customer names and contact details.
- Print reservation stub for customer.
- Advise the customers to pay for and collect the tickets 30 minutes before performance.
However, the new system designed lacked some functionality, and would not perform efficiently. For instance, when a customer selects performance on the system, the booking clerk needs to take the details on paper and enter them later in the system.
After choosing the seat, the booking clerk must wait until performance details are on the system, before taking the customer’s name and contact details. The system also fails to account for the risks involved in the ticket booking process. For example, a customer may decline the seat offered, which leaves the clerk with an option of allocating a different venue, seat number, or even cancelling the transaction.
This kind of a situation calls for sound skills in decision making; since the customer is key to the business, persuasive skills are required to make the consumer buy the services of the insurance and banking. The system has also failed to put into account the possible failure of printers due to technical errors.
A clerk is left with no alternative as per the designed ticket booking system. In case of such a technical failure, the clerk should have the option of handwriting the reservation details, which are later on entered into the system (Topper & Jorgensen, 2008). Due to the loopholes in the new system, mentioned above, a proposed diagram for the booking process is shown below.
The payment activity of the newly designed system involved the following procedure for booking tickets for the insurance and banking:
- Advise customers of tickets price.
- Request payment method (cheque offered).
- Take payment by cheque.
- Print tickets and hand to customer.
- Thank customer.
However, the entire process lacks sufficient details. For instance, a customer might be willing to pay by cash and not by cheque. The systems should incorporate various methods of payments such as cash, credit card, and cash. In case the cheque is refused, “the customer has the option of paying by either credit card or cash.
Notably, the credit cards can be refused on the grounds of invalidity, expiry and insufficient amount available for transaction” (Fowler, 2010). The cash payment is not safe either since it is prone to theft, or can at times be very bulky. Due to these transaction risks, the insurance and banking organization has other options available, such money bookers, wire transfer, and other online methods of payment (Fowler, 2010).
The payment by credit card should incorporate the following procedure:
- Swipe credit card.
- Enter amount.
- Wait for acceptance.
- Obtain signature.
- Check signature.
- Enter amount on till and print receipt.
- Return credit card, voucher and till to the customer.
The procedures are represented diagrammatically as shown below.
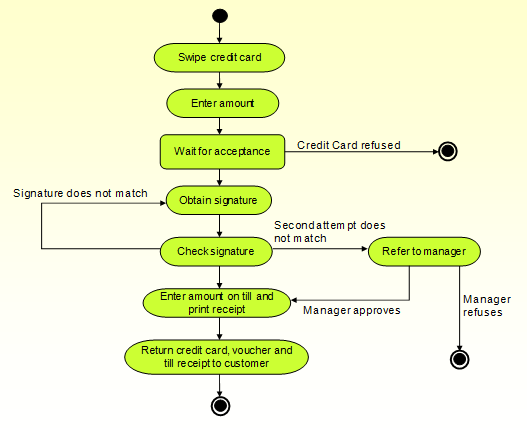
In the event that the signature on the credit card fails to match for a second attempt, the matter is referred to the insurance and banking manager. The manager makes a decision to either approves or rejects the transaction. Upon approval, the amount is entered on the till and a receipt is printed. Finally, the credit card, voucher and till receipt are returned to the customer (Edmonds, 2008).
The activities of a booking clerk can be presented using a case diagram for a ticket box, which include the following:
- Booking tickets: – add to mailing list and preservation stub.
- Print tickets: take payment.
The sample of book tickets used in the ticket booking systems above is as follows:
The book ticket for the proposed ticket booking systems (the improved version), can be represented as shown below.
Implementation plan
This projected would be implemented in phases. This can only be done after several runs have been done on the project. These test-runs will eliminate some of the possible mistakes that can be carried in the designed system. Though the chosen method has several benefits, it comes with some risks as well. It is beneficial in the sense that the errors and the mistakes will be minimized from the designed system.
However, the risks associated with this kind of method are those ones that include the information leakages to the outsiders. This puts the newly developed system at danger since some crooked individual can either copy it or crack into the same. The users and applications will be transferred in phases to the new system so as to implement changes gradually.
The potential changes that might come alongside this project would be handled gradually. For instance, rapid changes are likely to face opposition and rejection from the company’s employees. The risks can be minimized through proper financial planning and budgeting.
This will facilitate the minimization of costs that are associated with the projects. The need should be maintained within the budget to avoid cases whereby the proposed project fails to kick off (Biehl, 2010).
The system will be periodically maintained through firewall, antivirus, and security updates. The maintenance cost for the company would amount to $ 7,500. Finally, the responsibility of training the new users about the newly implemented system would be vested on both the IT department and the systems analysts. As a result, a training procedure manual would be created.
This will make it easy for the newly recruited employees to get the require information about the system. Besides, the employees of the company can follow the procedure manual so as to keep themselves updated on the operational procedures of the new system.
Conclusion
In sum, the newly proposed project would be met with little resistance from the employees of the Wells Fargo Company. This is due to the fact that both the IT department and the systems analysts would work in unity to train the other employees on the user requirements.
In essence, it is importantly to know the success of the new system will be pegged on the cooperation of both the IT department and the finance departments of the company. In addition, the risk mangers would play a critical role in making sure that the risks associated with the project are identified and mitigated in time.
The project manager must properly plan and budget for the resources allocated for the system. The design and implementation of the project should be carried out in phases so as to discourage high resistance from the employees. This would involve the input of both the systems analysts and the IT department members who were entirely involved in the training about the new system.
References
Biehl, R. (2010). Data Oriented Quality Solutions. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall Publishers.
Edmonds, E. (2008). A process for the development of software for non-technical users as an adaptive system. Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Fowler, M. (2010). Appeared in extreme programming explained. Boston: Addison- Wesley.
Gane, C. & Sarson, T. (2007). Structured Systems Analysis. Missouri: McDonnell Douglas Publishers.
Haag, S. & McCubbrey, D. (2008). Management Information Systems for the Information Age. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Larman, C. & Basili, R. (2006). Iterative and incremental development: A brief history IEEE computer. Boston: Addison-Wesley.
Oatman, R. (2007). Physical Security: The Art of Protection. Baltimore: Nobel House.
Peltier, T. (2010). Information Security Risk Analysis. London: CRC Press.
Topper, A. & Jorgensen, P. (2008). Structured Methods. New York, NY: McGraw- Hill.
Wells Fargo (2012). Our vision: Where we’re going. Web.
Wells Fargo (2012). Mission and Approach. Web.