Introduction and the Competency Framework Outline
ADNOC is the company that is engaged in the sphere of health, safety and environmental protection. Hence, the competency framework of this organization will be closely associated with the matters of biological researches, medical considerations, and environmental solutions in general.
In fact, this framework is based on hazard identification and assessment of the surrounding environment. In the light of this fact, it should be emphasized that the actual importance of the analysis of the company is based on the analysis of the competency framework of the other companies engaged in the same sphere. The actual aim of the paper is to compare the competency sphere of ADNOC with the hypothetical company (ACA – Applied Care Associates) engaged in the sphere of healthcare and the aspects of environmental protection.
In general, the Technical community of any firm requires a continuing development in its skills for development. This is a very vital strategy for the future of the particular organization. Companies are in competition for high technical talents in the industry through a framework of knowledge management, process, and tools of implementation to all the stakeholders needs a well-formulated framework of technical activities as argued by Stanton, Miller & Layton (1994).
Contrasts
- The technical framework focuses on both the improvement of employee performance as well as the safety of employees while the ADNOC framework has proved to focus only on the focuses of the performance of the institution
- The ADNOC strategy has not being used in other companies (it is the first time it is being tried in China and has not yet been implemented) as opposed to the technical framework method, which has been proved operational in the UAE and abroad.
In accordance with the competency reports provided by ACA Company, the key aim of any company is to focus on the technical competence framework mainly due to the recent ill performance of the company as compared to other oil giants in the industry. Focus on the technical system, which calls for the recruitment of more competent workers so that such mistakes will not be experienced again. Focus on improving the skills of its technical community to match the pace of the ever-increasing high level of professionalism. This is a very vital strategy for the future of the organization.
According to Prahalad (1990), management should not forget that people are the third most important resource in the company after production and sales. The company therefore should join other major companies in the on going competition for high technical talents in the industry.
Development and Implementation
The importance of the competency framework analysis generally depends on the actual importance of the company’s activity. Considering the fact that ADNOC is engaged in the sphere of public health, the ACA Company analysis is closely linked with the principles of heath care and environmental protection from the perspective of protecting the publicity from various hazards. Hence, as it is stated in Collins and Montgomery (1995, p. 319), the company resorts to semi-quantitative approach towards performing the working assignments and implementation of the plans:
The semi-quantitative approach depends on a select team of experienced personnel who have access to accident, historical and failure data to make “professional” probability decisions. The probability categories relate to the theoretically calculated chance of major incidents happening. They do not relate to actual events as experienced on specific plants, locations or companies.
In the light of this statement, it should be emphasized that the actual importance of the semi-qualitative approach towards performance helps to unite the advantages of both qualitative and quantitative management approaches, as well as exclude the disadvantages of purely qualitative approach. The following procedure outlines the process that is currently being used by the company from the perspective of the improved performance. In order to achieve the maximum performance, the company should orient the successes of ADNOC, and perform the following changes:
- To introduce a framework of knowledge management, process, and tools of implementation to the workers – The most difficult part in the process of implementing change comes in the part of adoption. Some employees do not react well to change and this could pose a major set back for the whole process. This calls for training of the employees
- Provide a practical experiment, which all members of the giant energy company can take part in – This, take into consideration the company’s systems, culture, and processes.
- To highlight how the company uses the principles of knowledge management to embed the core processes of the company.
This strategy will be implemented with a major aim of producing a new ‘goals and values’ statement, an articulation of deeply held values about cultural and business behavior including how the process of change should be managed. Nevertheless, what are the methods to be adopted at the company to bring about these changes given the ever-increasing convergence on the consultative style of management applied? The firm does not have the all-encompassing human resource systems typical of some organizations. It follows a solid and well-encompassed approach that can be simply summarized as follows: ‘recruiting the best from universities and graduate schools; train on the job and pay top money.
The implementation of the improvement plan will depend on the determination and motivation level of the company’s personnel. In fact, the ACA Company needs to improve the existing resource management practices for achieving the competency level of the ADNOC Company. As for the competency framework of the ACA, it should be emphasized that the key principles of improvement are based on the creation of an improved competency, and innovative response allocation system.
According to the current market state, the company may need to consider a more systematic approach to its human resource policies in the future in order to maintain the pace. The priority areas in human resources practice includes:
- The selection process (the company will need to focus on developing its own staff by introducing graduate trainees in its selection procedure)
- Appraising on performance
- Good rewards
- Organizational development
In the light of this fact, the reasonable question will be associated with the necessity by ACA maintain the incremental strategy and achieve such outstanding performances in the circumstances of the dynamic environment. From an analyst’s point of view, the answer to this is that if the above competency strategies are well implemented, there will be a unified combination of diversified niche strategies with a loosely coupled flexible organization. Its large communication chains and collegial workforce culture will lead to considerable flexibility in responding to changing market demands.
How to Expand the Management role to Minimize Risks
Mandated compliance is one of the core leadership approaches in leading an organization to limit risks. To work effectively, mandated compliance draws functionality from a leader’s discipline. The ACA top executive should exhibit adherence to tight policies and procedures is indicative of discipline. This goes a long way to impress those down the leadership ladder. The ACA leader should consistently pursue enforcement of policies to send a stronger signal about compliance not only with safety practices, but also with policy and company procedure consistently as projected by Lehmann and Winer (1996).
As the leader, taking the lead role to exemplify how the workers should take up responsibility is vital. The following are core competency policies in leadership roles in safety management.
- Use behavior-based psychological influence on others. This approach involves relating with employees to insist on injury prevention through establishing relationships between the employee behaviors and injury prevention.
- Employ person-based psychology to influence positive attitude across the workplace. The ACA top executive should be actively involved in establishing a framework of managing the employee’s safety triad. As a leader, showing the right attitude and feelings with regard to the safety of the employee and the workplace creates a feeling of responsibility within the organization. This approach transforms the feelings and attitudes of the employees.
- Indentify and empress safety related behaviors across the workplace. This helps the company leader inspire the organization who sees him as an objective and caring leader. The organization will take up safety culture and become more involved in effective safety practices.
Safety practices and entrenching safety values on a culture of safety will play a key role in developing an organization that is seriously committed to maintaining safety in principal. Apart from approaching leadership from such an active perspective, the leader should understand how to apply key psychological guidelines of safety. Presence of safety management systems within the organization is important. The leader has a role to ensure that these systems check on the overall discipline, other leaders’ commitment to risk reduction, and analyze accidents. This analysis and consistency in checking risks will develop the organizations safety culture.
Additionally, it should be emphasized that the actual importance of minimizing risks while performing the actual changes depends on the competency framework shaped. Thus, the principle of risk minimization will be based on the process of competency development. In accordance with Flouris (2009, p. 124), the following statement should be emphasized:
The Competency Development Framework is based on the premise that competencies have a direct effect on performance. The degree or extent of this impact may vary, depending on certain factors such as project types and characteristics, or organizational context. Although the Competency Development Framework recognizes these factors, at this point in the development of the standard, it does not attempt to address them directly. The Competency Development Framework defines the key dimensions of project manager competence and the competencies that are most likely to impact project manager performance.
From the perspective of this statement, it should be emphasized that the actual importance of Competency Framework is defined by the application of the competency framework factors towards the business environment analysis. Regardless of the results of the analysis, the framework is required for further extension of the personnel competency and professionalism.
Expected outcomes
Judging from precedence, the above process is the best that ACA can implement given the current system of things. A study on a Texas refinery gave out the following results using ‘The river diagram’ to depict the expected results if the program is well implemented
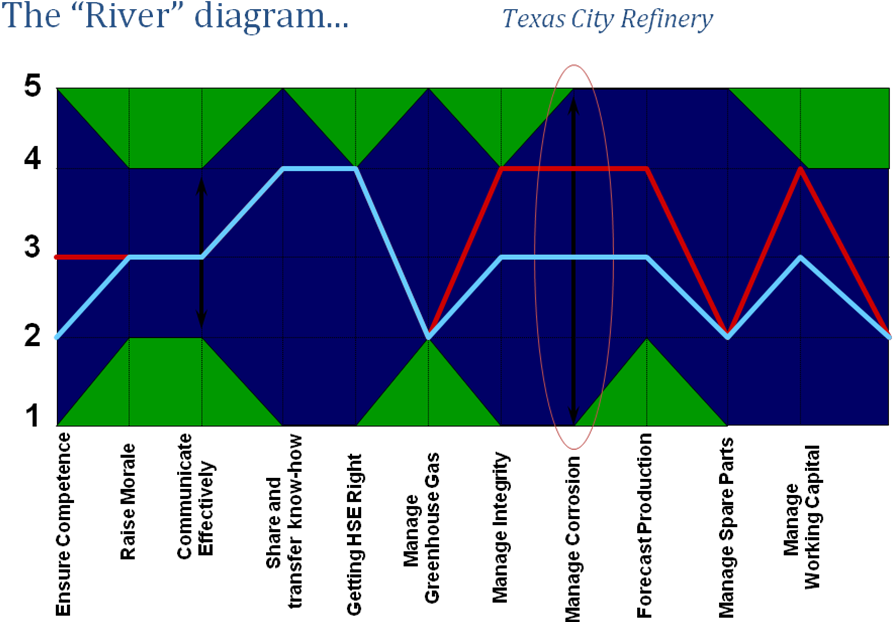
Management is one of the most important factors determining the future of an organization. In fact, management is what purely shapes the future of an organization. However, management can deter the growth and development of an organization. Stunting growth can put the organization at risk. Checking on how management policies influences safety in the organization is very important.
Another factor that may hinder implementation of safety management incentives by the top leadership is ‘other duties.’ The role of the organizations leader is not to manage rather to show direction and steer the organization to greater corporate heights. A chief executive is pre-occupied enough to be unable to carryout the above tasks. This might force him to assign such duties or roles to his deputies who may fail to impress or even provide the relevant guidance.
Lack of access to safety like roads, fire equipment, emergency doors, and awareness can also hinder implementation.
Other factors include the following
- Resistance – This is the most likely problem, which could arise while implementing the framework. Zack (1999) speculated that not all people react well to change and the best way to install change in people is through education. This can be addressed using online training manuals
- Communication – Information tend to change meaning as it goes down the ladder to all branches of a company
- Difference in country rules and regulations – Difference countries has different rules, which cannot be bended to accommodate corporate rules.
- Organizational complexity – The greater size and complexity created problems of co-ordination. The obvious answer to this dilemma is to create additional structures, system, controls that may appear foreign to the collegial values of the company, which is staffed mainly by a complex range of professionals both qualified, and none qualified.
Considering the outcomes of the project, it should be stated that the key factor is the dimension of the competency. In general it is defined by the processes within an organization, nevertheless, managerial team should consider the fact that project performance (Including scope, time, costs, quality, risk, and satisfaction of the stakeholder) depends on the competency knowledge, which is formed by personal competence and personal attributes of every worker and every manager. Hence, as Lehmann and Winer (1996) emphasized:
Focusing solely on project manager competence, regardless of the organization’s performance, is too simplistic. There are too many organizational maturity factors and other contingencies that influence the outcome of the project as well. In fact, it is possible to have a “competent” project manager working within an “immature” organization, which could result in an unsuccessful project, or vice versa.
Consequently, the company should first focus on the qualification improvement of the personnel, and study of the performance by other companies.
Discussion
Management Commitment for Safety
The management is committed to provide health and safety measure at work place. Here are some important points of management commitment and employ involving in the safety process at the work place:
- Develop and communicate the safety and health policy to all the employees.
- Demonstrate management commitment to show that other should empress safety measures. Leaders should show accountability, a sense of responsibility for health and safety to make sense of their commitment and need employees to be safe. Reviewing accident reports and obeying safety rules as advised by Dawes, J, et al (1994).
- Conduct safety and health meetings, regularly, that involve managers, employees, and supervisors.
- Assign a responsible person for coordination of health and safety activities.
- Integrate health and safety relating activities
- Involve employees in health and safety related activities, such as self-inspections, developing safe practices and accident investigation.
- Recognize employees for healthful and safe work practices.
According to Jain (2000), top performing companies can express their commitment to safety by developing a process that the workforce can practice. The company should make it possible to implement and monitor the process such that they can receive feedback. The core idea is to focus workers attention and their actions on the safety. Such a behavior will make them avoid injury and accidents. The aim of interventions is entirely dependent to observable interactions between working environment and safety behavior.
Kotler et al (1998), argue that commitment of an organization can be defined as its engagement in and maintenance of behaviors that are helpful. Such an approach is directly responsible for how well the organization will achieve its goals. Senior level management can play a primary role in shaping employee behavior, and can play secondary role by shaping lower management behavior. This will help develop a safety culture. Information is very important in all aspects of life.
Cooper (2006) argues that; enlightening the employee about the need for good practices at the work place is very important. (Bradmore and Kimberley, 1997) Cooperation and practicing safety drills is very important. Companies have set aside some days where employees conduct fire drills as advised by Adner and Helfat (2003). These drills go a long way to keep employees aware of steps to take when under threat. Workplace hazards vary and each threat poses a varying degree of injury.
Minimizing threats, helps keep the level of concentration in the workplace high. People are more productive when comfortable. Using modern technology to assess threats, include burglary, movement, and monitoring the state of the environment around is very important. David (2010) argues that effective safety management requires the active participation of the organizations leaders. It emphasizes the importance of managing safety in a proactive, systematic, and explicit manner. According to Flouris, (2009) safety management activities are conducted in predetermined and well-documented plan.
Additionally, there is an importance of emphasizing the factor of project success orientation. On the one hand this may be regarded as a motivation and determination factor, nevertheless, this is the key factor of the competency framework. In general, it should be emphasized that the highly competent team is always oriented at success, while teams with lower qualification are ready to accept failure, and often aim the lower aims in comparison with professional teams. Finally, the organization needs to observe the structure of competency framework creation. The elements of this structure are as follows:
- Units of Competence: definition what is expected from the project management improvements.
- Competency clusters. These are Initiating, Planning, Executing, Controlling, and Closing
- Elements: expectations from the managerial team
- Performance Criteria. The scale of achievements, linked with the aims of the company.
Conclusion
Collins and Montgomery (1995) point out that, effective and efficient management of any organization depends on management of the business to process. The business processes involves budgeting, financing, allocating resources, communication and so forth. Organizations must take necessary steps when an injury or accident occurs. There is need for continuous planning, implementation, and monitoring of safety and health measures. This ensures employees of an organization and the people nearby are safe.
Dawes, J, et al (1994) argue that effective communication among the managers and the employees if crucial in ensuring safety is optimized. Communication ensures enforcement and implementation of the safety rules at the workplace. The communication may be in the form of advice, training, assistance, information, learning, seeking help, motivation, questions, etc. Davis (1997) insists that safety barriers be removed.
Harvey (1999) argue that these barriers include lack of information, lack of attention to the details of instructions, not understanding the goals clearly, failure to find alternative solutions, poor judgments, and preconceived ideas etc. the training for the safety and risk management can be handled by improving the communication skills at the work place.
There is need for a proactive approach to management issues, such as workers health risks. Adapting new safety measures and requirements is crucial. Such safety level is achievable through qualitative risk assessment. Global applicability of technological safety measures to keep employees safe is important. Precaution should be embraced as a safe measure. Stakeholder involvement and eliciting voluntary cooperation of companies will go a long way to keep employees safe (Marashov, V. & Howard, and J. 2009).
Reference List
Adner, R. and Helfat, C. E. 2003, Corporate effects and dynamic managerial capabilities. Strategic Management Journal, 24: 1011–1025.
Bradmore, D., Joy, S., Kimberley, C., and Walker, I., 1997, Marketing Visions: classical and topical readings, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, Australia.
Collins, A., D, Montgomery, C, 1995. Competing on resources: Strategy in the 1990. Boston: Havard UP
Cooper, P. D. 2006. The Impact of Management’s Commitment on Employee Behavior: A Field Study.American Society of Safety Engineer. [Online]. Web.
David, L. 2010. Understanding and transforming organizational security culture. Information Management and Computer security, 18 (1) pp. 4-13.
Davis, D. 1997. Risk Management – holistic Risk Management. Computer Law and Security Report, 13 (5) pp. 336-339.
Dawes, J, et al 1994. A Review of Strategy Typology. Southern Marketing: Theory & Applications, AMI, Australia.
Flouris, T. 2009. Change Management as a road map for safety management system implementation in aviation operations: focusing on risk management and operational effectiveness. International journal of civil Aviation, 1 (1) pp. 1-19.
Harvey,L., 1999, ‘Evaluating the evaluators’ Opening keynote of the Fifth Biennial Conference of the International Network of Quality Assurance Agencies in Higher Education. Santiago, Chil
Jain, S., 2000, Marketing: Planning & Strategy. 6th Edition, South-Western College Publishing, Australia.
Kotler et al 1998, Marketing. 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, Australia.
Lehmann, D, and Winer, R. 1996. Analysis for Marketing Planning. 4th Edition, Irwin, Boston, U.S.A.
Marashov, V. & Howard, J. 2009. Essential features for proactive risk management. Nature Nanotechnology, 4 pp. 467-470.
Prahalad, C., K., & Hamel, G, 1990. The Core Competence of the Corporation. Harvard Business Review, May-June 1990
Stanton, W., Miller, K., & Layton, R., 1994, Fundamentals of Marketing. 3rd Edition, McGraw Hill, Australia.
Technical competency framework 2010. Big lottery (UK).
Zack, M. 1999, Knowledge and strategy. Butterworth – Heinemann, Woburn.