Introduction
The concept of Internet Market or online marketing is very young and started less than a decade back when the World Wide Web became affordable and accessible to the public. The medium of the Internet provided an easy way for manufacturers and sellers of products and services to make potential buyers aware of their products. The net costs less than a fraction of what a print media or a TV spot would cost and the reach is more focussed and the possibility of the target market being reached directly improved very much. But the fact remains that if the Internet is easy and convenient for one company it was equally easy for the competition. Thus was created the opportunity to ‘catch the eyeballs’, ensure that your product stood out among the others and the birth of specialized Internet marketing. This paper provides an analysis of Internet Marketing and examines various features that make up the Internet.
About Internet Marketing
Gladding (2006) has suggested that the eCommerce marketplace has revolutionized the way in which businesses and consumers interact, by providing a medium through which one party can search, order, pay for and even receive the service or product. The World Wide Web, as its name suggests is a global marketplace, allowing anyone with access to the Internet to order products and services just as easily from a supplier on the far side of the world as from a business in the same town. In practice however, the global market is unevenly distributed with the highest concentration of Internet hosts and users in US, Europe, Australia and a few countries in Asia such as India, China, Japan and others. The growth in online access is being fuelled by several factors including changing consumer attitudes (particularly among the cash rich, time poor), mass media attention, the evolution of a computer literate population, and government initiatives.
Internet Market Size
Furness (2007) has suggested that global online consumer spending was valued at US $24 billion in 1999, and this figure rose to US $660 billion by 2005, as consumers transfer an increasing proportion of their expenditure to Internet-based e-tailers. The figure does not include corporate opportunities that are created as a result of Internet based queries, accessing large construction projects, aerospace projects, shop building contracts and others through the Internet. The author contends that if this market segment is also considered then the figure may very well cross 10 trillion US $. The author suggests that there will be a shift in the method of business-to-business eCommerce, with a distinct shift away from Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) to Internet-based applications. The market for EDI software and services will decline at an annual average rate of 2%, whereas the Internet market will grow at 70% annually, highlighting the significant investment that companies are now making in B2B applications and the importance of this process to their future strategies.
Internet Market Drivers
Eid (2005) argues that the business-to-business market is being driven by a number of distinct drivers. Of these, the efficiency gains from improving supply chain efficiencies are key, as they both reduce the overall cost of these functions and provide key management information for companies. Tiago (et all, 2007) suggest that the market for online procurement of indirect goods that do not form part of the final product or services of businesses will be the major growth area for business to-business eCommerce. However, there are substantial efficiency savings from moving supply chain and distribution system management onto the web for those that intend to fully integrate their systems.
Falk (et all, 2007) have proposed a matrix for the e Commerce model and the model is shown in Figure 1.
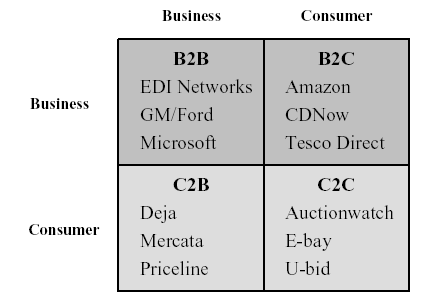
The matrix shows the way in which businesses and consumers can be linked through eCommerce. The largest of these at present is business-to-business, typically for suppliers to large manufacturers such as General Electric, Ford or General Motors.
Internet and Online Advertising
Tom (2004) suggests that as the online population achieves a critical mass, the Internet is becoming an important advertising medium. Advertising online is becoming more popular than ever as companies spend aggressively to build their online presence. Online advertising expenditure is increasing at a rapid pace and increased from US$ 3.1 billion in 1999 to US $29.2 billion by 2004, representing a compound annual average growth rate of 57%.
Methods of Internet Advertising
Taylor (et all, 2006) suggests that there are several methods of advertising on the Internet and they are:
Direct email: There are three types of direct e-mail: blanket e-mail, subscription email and query response e-mail. Subscription e-mails account for the vast majority of e-mail advertising following consumer hostility towards blanket e-mailing. Subscription e-mails form a key part of an online loyalty reinforcing campaign as it maintains a brand’s position in the mind of consumers and encourages them to interact with the company.
Banner advertising: banners are small windows sold to advertisers at the top of web pages and allow surfers to click through to the advertiser’s website. The Advertising industry forecasts predict that such advertising will account for as much as 60% of online advertising spend by 2008.
Content sponsorship: the sponsorship of a website run by an organization independent of the manufacturer. Often used as a cheaper alternative to manufacturer provided websites, this form of online advertising is highly effective at raising consumer awareness of a brand, product or service, by association to a website.
Brand/manufacturer websites: because they provide a high volume of communication to the consumer, brand websites are at the centre of online marketing. Brand websites are used extensively by consumer goods’ manufacturers, services, travel, fast food, beverages and many other.
Conclusion
The development of the Internet as an information provider and a medium for trade means that an ever-growing number of businesses and consumers are going online. The Internet has developed fastest in US. Europe, Asia and Australia, where low cost access and innovative dotcom companies simultaneously stimulated demand while providing pioneering services. The Internet provides and easy means for people to advertise product and services.
References
- Eid Riyad. 2005. International internet marketing: A triangulation study of drivers and barriers in the business-to-business context in the United Kingdom. Journal of Marketing Intelligence & Planning. Volume 23. Issue 2/3. pp: 266-281
- Furness Victoria. 2007. SMB Vendor Opportunities and Strategies. SMB Vendor Opportunities and Strategies. Business Insights Ltd. Datamonitor Analysis. England
- Falk Louis K. Sockel Hy. Homer Warren. 2007. A Holistic View of Internet Marketing. Journal of Competition Forum. Volume 5. Issue 1. pp: 9-15
- Gladding Nick. 2006. Internet Market Place Review. Business Insights Ltd: Datamonitor Analysis. England
- Taylor M J. England D. 2006. Internet marketing: web site navigational design issues. Journal of Marketing Intelligence & Planning. Volume 24. Issue 1. pp: 77-86
- Tiago Maria Teresa Borges. João Pedro Couto. Maria Manuela Natário. Ascensão Braga. 2007. International Reality of Internet Use as Marketing Tool. Journal of American Academy of Business. Volume 11. Issue 1. pp: 138-144
- Tom M Y Lin. Pin Luarn. Peter K Y Lo. 2004. Internet market segmentation an exploratory study of critical success factors. Journal of Marketing Intelligence & Planning. Volume 22. Issue 6/7. pp: 601-116