Abstract
The paper seeks to discuss the structure of the local government of Atlanta, Georgia. The results of the research show that the local government has a complex structure that enables it to fulfill its key functions efficiently. Nevertheless, the city faces a crucial problem of crime, and action is needed to improve police department staffing, turnover, and motivation. The recommendations include increasing the APD budget to offer better salaries for officers, surveying working conditions in police departments, and providing training to the leaders of police departments.
Introduction
Atlanta is the largest city in Georgia, which is characterized by fast development and a diverse economy. Despite these features, the city is also famous for its high levels of crime, including violent crime. The primary aim of this report is to explore the structure of government in Atlanta and offer recommendations for addressing the problem of crime. The objectives of the report are to provide background information on the City of Atlanta, describe its government structure, explain the problem of crime, and provide recommendations on how the local government could address the issue.
Background Information
Atlanta is the Capital city of the southeast and one of the largest metro areas in America. According to Reed (2017), the 2016 city population was 472,522; however, the Atlanta metropolitan area has a population of 5.7 million and is growing rapidly. Atlanta is home to important national and international companies operating in various industries, including filmmaking, logistics, transportation, and information technology. Therefore, the city’s economy and GDP are increasing steadily, and it is expected to develop further in the next decade. The 2018 operating budget for the City of Atlanta was $2.1 billion, which included a general fund appropriation of $648.6 million (Reed, 2017). The local government is highly focused on enhancing the quality of life in the city, as well as on developing its infrastructure and addressing public issues.
Government Structure
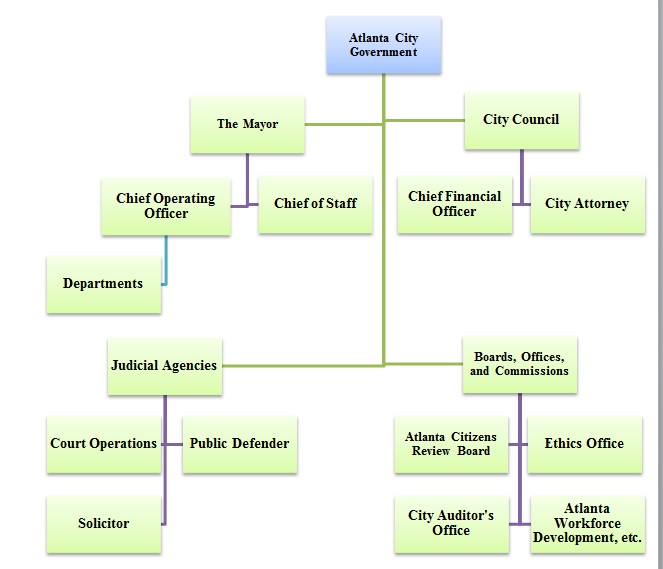
Atlanta has a mayor-council type of government structure. This government system includes an elected official (the Mayor), who performs the executive functions, and the City Council, which is the main legislative body, as well as judicial agencies. Figure 1 presents the organizational chart of the local government of the City of Atlanta. Besides the judicial, executive, and legislative branches, the structure also includes a variety of boards, offices, and commissions, which assist in upholding the democratic governance structure.
The organizational structure of Atlanta’s government is rather complicated, which ensures a thorough oversight of all government functions. Offices and boards, such as the Atlanta Citizens Review Board and the Ethics Office also assure that citizens play a part in the local government, which is essential to promoting the integrity and effectiveness of the government. Overall, such a structure appears to be efficient in facilitating the city’s development and addressing the needs of its residents
Crime in Atlanta
Crime is a persistent problem in the City of Atlanta. Despite the local government’s efforts for reducing crime rates, Atlanta remains above the national average crime rates. For instance, between January 2017 and June 2017, there were 2,165 violent crimes committed in Atlanta, which is much higher than in cities with similar populations (FBI, 2018). Similarly, the incidence of crimes such as robbery, property crime, and murder is above the national average. Atlanta is also famous for its rates of drug-related crime, particularly due to the presence of five major Mexican drug cartels in the area (Stinchcomb, 2018). For the last two decades, the local government has been making efforts to address the problem of crime in the area. As a result, the overall crime rates decreased by 27% between 2009 and 2017 (Boone, 2017). Nevertheless, the crime rates remain high and will require further action by the local government.
One of the critical reasons for the high crime rates in Atlanta is the ineffectiveness of the local police department. According to Godwin (2017), at the beginning of 2017, over 50 homicides committed in 2016 remained unsolved, and high turnover and low staffing in the Atlanta Police Department (APD) is among the root causes of the issue. High turnover is a crucial issue for the police, as it shows that the officers are not satisfied with their working conditions. In particular, the lack of pay increases, and benefits were highlighted as a significant problem area in the APD (Shapiro, 2013). Police officers’ dissatisfaction with working conditions affects public safety by reducing their morale, motivation, and effectiveness in preventing and investigating crimes.
The issue of crime is important for the community as it has a direct influence on public safety. High rates of violent crime and murder pose a threat to the lives and health of thousands of people living in Atlanta. Increased crime rates also affect the mental health of community residents, causing anxiety and fear. Furthermore, the perceived ineffectiveness of the police contributes to the psychological effects of the problem, provoking distrust, and feelings of unsafety. As a result, by addressing the issue of high crime rates, the local government could improve the life and safety of Atlanta’s citizens.
Recommendations
Crime is an important factor that affects the community of Atlanta in the 21st century. As outlined in the previous section, high turnover and low staffing of police departments are the primary reasons for this issue. Therefore, leaders should take action to address the problem from a human resources viewpoint, focusing on improving working conditions and motivation of police officers.
The first recommendation would be to increase the budget of the APD, providing enough funds for adequate pay increases and benefits. This would have a direct effect on staffing and turnover in police departments and have a positive effect on the officers’ motivation. Secondly, the government should order the APD to conduct an internal survey of working conditions to identify any other factors affecting turnover and motivation in police departments. Lastly, the APD should also conduct a training program for leaders, which would focus on promoting positive leadership strategies, increasing employee engagement, and enhancing motivation. These recommendations would improve the effectiveness of the police in Atlanta, thus assisting in the government’s efforts to reduce crime rates.
Conclusion
Atlanta’s local government has a complex structure, which allows it to be effective in fulfilling its administrative functions and responding to the residents’ needs. However, crime remains a prominent issue in Atlanta due to the ineffectiveness of the police. To decrease crime rates, the local government has to address low staffing, high turnover, and impaired motivation in police departments. The recommendations provided in the report would complement the government’s strategy for reducing crime rates, thus enhancing public safety in Atlanta.
References
Boone, C. (2017). Murders in Atlanta are way up, but overall crime is way down. My AJC. Web.
Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). (2018). Preliminary semiannual uniform crime report, January-June 2017. Web.
Godwin, B. J. G. (2017). 51 Atlanta homicides from 2016 remain unsolved. These are the victims. The Atlanta Journal Constitution. Web.
Reed, K. (2017). Fiscal year 2018 adopted budget. Web.
Shapiro, J. (2013). 2,000 Atlanta police officers, but gripes remain over pay.WABE. Web.
Stinchcomb, L. (2018). DEA: Mexican cartels have large presence in metro Atlanta. CBS46. Web.