Background
The automotive industry is one of the major industries in Australia. Australia is capable of designing and making automobiles. The isolation of Australia necessitated the local production of cars. This was more economical than importing cars from distant locations. Holden and Ford Australia are the major automobile manufacturers. Holden is a subsidiary of General Motors. In addition, Toyota Australia also manufactures various models in the country.
The Camry is one of the major models that Toyota Australia manufactures. Ford Australia was the first automobile company to manufacture automobiles in Australia. However, Holden was the first company to engage in mass production of cars designed in Australia.
Australian automobile companies generally specialise in the production of ‘large’ passenger vehicles. However, there has been a steady decline in the market of cars in this category. This has resulted in cutbacks and shutdown of various plants that used design and manufacture cars in this category.
Closure of the Mitsubishi Motors plant in Australia is a clear illustration of the dwindling fortunes of companies that manufactured cars in this category. Currently, most Australia imports most of its cars from Europe and Asia.
The global automotive industry is one of the most complex global industries. There is a high likelihood that the complexity of the industry would increase in the future. The complexity of the global automotive industry makes it difficult to predict the future changes in its structure.
Government policy is one the variables that determines the structure of the global automotive industry. However, it may not be one of the major variables. Therefore, it is difficult to predict the future changes in the industry with a high degree of certainty.
Increased globalisation has several effects on the Australian automotive industry. The presence of excess capacity globally necessitates the Australian automotive companies to improve their performance. In addition, increased competition in the domestic market also necessitates the companies to improve their performance. The government’s assistance program is one of the major factors that has helped in sustaining the industry.
However, the government is reducing the assistance that it offers various companies in the industry. The level of intervention of the government is one of the critical factors that helps in shaping the industry. The decision of the governments of other countries also helps in shaping the industry.
There are a few dominant companies in the global automotive industry. However, overseas operations of these companies accounts for a sizeable percentage of their revenue. These companies usually strive to ensure the sustainability of their overseas operations.
Ford and General Motors are the parent companies of the automobile companies that are dominant in the Australian market. Therefore, the pressure that these parent companies exert on the Australian subsidiaries is one of the major factors that helps in shaping the industry.
Passenger motor vehicle (PMV) is one of the major market segments in the Australian automobile industry. Australian automobile companies that manufacture PMVs usually compete with their parent companies. Parent companies usually have several options to supply a certain region with a certain model. They may source the model from various locations. This creates competition between the parent company and the subsidiary.
Changes in the global automotive industry have led to several changes in the Australian automotive industry. In the past decade Australian automotive industry has experienced significant changes. The automotive manufacturing industry has been under intense pressure to improve its performance. Reducing costs and increasing productivity are the major factors that enable automotive manufacturers to improve their productivity.
Government Policy
Tariffs
The government plays a major role in shaping the Australian automotive industry. Tariffs and subsidies are the major tools that the government uses to safeguard the industry. However, various parties claim that there is no justification for the use of these measures to safeguard the automotive industry. They claim that it is wrong for the government to use tariffs to safeguard an industry that’s is destined to fail.
The Australian government uses tariffs to protect the domestic automotive industry. Previously, the government imposed a tariff of 10% on all imported vehicles. This reduced the ability of imported vehicles to compete with locally manufactured vehicles. However, from 1st January 2010, the government reduced the tariff from 10% to 5%. The 5% tariff is applicable to all PMVs and light commercial vehicles.
In addition, the tariff is also applicable to the components of these vehicles. A tariff of $12,000 per vehicle is also applicable to all second-hand vehicles imports. This measure is aimed at reducing the attractiveness of buying imported second-hand vehicles.
Reduction in tariffs led to a significant reduction in the price of imported vehicles. This enabled them to compete with locally manufactured vehicles.
Figure 2.1 effect of tariffs on price of imported vehicles
Significant reduction in the price of imported vehicles increased their demand in the local market. Customers were willing to buy more imported vehicles. In addition, increased demand of imported motor vehicles had a flow-on effect on the entire industry. It increased the demand for components of the imported vehicles. This had a detrimental effect on the local parts manufacturers.
Figure 2.2. Effects of tariffs on demand of imported vehicles
Increased demand of imported vehicles reduced the demand of locally manufactured vehicles.
Figure 2.3 effects of tariffs on demand of locally manufactured vehicles
Australian imports usually attract a sales tax of 22%. Imported vehicles also attract this tax. Imported goods also attract a tariff o between 3% and 5%. However, motor vehicles attracted a tariff of 10%. This was significantly higher that the tariff of other products. The tariffs increased the price of imported motor vehicles.
This reduced their ability to compete effectively with the locally manufactured vehicles. However, tariffs reduced the affordability of motor vehicles. This had a detrimental effect on the economy. Therefore, it was vital for the government to reduce the tariff on imported motor vehicles. This increased the affordability of motor vehicles.
Tariffs helped in insulation local automobile manufacturers from competition by importers. However, it led to complacency in the costs and quality of motor vehicles. This made customers not to get value for their money. Therefore, it was vital for the government to reduce the tariffs. This would increase competition in the automotive industry. Increased competition would lead to a significant improvement in the affordability and quality of motor vehicles.
The government also reduced the tariffs on imported motor vehicles since they had a negative effect on the economy. The tariffs distort the manufacture and consumption of motor vehicles in the Australian market. This makes them to lead to more economic losses. Spreading the indirect tax across all goods and services would reduce the economic losses due to the tariffs on imported motor vehicles.
Subsidies
The Australian government provides subsidies to safeguard the automotive industry. In the last 13 years the government has provided more than $ 6 billion in assistance to the industry. The government provides production subsidies to encourage Australian automotive companies to increase their production. The government also provides capital subsidies to companies in the automotive industry. Research and development subsidies facilitate innovation in the industry.
Parties that support the government subsidies usually claim that for every dollar that the government provides in subsidies, the companies give back at least $5 to the economy. On the other hand, failure to provide subsidies may lead to the ultimate collapse of the industry. It would make the industry be less competitive. However, over the past few decades, the government has reduced the amount of subsidies it provides to the industry considerably.
Subsidies reduce the operating costs of companies in the automotive industry. The government covers some of the costs associated with the production of motor vehicles. Reduced costs of production enables companies in the automotive industry to increase their production capacity. Therefore, increase in the subsidies that the government provides leads to a corresponding increase in the production capacity of companies in the automotive industry.
Figure 2.4. Effects of subsidies on number of vehicles produced locally
Reduction in the operating costs enables the automotive manufacturers to pass the reduced costs to their customers. The subsidies cover some of the operating costs of that the manufacturers would incur in the production of the vehicles. Therefore, increase in subsidies would lead to a corresponding reduction in the price of motor vehicles.
Figure 2.5. Effects of subsidies on price of locally manufactured vehicles
Reduction in the price of vehicles due to the increase subsidies that the government provides to companies in the automotive industry increases the affordability of the vehicles. Increased affordability enables customers to purchase more vehicles. Increased sales of vehicles increases the profitability of companies in the industry.
Figure 2.6. Effects of subsidies on number of locally manufactured vehicles purchased
The government may also provide subsidies to the buyers of motor vehicles. Provision of subsidies to the buyers of motor vehicles would increase their purchasing power. This would enable them to buy more vehicles.
Figure 2.7. Effects of subsidies on price of locally manufactured vehicles bought
However, provision of subsidies to customers would have limited effect on the price of motor vehicles. It is a fact that increase in subsidies would lead to increased demand for motor vehicles. This would necessitate the automotive companies to increase their production capacity. This would enable the companies to benefit from economies of scale. However, the automotive companies are less likely to reduce the prices of vehicles due to the economies of scale.
Figure 2.8. Effects of subsidies on price of vehicles
Subsidies help in supporting the automotive industry. They enable companies in the industry to increase their production capacities. In addition, they facilitate quality improvements in the industry. Failure to provide subsidies would reduce the attractiveness of the industry. It would also make it hard for local manufacturers to compete effect with imported motor vehicles.
The government also provides subsidies to prevent collapse of the industry. The automotive industry employs a sizeable percentage of Australians. Therefore, its collapse would have detrimental effects on the economy. In addition, export of motor vehicles enables the government to earn valuable foreign currency.
Australian Market Trends
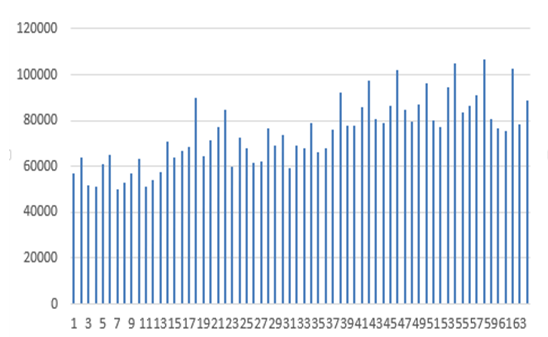
Key
Figure 3.1. Quarterly sales of motor vehicles from 1994-2009
From the graph it is clear that the demand for motor vehicles is seasonal. The demand is highest during the second quarter of the year. Summer is usually the month when most people travel around the country. Australia has conducive weather for travelling during the summer.
This increases the demand for motor vehicles during the summer. The graph shows that the demand of motor vehicles has been increasing steadily. During the 1990s the demand for various motor vehicles was very low. Passenger motor vehicle is the category that has the highest demand.
From the graph it is clear that between June and September 2008 had the highest demand of motor vehicles. During this period, the Australian economy had unprecedented economic growth. This increased the purchasing power of most Australians. During this period, imported vehicles still attracted a 10% tariff. This reduced the ability of imported vehicles to compete with locally manufactured vehicles.
The global financial crisis was detrimental to the economic well-being of the Australian economy. It reduced the purchasing power of consumers. Therefore, it led to a significant reduction in the number of vehicles sold. From the graph it is clear that the first quarter of 2009 had one of the lowest sales motor vehicles. During this period, the Australian economy faced several problems. This necessitated the government to reduce the subsidies that it offered various companies in the automotive industry.
The graph shows the sales of motor vehicle prior to the reduction of the tariff on imported motor vehicles. It does not capture the effect the reduction on tariff on imported motor vehicles on the sale of locally manufactured vehicles. The graph that there were signs of recovery of the Australian automotive industry.
Therefore, the reduction of the tariff on imported motor vehicles may have prevented the full recovery of the local Australian automotive industry. The effects of the global financial crisis is one of the major factors that led to the collapse of the Australian Mitsubishi plant in 2008.
The Australian automotive industry has been unable to fully recover from the effects of the global financial crisis. Analysts expect the gloom outlook of the Australian automotive industry to persist. Currently, Toyota, Holden and Ford Australia are the major automotive companies in the Australian markets. However, Ford Australia faces imminent collapse. The company has reduced its output and employees significantly since the reduction of the tariffs on imported motor vehicles.
Marketing Power of the Australian Motor Vehicles Industry
The Australian automotive industry is worth more than $100 billion. It provides employment to more than 50,000 Australians. Therefore, it is vital for the government to support this industry. Collapse of the automotive industry would have detrimental effects on the Australian economy. The Australian government supports the automotive industry using subsidies and tariffs. Australian automotive manufacturers usually export motor vehicles to nearby countries.
This makes the Australian automotive companies to compete with their parent companies. However, Australian automotive companies are usually disadvantaged. The cost of production of the vehicles is usually than in other countries. This reduces the profit margin of Australian automotive companies.
Australian automotive companies face stiff competition from imported motor vehicles. Tariffs on imported motor vehicles increase their costs. This reduces the ability of the motor vehicles to compete effectively with Australian automotive companies. The government skews the competitive forces of the market to favour the Australian automotive companies.
In addition, the government restricts the importation of used motor vehicles. In a perfect competition, the government does not interfere with the market forces to make them favour a certain party. The market forces are the major factors that determine the price of various products.
Therefore, interference of the Australian government makes it not to be perfectly competitive. Tariffs increase the price of imported motor vehicles. This reduces the ability of the motor vehicles to compete with locally manufactured vehicles. This measure helps in safeguarding the industry. The government also provides subsidies to Australian automotive companies. The subsidies increase the competitiveness of Australian automotive companies.
Subsidies on research and development enable Australian automotive companies to develop high quality products. In addition, subsidies on acquisition of assets enable the automotive companies to acquire assets that are vital to their activities. Therefore, the subsidies violate the perfect competition in the automotive industry.
However, the major assumption is that the governments of the companies that manufacture the imported motor vehicles do not provide them with subsidies or other incentives. Provision of incentives would provide the companies with an unfavourable advantage over other companies. However, it is a fact that most governments provide subsidies local automotive industries. The subsidies facilitate the development of the industries.
The government can increase the power of the Australian automotive industry by putting more emphasis on investments in research and development. This would facilitate the development of innovations that would improve the competitiveness of the Australian automotive companies. This would enable them to compete effectively with imported motor vehicles. The automotive industry is a technology intensive industry.
It is vital for Australian automotive companies to ensure that they adopt new technologies at an early stage. This would enable the companies to compete effectively with companies that use the advanced technologies. However, the Australian automotive companies should ensure that they do not violate the patents of companies that developed the new technologies. Patent violation may lead to costly litigation. In addition, it may reduce the image and reputation of the Australian automotive companies.
In addition, consolidation of the supply chain would help in improving the power of Australian automotive companies. Consolidation would enable them to achieve a global scale. However, it is vital for the supply chain to retain its core capabilities after consolidation.
Improvement of the supply chain would help in reducing some of the inefficiencies that are inherent in the current supply chain. Inefficiencies in the supply chain reduce the competitiveness of Australian automotive companies in the global market. Therefore, improvements of the supply chain would enable Australian automotive companies to venture into the global market successfully.
Future Prospects
The Australian automotive industry has a shaky future. In the past, government subsidies and tariffs have helped in sustaining the industry. However, the government is reducing the subsidies and tariffs slowly. In addition, there has been a significant reduction in the number of consumers who are willing to buy locally manufactured vehicles. Consumers are opting to buy smaller imported cars. This has forced local manufacturers to cut their output and jobs.
This is in line with the significant reduction in the demand of the locally manufactured vehicles. Various parties that federal support also delay the inevitable collapse of the automotive industry. They claim that local manufacturers should strive to find new buyers of their vehicles. Unless they do so, the industry would collapse within 5 to 10 years.
Technological innovation is one of the major factors that would guarantee the future growth and profitability of the Australian automotive industry. Ford Australia is one of the leading companies in technological innovation in the industry. Technological innovation would enable companies in the industry to build vehicles from the ‘ground up.’
However, technological innovation may also be the subject of criticism from parties that advocate for ‘human centred’ approach to production. Currently, there have been more innovations among blue collar-employees of the automotive industry. There has been a shift towards the implementation of lean production systems in the Australian automotive industry. The Toyota plant is a clear illustration of the lean production systems.
The Australian automotive industry is not sustainable. Tariffs and subsidies have helped in sustaining the industry. The operational costs of Australian automotive companies is twice that of companies in Europe. In addition, it is four times the operational costs of companies in Asia. Tariffs and subsidies have helped in reducing the operational costs. Therefore, if the government did not provide the subsidies, the automotive industry would have collapsed many decades ago.
However, despite the provision of subsidies, Australian automotive companies have collapsed one after another. Currently, there are only 3 major automotive companies in the Australian market. These include Ford Australia, Holden, and Toyota. In the next 3 years analysis expect only two companies to be in existence in the Australian market due to the imminent collapse of Ford. Analysts claim that the continued support of the automotive companies has made them be addicted to subsidies.
This has reduced the sustainability of companies in the industry. The closure of the Mitsubishi firm is 200 is a clear illustration of the lack of sustainability of sustainability of the industry. Therefore, it is vital for the government to reduce the support that it offers these companies. This would necessitate the companies to formulate strategies that would enable them to increase their sustainability.
The end of the government support on the automotive industry would cause a seismic shift in the industry. It would necessitate industries to formulate innovative strategies that would help in increasing their productivity.
The government would divert the funds to other major infrastructural projects. This would help in improving the Australian economy. It is a fact that it is better to end the support on an industry that is not sustainable. The support siphons billions of tax payers’ money from the government’s coffers.