Executive Summary
Barclays Bank Plc is one of the leading financial institutions in the global market. For the last 325 years, the firm has registered impressive success. However, the market now faces a number of challenges, top of which is stiff market competition that has made it consider quitting the African market. It is advisable for this firm to embrace change and innovation as the best way of overcoming market challenges.
Introduction
Background information
Barclays Bank was founded in 1690 in London City by James Barclay (Fasnacht 2009). Since its foundation, this financial institution has experienced an impressive growth to become one of the world’s leading financial institutions. Barclays Bank benefited a lot from the fact that Great Britain was a leading world power with colonies all over the world. It was able to spread its operations to all the continents around the world as it tried to expand its market share beyond its home country.
In those early years, this firm enjoyed operating in a market that was less competitive. However, this changed sharply from the 19th century when the number of financial institutions started to increase. Currently, there are numerous financial institutions around the world and Barclays Bank faces very stiff competition in the home and in the international markets. Financial institutions are now forced to find best strategies of remaining competitive, and some of these strategies only affect the ability of these firms to be profitable.
According to Ucimura and Wu (2013), the shrinking banking sector is one of the biggest worries to large financial institutions such as Barclays Bank. Online money transfers and banking systems have eaten up a huge share of the market that was previously exclusively enjoyed by banking institutions. Technology is also moving very fast and financial institutions are finding themselves on the receiving end as customers have numerous ways of keeping their money even if they want to avoid financial institutions.
Regulatory challenges are also becoming an issue. In most parts of the world, governments are coming up with regulatory policies for financial institutions which reduce the profitability of these firms (Mazzucato 2014). In light of these challenges, Barclays Bank has decided to sell off its Barclays Africa because it is no longer a profitable venture (Dell’Atti & Trotta 2016). These are challenges that this firm has to deal with in order to remain relevant in the market. In this paper, the researcher will discuss these challenges and propose strategies that can be used to manage them.
Discussion
The financial sector remains a very important industry in any economy around the world. Organisations, government entities, and individuals need financial institutions to manage their finances properly. However, the stiff market competition, the changing technological world, and stringent regulatory policies are all affecting the ability of financial institutions to achieve optimal success in the current market (Burn & Cartwright 2011).
Barclays Bank finds itself in an awkward situation where it has to deal with numerous challenges not only in the home but also in the international market. The management has decided to reduce its geographic coverage and to concentrate its operations in specific markets that have the potential to give it maximum benefits (Burrows & Bridge 2015). This was one of the most challenging decisions that the management of this firm was forced to make.
As other firms were spreading their operations to other parts of the world, including in Africa, this firm was shrinking its operations as a way of achieving sustainability. Some financial experts have questioned the prudence of this decision. It is important to look at the existing theoretical models that can help explain how a firm can deal with these challenges before making appropriate recommendations to the management of this firm.
Innovation theory
Innovation theory is one of the modern theories that have achieved massive acceptance all over the world as firms try to grapple with the changing business environment. According to Greuning, Scott, and Terblanche (2011), the only way through which a firm can achieve success in the market is to be innovative. A firm that is able to reinvent itself finds it easy to manage most of the environmental challenges that it faces.
Innovation has been explained using a number of theories to help in explaining how a firm should approach change and the possible consequences of rushing to change or ignoring change that occurs in the business environment. Diffusion of Innovations Theory is one of the models that have been widely used over the years to help explain the pattern of innovation and how a firm can manage it to become competitive in the market (Blankley 2006). The following figure shows the pattern that innovation takes as explained in this theory.
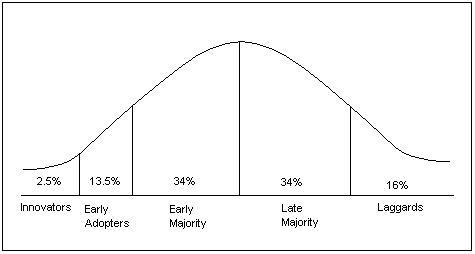
As shown in the figure above, there are five stages of innovation that a firm can choose to belong. Barclays Bank can choose any of the five stages when embracing the emerging changes in the market. In the first stage are the innovators. They only account for about 2.5 per cent of all the firms within a given industry. These are highly creative firms which are keen on developing new ways of dealing with the emerging environmental changes.
They drive change within an industry by always coming up with new ways of doing business. They know how to monitor the changing market trends and how to develop measures that can help overcome the challenges associated with them. Barclays Bank was once in this category of the innovators. It was the first financial institution to develop and use cash dispensers (ATMs) that have become very popular all over the world (Tan 2014).
However, it has failed to be in this category of the early innovators in the recent past (Leditschke 2005). A clear indication that this firm is moving from the class of the innovators was the emergence of online banking services. Although the bank currently has an online presence, it took it some time to appreciate and embrace this changing environmental factor.
Early adopters are firms that are keen to identify and embrace the new changes which are taking place in the market. They do not initiate change, probably because of their limited capacity or unwillingness to sponsor expensive research that brings about such changes. However, they monitor what the markets leaders are doing and try to embrace new practices that they believe are of benefit to them.
These institutions form about 13.5 per cent of the total population of firms in any given industry. The early majority are cautious firms which appreciate the need for change but are keen to ensure that they only adopt new systems that have been confirmed to have a positive impact (Ellinger, Lomnicka, Hare, & Ellinger 2009). As soon as they are able to understand the consequences of a given change, then they will embrace it as a way of improving their operations in the market. They account for about 34 per cent of the population of a given industry.
The late majority are those firms which embrace change only when they have empirical evidence that the new approaches are able to bring about positive change. In most of the cases, these are large organizations such as Barclays Bank that cannot afford to make mistakes because of the possible implications that mistakes may have on their operations. They may not benefit much from the change, but they also avoid the disruptive nature of change when it becomes necessary.
The last stage has the laggards, firms which are very sceptical about change. These are firms that believe in maintaining their strategies for a long time before embracing change. They often face the danger of being faced out of the market, especially if the emerging change has a significant bearing on the way firms operate within a given industry (Claessens & Feijen 2007). It is a stage that any firm should avoid in the modern dynamic business environment.
The first two stages are very important for any firm that wishes to remain competitive in the market. The financial institutions all over the world are faced with numerous challenges, from online fraud to competition, stringent regulatory policies, and changing face of technology in the market. The best way of dealing with these challenges is to find new ways of dealing with new and existing problems. A firm must be creative in dealing with internal and external problems.
As Plunkett (2007) says, a firm may not be an innovator all the times. Sometimes a rival firm may come up with a new approach of managing the market forces. Being an early adopter may be of great help in such instances. Understanding what others are doing better and following their pattern may help a firm to change when it matters the most.
Innovation organisation
Barclays Bank Plc is one of the leading financial institutions in the world, with branches in over 50 countries. It has remained successful even in the face of numerous market challenges that have affected other financial institution. It is important to critically analyze this firm to determine its innovative capacity and how it can manage some of the challenges it faces in the market. Conducting a SWOT analysis at this stage would be very important in understanding the internal strengths and weaknesses of the firm, and external opportunities and threats.
The financial success that this firm has experienced over the years is considered its main strength. It gives it the ability to undertake various developmental projects without having to resort to loans or other sources. Given that Barclays Bank has been in existence for over 325 years, it has a wealth of experience unmatched in the market. It has survived the test of time and proven that it has the capacity to achieve success even in cases where other firms are unable to withstand the external forces in the environment. Its brand is one of the top brands in the financial sector both in the developing and developed economies. The firm also has a team of highly skilled employees and an able team of managers that work very closely to manage challenges that it faces in the market.
The firm has a number of weaknesses which are worth discussing. The large size of the firm makes it less flexible in the market. It is not easy to introduce sudden change within the firm given its massive size in terms of the number of employees who have to be trained to understand how to work under new environmental forces. The decision to leave Africa has also been seen as a weakness because it demonstrates that the firm opts to run away from a problem instead of facing it.
The market has a number of opportunities that this firm can take advantage of if it acts in a smart way. The growing middle class all over the world means that those who are using financial products such as those offered by Barclays Bank are on the rise (Acharya, Beck, & Evanoff 2013). This is a sign of a better future. The emerging technologies, however disruptive they might be, can help this firm to overcome some of the challenges it is facing in the market today. Increasing globalization also makes it easy for the firm to conduct business in the global market with ease.
It is important to appreciate that the market has a number of threats that the firm must find a way of overcoming. Stiff market competition in the financial market is one of the biggest challenges that this bank is currently dealing within the global market. Cyber insecurity is another major problem that affects the ability of the firm to manage its online business transactions (Barajas 2013). In some countries, issues such as high taxation and interference by corrupt governments are also hampering the operations of Barclays Bank. This information is summarized in appendix 1.
Innovation strategy
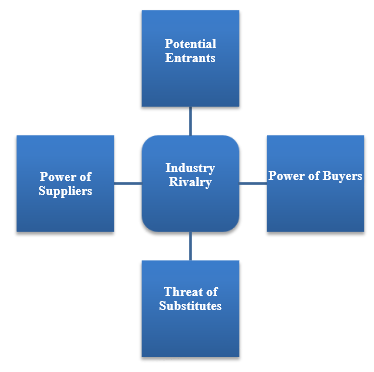
According to Ackrill and Hannah (2001), the banking sector has experienced massive development over the past few decades and it is very likely that the competition currently being experienced in the market is unlikely to disappear in any near future. As such, it is necessary for Barclays Bank to come up with ways of managing environmental forces in a way that will give it a competitive edge over its market rivals. The management should start by clearly outlining these challenges before coming up with strategies of managing them. Porter five forces may be useful at this stage in understanding these forces.
Industry rivalry is one of the major issues that this firm has to deal with in the market today. Barclays Bank faces stiff competition from large multinationals such as City Bank, HSBC, Chase Bank, and Standard Chartered Bank among a host of other major financial institutions (Battilossi 2002). The rivalry within the financial sector is stiff as the traditional banks try to remain relevant in an industry where technology has been very disruptive. Banks are doing everything to ensure that they gain a competitive edge over their rivals. This company can manage this threat by offering superior products to its clients.
The potential of new entrants is at its highest point since the emergence of the banking sector over three centuries ago. Governments all over the world are trying to promote local banking and as such, are willing to relax some rules to enable new entrants to enter the industry and compete with foreign banks. Barclays Bank can manage this threat by maintaining high standards in customer service and improving the quality of its products.
The threat of substitutes in the market is real, especially with the emergence of Sacco and other online banking facilities such as Skrill and Payoneer (Scott & Zachariadis 2013). Those who initially relied on banks for all their financial transactions can now use other alternatives which are readily available, especially when it comes to sending and receiving money from abroad. To manage this challenge, this company may need to expand its product base to offer more services in the market.
The power of suppliers is an issue in the financial sector today. Those who deposit their money in the banks are now demanding for higher interests (Beck & Maimbo 2013). They look for banks that offer the best interest on their savings, forcing firms such as Barclays Bank to adjust their interests. The power of the buyers is also increasing. The borrowers are now demand for low interests charged on their loans. These two forces affect the profitability of financial institutions. To manage these threats, this bank may need to spread its product delivery in the market. This information is summarized in appendix 2.
Conclusion and Recommendations
It is clear from the above analysis that Barclays Bank faces a number of challenges in the market today. The shrinking banking sector, the disruptive technologies, regulatory challenges, and the falling profits are the primary reasons why the firm has decided to sell off its Barclay Africa business segment. The management has realized that this is the most appropriate way of recovering its investment and avoiding financial losses which are believed to be an inevitable eventuality based on the trends that have been witnessed over the past. Leaving a market is not a solution. The management should consider the following recommendations based on the analysis conducted above.
- Barclays Bank should spread its product offerings in the global market instead of shrinking its operations. The strategy of leaving the African market may send a wrong message to its global clients and investors who will view it as being incapable of dealing with strong market forces.
- The management of this bank should promote a culture of creativity and innovativeness among its workforce as a way of overcoming the new market challenges. Having an incubation centre in all the countries where it operates will make it possible for the top talents to meet and share ideas on how to overcome market challenges.
- The firm should embrace technology as a way of remaining competitive in the market. As explained in the Innovation Theory, the firm should be an innovator or early adopter of emerging market changes. This way, it will benefit from what the new technologies have to offer.
- The marketing department of this firm should invest in research and brand promotion. The department should understand the changing market trends and come up with ways of changing internal operations.
Appendix
Appendix 1: SWOT Analysis.
Appendix 2: Porter’s Five Forces Model
List of References
Acharya, V, Beck, T & Evanoff, D 2013, The Social Value of the Financial Sector: Too Big to Fail or Just Too Big, World Scientific Publishing Company, Singapore.
Ackrill, M & Hannah, L 2001, Barclays: The business of banking, 1690-1996, Cambridge University Press, London.
Barajas, 2013, Too cold, too hot, or just right? assessing financial sector development across the globe, International Monetary Fund, Washington.
Battilossi, S 2002, European banks and the American challenge: Competition and cooperation in international banking under Bretton Woods, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Beck, T & Mambo, S 2013, Financial sector development in Africa: Opportunities and challenges, World Bank, Washington.
Blankley, W 2006, Measuring Innovation in OECD and non-OECD countries: Selected seminar papers, HSRC Press, Cape Town.
Burn, E & Cartwright, J 2011, Cheshire and Burn’s modern law of real property, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Burrows, A & Bridge, M 2015, Principles of English commercial law, McMillan, London.
Claessens, S & Feijen, E 2007, Financial sector development and the Millennium Development Goals, World Bank, Washington.
Dell’Atti, S & Trotta, A 2016, Managing reputation in the banking industry: Theory and practice, Springer, New York.
Ellinger, E, Lomnicka, K, Hare, C & Ellinger, E 2009, Ellinger’s modern banking law, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Fasnacht, D 2009, Open innovation in the financial services: Growing through openness, flexibility and customer integration, Springer, Berlin.
Greening, H, Scott, D & Terblanche 2011, International financial reporting standards: A practical guide, World Bank, Washington.
Leditschke, S 2005, Successful Branding in the Financial Sector, GRIN Verlag GmbH, Munich.
Mazzucato, M 2014, The entrepreneurial state: Debunking public vs. private sector myths, McGraw Hill, New Delhi.
Mention, A & Torkkeli, M 2014, Innovation in financial services: A dual ambiguity, Cambridge Scholars Publishing, Newcastle.
Plunkett, J 2007, Plunkett’s Banking, Mortgages & Credit Industry Almanac 2008: Banking, Mortgages and Credit Industry Market Research, Statistics, Trends & Leading Companies, Plunkett Research Ltd, New York.
Scott, S & Zachariadis, M 2013, The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT): Cooperative governance for network innovation, standards, and community, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Tan, Y 2014, Performance, risk and competition in the Chinese banking industry. Oxford, UK: Chandos Publishing.
Uchimura, H & Wu, H 2013, Raising awareness of anticompetitive behaviour in the financial sector of the People’s Republic of China, Cengage, New York.