Assessment of the Financial Position and Performance of the Barton Firm
In order to assess the financial position and financial performance of the Barton engine business, it is important to consider carefully the ratio analysis of the company, as it assists comparisons, simplifies financial-statement, aids the top-management to recognize whether the business’s financial position is enhancing or worsening by showing a yearly-trend, evaluates the long-term financial aptitude, and operating efficiency.
To conduct the ratio analysis of this firm, the focus should be on analyzing total current ratio, gross profit margin, net profit margin, and quick ratio or asset test ratio for three years (1999, 2000, and 2001), and compare between these ratios in order to come into a conclusion about Barton firm’s financial situation.
Ratio Analysis for the Barton Firm
Total Current Ratio
(Total Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities)
Table 1: Total Current Ratio for Three Financial Years of Barton Engine. Source: Self-generated from Barton Case Study.
Current ratio is a common and quick evaluation of liquidity of Barton firm, as it shows the margin of safety or cushion accessible to the creditors; moreover, it is an index for Barton’s financial stability and practical solvency and a directory of the strength of its working capital. As shown in the table 1, from 1999 to 2000, there has been a slow increase in the current ratio of Barton (1.454 in 1999, 1.433 in 2000, and 1.575 in 2001).
As this kind of rise in the ratio demonstrates the enhancement of the liquidity position of the business, it is notable that the liquidity position of Barton had a slow development over these three years. On the other hand, if there was a decline in the current ratio, it was quite natural that the liquidity position of the business has worsened with time and that it should improve in order to have better position.
Gross Profit Margin
(Gross Profit Margin = Gross Profit / Revenue from Sales X 100)
Table 2: Gross Profit Margin for Three Financial Years of Barton Engine. Source: Self-generated from Barton Case Study.
The gross profit margin is the proportion of the turnover, which a business preserves following the direct-expenses linked to generating the materials traded throughout a certain period; moreover, a rising profit margin means that the firm has good pricing strategy (it is able to lift prices with small or no effect on sales) or that it possess a rising productivity.
However, as illustrated in table 2, there has been a substantial decrease in the gross profit margin from 1999 to 2000, which were consecutively 20.991%, 20.605%, and 19.209% – decreasing margin could indicate that variable costs have risen while selling price has remained constant; it could also mean that Barton has cut prices to make an augmentation in sales.
Net Profit Margin
(Net Profit Margin = Net Profit / Revenue from Sales X 100)
Table 3: Net Profit Margin for Three Financial Years of Barton Engine. Source: Self-generated from Barton Case Study.
High net profit margin ratio shows how successful the firm is at changing sales into profit, and that the firm is capitalizing on some competitive-advantage, which can give it some additional capability and suppleness throughout the difficult financial periods; conversely, low net margin means the firm is not generating enough sales or it is not keeping your operating-expenses under control.
Throughout 1999, 2000, and 2001, it is notable that the net profit margin has decreased so much that it took on a negative figure (0.216% in 1999, – 0.199% in 2000, and – 1.69% 2001). Such a decline in the net profit margin ratio throughout the three stated financial years might point out cost binges, which necessitate competence development; the Barton firm, having a low ratio, might need to take on debt to pay its expenses.
Quick Ratio or Asset Test Ratio
(Quick Ratio (Asset Test Ratio) = (Current Assets-Inventory) / Current Liabilities)
Table 4: Quick Ratio (Asset Test Ratio) for Three Financial Years of Barton Engine. Source: Self-generated from Barton Case Study.
Asset test ratio would decline while cash or accounts obtainable balances reduce, devoid of an equivalent diminish in current liabilities, or boost in a current liability devoid of an equivalent boost in cash or accounts obtainable (for example, cash spent to buy fixed assets, cash spent to give off a long term debt, or cash spent to disburse dividends).
In 1999, 2000, and 2001, the asset test ratio diminished respectively by 0.962, 0.936, and 0.813, which shows Barton had a small liquidity ratio demonstrating that the firm’s liquidity position has needed further amplification.
Suggestions for Ms. Payne Regarding the Financial Situation
- It is very important for Ms. Payne to provide a closer observation to improve the gross profit margin. This is achievable by two ways, either by augmenting the sales revenue when keeping the cost of sales the same, or by lowering the cost of sales, when upholding the same level of sales revenue.
- It is essential to note that Barton firm had an increase in its current ratio throughout the three years. However, in order to further enhance its current ratio and liquidity position, Ms. Payne should try to bring more cash into the balance sheet either by selling the under used assets, increasing loan capital and long term borrowings, or postponing intended investments.
- Moreover, the chief financial officer should also focus on raising the gross profit, or lowering the expenses and overheads. This will develop Barton’s net profit, which in turn will help it to enhance the net profit margin.
- According to table 4, the quick ratio or asset test ratio of the Barton firm has lowered constantly in 1999, 2000, and 2001. In order to enhance Barton’s asset test ratio, Ms. Payne should focus on two things, firstly, operate at increasing sales from the existing asset base, and secondly, sell of under utilized assets profitably, so that the sales figure has divided by a lower asset total.
SWOT Analysis of Barton Engine Works Co
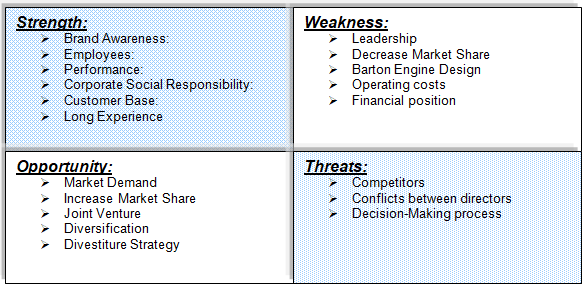
Figure 1: SWOT Analysis of Barton Engine Works Co. Source: self generated.
Strengths
The internal strengths of Barton Engine are its glorious history, brand image, human resources, and performance of few departments, customer vase in the US market, and so on.
- Brand Awareness: Barton Engine Works Co had strong brand awareness for its consumer oriented five horsepower engine market;
- Employees: this company was the largest employer of the Barton County and it had more than 400 employees;
- Performance: According to the Barton Case Study, Earl and his engineering department’s little customer engine business is doing well. In addition, Earl stated that there is no immediate risk of losing the customer “Mulch & Co” and 164 licensed dealers have doubled their purchase order from Barton Engine;
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Barton Engine has a significant level of budgetary involvement for its CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) policy and practice, for instance, the company provides scholarship to the children of the employees and talented students, send Christmas cards to the employees, and take care them;
- Customer Base: The strong base of loyal customers helped the company to continue its business and to compete with Japanese manufactures;
- Long Experience: Barton Engine Works Co has long experience to carry on its business with remarkable footprint in the US market.
Weaknesses
Besides strong points, Barton Engine has many weaknesses, such as –
- Leadership: Once upon a time, this company was reputed for the financial strengths as predecessors were built a well-respected, $110 million company. However, the unfortunate death of William and his son by commuter plane crash created leadership gap though Ms. Payne is enough competent person to control the company as she has practical experience with high educational background;
- Decrease Market Share: The market share of Barton had decreased dramatically from 1985, for instance, it had at least 37% of consumer oriented five horsepower auto market in 1885 but it was only 4% in 2001, which indicates that 70% of total sales had down within last 15 years. In addition, its industrial market share had also dropped to 19%;
- Barton Engine Design: Integration of modern technology is an important factor in order to meet the demand of the products and create new fields of business operation but this company was not concentrated this issue. According to the case study, this company has been captured a significant market share 50 years ago when the owner of this company was designed high-tech model but the successors of the owner ignored this issue and lost market share;
- Operating costs: it was not possible for the management to reduce operating costs, and in 2001, its engineering, selling and administrative costs were $22,188,000;
- Financial position: This company has experienced huge financial problems as its net operating profits have decreased dramatically, for instance, its net income was 2065 thousands in 1999 where as it was (1058) thousands in 2001.
Opportunities
Key opportunities of the company have discussed below –
- Market Demand: The top-level management of the company believed that they have strong customer base because still customers seek Barton Engine though Japanese manufactures sale few more engines in the US market. According to the Barton Case Study, this company has also largest market share, which indicates that it has huge opportunity to increase customer demand in the US market by restructuring and implementing new strategies;
- Increase Market Share: Most of the countries of the world are now member of WTO, which gives the scope to the company to enter new market by adopting suitable entry mode strategies to increase market share;
- Joint Venture: As many customer intended to purchase Barton Engines, it has the opportunity to joint venture with renowned companies to share technology of the partners, assets, manpower and so on;
- Divestiture Strategy: According to the Barton Case Study, the performance of few subsidiaries was not stable to carry on the business. As a result, the management of this company has opportunity to adopt divestiture strategy to concentrate on the core business or profitable units;
- Diversification: This Company has opportunity to diversify its product range both vertically and horizontally to attract the customer.
Threats
As per the case study, major threats for the company’s were –
- Competitors: Japanese competitors were main problem for the company because Barton lost the market share and its glorious position due to strong presence of the Japanese products, for instance, in 1985, Japanese had only 6% and 2% share of consumer oriented five horsepower and ten horsepower auto market accordingly but it is now market leader of this sector. On the other hand, Japanese manufactures offered technologically advance products and designed new models over time;
- Decision-Making process: Taking right decision in proper time is one of the most important factors for the development of the company. However, the company may become insolvent due to undertake inappropriate steps;
- Conflicts between directors: Williams intended to carry out the business with old equipment, as he was spent huge fund for purchasing new products in 1978. On the other hand, the son of William was interested to purchase new machine to develop quality of the products and increase efficiency of the employees. However, Williams argued that it should require more than $100 million to purchase new equipments, and need sufficient fund to train employees, so, this conflicts between directors had influenced to decrease the performance in the US market;
- Sales Report: The marketers scrutinised the sales data of profitable units and found that the earnings from 10-horsepower engine would decreased by 75% within the next fiscal year.
Recommendation
- Ms. Payne should increase budget for promotional activities as it can increase customer base and market share;
- Moreover, she should decrease production costs by purchasing few machine and repairing old machine as the customers never compromise with the quality of the products;
- To reduce operating costs, the company should recruit efficient and low cost employees from South Asian countries like Bangladesh, India, and China;
- In addition, Ms. Payne should compare the performance of all subsidiaries and sale the non profitable units to concentrate on the core business;
- She should try to work as a team to develop the performance of the employees;
- Ms. Payne should review the performance of the competitors to take decisions;
- She should consider the opinion of the top management and employees;
- However, Ms. Payne should restructure the pricing strategy in order to compete with the Japanese engine manufacturing companies.
Suggestions about the 10-Horsepower Engine
According to the Barton Case Study, in 1985, Barton had 21% share in consumer oriented 10-horsepower engine market whereas Japanese had captured only 2% market share. The US customers of generators, pumps and compressors were relied on Barton’s products for its quality and design, but Mr. William never upgraded the design and technology of 10-horsepower engine.
As a result, this company failed to retain their glorious position and Japanese manufactures captured major portion of market share though some dealers of Barton is doing well and they have created a loyal customer base. Therefore, besides of upgrading the design of the engine, Barton firm should undertake the strategies suggested below.