Abstract
The preferences of consumers change with the change in technology. RIM Blackberry failed to keep-up with such changing technological trends in 2013. Considering the fact that the mobile market is highly competitive, it is imperative for the mobile manufacturing companies to be coherent to the technology being used globally. The market shares decline, that Blackberry faced needs to be analyzed by a Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) in order to understand the perceptions that exist and to find a solution. This report looks at ways to apply the SSM to solve the problem that Blackberry faces due to the current technological challenges. Overall, it demonstrates the overview of Blackberry as a company and its struggle to improve its market shares and reputation within the industry.
Introduction
Unlike other industries, the mobile industry is all about adaptation. Such adaptation has to be from both the manufacturer and the consumer. The manufacturer has to adapt to new and innovative techniques and the consumer has to adapt to change (new versions or models). If both these entities perform their individual roles of adaptation in a perfect manner, there is no possibility of a particular mobile manufacturing company not performing well.
In September 2013, the Blackberry Company “reported a net loss of $965 million for the second quarter” (Blackberry reports Q2 loss of $965 mn, 2013, para. 1). The loss was ascribed to lower revenue from its latest smart-phone. Blackberry experienced great financial crisis due to this incident. In an attempt to come out of the financial crisis, the company declared that it would scrap more than 4,500 jobs globally. It is worth mentioning that during the same period, Apple, its competitor, was able to sell not less than 9mn units of the company’s new smart-phone.
Five years back, the Blackberry Company was among the best technological performing companies with a significant market share (Hicks, 2012). Things did not seem rosy since the past two years when its sales started dwindling. The huge second quarter loss of 2013 confirmed that all was not well with the company. The only thing that people wanted to know was the reason for this downfall. This paper makes use of the systems thinking methods and techniques to explain the origin of the decline in Blackberry’s performance. In addition, these methods are utilized to chart a course of recovery from the decline and re-establish the company as a leading technological company.
It is very unfortunate that Blackberry is now poised for a change in its management. It is surprising to note that the news of such a change (in August, 2013) suddenly improved the market position of the company’s shares. There was an increase of 10% (Miller, 2013). The following paper discusses the factors responsible for this debacle.
Research in Motion (RIM) and Blackberry are common names associated with smart phones that revolutionized mobile communication and other related services. It is understood that companies experience changes (depending on their way of dealing with issues) that are either beneficial or detrimental to their overall performance. Blackberry had a success story for its competitors to emulate and clients to appreciate, but the present scenario demands a great struggle by the company to regain its ground and overcome the financial challenges it is experiencing.
Background
In order to maintain an upper edge in the competition race, it became imperative for Blackberry to introduce a new phone model that would be able to replace all other similar products and compete effectively with other similar companies. Unfortunately, the idea flopped and Blackberry started experiencing its downfall shortly after it released its first Smartphone. The downfall forced Verizon to switch over to other companies. His intention was to ensure that Blackberry produced a touch screen phone that would ensure that its market is retained and expanded.
This did not happen and the efforts by co-CEO, Jim Balsillie, to develop instant messaging software, were opposed by the current CEO, Thorsten Heins. Balsillie was forced to quit the Blackberry board and seize his relations with the company because he thought his presence in the company was not adding value. The Blackberry directors, led by Heins, ignored Balsillie’s advice and went ahead with their plans, that later had serious implications for the company. These are some of the reasons that triggered Blackberry’s long journey to financial crisis. The crisis forced some of its top office bearers to resign for fear of being condemned of failing the company.
The year 2012 witnessed a mobile war and to combat it, Thorsten Heins (CEO) and members of the board decided that the company’s weapon would be the fully touch screen Blackberry Z10. Michael Lazaridis opposed this plan. According to him, the company had learnt various lessons from its previous products and there was no need of investing in a device that had already reached saturation in the market. Kristian Tear and Frank Boulben opposed Michael’s idea claiming that the keyboard-equipped mobile phones were no more in demand. This episode marked a turnaround for Blackberry’s performance because it failed to meet its financial targets after launching the Blackberry Z10.
It reported a $ 965 million fiscal second quarter loss because of a huge write down of this product. The plan had flopped because the company had not met its target even eight months after launching this product. The company is unable to meet the cost of paying its workers and has already reduced 4,500 jobs. This means reducing its employees by 40%. Even though Blackberry invented the smart phone concept, it is unable to compete with similar companies and this has lowered its market value by $75 billion within the past five years. It is evident that significant rifts between board members are to be blamed for causing serious conflicts and barriers while implementing the projects of this company.
Balsillie resigned from the company’s board because his proposal to introduce a universal product that would promote instant messaging on all phones was opposed. This and other similar happenings have cast the future of this company in doubt. Fairfax Financial Holdings announced its intention to take over Blackberry at an estimated cost of $ 4.7 billion. The Apple iPhone was a grave warning for Blackberry because of the complexity of its services. It was a mini computer and this baffled Balsillie who downplayed this innovation by casting doubts on the new software and propagated its threat to collapse networks. The launch of its two way email pager managed to compete with Apple’s iPhone and minimized its influence on the global market.
The post iPhone period dealt a serious blow to Blackberry because it required the use of different data packages from the traditional wireless carriers. This forced Lazaridis to buy Torch Mobile. The company made software that enabled mobile phones to have web connectivity. However, it was very challenging to fix this application in a Java supported device because it was only compatible with Android and Apple systems. This showed that the company was neither prepared nor positioned for the future of smart phones. The DNA of Blackberry was very old and it was necessary to change it to enable the company to extend its life.
Blackberry’s structure was very complicated and even though the two CEOs worked in unison, their subordinates were a big hurdle to decision making. It took too long to account for shortcomings and new products were never launched as planned due to long consultations. The plan to launch its first notebook (PlayBook) did not help the company recover from perennial failures and led to serious losses. Lazaridis is optimistic that the Blackberry story will never end and there is a possibility that he may be in the team planning to buy his former company and rejuvenate its performance.
Soft Systems Methodology
Reliability
Root Definition
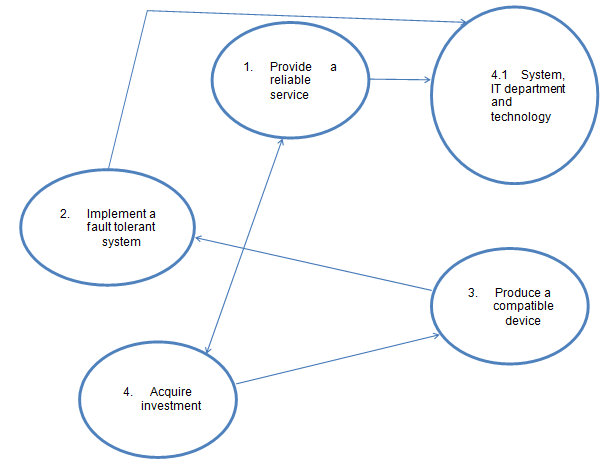
BlackBerry will provide a reliable service (W) that depends on a fault tolerant system (T) to keep consumers (C) satisfied in using the latest technology (E), which now has investment (E) for the IT department (A) in the company that is owned by RIM Blackberry (O).
CATWOE
Table 1: CATWOE for the reliability.
E’s Criteria
Table 2: E’s criteria for the reliability.
Conceptual Model
Security
Root Definition
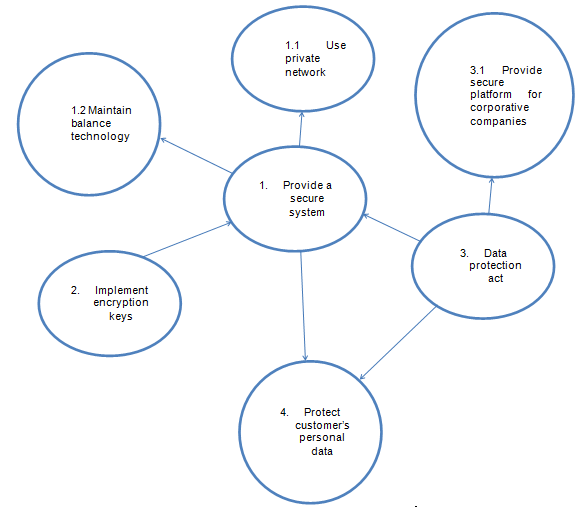
The company will provide a secure system (W) by using the encryption keys and data protection act (E) that is implemented by the IT department (A) which safely secures customers’ personal data (T) to keep the consumers (C) loyal to RIM Blackberry (O).
CATWOE
Table 3: CATWOE for the security.
E’s Criteria
Table 4: E’s criteria for the security.
Conceptual Model
Phone Design
Root Definition
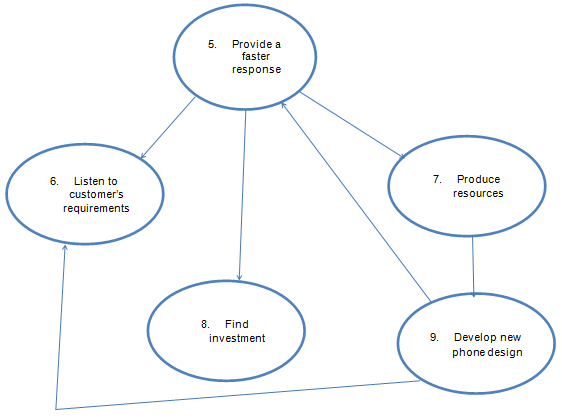
The company will provide a faster response to technological trends (W) by responding quicker to the customers’ requirements (T). RIM Blackberry (O) needs to generate the resources and finance (E) in order, for the Media department, and the CEO (A) to produce a new phone design, that should regain the confidence of consumers (Individual users and Businesses) (C).
CATWOE
Table 5: CATWOE for the phone design.
E’s Criteria
Table 6: E’s criteria for the phone design.
Conceptual Model
Accessibility
Root Definition
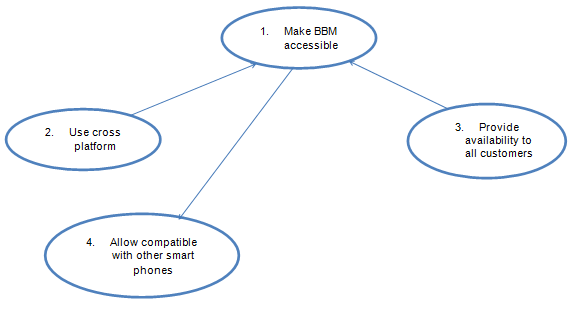
The company needs to make BBM accessible to other consumers (W) by making it a cross platform application (T), which would allow accessibility to all consumers (C) using other popular smart phone devices. RIM Blackberry (O) is unable to produce this, due to mobile phone network constraints (E), which is controlled by the mobile phone network companies (A).
CATWOE
Table 7: CATWOE for the accessibility.
E’s Criteria
Table 8: E’s criteria for the accessibility.
Conceptual Model
Conclusions
The Soft System Methodology indicates that organizational problems, intensive technology, and industry competition are the reasons behind the decline of the Blackberry Company in the market. The corporate culture of the organization prevented organizational learning and change; this resulted in the loss of its market share. Analytical thinking suggests that a cultural change is necessary for a company to recover in the long run. In addition, technological innovation is critical for the organization to remain competitive in the market. By hiring a new CEO, Blackberry hopes to bring-in a range of new technologies and ideas that should have a knock on effect so that Blackberry’s staff may feel more secure about their future with the company. As is evident from the rich picture below, the suggested model is totally different from the real world model.
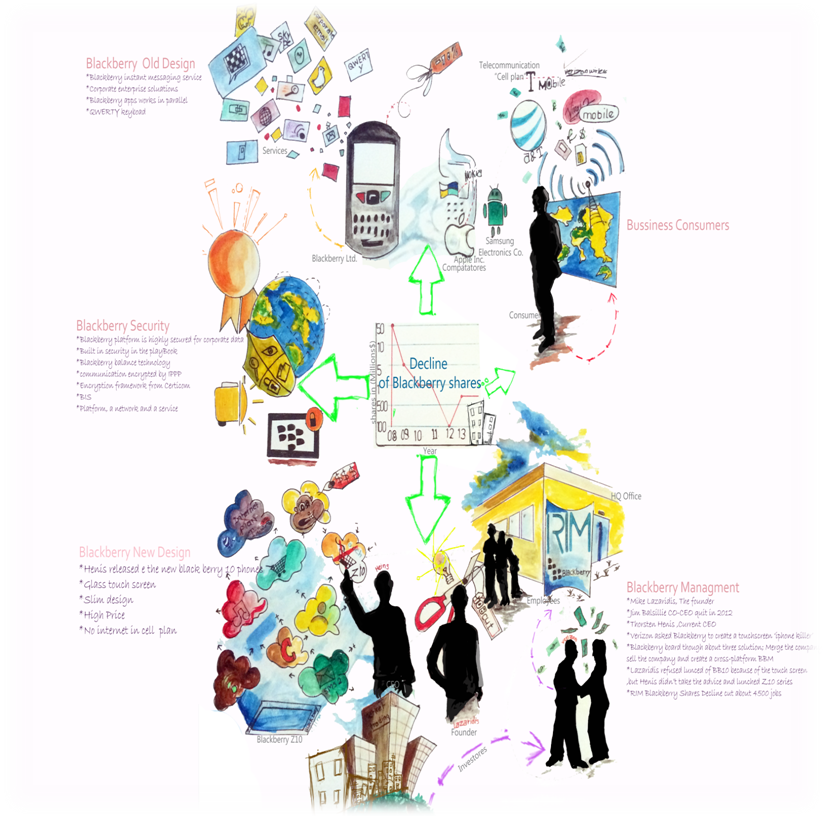
By using the SSM, it was revealed that RIM Blackberry was overloaded with environmental pressure which caused the decline of the shares. In concluding, it is understood that the business environment for the Smartphone industry is becoming more and more competitive. We have realized that progressing while considering the internal and external changes is critical for the organization’s success. RIM Blackberry achieved its success through the transformational level that we suggested in the CATWOE, when the company started facing industry challenges from its competitors (Apple’s iOS and Google’s Open Source Android Platform).
SSM explains that problems cannot be solved by disintegrating them into individual components. This is because such activities can only be examined when they are together due to the interaction of its components. System thinking is a process that involves a methodological comprehension of problems and identification of their solutions. The system has to be analysed within its environment by taking account of its external environment. Through analysis, solutions to a problem are obtained and organizations are able to have a learning system (Cabrera, 2006).
Recommendations
In providing a solution for the recovery of Blackberry, the infusion of money is not the only solution for the company. Analytical thinking shows that the company needs to change its corporate culture to facilitate a learning system where the executives are ready to adopt new ideas. In the fast moving smart-phone industry, the company needs to re-invent its technological base and develop operating systems that are flexible to the shifting customer trends. The competitive applications of eco-systems and a competitive marketing strategy should be put in place by the company to re-gain its market share. The company needs to utilize consumer feed-back in the development of competitive products that match the changes in the industry.
References
Blackberry reports Q2 loss of $965 mn. (2013).
Cabrera, D. A. (2006). Systems thinking. Web.
Hicks, J. (2012). Research, no motion: How the Blackberry CEOs lost an empire. Web.
Miller, H. (2013). Blackberry CEO to make $55.6 million if he sells company. Web.