Introduction
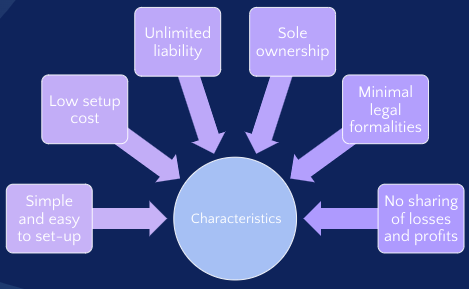
Launching a new business is a thrilling endeavor, but it also necessitates making crucial choices regarding the setup and management of the enterprise. Choosing the appropriate business organization is one of the most important considerations. A sole proprietorship is a concept of organizational structure in which a single person serves as both the owner and the company’s financial representative.
Taxation & Liability
As the sole proprietor, the owner is responsible for all aspects of the business, from management to losses. There is no legal separation between the owner and the business, meaning the owner is personally liable for all associated debts and liabilities. Consequently, this puts the owner’s personal assets at risk in the event of financial difficulties or legal claims against the business. Additionally, the business is free from corporate taxes since it is not a separate legal entity (Bernoster et al., 2019).
Advantages
Unlike other business types, there are no official prerequisites to establish a single proprietorship. One only needs to begin operating under their name or a trading name. Because of this, it is a desirable choice for people who wish to launch a business swiftly and cheaply (Bernoster et al., 2019). In addition, they own the company’s entire profit and are not required to distribute it to any shareholders or partners (Bernoster et al., 2019).
Disadvantages
Operating a sole proprietorship, however, has several drawbacks. The primary problem with this type of business is that the owner is liable for any debts and obligations incurred by the business. This implies that the owner’s assets may be in danger if the company is unable to make its payments on time or meet its financial obligations (Bernoster et al., 2019). Getting loans or investment capital could be challenging because the company is solely owned and controlled by one person (Bernoster et al., 2019).
Internal Control
Internal control plays a vital role in safeguarding the company’s assets, ensuring the accuracy of financial records, and preventing fraudulent activities. Tien (2019) defined internal controls as a set of policies and procedures that a business implements to achieve set objectives. The advantages of having internal controls in place include protecting assets, ensuring financial accuracy and compliance, and improving overall business efficiency.
Advantages of Internal Control
Internal controls can help safeguard a company’s assets, such as cash and inventory, to minimize the risk of losses due to theft or misappropriation. Sujana et al. (2020) highlighted that internal controls check on the accuracy and reliability of financial records. Regular account reconciliations and reviews can ensure that financial records are up-to-date and free from errors. Additionally, internal controls can aid in preventing fraudulent activities by detecting and deterring fraud before it occurs.
Role of Internal Control and Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietors can mitigate the drawbacks of their business structure by establishing internal controls, which provide a system of checks and balances. By incorporating tools like trial balance, sole proprietors can enhance their business management shield themselves from legal and financial risks, and minimize the chances of errors and fraudulent activities. Furthermore, sole proprietors are responsible for any financial challenges their business encounters, which internal controls can assist in addressing by tracking the business’s financial status (Sujana et al., 2020).
Trial Balance
Examples of internal control include separation of duties, access controls, physical controls, audit trail, reconciliation, budgeting and forecasting, segregation of duties, and trial balance. For the sole proprietorship, I picked the trial balance to ensure the accuracy of recording transactions by listing all accounts and balances in the general ledger (Murdihardjo et al., 2020). Upon completing the trial balance for my company, I confirmed that all accounts were correctly balanced, ensuring the accuracy of the financial statements.
Furthermore, it highlights the company’s financial position by analyzing the balances of different accounts, enabling effective decision-making. Another benefit of the Trial Balance is identifying discrepancies that may indicate fraud or financial mismanagement (Murdihardjo et al., 2020; Saputra & Anggiriawan, 2021). Negative balances may signal incorrect distribution of funds or financial difficulties in the company.
Chart of Accounts
For sole proprietors, it plays a crucial role in distinguishing personal and business expenses, monitoring revenue and expenditures, creating financial statements, and forecasting for the future. A chart of accounts provides a comprehensive record of all the accounts used by a business to monitor its financial activities.
Table 1. Chart of Accounts
The minimum required accounts for the company include asset, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expense accounts. Assets such as inventories provide a business with future economic benefits, while liabilities take money out (Warren et al., 2020). Revenue is used to invest in assets, whereas equity represents an owner’s stake in a company.
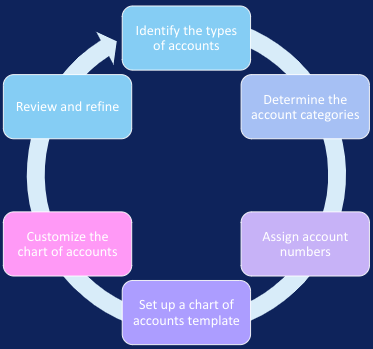
Steps for Developing a Charts of Account
To develop the chart of accounts, I will begin by identifying the necessary account types and then determine the required categories of accounts within each type. Next, I will assign account numbers to each account before creating a standard list of accounts using a chart of accounts template. After customizing the list to match the unique needs of the business, I will review and refine the chart of accounts to ensure its completeness and accuracy.
Balance Sheet
I will use the chart of accounts to create a balance sheet for the business. A balance sheet gives insight into a company’s liquidity, which refers to its ability to pay short-term obligations but also determines its solvency, which relates to its ability to pay long-term debts (Weygandt et al., 2019).
Table 2. Example of a Balance Sheet
A balance sheet offers an overview of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time by reporting its assets, liabilities, and equity. The chart of accounts is integral to the balance sheet since it serves as the foundation for recording financial transactions that are subsequently reported on the balance sheet. For instance, when a company purchases inventory on credit, the transaction is recorded in the accounts payable account in the chart of accounts. This data is then used to compute the company’s liabilities on the balance sheet.
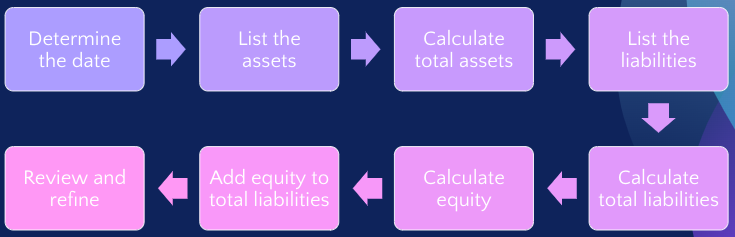
Steps for Developing a Balance Sheet
To create the balance sheet for the business, the first step will be to select a specific date. I will proceed to list all the company’s assets and calculate their total value. Similarly, I will list all liabilities and calculate their total value. After that, I will calculate the equity, which includes retained earnings, and ensure that the sum of equity and total liabilities matches the total assets.
Conclusion
In summary, for those seeking a fast and cost-effective way to start a small business, a sole proprietorship can be an attractive option. However, it is important to carefully consider the disadvantages before deciding on this structure, such as limited access to financing and personal liability for the business’s obligations. To ensure the accuracy of a business’ financial statements, a trial balance, chart of accounts, and balance sheet can be valuable tools.
References
Bernoster, I., Khedhaouria, A., & Thurik, R. (2019). Positive affect, the entrepreneurial process, and the entrepreneurial success of sole proprietors. Management, 22(2), 273-296. Web.
Murdihardjo, L., Nurjanah, Y., & Rendy, R. (2020, May). Implementing INTACS Dynamics enterprise resources planning system for financial statements. In 2nd International Seminar on Business, Economics, Social Science and Technology (ISBEST 2019) (pp. 228-233). Atlantis Press. Web.
Saputra, K. A. K., & Anggiriawan, P. B. (2021). Accounting, auditing and corruption in Kautilya’s Arthasastra perspective and psychogenetic Hindu: A theoritical review. South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business, Economics and Law, 24(2), 67-72. Web.
Sujana, E., Saputra, K. A. K., & Manurung, D. T. (2020). Internal control systems and good village governance to achieve quality village financial reports. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 12(9). Web.
Tien, N. H. (2019). International economics, business and management strategy. Dehli: Academic Publications. Web.
Warren, C. S., Jonick, C., & Schneider, J. (2020). Financial accounting. Cengage Learning. Web.
Weygandt, J. J., Kimmel, P. D., & Kieso, D. E. (2019). Financial accounting. John Wiley & Sons. Web.