Introduces Self and Topic
I am a nursing student who will present today on the topic of cannabis and mental health, providing you with an overview of the adverse effects of marijuana and the possibilities of addiction treatment. Mental health remains a significant aspect of wellness that requires heightened attention from medical professionals. Therefore, with the rising demand for cannabis in modern-day medicine, the number of people whom the substance has affected negatively through side effects and addiction has increased, necessitating recognizing the adverse effects of marijuana.
Who are They?
Helping to tend to those whose mental health cannabis has impacted, as a student currently studying to be a nurse, is one of my goals in life. Thus, I find it essential to create an informed and knowledgeable opinion on such a complex issue. As a future professional, I want to understand the severity of this problem and spread awareness of the sickness caused in peoples’ minds by cannabinoids.
What is the Topic and How is It Defined in Literature?
My topic is linked with presenting the adverse effect of cannabis on mental health, how to intervene in potentially damaging situations, its treatment, and expected outcomes. Literature precariously states, and my clinical experience supports, the fact that the relationship between mental health and cannabinoids has the potential to detriment the patient’s wellbeing. Can anyone from the audience name a few of the negative effects of cannabis on patient’s health? From a lessened attention span to psychosis and anxiety attacks, marijuana remains a dangerous substance for people’s mental health. As cannabis becomes more popular as a medicine, rather than a recreational drug, it is essential to keep in mind these detrimental effects instead of focusing merely on positive results (as seen in Figure 1). As an example, we may examine medical cannabis, which demonstrates the fact that patients use it more frequently but exhibit worse health results than those achieved during traditional treatment.
Why is it of Interest to Them or Important/Significant?
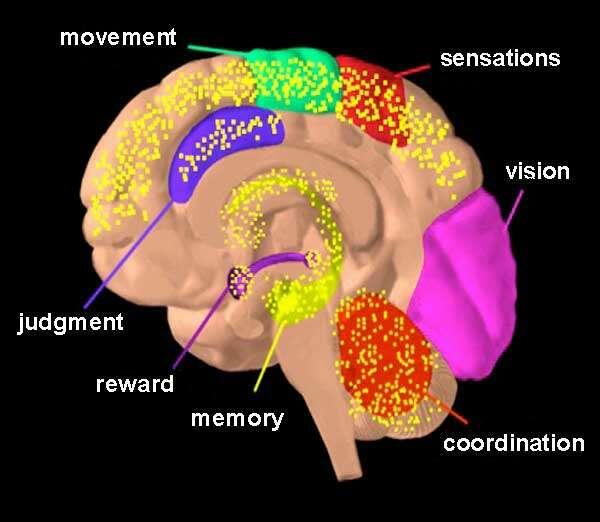
For me, the topic holds significance as I am deeply engaged in the cannabis debate, hoping to uphold the case that proves the extent of its negative effects over positive ones. Thus, with thorough support from relevant literature, it is possible to present an overview of a complicated addiction issue in modern Australian mental healthcare. The significance of this problem lies in the rising popularity of medical cannabis and tetrahydrocannabinol, often linked with overlooking its adverse effects on a variety of the brain’s functions (as seen in Figure 2). Contemporary Australian care of the consumer allows prescribing cannabis for some reasons, such as multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, chronic pain, palliative care, and during chemotherapy. However, the effects of cannabinoids do not surpass the effectiveness of traditional medicine, instead potentially negatively affecting the clients’ future symptoms, making medical cannabis today no different from 19th-century opium prescriptions.
Discusses the Contemporary Care of the Consumer
I have chosen the sources for this presentation by their direct relevance to the subject, as they provide a valuable overview of the Australian perspective and experience of cannabinoid treatment. The literature was managed successfully to include a wide variety of research on both the medical benefits and real-life drawbacks of cannabis use in Australia and abroad, thus creating a supported argument. These specific sources help present a structured overview of the nature of the use of cannabis on patients’ mental health, urging them to take care and understand the dangers of using it for medicinal purposes.
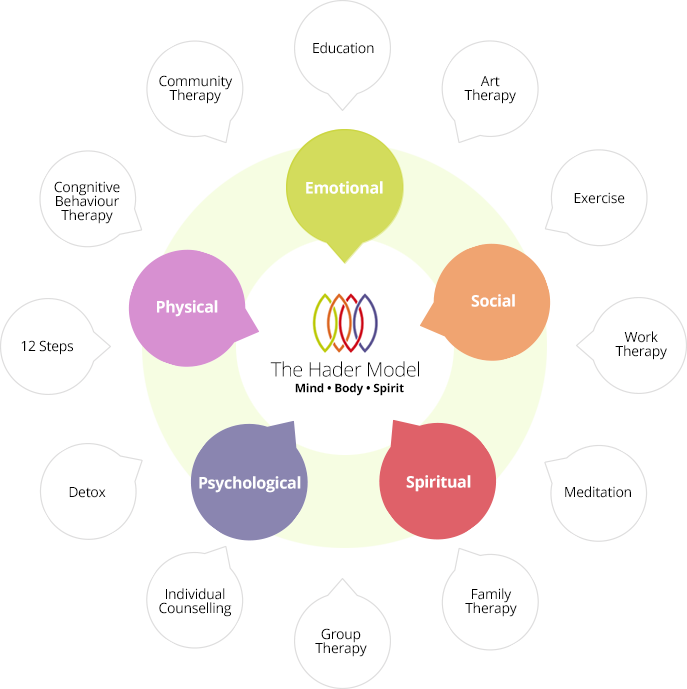
Contemporary consumer care begins with screening for cannabis addiction. Modern treatment is the same as for any drug addiction, with rehabilitation programs, hospital treatments, and detoxification programs aimed at helping the client to overcome their obsession with the help of professionals (see Figure 3). Admitting the patient to a facility, assessing and effectively detoxing them, followed by extensive inpatient care, initiates the process of wellness. The expected outcomes of care, which are based on behavioral therapy and trauma resolution, aims to create citizens who are free of both addiction and its lasting effects on their mental health. Patients are taught everyday tactics that help them avoid relapsing back into addictive behaviors and are sustained by a variety of resources, for example, communication lines with their facility and support groups. Negating drug-deprivation symptoms, withdrawal-induced anxiety, and possible aggressive tendencies, which the patients may exhibit during this period is imperative, as well as establishing secure communication lines with clients to help them maintain their healthcare endeavor.
The worsening of symptoms and an adverse effect on the patient’s life, for example, major depression, psychotic symptoms, and educational deterioration become supportive evidence for addiction treatment (see Figure 4). Intervention tactics are linked with decreasing the number of drugs taken by the patient and transferring them to non-cannabinoid-based medicines if they become dependent on therapeutic cannabis. Queries, such as the Severity of Dependence Scale, the Cannabis Problems Questionnaire, and the Cannabis Withdrawal Scale, help identify the issue’s extent. Unfortunately, the stigma of addiction treatment may prevent successful outcomes and pose additional social barriers to patients’ wellness. Nonetheless, understanding the process of treating cannabis addicts is essential in the modern world, which is increasingly shifting to ignoring its negative effects on people’s mental health. The dangers of drug dependence continue to pose a threat to the Australian public, with decreasing social awareness of the repercussions of substance consumption.
Engages the Tutorial Group
- What do you do when cannabis affects patients’ wellness negatively on a long-term scale?
- What experiences have you had with treating cannabis addiction?
- How do you deal with addicted patients who demand cannabis treatment?
- What unachievable by traditional medicine effects do you anticipate when prescribing mental health patients with cannabinoid treatments?
- What argument convinces you of the prevalence of negative implications of cannabinoid treatment on clients’ mental health?
Effective Use of Handouts and is on Time


References
Addiction treatment model. (n.d.). Web.
Boden, J. M., & Fergusson, D. M. (2019). Cannabis law and cannabis-related harm.The New Zealand Medical Journal (Online), 132(1488), 7-10. Web.
Cook, J., Lloyd‐Jones, D. M., Ogden, E., & Bonomo, Y. (2015). Medical use of cannabis: An addiction medicine perspective. Internal Medicine Journal, 45(6), 677-680. Web.
Copeland, J., & Alperstein, D. (2016). Cannabis: Use, harms, disorder, and interventions.Australian Clinical Psychologist, 2(1), 782. Web.
Gage, S. H., Hickman, M., & Zammit, S. (2016). Association between cannabis and psychosis: Epidemiologic evidence. Biological Psychiatry, 79(7), 549-556. Web.
Gullo, M. J., Matveeva, M., Feeney, G. F., Young, R. M., & Connor, J. P. (2017). Social cognitive predictors of treatment outcome in cannabis dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 170, 74-81. Web.
Hall, W., Hoch, E., & Lorenzetti, V. (2019). Cannabis use and mental health: Risks and benefits. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 269(1), 1-3. Web.
Lamy, F. R., Daniulaityte, R., Nahhas, R. W., Barratt, M. J., Smith, A. G., Sheth, A.,… Carlson, R. G. (2017). Increases in synthetic cannabinoid-related harms: Results from a longitudinal web-based content analysis. International Journal of Drug Policy, 44, 121-129. Web.
Lin, L. A., Ilgen, M. A., Jannausch, M., & Bohnert, K. M. (2016). Comparing adults who use cannabis medically with those who use recreationally: Results from a national sample. Addictive Behaviors, 61, 99-103. Web.
Lopez, M., & Blanco, C. (2019). Epidemiology of cannabis use disorder. In I. D. Montoya & S. R. Weiss (Eds.), Cannabis use disorders (pp. 7-12). Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Lucas, P., Walsh, Z., Crosby, K., Callaway, R., Belle‐Isle, L., Kay, R.,… Holtzman, S. (2016). Substituting cannabis for prescription drugs, alcohol and other substances among medical cannabis patients: The impact of contextual factors. Drug and Alcohol Review, 35(3), 326-333. Web.
Notcutt, W., & Clarke, E. L. (2014). Cannabinoids in clinical practice: A UK perspective. R. G. Pertwee (Ed.), Handbook of cannabis (pp. 415-432). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Penington, D. G. (2015). Medical cannabis: Time for clear thinking. The Medical Journal of Australia, 202(2), 74-76. Web.
Reavley, N. J., & Jorm, A. F. (2014). Mental health reform: Increased resources but limited gains. The Medical Journal of Australia, 201(7), 375-376. Web.
THC acts on numerous areas in the brain (in yellow) [Image]. (2018). Web.
Walsh, Z., Gonzalez, R., Crosby, K., Thiessen, M. S., Carroll, C., & Bonn-Miller, M. O. (2017). Medical cannabis and mental health: A guided systematic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 51, 15-29. Web.
Weber, L. (2015). Negative, adverse effects of marijuana. Web.
Weber, L. (2016). The negative effects of marijuana on the brain. Web.