Internal Analysis
Company Overview
The company initially started as Caterpillar Tractor Co. in 1925 in the State of California. The name of the company changed its name to Caterpillar Inc. five decades later. The company tops all the other rivals all over the world in producing various machinery and hardware for construction. The organization likewise is the main service supplier through Caterpillar Financial Services, Caterpillar Remanufacturing Services, and Progress Rail Services (Akroush 122).
History
The company was formed in 1925. Two companies came together to form in. The two companies are Holt Manufacturing Company and C. L. Best Tractor Company. The merger happened in 1925. Consequently, Caterpillar Inc. was formed in California. Caterpillar hardware is conspicuous by its traditional trademark “Caterpillar Yellow” uniform and the “CAT” logo (Bales 440).
Human Resources
Mr. Douglas R. Oberhelman is both the chairman and the CEO of the company. The vision is to make a situation in which all individuals’ fundamental needs are satisfied in a naturally practical way and an organization that enhances the nature of the environment and the surrounding community. The mission is to empower financial development through infrastructure and energy improvement and to give solutions that bolster groups and protect the planet. The strategy is to give workplaces, items, administrations and solutions that make beneficial and effective utilization of assets as we endeavor to accomplish the vision (Archie and Juha 48).
The company applies development and innovation to enhance the manageability execution of Caterpillar’s items, services, arrangements, and operations. The company holds that sustainable advancement is improved by creating frameworks that boost life cycle advantages while additionally minimizing the financial, social and ecological expenses of possession, as reflected in the manageability standards (Barnard 102).
Operations Analysis
The company’s items are sold through an overall system of dealerships, 50 of which are situated in the U.S. There are 141 other merchants outside of the U.S. CAT (Caterpillar Company) merchants reach out to more than 180 countries with CAT and CAT related offices traversing more than 500 areas around the world. This permits CAT to be near their worldwide client base. The company provides a wide range of products which are more than 300. The company is based in the state of California. In addition, there are several offices located across the world. The organization’s structure is a top-down approach, where there is a central authority giving all the instructions and making the key decisions.
The expansion in local energy generation bringing about lower household energy costs and higher energy fares will keep on supporting domestic production, pull in foreign production to the U.S., and generally reinforce the U.S. economy. Considering the greater part of this, I trust we will keep on seeing moderate but positive U.S. and worldwide financial development throughout the following couple of years. In like manner, I trust this current monetary cycle will be extended longer than noteworthy standards.
Marketing
In view of the examination of the company’s current method, brand qualities and shortcomings, aggressive business position, and possible key course for the future, another incorporated advertising correspondences crusade can be created. The main concentration of the company’s IMC campaign will be on two levels – first and foremost, to convey an engaged, exceptional brand picture to possible clients and secondly, to construct passionate customer brand association by advancing the psychosocial advantages of its consolidated faithfulness plan.
The campaign will go for the satisfaction of the accompanying goals inside of a 12-month period, which began in June 2015 (Barney 101).
Corporate Targets
- To be the fastest growing machinery production firm through acquisition of new clients;
- To re-assemble brand personality to dispense with the current brand picture related disarray among customers.
Business Targets
- To expand total turnover by 25% in the one-year period;
- To develop the present dynamic client base by 20% in the one-year period;
- To build a piece of the overall industry by 1% in the one year period.
Advertising and Communications Targets
- To improve the brand’s premium, by moving concentration far from its value coordinating action;
- To plainly characterize brand character and make a convincing message to bolster it;
- To make a passionate bond with potential clients by emphasizing the advantages of the brand for the clients.
Products and Services
Development Industries
Development commercial ventures items are principally utilized as a part of framework and building development applications. A great part of the development in the construction businesses fragment has happened in third world and second world countries. So many times, the turnover realized for the machinery and hardware for construction has surpassed the sales target. The volume of sales has additionally expanded in advanced nations driven by the requirement for replacing or upgrading the existing equipment and machinery for construction and development. CAT’s equipment and machinery for construction have basically been utilized for the most part in the U.S., Brazil, and Asia since the end of the global financial crunch in the year 2008.

Asset IndustriesThe asset fragment for The Company essentially bolsters clients utilizing their equipment as a part of the application in mining and quarry. This fragment likewise serves customers who deal with ranger service, burrowing, and paving. Caterpillar Company has been acquiring some of its competitors, including Bucyrus International Company. This is for it to be the leader in the market. CAT now boasts of the status of owning the widest line of mining hardware and gear of than any organization all around. CAT is putting intensely in its mining apparatus business in the U.S. also, Asia. CAT’s biggest worldwide rival in mining apparatus is Joy Global; however, CAT has various different contenders with other hardware sorts in their Asset Industry portion. Joy Global has a limited line of products as compared to CAT.
Power Industries
CAT’s Power Industries portion serves clients utilizing responding engines, motors and allied sectors for commercial enterprises providing electric power, petroleum applications, nautical applications and, in addition, rail‐related organizations. A significant part of the development in this fragment, as in CAT’s different portions, is happening in third world and second world nations. CAT’s fundamental rivals all around in this portion incorporate GE Energy base, Siemens Energy, and Wartsila Corp.

Monetary Products
The standard objective of CAT Financial is to give retail and wholesale clients financing choices to buy CAT items. CAT uses its financing role to drive interest for its items everywhere throughout the world, yet particularly in third world and second world nations where financial resources to make such expensive buys are quite difficult to access. Notwithstanding expanding the volume of sales for CAT items, CAT Financial likewise generates financial revenue in terms of the amount of interest receivable. CAT Financials real rivals incorporate business banks and other monetary foundations.
Financial Analysis
Both CAT administration and expert agreement conjecture positive GDP development around the globe through 2016. Investigator accord estimates likewise anticipate gradually declining unemployment around the globe through 2016. The U.S. real estate market has been seeing development in construction, stock has been tight, and private home costs have encountered their seventh straight month of appreciation. The recent boom and bust in the real estate market have surprised many analysts as its timing is just after the recent global financial crunch in 2008. So far, the global financial recovery has been promoted principally by fiscal arrangement and venture.
On the off chance that the U.S. real estate market proceeds on its present recuperation track, this will probably help monetary development in the U.S, enabling the creation of employment opportunities, expanding household spending, and bolstering purchase certainty. As the main focus for the central banks for different countries across the world purpose to avert deflation, support inflation, give liquidity, and by and large, counteract another global financial crisis, they have been bringing extremely forceful activities with their fiscal and monetary strategy to accomplish these objectives. On account of this, I trust we might encounter higher than typical levels of inflation in the near future, adding to nominal development, making it worthwhile to put resources into physical resources that have real quality, whether that be real estate corporations that deliver physical items, for example, CAT. Due to this blend of forceful financial arrangements and the late financial recuperation in the U.S. real estate market, this financial cycle will probably extend longer than the notable standards.
Developing markets are liable to keep outpacing third world and second world nations in monetary development, consequently developing the worldwide white collar class (especially in China), which will bring about more prominent interest for foundation improvement and customer products; both drivers for normal asset utilization which ought to prompt an expansion in mining action over the long‐term.
Finally, the expansion in local energy generation bringing about lower household energy costs and higher energy fares will keep on supporting domestic production, pull in foreign production to the U.S., and generally reinforce the U.S. economy. Considering the greater part of this, I trust we will keep on seeing moderate but positive U.S. and worldwide financial development throughout the following couple of years. In like manner, I trust this current monetary cycle will be extended longer than noteworthy standards. Along these lines past cycles are presumably not a decent pointer of the present cycle. This can be interpreted into CAT additionally encountering moderate development for the following couple of years as CAT’s stock value moves in line with the U.S. and worldwide economies and the elements recorded previously.
Financial Ratio Analysis
Financial analysis is a very significant aspect of case study analysis. In any case, financial analysis reflects on the performance of the company in relation to its strategies and structure (Gorsky 66). The financial ratios can effectively shoe the true financial position of any company. The financial ratios are classified into five main categories, namely: profitability tests, Liquidity tests, Activities tests, Leverage ratios, and Solvency tests (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 1).
Profitability Ratios
These ratios show whether the company is making progress or going down. Profitability ratios include Net Profit Margin, Return on Total Assets (ROA) and Return on Stakeholders Equity (ROE). Profit margin= Net Income/Net Sales Revenue. On the other hand, Return on Total Assets (ROA) = Net Profit/ Total Assets, whereas Return of Stakeholders Equity (ROE) = Net Profit/Stakeholders Equity (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 2).
Net Profit Margin (NPM)
Net profit margin shows the company’s level of profitability (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 2). Net profit margin for CAT experienced ups and downs between 2010 and 2014 with the highest in 2013 and the lowest in 2014 of 0.179% and 0.134% respectively. The poor performance in 2014 is linked to increased equity multiplier and low net income earned by every pound of net sales.
Profit margin= Net Income/Net Sales Revenue
Actual Calculation= Net Earnings Attributable to CAT/ Net Sales
Table 1. Net Profit Margin
Return on Total Assets
Return on Assets ratio of any financial institution like CAT shows how proficient assets are used to generate returns. In most cases, constituents of company’s Return on Assets ratio are net interest margin, net non-interest margin, and unique transaction. When these constituents are added together they result in ROA of a company. Such a breakdown of the constituents of a company’s ROA can be extremely useful in clarifying a number of latest changes that company have encountered in a specific money-related position (Shams 18). Under normal circumstances, Return on Assets= Net Income/ Average Total Assets. Actual calculations= Net Earnings/ (Beginning + Closing Assets). The table below highlights CAT’s Return on Assets ratios with its breakdown.
Table 2. CAT’s ROA
The Return on Asset ratio for CAT also experienced ups and downs between 2010 and 2014 with the highest in 2011 and the lowest in 2014 of 0.178% and 0.149% in that order. The increase of ROA in 2011 is attributed to the growth of net interest margin, which increased by 0.176 percent. The net non-interest margin was the highest in 2010 at 0.009 percent.
Return on Equity
The ratio computes the earning from every unit of equity. It is more reliable than earnings per share when comparing the performance of different companies (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 2). ROE is a ratio that determines a company’s success by disclosing the volume of returns it generates out of the money invested by the shareholders. The figures are given in percentage. Return on equity is determined using the following components, namely: level of asset use, net profit margin, and equity multipliers. Each constituent acts as an indicator of various elements of the CAT’s operations.
Table 3. CAT’s ROE
Table shows the three components of ROE. When the three ratios decrease, ROE also decreases. ROE is the product of the level of asset use, net profit margin, and equity multiplier. The ROE for CAT between 2010 and 2014 was at the peak in 2013 (0.125%) and at the bottom in 2014 (0. 076%). The equity multiplier was the highest in 2010 and lowest in 2014, which is sound for the business. The equity multiplier reflects on how an organization is using borrowed funds to finance assets. This ratio shows CAT’s overall assets per unit of shareholder’s equity. A higher equity multiplier signifies higher leverage, which implies that the company is over depending on external borrowing to finance its assets. The performance of CAT was outstanding in 2013 when the NPM was the highest at 0.179 percent and the equity multiplier was considerably small at 15.532 percent. However, in 2014, both equity multiplier and NPM went down at 14.472 percent and 0.134 percent respectively.
Earnings per Share
Earnings per Share = Net Income/Average Number of Common Stock Outstanding
Table 4. Earnings per Share
This is the monetary value of returns for every share of an organization’s common stock. Earnings per share of CAT were at the peak in 2011 and lowest in 2014 at £ 0.57 and £ 0.42 in that order. The overall average value for the five-year period was £ 0.54, which is economically sound. However, earnings per share of CAT keep on fluctuating, hence not stable.
Earnings Spread
This ratio measures the company’s earning efficiency (Shams 33). It is calculated using the following formula:
Earnings Spread= (Overall Interest Income/Overall Earning Resources)-(Overall Interest Cost/Overall Interest Liabilities).
Table 5. Earnings Spread
The company’s earning spread was positive for the five-year period, which is fiscally acceptable. However, earnings spread has not grown up to date. Instead, it has been decreasing since 2012.
Liquidity Test
These ratios measure the ability of the company to meet its short-term obligations. Liquidity ratios include Current ratio and Quick ratio (Shams 34).
Current Ratio
Current ratio=Current assets/Current liabilities and it should be more than one. However, high current ratio, particularly the current ratio larger than 2 may mean the company is using its resources unproductively.
Table 6. Current Ratio
The current ratios of CAT are above 1.0 in the five-year period, which means the company is able to pay off the current debt. In other words, the company can meet short-term obligations without borrowing. This is good financially. The ratio keeps on increasing showing that the company is improving.
Quick Ratio (Acid Test)
Quick Ratio= Quick Asset/ Current Asset
Actual Calculations= (Cash Equivalent Investment Securities+ Account Receivable)/ Total Current Liabilities.
Table 7. Quick Ratio
The quick ratio confirms a solid level of CAT liquidity. It is a more reliable ratio than current ratio as it considers the quick asset and excludes stock, which may not be converted to cash. The low ratio shows the company is not in a good position. Still, the ratio is increasing, which means the company is increasingly growing.
Leverage Ratios
These ratios show the amounts of debt or equity used to finance the business. Businesses are highly leveraged if they use more borrowings than equity. The balance between the two is normally referred to as the capital structure. The main leverage ratios include Debt to Asset ratio and Debt to Equity ratio.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Debt-to-Equity Ratio= Total Liabilities/ Stakeholders’ Equity
Actual Calculations= Total Liabilities/ Total Shareholders’ Equity
Table 8. Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Based on the Debt-to-Equity ratio, for each dollar of stockholders’ equity, the company has a greater worth of liabilities. A high ratio suggests that CAT depends heavily on funds provided by creditors, which puts the business at a high risk. However, the company is reducing its rate of borrowing.
Debt-to-Asset Ratio
Debt to Asset Ratio= Total Debt/Total Assets
Table 9. Debt-to-Asset Ratio
The table above shows a decreasing trend of leverage, which is good for the business. The company had a high leverage in 2013. It may be due to long and short term borrowing for some new product inventions. From 2010 to 2014, the demand for debt had decreased considerably.
Capacity Ratio
Capacity ratio= Net Loan/Total Assets. Since loans and leases are usually regarded as some of the most illiquid assets that the company can hold on, capacity ratio acts as a negative liquid indicator.
Table 9. Capacity Ratio
The company has been incredibly steady at maintaining their capacity beneath 50%. Given the size of CAT, this is considered fiscally sound. Nevertheless, the company should invest more in instruments that can be liquidated very fast.

Net Interest Margin
Net interest margin is the ratio that assesses how efficient a company manages its investment decision with respect to debt condition.
Table 10. Net Interest Margin
CAT enjoyed a positive interest margin from 2010 to 2014. However, the margin has been decreasing steadily. For this reason, necessary measures should be put in place to reverse the situation.
Interest-Sensitive Gap
Table 11. Interest-Sensitive Gap
The interest receptive liabilities have always exceeded interest receptive assets in the company for the last decade. Interest receptive liabilities were the highest in 2013 and they have been on a progressive trend since 2010 (except 2014). This puts the company at a very high risk in case of considerable change in interest rate.
Relative Interest-Sensitive Gap
Relative Interest-Sensitive Gap is the ratio of the interest sensitive gap and the size of the company. A relative interest-sensitive gap more than zero describes an asset-sensitive company, whereas a relative interest-sensitive gap means the company is liability-sensitive.
Table 12. Relative Interest-Sensitive Gap
Since the figures above are below zero, it means that the company is liability sensitive. Nonetheless, the figures have never slumped beyond -0.05 and it has been stable since 2012.
Interest Sensitivity Ratio (ISR)
Interest-sensitive ratio is the difference between interest sensitive assets and interest sensitive liability. An interest-sensitive ratio of less than 1 describes a liability sensitive company, whereas an interest sensitive ratio of more than one describes an asset-sensitive company. Given the fact that all the ISR values from 2010 to 2014 are below one, it means that CAT is a liability-sensitive company.
Table 13. Interest-Sensitive Ratio
Cash Position Indicator
This ratio measures the company’s efficiency in handling immediate cash needs. It is measured by dividing cash and deposits from depository institutions. A higher cash position indicator means the company is in a stronger position to take care of immediate cash needs.
Table 14. Cash Position Indicator
CAT maintained an average of 75% cash position from 2010 to 2014, which is decent for a company. This means the company is very capable of handling immediate cash needs. Though in 2012, the company had the lowest cash position in the five-year period.
Liquid Security Indicator
This ratio measures the capability of a company to hold on to marketable securities given its asset portfolio. The company is considered to be highly liquid when it has a higher liquidity security indicator. It is calculated using the following formula:
Liquid Securities Indicator=state securities/total assets
Table 15. Liquid Security Indicator
The company’s liquid security indicator is very small. It is almost nonexistent. This implies that CAT does not depend on marketable securities for immediate cash needs.
Tier 1 Core Capital
A company’s capital base is normally categorized into three for a regulatory purpose, namely: tier 1, tier 2 and tier. This form of classification depends on the level of perpetuity and loss absorbency. The core tier 1 category constitutes of stockholder’s equity and non-controlling interest. For the purpose of capital sufficiency, the book values of immaterial assets are subtracted from this category and additional amendments are made for items that are included in stockholder’s equity.
Table 16. Tier 1 Core Capital
The tier 1 core capital entails common stock and excesses, ploughed-back earnings, aggregate stock, marginal interest and immaterial assets. This ratio basically describes the company’s financial strength. From 2010 to 2014, the ratio has increased by £1636562.million. This makes CAT be ranked among the leading financial institutions globally.
Tier 2 Supplementary Capital
Tier 2 Capital constitutes of secondary loans, associated non-controlling interest, permitted combined risk allowances and unrealized returns originating from a fair appraisal of stocks. It also comprises of reserves arising from the re-evaluation of assets.
Table 17. Tier 2 Supplementary Capital
The company’s tier 2 capital has been decreasing since 2010. However, it is still strong at £20135 million. The decline is attributed to the company’s emphasize on tier 1 capital.
Internal Capital Growth Rate
This measures the rate at which the company allows assets in order to avert the decline in capital to asset ratio. Internal capital growth rate is calculated by the following formula:
Internal Capital Growth Rate= Retained Earnings/ Net Income after Taxes
Table 18. Internal Capital Growth Rate
The company’s Internal Capital Growth Rate went down by 0.02 percent from 2010. However, the rate has been steady since 2010. Nonetheless, the company is still vulnerable at 0.62 percent.
Activity Ratios
These ratios show how their company is overseeing the use of its assets.
Return on Assets
Return on Assets= Net Profit/ Total Assets
Table 19. Return on Assets
From 2010 to 2014, the return on assets was on a rising trend. It may be due to several reasons. Firstly, the sales increased and expenses reduced. Secondly, the asset turnover increased. This may also be attributed to efficiency in revenue collection and inventory management. However, in 2013 in slumped a little bit.
Industrials Sector Analysis
The industrial segment is to a great extent composed of stocks that identify with the creation and appropriation of products utilized as a part of construction and manufacturing. Organizations in the industrial segment are included with (however not restricted to) aviation and defense, hardware, instruments, lumber generation, development, metal manufacture, and dissemination and transport. CAT lives in the machinery and equipment business.
Execution in the industrial segment is to a great extent driven by supply and interest for building development and manufactured machinery. In that capacity, the industrial and allied sector nearly tracks the U.S. and worldwide economies. As clarified in the Financial Analysis area above, I trust we will keep on encountering monetary development, in the middle of slow development. In this manner, the industrial segment ought to be tolerably well throughout the following 2‐3 years. The industrial sector’s aggregate business sector cap is $1.32 Trillion. With such a differing exhibit of commercial enterprises inside of the sector, there is a lot of adaptability in making a venture technique relying upon where we are in the financial cycle. Accordingly, mechanical organizations have an extensive variety of betas and execution designs in respect to monetary cycles (Besser 28).
Taking into account verifiable information, the industrials segment ought to be mid‐cycle, drawing closer to late cycle; in any case, as said above, as we recover from a profound worldwide financial crunch, with central banks being exceptionally forceful with money related strategy, this cycle will probably extend longer than the noteworthy standard. Rather, I trust we are as yet drawing nearer to mid‐cycle.
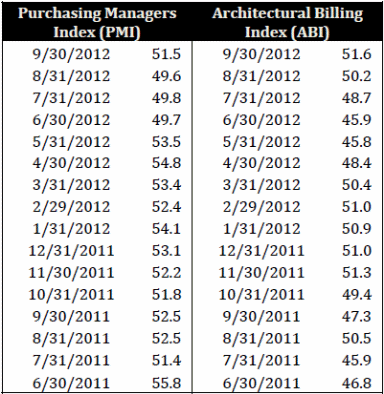
Two driving markers of industrial segment execution, the Architectural Billing Index (ABI), and the Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) are both slanting positively. These are both great markers for the heading of CAT’s execution as CAT is an apparatus producer with a vast piece of its business subject to the development business. The ABI is the main marker of development movement. Any score more than 50 demonstrate an expansion in engineering billings (Chernow 100).
Development movement commonly slacks the ABI by 9‐12 months. For the most recent 18 months, the ABI has been drifting quite recently above or just underneath 50 as demonstrated in the ABI outline (Table 10). With the two late scores simply above 50, this demonstrates positive however moderate development in the coming years. The PMI is a pointer of the soundness of the assembling sector. It depends on new requests, stock levels, generation, supplier conveyances, and the livelihood environment (Cho and Pucik 562). Like the ABI, any score more than 50 demonstrates an extension of the assembling part over the former month.
Performance of the Industrial Sector
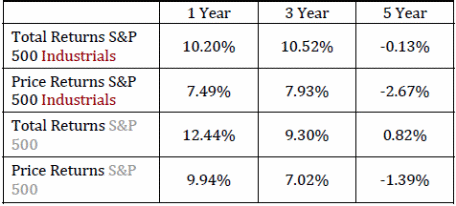
The returns from the industrials segment have slacked the S&P 500 in total over a 5‐year period and also throughout the previous 1 year; in any case, for as long as 3‐year period, the industrial segment has surpassed the S&P 500. The industrial segment has additionally failed to meet the expectations of the S&P 500 year-to‐date; be that as it may, as of late with the pull‐back in worldwide economies, the industrials division has lost not exactly the S&P 500; a moderately positive sign of financial specialist supposition towards the sector (CIM 2).
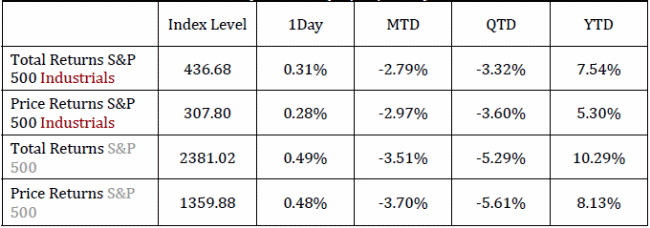
In total terms, industrial sector products are exchanging underneath their 10‐year verifiable median. As the recent financial crunch is valued into the median products and I trust we have not yet hit the crest in this cycle, the industrials segment has all the earmarks of being underestimated. With respect to the S&P 500, the industrials segment products are exchanging marginally beneath their 10‐year medians. With respect to the S&P 500, the industrials segment seems all the more genuinely esteemed.
Organization Analysis
Accumulation toward the end of 2011, 2010, and 2009 was around $30 billion, $19 billion and $10 billion respectively. The backlog starting the third quarter 2012 is at $23 billion and reducing. With the overall diminishing in the mining venture and the start of the construction season a couple of months off, accumulation will remain moderately low in the near‐term (Coch and John 522).
Company’s Strategy
The company is a recurrent organization; however, the administration has been endeavoring to hose cyclicality through item and geographic enhancement. Early cycle action ordinarily happens in private construction; however, with the late recuperation of the real estate, this could be characteristic of development in the close term for CAT. Government expenditure on infrastructure and roads development likewise normally happens right on time in the cycle; however, with the U.S. surpassing the $105 billion ‘highway and infrastructure’ bill in July 2012, and China reporting a $158 billion stimulus package in September, 2012, this could likewise give development chances to CAT throughout the following couple of years. The mining movement ordinarily happens in the mid‐late cycle and is required to decrease in the near future before it starts to increase (Simpson 4).
In respect to monetary movement and CAT business action, if we somehow happened to investigate this cycle beginning right now, it seems to impersonate the early part of a cycle recovering from the global financial crisis. CAT has a tendency of acquiring its biggest rivals in the market space, including Bucyrus Company. This, combined with what might be a developed financial cycle could make this cycle for CAT an extremely one of a kind one, and hard to anticipate in view of past cycles. The assets industry’s incomes expanded by $7.2 billion from 2010 to 2011 as a result of the acquisition of Bucyrus, a 16.4% expansion in general incomes from this procurement alone (Shams 21).
A lot of CAT’s worldwide development happens through acquisitions and in addition through natural development. The essential drivers of CAT’s natural development and securing targets are through construction apparatus, mining hardware, and related reseller’s market administrations. All through the world, CAT offers its items to CAT dealerships who thus offer to development contractual workers and hardware and gear rental organizations. CAT keeps fabricating its distribution system all through the world, frequently utilizing the current dealership systems acquired through gained organizations, and deliberately finding merchants in the right places. This is a continuous procedure and one which is critical to CAT’s secondary selling service business. Accordingly, CAT incomes are additionally determined by its high returns on post-retail benefits which give support to hardware through upkeep, spare parts, and specialized support (Regani 24).
External Analysis
Legal/Political
Right now, The company focuses on a fairly wide client section, and can be regarded as lacking concentration because of the premium cost of its various offers, whilst advancing itself as less expensive than the others competitors’. The brand is right now focusing on clients who might ordinarily shop at The Company. This inexorably prompts a certain level of perplexity as to what The Company remains for, and an integrated marketing communication crusade would need to focus on this. It could hence be presumed that the centered retailer now targets high profile clients; what’s more, needs to narrow this down to all the other clients in light of a legitimate concern for better characterizing its market suggestion, hence, expanding its deals in the long haul (Neiderhauser 8).
Their principle leeway is that they work physical stores, which clients are acquainted with and are thusly more prone to trust these brands’ administration. On the other hand, this test can be overwhelmed by essentially dodging direct rivalry with these retailers. Joy Global is usually connected with lower costs and is accordingly pulling in an alternate sort of clients. In the meantime, The Company, having been connected with many clients, because of their long haul association, is more inclined to draw in the competitors’ clients, instead of simply looking for ones who rely on discounts. The test that The Company is confronted with is persuading potential clients that it remains for high caliber at a premium value, and is pretty much as solid as any physical store, however, with a more proficient online business model. This can be accomplished by utilizing a painstakingly organized IMC campaigns directed to probable clients. Cautious knowledge into the objective client profile would help in distinguishing key customer conduct and inclinations, which need to be tended to by The Company (Morgan 57).
International
Altogether, for the company newly incorporated campaign to be effective in accomplishing the set destinations, it needs to be completely adjusted regarding the methods and the execution. The mechanical industry can possibly make a perfect association between the brand and the purchaser, however that would just be conceivable if the center procedure supporting the campaign is completely actualized all through the entire organization, with a specific end goal to accomplish full coordination of exercises and operations working towards the same objective aimed at the business achievement. The company’s two primary marking communications objectives are to convey a premium picture and to stress the psychosocial advantages of its dedication plan, and the retailer by and large. These two objectives, in spite of being independently recognized, can be accomplished all the while, through a painstakingly executed incorporated campaign, which is high quality, while connecting with the customers on an enthusiastic level (Miller 8).
Presently, The company’s business is composed around the thought of providing valuable services to the clients. This is reliable with the marketing campaigns which have not been exceptionally effective previously, as they have produced perplexity and suspicion among customers. That is the reason why another focal thought needs to be produced, which will bolster the vital change of brand picture and will assume a focal part in the newly incorporated marketing crusade. The new thought and trademark will characterize the adjustments in the key course for the business, and will help in wiping out perplexity about the brand later on. The newly coordinated advertising campaign will be implemented under the thought of the time, instead of expense, sparing the point of interest of the business and will go for setting up a passionate association with the objective buyers, who are in the upper middle class. These buyers are associated with a substantial work timetable and minimal extra time to go through with their friends and family (Merrikh 21).
The new motto of the company will be updated on the company’s website. Also, the motto will be printed on the company’s official vehicles and on all direct correspondence with buyers. The motto will bolster every promoting communication to help in accomplishing a predictable brand picture over all channels. As the US economy is gradually recouping and turning out to be steadier, purchasers and the upper middle class specifically are less inclined to be keen on value reductions and more inclined to contemplate premium, yet basic and effective ordinary answers for their absence of extra time. That is the reason why the company’s modified image picture is prone to engage the key market segment, and make a state of separation in a jumbled business (Lundberg 17).
Push marketing involves advertising and circulation networks and is gone for persuading outsiders to advance the organization advertising. Push techniques incorporate exchange shows, displays, engaging suppliers, and making a production network to encourage circulation. Such a methodology is, for the most part, treasured to producers hoping to construct a conveyance system for their items. On account of the company, it being a mechanical company as opposed to an organization offering a solitary item, it does not fundamentally need to actualize a push procedure of marketing in the customary sense. Due to the fact that push methodologies are principally concerned with pushing a solitary item through different circulation channels to the buyer, such methodologies are not significant to The company as the organization is in control of its own appropriation and is indeed more inclined to be an objective of push procedures, instead of a dynamic implementer of such. Push promoting ordinarily includes building associations with wholesalers to backing the vicinity of an item available in-store or on the web. In any case, as a merchant itself, the company is the last purpose of contact in the middle of the brand and the customer and is hence in charge of its own business identity (Lamb, Hair and McDaniel 41).
With the goal for the company to be a favored wholesaler for premium items, it needs to have an interest in such items by shoppers. By making the machinery company more obvious to customers, and a favored shopping destination for vehicles, a pull marketing technique would help build interest for the company’s sourced items and would, therefore, make free suppliers more intrigued by building an association with the company. It is, thus, of basic significance for the company to execute a pull marketing method keeping in mind the end goal to continue adding to the business, on both the supply and the demand side. The pull marketing showcasing is the demonstration of executing promoting and special methods that are intended to tempt the prospect to purchase your item or administration (Keen 28). Pull marketing showcasing is coordinated at buyers, as opposed to promoting or conveyance channels, welcoming them to look for the item or the benefit themselves through alluring promoting and/or persuasive exercises.
The company can take advantage unequivocally from the usage of different pull marketing procedures, thus, exercises would elevate the company to the objective buyer and make it more unmistakable, which could conceivably prompt client securing and maintenance. As of now, the company is expanding its client base at a relentless level; even though it needs a correspondence push so as to plant it in the purchaser minds for the long haul. Numerous internet shopping-favoring shoppers might not have offered thought to the company, and an in number coordinated promoting interchanges campaign in light of the drawn procedures (Katz 45). This would assume an indispensable part in expanding levels of thought and transformation. The previously stated examination of the importance of push marketing and pull marketing procedures to the company’s new campaign prompts the determination that a pull marketing procedure would be most fitting for the automobile company for the motivation behind re-marking and client procurement. A pull marketing method can be executed by different components, for example, promoting in distinctive structures, public relations, direct advertising, advanced promoting, and that’s just the beginning (Kathleen 502).
Economics and Technology
Brand Target
The company’s current low-cost offer loans joined with an interest rate valued conveyance administration produces disarray among customers, which brings about the view of untrustworthiness and absence of reliability. Concentrating on a limited target business is the initial phase of creating a brand, which addresses better-characterized client needs. Right now, the company is endeavoring to achieve customers of a vast age reach and social evaluation classification. This is mostly because of its endeavor at a value war with enormous names like Joy Global. This may bring about wealthier high-class clients to be put off and to scrutinize the company’s amazing administration claims (Kalb 2).
All together for the retailer to pull in and hold high profile clients, it needs to move the concentration far from its value reductions, and towards the premium nature of its administration. This is not another system for the company, yet in any case, it has not been investigated to its maximum capacity. The initial phase of understanding this system would be to characterize the objective market that the integrated marketing communication campaign will address. Right now, the company just covers 70% of the available market. Then again, the company is especially solid in California, where the quantity of individuals with a higher economic wellbeing, is more ideal for the business. Along these lines, it would be reasonable for an integrated marketing communication campaign to be focused on California-based people of the higher social class. So as to measure the objective business for The company’s new integrated marketing communications campaign, information from the most recent survey done in 2011 by the Office for National Statistics to establish the total number of the population has been separated and broke down. The total population of the Californian territory proposes that roughly 3.5 million individuals fit in with the high-profile social class. This represents about 26.5% of the aggregate populace of the city (Jones 1).
Customer Profile
The normal client that the company is presently focusing on is hard to characterize because of the company’s fairly unfocused methodology. Nonetheless, The company’s present situating may be pulling in youthful, and also more seasoned, prosperous clients driving occupied ways of life. A recently dispatched integrated marketing communications crusade ought to focus on a very much characterized sought client profile with a specific end goal to accomplish better concentration and convey a clearer message (James 665). Utilizing the normal competitors’ customer profile as a perspective, a The company’s purchaser profile can be created, with the accompanying qualities: They would lean toward great service and convenient conveyances – planned at helpful times through the time period as opposed to driving online requests, where helpful time spaces are less inclined to be accessible (Hill and Thomas 140).
Demographics
The acquiring propensity for a customer is attached to his essence of the item, impression of the item, and his way of life. The purchasing conduct of the purchaser is impacted by various inside and outer variables; this makes it an unpredictable marvel by and large. The buying propensity for the purchaser is separated into five stages as stipulated below:
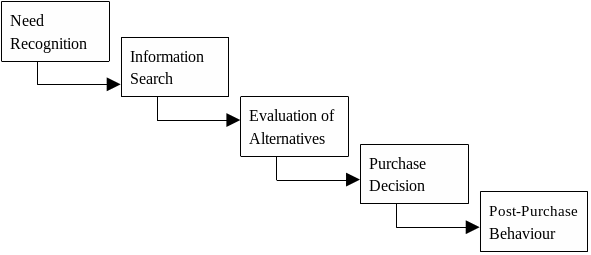
The above graph outlines the stages included in the buying propensities for the consumers. It admires the way that the consumers settle on choices in a five stage model.
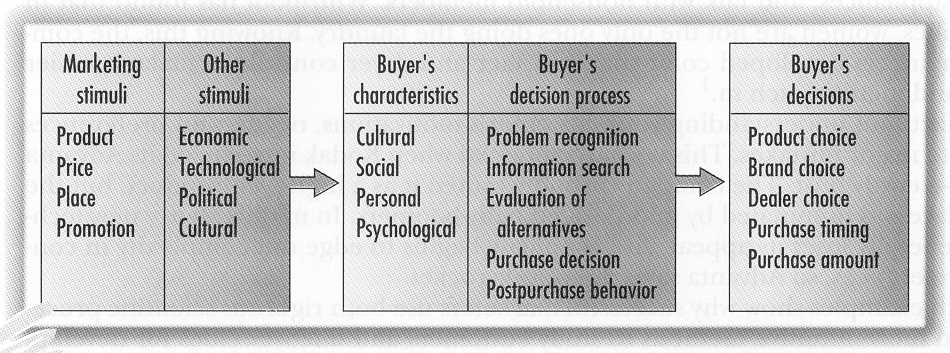
Relationship Between Nature of the Brand and Consumers’ Decision
It is critical for any business enterprise to have a reasonable picture of what the client anticipates from them. The consumers’ decision on the nature of a brand is altogether different from their decisions concerning picking merchandise or items. This is on account of the brands are considerably more not quite the same as wares. Merchandise are unmistakable and can be touched while brands are not substantial; merchandise are perishable, the brand is not, and so. In this way, these difficulties are faced by the clients when looking at brands and items (Guth and Ian 318).
Brands cannot be felt, or touched, or tasted, or seen, unlike products or items. Clients are known to settle on decisions, taking into account both unmistakable and impalpable components. Measurements like the nature of the nourishment or administration, and the cost of the item in connection with the administration are a few cases of elusive variables that impact the choice making methodology of the consumers. The company ordinarily selects to focus on substantial components that are gone for impacting the clients’ choice making. The substantial measurements that they embrace are quality of service, enhanced offices, and so forth.
A brand differs from one supplier to another, furthermore from a client to another. Because of this variability, consumers have a tough undertaking to settle on choices to pick one service provider over another. The company’s proprietors likewise have a tough errand of keeping up an unfaltering level of operation regarding the nature of the sustenance or administration. For instance, if an organization’s employee gets a complaint from a customer, the complaint will influence him/her to provide low-quality services (Grusky 64).
A company’s proprietor will gauge the efficiency of the brand only after he/she has sold the service. On the other hand, a customer will gauge the efficiency of the brand only after he/she has bought it. The level of professionalism of the company’s employees will give the customers an insight in regards to the brand quality. In the same context, the feedback or responses received from customers will give the company’s proprietors a perception in regards to the customers’ satisfaction regarding the company’s brand (Goldman and Papson 201).
Consumers can buy physical items at any given time because of the way that they can be put away and sold whenever a consumer gets some information about their accessibility. Then again, it is impractical to store a brand. At the point when a brand is not sold, it means the way that the brand does not exist in any case. One way of illustrating this is to take, for instance, a customer who has made a reservation and fails to show up. The restaurant will fail to serve other customers when the restaurant becomes full because they are anticipating the arrival of the customer who reserved the table. Due to the fact that the nature of the customers is uncertain, the restaurant proprietors find it challenging to find the balance between the supply and demand for their services (Drucker 21).
Competitor Analysis (Porter Five Forces)
Threats of New Entry
- High costs that are involved in setting up and producing the machinery and equipment system imply that CAT’s experiences low threats of new entrants,
- The market target segment for CAT’s customers encompasses people who are looking for complex products, and
- New entrants lack reputation, and, hence, they suffer from incapacity to outdo those with already well-established customer loyalties.
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power
- CAT experiences high bargaining power from its suppliers since it does not purchase commodity type of goods,
- Relies on suppliers from different places and in different areas of specialization to ensure sustained manufacturing processes,
- More than 33 suppliers did business with CAT to facilitate the production of small, medium and large track excavators, and
- CAT’s’ suppliers can set their prices at higher levels without considering the unwillingness of the organization to pay.
Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
- The market demand influences the organization’s market price due to the lower number of competitors who offer products with similar performance, technology, and luxury characteristics,
Buyers’ Bargaining Power
- CAT’s’ buyers have a low bargaining power
- CAT positions its brands as high-performance products.
- High-cost technology that is involved in its production drives the prices of CAT’s products higher compared to other machinery which has an equal carriage capacity.
Threats of Substitute Products/Services
- Threats posed by substitute products are low,
- The company is the only construction and mining machinery maker that specializes in the production of zero green gas emission machines, and, therefore, eco-friendly customers have CAT’s products and services as the only option
Summary of Porter Five Forces
Industry environment is a risk to an organization in terms of threats of new entrants, supplier and buyer bargaining powers, industry rivalry, and threats posed by substitutes. Tesla experiences high bargaining power from its competitors, as it does not purchase commodity type of goods. It depends on suppliers who are derived from different places and in different areas of specialization to ensure sustained manufacturing processes. More than 33 suppliers did business with CAT to facilitate the production of construction and mining machinery. This move suggests that in the case of failure of the organization to pay a specific amount of money as demanded by a given supplier, the entire production process becomes halted. This situation disadvantages CAT since its suppliers can set their prices at higher levels without considering the unwillingness of the organization to pay.
Buyers possess a low bargaining power. CAT positions its brand as a luxurious and high-performance product. High-cost technology that is involved in its production drives the prices of the products higher compared to the rivals. The market demand influences the organization’s market price due to the lower number of competitors who offer products with similar performance, technology, and luxury characteristics. High costs that are involved in setting up a construction and mining machinery production system imply that CAT experiences low threats of new entrants. The demanding technology in the production makes capital requirements prohibitive to small-scale automakers. The market target segment for CAT’s customers encompasses people who are looking for luxurious products. Such people consider quality and performance essential attributes of the product before arriving at purchasing decisions. This observation highlights the significance of good reputation as a major component in branding luxury products. New entrants lack reputation. Hence, they suffer from incapacity to outdo those with already well-established customer loyalties.
While the industry loyalty for CAT is high, the threats posed by substitute products are low. CAT constitutes the only automobile maker that specializes in the production of zero-green gas emission machinery and equipment. This case implies that eco-friendly customers have CAT’s products and machinery as the only option. However, even though CAT is the only organization that is currently producing eco-friendly machines, several other well-established companies are focusing their attention on research and designs of eco-friendly machines in the effort to have a share of the market in the future as the trend in the adoption of the model continues to pick.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Has a strong brand that is built around the perception of high performance, reliability, and luxury,
- It has devoted customers, and
- It demonstrates an uncompromising attitude towards its future success in terms of creativity and innovation.
Weaknesses
It depends on external suppliers, an unknown brand, and a dynamic new technology for its operations,
It eliminates the use of fossil fuels in the propulsion of automobiles, and
The new technology poses the challenge of uncertainties associated with negative preconceptions about the performance of the electric vehicle in comparison with the oil or gas engines.
Opportunities
- The existing external environment, which can make the organization improve its performance,
- The increasing number of people who are becoming cautious over degradation of the natural environment,
- Unstoppable growth boosted by constant construction opportunities, and
- It can break free any negative notions and preconceptions about machinery and mining products.
Threats
- Incumbent machinery and equipment makers,
- The twin threat of introducing a new company and a new product on the market, and
- Dependence of info-structure.
For the viability of marketing plans, SWOT description for a new or existing brand is necessary with the aim of determining whether an organization has the capacity to place the product on the market. This approach calls for the strategic planning approach for evaluating the strengths, restrictions, prospects, and threats that a business establishment encounters. The company has managed to establish a strong brand that is built around the perception of high performance, reliability, and luxury. The model demonstrates how technology can be deployed in the development of alternative products with high performance and high safety features. The company also possesses incredibly devoted customers. It also has an uncompromising attitude towards its future success in terms of creativity and innovation.
Although the company has strengths that can favor the success of the products, it has some weaknesses. It depends on external suppliers, an unknown brand, and a dynamic new technology for its operations. Apart from the brand being new in the market, assuming it is not well known by all potential customers, the new technology poses the challenge of uncertainties associated with negative preconceptions about the performance of the electric vehicle in comparison with the oil or gas engines (Dent and Goldberg 38).
Opportunities include the existing external environment, which while utilized well, can help an organization to improve its performance. One of the major opportunities for success of the products encompasses the increasing number of people who are becoming cautious over degradation of the natural environment due to high carbon emissions that are associated with the rising number of machinery. With already developed superior features, the company’s products have the opportunity for unstoppable growth when companies or countries venture into the construction business (Crossan and Dusya 226).
Strategic plan
Overview of the Selected Brand
The vision of the company is to make a situation in which all individuals’ fundamental needs are satisfied in a naturally practical way and an organization that enhances the nature of the environment and the surrounding community. The mission of the company is to empower financial development through infrastructure and energy improvement and to give solutions that bolster groups and protect the planet. The strategy is to give workplaces, items, administrations and solutions that make beneficial and effective utilization of assets as we endeavor to accomplish the vision. The company applies development and innovation to enhance the manageability execution of Caterpillar’s items, services, arrangements, and operations. The company holds that sustainable advancement is improved by creating frameworks that boost life cycle advantages while additionally minimizing the financial, social and ecological expenses of possession, as reflected in the manageability standards.
Upon considering that CAT is the only organization that produces construction and mining machinery. It has good opportunities for building its reputation to establish significant customer loyalties. This success depends on the ability of the organization to establish effective marketing communication strategies. Unfortunately, CAT had no budget for its marketing, although it had attained revenue growth of above 75 percent by 2010-2011 fiscal year and 102 percent in the 2011-2012 fiscal year amounting to $ 413m. Incorporating brand communication strategies can help in pushing the products into the market.
However, without specific marketing communication budget, CAT attempts to brand itself as ‘Apple automaker’ akin its use of technology in. Upon considering that it is a new brand, it needs building a strong brand identity. Taking the benchmark of Apple Company is perhaps an important starting point. However, the creation of consumer awareness about the brand remains significant for increased performance. This strategy needs to be accompanied by the production of more innovative products. Through budgetary allocations to initiate brand communication over new and traditional media, CAT can increase its brand identity across the globe. Perhaps, this step is the biggest strategic marketing opportunity available to the organization (Correa and Nick 61).
Strategic Marketing Opportunities
In its marketing initiatives, CAT needs to consider introducing creative strategies in order to manage customer relationships. Keeping potential clients up to date with information is of important methods of maintaining positive relationships with customers.CAT needs to update its customers constantly with new features for the machines so that they can update their machinery and equipment using the internet. These attempts would be done for the commitment of financial resources in communication. Although the strategy increases the cost of running CAT, it is justifiable because marketers are quick to recognize that the value of the customer asset is the sum of the discounted net contribution margins of the customer over time. The claim here is that attempting to build customer relationships comes at a cost, which CAT must be willing to incur, notwithstanding its past loss experiences (Coetsee 21).
Ensuring that CAT’s’ website is up to date with the information on innovative and technological developments that are aimed at making the construction and mining machinery offer even higher customer experience is critical in the development of the brand image of the organization. Potential customers are likely to buy products from a manufacturer whose information on what is available in-house is easily accessible. This claim suggests that through the commitment of financial resources in online communication, CAT acquires a higher probability to capture the loyalty of both the existing and potential clients to gain competitive advantage (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 1).
Advertising to potential customers encompasses a major milestone towards enhancing the performance of CAT. However, retention of the clients is a function of how well the products satisfy their needs, in this, case luxury and technological innovativeness and performance. This claim underlines the significance of the utility of a product in terms of helping build good customer relationships. Potential clients can also arrive at their decisions to seek products from an organization that engages in online communication based on how the communications personnel handle them and/or how the sales personnel handle them at the physical premises of the organization. In the quest to build positive customer relationships, it is vital for an effort to be made to select people who can represent the interests of the organization in the most pragmatic way (Hill and Thomas 140).
Customers not only buy a product but also pay for the brand image. Brand image is a perception of customers when they see a brand reflected by brand associations in their mind. These associations are multidimensional. They contain a myriad of attitudes or dimensions, which are emotionally instigated in relation to customer perceptions on brand quality and the degree to which the brand satisfies customer needs. In the case of CAT, the brand image can be enhanced using the power of the internet as the main approach for developing and creating awareness of the brand.
Using the internet as the means of creating the brand image of the products implies that it can serve the dual purpose of distribution and communication. Using social networks, websites, and traditional media such as TV and contests among others makes it possible to influence the demand for the construction and mining machinery. Internet aids in helping an organization focus on enabling customers find information about products. Brand image cannot be satisfactorily developed if potential clients are not aware of the existence of an organization that offers products (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 1).
In the effort to create alertness of the existence of an organization, social media is incredibly helpful. Such a strategy for building positive brand image is opposed to traditional approaches of brand communication in which organizations mainly focused on controlling what was said about their products and brands by dominating communication channels with carefully planned messaging. However, in the modern business environment, control of messages is immensely difficult since the ability of customers to access information through online interactions has become incredibly sophisticated. This sophistication entails online communication through B2B (business to customer) platforms. Therefore, CAT needs to deploy the latest developments in web 2.0 applications in enhancing communication to its market segment both cheaply and effectively.
Quantification of Marketing Objectives
The objective of engaging in both traditional media and online communication for the construction and mining machinery is to achieve a sales target of 40,000 units over the 2015-2016 fiscal years. This sales level is achievable upon considering that the company receives more than 1 million people who visit its stalls in 2013, with 35 percent of them testing the machines. This observation suggests that with increased promotion of the product, it is possible to increase the number of people who visit the stall either physically or through an online platform, later making purchasing decisions. CAT can currently produce 50,000 machines at 25% capacity utilization. This observation implies that initiating a marketing communications plan for marketing 45,000 machines and equipment annually is achievable within the range of the available resources. Indeed, increasing production potential can help the organization take the advantage of economies of scale to lower costs, which in turn increase its profitability levels (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 1).
The overall objectives of the marketing communications plan are increasing sales, enhancing CAT’s brand awareness, and/or driving potential consumers to access the organization’s online communication platforms. The sales target of 45,000 units per year is feasible upon consideration of the past sales level of the organization. The previous data indicates that when customers receive their ordered car, the organization acquires 3 more reservations from each customer. In this extent, verbal communication has proved that communication can aid in boosting the sales levels of CAT.
Objectives and the Scope of the Marketing Campaign
The idea of Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) has become an integral process in marketing in the current decade. It alludes to the procedure that advertisers utilize to arrange, create, execute and assess composed, quantifiable, powerful brand correspondence programs over the long run to focus on various segments of people. It is currently broadly accepted that the incorporation of all types of advertising interchanges is fundamental for business achievement. Indeed, the IMC methodology contends that shoppers see different interchanges by the same brand per say, instead of as individual messages, addressing them in better places and diverse ways. The real advantage of IMC is that a steady flow of messages is passed on to all intended interest groups by a method for every accessible type of contact and message channels. As a consequence of the consistency in the middle of instruments and messages, IMC has a tendency to be more viable and effective than customary marketing correspondences (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 1).
The company considers its future performance to oscillate around the better placement of machinery and equipment in the marketplace. Currently, it employs an excess of 2000 people across all its fully owned subsidiaries that are situated in Asia, North America, and Europe. It also opened a new outlet in Toronto in a bid to market itself in the Canadian market. This long-term strategic goal is not only to offer highly performing equipment to average consumers but also machines that have zero emissions. The company remains the only organization that offers highly functioning construction and mining machinery. It anticipates launching its new models of the machinery this year, 2014. It plans to develop a large number of recharging stations across the world whilst making a significant progress in terms of innovation of battery technologies as an attempt to boost the dependability of its products.
The company has experienced losses since its inception until 2013 when it began to make profits through sales of 15,000 units with an average price of $70,000 each. The company depended on the ‘word of mouth’ communication between people who came to purchase a vehicle and/or potential clients who interacted with them, to create awareness of its brand. Thus, the 15,000-unit sales level was achieved with zero allocation of financial resources on marketing communications. The current marketing communication plan proposes that with a budget of $45M, the company can increase its sales from 15,000 units to 30,000 units in 2015-2016 by incorporating online and traditional media marketing communication strategies. This way, the company can clear misconceptions and doubts on the usefulness of its products. This strategy can help with the solidification of the brand equity. The objective of the plan is to increase sales, enhance the company’s brand awareness, and/or drive potential consumer traffic into the organization’s online communication platform (Poznanski, Sadownik and Gannitsos 1).
There are seven key subjects which are normal for IMC. These subjects are correspondence, marking, relationship administration, cross-useful arranging, mix, cooperative energy and business sector introduction. These speak to a critical part of the IMC idea; however, one is especially prominent – relationship administration. Developing from a prior practice of advertisers corresponding with customers on a monolog premise, it is presently a generally acknowledged principle that connections need to be overseen in the long haul. IMC coordinates an awesome extent of the advertising exertion towards keeping up and overseeing long haul connections with all partners. This gives a strong premise to business gainfulness and long haul achievement and the company needs to give careful consideration to the way it is dealing with its client connection. The new battle for the company will have all commonplace IMC attributes, and, vitally, will be gone for enhancing a decent relationship and passionate bond with buyers, rather than simply depending on substantial advancement.
Integrated Marketing Communications Performance Objectives
The centered basic supply retailer, the company, is at present confronted with solid rivalry from the other related players in the same line of production. As of late, some players were propelled, making the business significantly more defenseless against brand-exchanging and unfaithful client conduct. The company is not in a sufficiently viable position to have the capacity to contend head-to-head with the other competitors. Notwithstanding, it can settle on a decision – to either draw in a single competitor’s clients or to concentrate on the other competitors’ clients. The company needs to construct their decision of heading with respect to what might be most steady with the sought brand picture and personality. Joy Global is a fairly powerless competitor, however, their objective client is basically distinctive to the company – the little brand is focusing on the cost cognizant, by vigorously advancing low costs of its item run. Then again, Joy Global is focusing on a more complex, prosperous sort of client – an objective which is steadier with the company’s image picture. Being in an association with other competitors right now, it would bode well for The company to continue pushing for a bigger bit of the premium section, as opposed to profoundly alter its key course and change the brand character to its exceptionally center.
With the end goal, The company should accomplish a practically identical level of intensity on the online staple business sector, it needs to embrace a painstakingly arranged and executed IMC battle, went for situating it singularly as the main competitor for Joy Global, instead of a contender of the majority of the top four competitors in the meantime. By concentrating its endeavors on a barely characterized target market, The company does not just has a superior possibility of coming to its business goals, additionally, it would accomplish a superior designation of assets in doing as such. Currently, the company is still in a semi-association with other firms, which is situated to terminate by the year 2017. In any case, the associated firms have officially rebranded to and have started conveying inside the marketing zone, which implies they are currently contending straight on with the company for the consideration of the working class market.
The company’s present suggestion is in light of high caliber of items sold, the complexity of site innovation and premium client administration. The brand has figured out how to gain from other enormous chains errors, by offering brilliant administration, which is one of the primary client disillusionments with the increased shopping for cars; most clients would typically grumble about deficient item substitutions or issues with conveyance times. Accordingly, the premium valuing of the organization can be supported, particularly when contrasted with any semblance of the company or even Joy Global, which is yet to get the online basic need retail business right.
Utilizing the company now highlights as a discussion piece at working class preferences and perpetually in sanctioning terms. Notwithstanding phenomenal client administration, the company is additionally anticipating offering interesting items, which cannot be found with any of the top competitors. In the year 2014, the company identified with the other top players and resorted to large supplies rather than little or medium-sized suppliers hoping to market a good quality automobile that is not offered by the other competitors (Hill and Thomas 140).
Evaluation of Advertising and Correspondence
Customary Promotion
Marketing is any paid non-individual interchanges through different media by a recognized organization, non-benefit association or person. The primary advantage of this way to deal with interchanges is that it furnishes the publicist with complete control of what message and feeling to bestow into the promotion. Any brand can advance its advantages in a powerful manner to purchasers and endeavor at drawing in them with a message of useful and/or enthusiastic qualities, to expand brand/item thought and deals. As a consequence of good purchaser and contender knowledge, brands can make promoting which displays them in the best conceivable light, to engage potential clients. Media stations, techniques and innovative yield are all measured and are chosen by the brand/organization, making the outcome useful much of the time.
On the other hand, it has been contended that regardless of the brands’ best goals to put in the most convincing and positive message into their publicizing, shoppers may translate the message diversely to what it is proposed to be interpreted as. The translation of boosts and signs in the environment is reliant on numerous individual qualities of the message beneficiary which is the reason the same boost may be understood diversely by diverse individuals. This likewise remains constant in promoting, as in spite of promoters’ earnest attempts; outer element outside their ability to control may influence a shopper’s key message deciphering process and result in unfavorable disposition towards the brand (Hill and Thomas 140).
Keeping in mind the end goal to survey the suitability of distinctive sorts of promoting to the company’s new campaign, a more intensive examination of the conduct of the intended interest group needs to be taken. Firstly, the company’s new targets are California-based people, which imply that a substantial number of this gathering would in all probability be general workers, and would not be utilizing an individual engine vehicle regularly. This, thus, implies that they fall outside of the typical radio promoting target bunch. Besides, radio publicizing, in spite of being a less expensive mass reputation alternative, is viewed as outdated and obsolete, which is the reason it would not resound with The company’s more advanced, computerized picture. Print publicizing may be especially fit for the online retailer’s new campaign as it considers the focusing of workers, and it likewise has the capability of conveying messages capably through the great nature of imaginative work. Print publicizing is an extremely regular segment of the incorporated promoting specialized tool, as it has a high crowd achieve and can be a good avenue for key message correspondence.
Direct Advertising
Direct promoting is broadly utilized by organizations for both the client obtaining and maintenance purposes. It can have a constructive outcome on deals if executed through the channels most pertinent to the objective shopper bunch. Characterizing the objective here is vital to great execution, as assets could undoubtedly be squandered if narrowed on an insignificant channel. Direct advertising is most likely worth investigating as a major aspect of a more extensive incorporated showcasing interchanges campaign, as it can accomplish great client procurement levels with high reaction rates and great engagement. Reaction rates can increase uniformly to the level of the center of the campaign by using different client databases giving nitty-gritty client profiling to suit the particular needs of the campaign.
There are two sorts of client database records that can be utilized as a part of direct advertising, for instance, cold and warm. Cold records give data on customers by gathering them into general classifications, for example, age or occupation. Then again, warm records separate customer profiles by particular qualities, for example, magazine memberships, acquiring propensities, and so on. The last are considerably more valuable for accomplishing particular campaign goals, as they help in sectioning the market all the more correctly, and focusing on the purchasers all the more adequately.
Digital Promotion
Advanced promoting has turned out to be greatly applicable in the previous 10 years with the ascent of advancement in innovation and far-reaching access to the internet. Most families today profit by no less than one gadget which joins with the Internet and an extensive number of family units have more than one gadget, for example, portable PC, tablet, or cell phone, which issues them access to the Internet. This has opened up unlimited open doors for advertisers to achieve buyers with customized advanced substance in progressively imaginative ways. For instance, the advertisers in association with distinctive organizations can now target purchasers by utilizing GPRS information got by their cell phones, and sending them instant messages about brand advancements in the zone shoppers are in. An amazingly advanced kind of direct computerized promoting, notwithstanding some moral concerns it may have raised. For an automobile firm like the company, advanced showcasing would be particularly significant as it would reverberate with brand picture and the business’ innovative capacities (Hill and Thomas 140).
Public Relations
Advertising crusades can be created for various purposes. While conventional promoting focuses on one partner particularly (the shopper), public relations ought to consider all the pertinent partners to a business, drawn out on a partner matrix which helps in distinguishing their association and significance to the business. Public relations exercises include, however, are not restricted to newspapers, occasions, and public deeds. Public relations can be valuable for business from various perspectives, some of them being, in times of emergency, new item dispatch, changes in the business framework, extension, and so forth. In spite of public relations’s high adequacy in imparting news about the business to the overall population, it would not so much be pertinent to the company’s amended system over the accompanying one year, as the business is not experiencing huge changes. It would be more practical for The company to center its assets on different channels of correspondence, which would all the more adequately interpret its adjustment in the brand picture, and help towards increasing great earned media consideration (Hill and Thomas 140).
Works Cited
Akroush, Mamoun. “The 7ps classification of the services marketing mix revisited: An empirical assessment of their generalisability, applicability, and effect on performance – evidence from Jordans services organizations”. Jordan Journal of Business 7.1 (2011):116-146. Print.
Archie, Ben and Noah Juha. “Understanding Stakeholder Thinking: Themes from a Finnish Conference”. Business Ethics: A European Review 6:1 (2007): 46-52. Print.
Bales, Fred. “Task roles and social roles in problem-solving groups.” Readings in social psychology 2:4 (2008): 437-47. Print.
Barnard, Chester. Functions of the Executive. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2008. Print.
Barney, Jay. “Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage.” Journal of Management 17:1 (1991): 99-120. Print.
Besser, Terry. “Rewards and organizational goal achievement: a case study of Toyota motor manufacturing in Kentucky.” Journal of Management Studies 32:3 (2005): 22-38. Print.
Chernow, Ronald. Titan, the Life of John D. Rockefeller, New York: Vintage Books/Random House, 2009. Print.
Cho, Hee-Jae and Vladimir Pucik. “Relationship between Innovativeness, Quality, Growth, Profitability, and Market Value.” Strategic Management Journal 26.6 (2005): 555-575. Print.
CIM. Marketing and the 7 P’s: A brief summary of marketing and how it works, Berkshire, United Kingdom: Chartered Institute of Marketing, 2009. Print.
Coch, Leo, and French John. “Overcoming resistance to change.” Human Relations 1:4 (2008): 512-32. Print.
Coetsee, Leon. From resistance to commitment. New York: Southern public, 2009. Print.
Correa, Henry, and Slack Nick. “Framework to analyze flexibility and unplanned change in manufacturing systems.” Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems 9:1 (2006): 57-64. Print.
Crossan, Mary, and Vera Dusya. “Strategic Leadership and Organizational Learning.” The Academy of Management Review 29.1 (2004): 226-227. Print.
Dent, Eric, and Susan Goldberg. “Challenging “resistance to change.” The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science 35:1 (2009): 25-41. Print.
Drucker, Peter. Management: Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices. New York: Harper and Row, 2010. Print.
Goldman, Robert, and Stephen Papson. Nike Culture: The Sign of the Swoosh, Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2008. Print.
Grusky, Oscar. “Organizational goals and the behavior of informal leaders.” The American Journal of Sociology 65:1 (2009): 59-67. Print.
Guth, Will, and MacMillan Ian. “Strategy implementation versus middle manager self-interest.” Strategic Management Journal 7:4 (2006): 313—27. Print.
Haley, James. “Economic Dynamics of Work.” Strategic Management Journal 7.1 (2006): 459-471. Print.
Haspeslagh, Philippe, and DB. Jemison. Managing Acquisitions: Creating Value through Corporate Renewal, New York: Free Press, 2011. Print.
Hill, Charles, and Jones Thomas. “Stakeholder-Agency Theory.” The Journal of Management Studies 29:1 (2012): 131-155. Print.
James, George. “The Business Firm as a Political Coalition.” The Journal of Politics 24:1 (2012): 662-678. Print.
Jones, Steve. A marketing Case Study on Nike. 2012. Web.
Kalb, Ira. One of the Nike’s Core Strategies is in Danger. 2013. Web.
Kathleen, Molly. “Agency- and Institutional-Theory Explanations: The Case of Retail Sales Compensation.” Academy of Management Journal 31:1 (2008): 488-511. Print.
Katz, Donald. Just Do It: The Nike Spirit in the Corporate World, New York, NY: Random House Inc., 2004. Print.
Keen, Peters. “Information System and Organizational Change.” Communications of the ACM 24:1 (2011): 24-34. Print.
Lamb, Charles, Joseph Hair, and Carl McDaniel. Marketing, Mason, Ohio: Cengage –Learning, 2012. Print.
Lundberg, Curt. “Toward Theory More Relevant for Practice.” Current Topics in Management 6.1 (2001): 15-24. Print.
Merrikh, Kian. 7 P’s of Marketing, Guelph: University of Guelph, 2011. Print.
Miller, Roger. “How Culture Affects Mergers and Acquisitions.” Industrial Management 2.1 (2000): 8-8. Print.
Morgan, Gareth. Images of Organization, Thousand Oaks California: Sage Publications, 2007. Print.
Neiderhauser, James. “How Nike’s Leadership Affects Brand Image Internally and Externally.” Journal of Undergraduate Research 15.1 (2013):1-10. Print.
Regani, Shirisha. Nike-The ‘Goddess of Marketing’, Nagarjuna Hills, Hyderabad: Centre for Management Research, 2003. Print.
Shams, Ishtiaque. Financial Analysis of HSBC, Mohakhali, Dhaka: BRAC University, 2013. Print.
Simpson, David. Recession: Causes and Cures, London, UK: Adam Smith Institute, 2009. Print.