The issues associated with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) include substitution bias and inadequate adjustment for quality changes and introductions of goods. The first issue is related to the tendency of consumers to adjust their preferences based on prices faster than the CPI can reflect, leading to inaccurate representations of the data in the index. The second issue is related to the index’s fixed basket and methods. They lead to assume a price of a good increased due to inflation when the actual cause was an increase in quality and ignorance of the introduction of new influential products until the basket is manually revised.
When the actual rate of unemployment exceeds the natural rate, the economy stagnates, as there are unfilled workplaces, and the nation’s output is reduced. In addition, the deflation caused by the weakening of the economy complicates future planning. Furthermore, more people go without income, and eventually, their skills deteriorate, and they become unable to hold the jobs they were previously qualified for, leading to a loss of self-worth. Ultimately, a substantially high unemployment rate can cause social unrest, an increase in the level of crime, and other antisocial tendencies in people.
Inflation has various costs for both people and the state, including a redistribution of incomes and uncertainty about the purchasing power of money. Lending money becomes less profitable, as the amounts of money paid back by the borrower do not change, but the value does. Savings become less valuable, as they are worth less and do not grow with the inflation. Writing contracts for future payments becomes difficult, and the costs of reducing inflation weigh down the government. Lastly, countries with high inflation become less competitive internationally, and their exports fall.
Money serves three primary functions: a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. The first role allows people to avoid a barter situation where a person needs to go through a complicated chain of trades to exchange a good he or she possesses for a product he or she wants. As a unit of account, money allows people to evaluate the relative values of different products or services and record debts. Lastly, as a store of value, money serves as a non-deteriorating good that can be saved indefinitely for later use, unlike normal goods, which may become outdated or perish.
Banks in America operate on a fractional reserve system, under which they are only required to keep a part of their deposits available for immediate withdrawal. The fraction is called the reserve requirement and can be held as cash in a bank’s vault or at the Federal Reserve as noninterest-bearing deposits. Banks are allowed and encouraged to use the rest of the deposited money to give out loans and charge interest on them. This ability enables them to maintain the growth rates of the deposits and make a profit for themselves in the process while keeping the deposited money in circulation.
The Federal Reserve uses three primary tools to change monetary policies: open market operations, the discount rate, and reserve requirements. The first tool can influence the volume of reserves held by banks, making it easier or harder for them to maintain sufficient resources and consequently expanding or contracting the economy. The discount rate is the interest rate that the Fed charges to the banks that borrow at its discount window, with increases meaning contraction and decreases meaning expansion. Lastly, the Fed can change its requirements for the reserves held by banks, with changes having effects similar to those in the discount rate.
Private savings are the difference between savings and investments in the private sector and are therefore equal to 50. Public savings are the difference between taxation and government spending in the public sector and can be calculated, with the result being -250. National savings are a combination of the two factors above it and are equal to -200. Net exports are functionally the same value as national savings in an open economy model, and therefore they are also equal to -200.
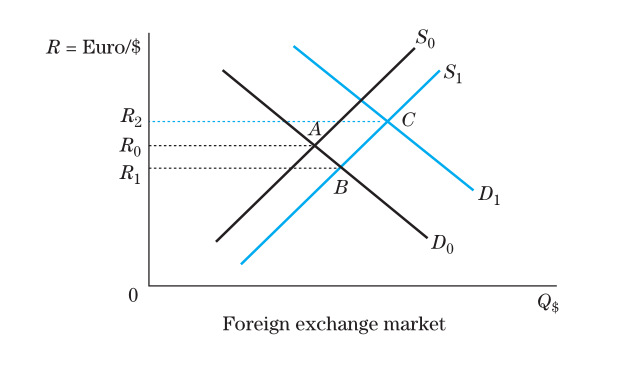
In the figure above, point C describes the initial equilibrium with an exchange rate equal to R0. Assuming a lack of interference, the situation would stay stable at that point. However, in a scenario where the interest rate in the U.S. becomes lower than that in other countries, income would decrease, leading to fewer imports. Consequently, the supply curve would shift to the left, making the unmarked point where S0 and D1 intersect the new equilibrium and leading to an increase in the exchange rate. However, due to an outflow of money to countries with higher interest rates demand would fall, moving downward and making A the ending point.
In a fixed exchange rate system, the Federal Reserve’s goal would be to eliminate the disequilibrium without disrupting the exchange rate. This aim means adjusting demand for dollars by selling the other currency for dollars in case of a U.S. deficit or buying it for dollars in an excess situation. The action simultaneously increases demand for dollars and reduces the supply (or the other way around), which keeps the exchange rate stable while eliminating the disequilibrium.