Definition of Relational Database Management
Relational Database Management involves managing the organizational data in terms of storage, access, security, and integrity. There are various software applications that organizations can use to manipulate data through addition, deletion, modification, or display in a given interface.
Relational Database Management originated from the works of Edgar Codd in 1970s (Codd, 1990). However, this technology gained popularity in the 1980s due to rapid development in computer technology. Thus, it was possible to store data in forms of related tables and access them on a real-time basis.
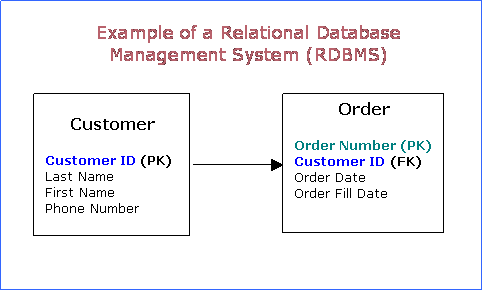
There are three concepts that Relational Database Management systems use to manage data. These include schema, data independence, and transaction. In the schema, the system relies on a set of logical schema to manage information. A logical schema can refer to names of rows and columns in the case of a cell in spreadsheets.
Complex data presentation requires an elaborate system that can provide users with several views of data. There is also a physical schema in the filing system that is useful in data storage. However, users cannot access physical schema, but programmers use it in developing the database system.
Relational Database Management also has data independence. This system separates database structure from its application system. This ensures that there is no redundancy in creating multiple, similar database for every user. Any change in the application system does not affect stored data. This is useful in areas where different groups rely on the same system. It provides flexibility for any group to perform independent modification of their applications. However, the data structure shall remain the same.
Users can make modification to the database through transaction processes. However, they must ensure that data can still be useful after transactions. Transaction, in a single part of the database, should lead to updates in other related parts. For instance, transactions in volumes should also result into changes of the total volumes.
In most cases, a single user does not pose much challenge to transactional aspects of Relational Database Management system. However, in cases of multiple users, the Relational Database Management system should guarantee all users that the database has no conflicting information. This is one of the main challenges facing Relational Database Management systems as its solution is still under study.
Relational Database Management systems have end user and developers as the main users. These systems have varied levels of complexity depending on the level of usages. Some can also use simple platforms such as PC to operate whereas others require elaborate technological systems for their operations. All of these systems have capabilities of organising data into useful forms by using character and numeric.
Capabilities or Advantages of Relational Database Management
The Relational Database Management concepts changed the manner of managing data. Before this revolution, accessing specific data from large volumes of data was difficult. Users had to access both irrelevant and relevant information before location the required information.
Relational Database Management systems brought advantages of extracting specific information needed. The system has enabled users to extract data that are only relevant to them. The system is also easy to create, manage, and maintain with regard to data management. Some of the benefits of the system include “security, continuity, access, availability, change, incident management, and capacity management of data” (Date, 2003).
Relational Database Management systems have capabilities of supporting data analysis from several perspectives. The multidimensional analysis of data is OLAP (online analytical processing). OLAP represents “relationships among data as a multidimensional structure, which can be visualized as cubes of data and cubes within cubes of data, enabling more sophisticated data analysis” (Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan, 2005).
The processes of analyses can handle large volumes of data in the physical database storage structures. Results from such analyses can aid the management team in predicting future behavior of relations and further aid decision-making processes.
The systems also have capabilities of the Web linking or interface so as to enhance access of information among many users relying on the organizational database.
The Relational Database Management systems have useful applications that have capabilities of analyzing and accessing data that are in store. These applications enable users to create new patterns, relationship among existing information, and provide useful insights that aid decision-making.
Application tools of these systems can consolidate, perform analyses, and offer convenience in accessing large amounts of data that aid users formulate best decisions for the business under a process referred to as business intelligence. Business intelligence requires specialized tools that can perform a database query. In addition, it also needs reporting tools that can perform several analyses and provide real-time reports.
Problems of Relational Database Management
Relational Database Management systems also have problems. Most software developers claim to have fast systems. However, Relational Database Management systems can be too slow. Retrieval of data involves running of optimization across the database to enable the system determine an appropriate method of accessing and retrieving such information.
This is a time-consuming process that has negative consequences on the system performance and service delivery. However, there are changes over time, but Relational Database Management systems have not achieved their full-scale efficiency.
These systems also have limitations with their capabilities of managing data. Storage and representation of complex data can be difficult. This is because Relational Database Management relies on the use of tables for holding data as unordered lists. Such systems can only retrieve ordered lists if there is additional inbuilt index for retrieving ordered lists.
Relational Database Management systems still fail despite advancement in technology and computer usages. We can attribute this to the manner complex of database structures and physical storage of data. Development of database storage structure is complex as it involves linking several tables together and to each other.
These systems have enhanced reliability in the data management. However, there is a serious challenge in cases where large volumes of data are factors under considerations. It can lead to a conflicting data due to many users manipulating data from the same database. This implies that organizations that handle such volumes of data need a full-time database administrator to handle issues at any given time leading to costs constrain.
Decision-Making using Relational Database Management systems
Organizations such as banks, airline companies, and hospitals among others can use Relational Database Management systems and processes to enhance their business decision-making and business performance. Such organizations can manage their information in to order to aid them increase efficiency and improve services through cost reductions, operational efficiency, and enhance performance through profitability.
Relational Database Management systems have powerful applications that can analyze and manipulate data in the system to serve the needs of the intended users. Relational Database Management systems capabilities of continuity allow them to consolidate past, and present information from many sources into a central system where users can manipulate such information for useful reports in decision-making processes.
References
Codd, E. (1990). The Relational Model for Database Management: Version 2. Boston: Addison Wesley.
Date, C. (2003). An Introduction to Database Systems, (8th ed.). Boston: Addison Wesley.
Silberschatz, Abraham, Korth, Henry and Sudarshan, S. (2005). Database Systems Concepts, (5th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.