- Introduction
- Analyzing the Premise and Major Themes of the Article
- Advantages of Word-of-Mouth Marketing in Relation to Traditional Methods
- Word-of-Mouth Concepts
- Identification and development of brand ambassadors
- The Concept of Buzz Marketing
- Data Collection Methods
- Marketing Implications
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The management process through which goods and services move from concept to consumer is carried out in different ways by companies. The strategies that are employed affect society in many ways. Marketing creates the link between the society’s needs or requirements and its economic response (Liu, 2006). It is through marketing that producers address the needs and aspirations of their consumers. A number of strategies are used to promote goods and services. In their article, Trusov, Bucklin, and Pauwels (2009) address word-of-mouth (WOM), which is one of the marketing strategies adopted by contemporary business organizations.
Trusov et al. (2009) analyze the various effects of WOM in comparison to those of other conventional marketing approaches. The authors do this by differentiating between word-of-mouth and social networks, internet, and traditional marketing strategies. In addition, Trusov et al. (2009) study the impacts of WOM marketing on member growth at an Internet social networking site. They compare this with traditional marketing vehicles.
In this paper, the author will analyze the issue of word-of-mouth marketing from the perspective of the article by Trusov et al. (2009). To this end, the author will analyze the premise of the article and its major themes. In addition, the general topic of WOM will be reviewed. The data collection methods used by Trusov et al. (2009) will also be reviewed. The societal and marketing implications of WOM will be analyzed in relation to the findings and conclusions made by Trusov et al. (2009).
Analyzing the Premise and Major Themes of the Article
Traditional Marketing
Traditional marketing is one of the themes in the article by Trusov et al. (2009). It is one of the oldest marketing strategies employed by many companies around the world. The effects that the form of marketing had on the people during ancient times cannot be compared to the effect that it has on the people in the modern world. The main reason for this is the change of times.
Traditional marketing is a broad category of strategies that comprises different forms of advertising (Vargo & Lusch, 2004). It can be broken down into four main categories. The first is print media. It includes newspapers, magazines, newsletters, brochures, and any other form of printed material that is produced for marketing (Liu, 2006). Broadcast involves the use of radio and television as a means of conveying messages to the people. The process also involves the use of an on-screen movie theatre for advertisement. The use of direct cards, mails, flyers, postcards, and catalogs also forms part of the traditional marketing.
Requested calling and cold calling of consumers, also known as telemarketing, is another traditional form of advertising that was invented time ago and still continues to be used. Nearly all businesses employ one of the traditional forms of marketing (Verhoef, 2003). However, traditional marketing has been overtaken by the modern ways of selling our products and services in the market. According to the authors of the article, in traditional marketing, different channels and plans have to be employed to ensure that the plan goes on successfully (Trusov et al., 2009).
Word-of-Mouth Marketing
Word of mouth marketing involves the use of human voice in transmitting a positive marketing message from one individual to another. The process can also use the means of the internet or text message to transfer information from one person to another. According to the authors, word-of-mouth has recently attracted the attention of many businesses (Trusov et al., 2009). The form of advertising has replaced the old form of marketing.
According to the findings of studies conducted in this field, marketers have shown interest in understanding WOM as many traditional forms of marketing are losing their effectiveness. When doing their research, the authors looked at the negative and positive sides of both tradition and word-of-mouth advertisement. In the middle of the article, the authors start by explaining the advantages of WOM over the traditional method of marketing (Trusov et al., 2009). Word-of-mouth advertising creates a one-on-one contact with the consumers, unlike traditional marketing.
Consumer Behaviour Theory
Consumer behavior theory tries to establish the relationship between a product and the consumer. It is enhanced through WOM marketing. A number of factors impact on consumer behavior. One of them, as indicated in the table below, is marketing. The marketing actions are determined by the location, price, type of product, and promotion. According to the authors, it is possible to know more about the perceptions, decision making, attitudes, and beliefs of consumers towards a certain product or service through a word-of-mouth advertisement (Hausman, 2000). The WOM might be direct or through the use of the internet as a platform for communication. Traditional forms of marketing can use different methods to analyse consumer behavior. However, most of these methods are long and tiresome. Some include surveys. The figure below is a graphical representation of consumer behavior theory:
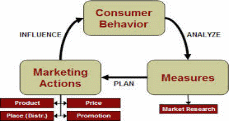
WOM offers a better solution as it creates a platform where the marketer and the consumer can freely interact. In such a platform, it is easy for the marketer to know the stimuli, attitudes, perceptions, beliefs, and categorization towards certain goods and services. Knowing the factors that affect consumer behavior is very important. In this case, there is negative and positive consumer behavior (Vargo & Lusch, 2004).
Positive consumer behavior is characterized by good feelings and perceptions towards a product or a service. Negative behavior is not healthy for a marketer or the producer of a commodity. Such behavior can be noticed and dealt with in the right way through the use of WOM marketing (Ahluwalia, Burnkrant & Unnava, 2000). It is recommendable for a marketer to employ a word-of-mouth marketing to deal with the negative consumption behavior. As shown in the diagram, analyzing the market comes first. It is meant to study the market to know the right marketing method to employ.
Advantages of Word-of-Mouth Marketing in Relation to Traditional Methods
In their article, Trusov et al. (2009) talk of how the strategies used in WOM are appealing to consumers as they help in overcoming resistance. The article expounds more on how WOM marketing is cheap and delivers fast results to its customers. It is true, as per the authors, that WOM is affordable and can deliver fast, even in times of urgency (Trusov et al., 2009). Word of the mouth involves the use of speech or the internet. When using the internet, only the browsing charges will be incurred. The information posted on the internet will reach very many people within the globe. The article explains the various platforms provided by the internet, where marketers can advertise their goods. Some of the examples given include social media like Facebook and Twitter (Chevalier & Mayzlin, 2006).
As per the authors, marketers can utilize these places to maximize their returns. Joining many of the social media platforms is free. Most people join social media to interact and have fun. It is a way through which people also communicate and share information. The aspect of marketing is also a form of interaction and communication. The process occurs whereby the marketer interacts and communicates with the potential consumers on the presence of a new deal regarding a good or service.
The platform does not cost anything to the customers. The only thing that the marketer is supposed to be aware of is the characteristics of the adverts that should be posted on the internet (Trusov et al., 2009). The internet is a place where different things are posted. For an advert to sail through the internet, it is important for it to be unique and appealing to all. Being appealing and presentable will help in capturing the attention of many consumers. Consumer satisfaction starts with what can be seen. It is possible for the consumer to dislike a product just by looking at its photograph. Such are the important elements that should never be neglected when doing WOM marketing. Marketing does not guarantee the purchasing of a product or a service (Erdem, Swait & Valenzuela, 2006). It is hence important to have a target group that can be potential consumers. The use of the internet and social media, in this case, is greatly emphasized in the article.
The affordability of the internet is evident. Both small and large businesses equal chances to showcase their products and services on different social media sites. In traditional marketing, large enterprises have the chance to reach out to the public through adverts in the media or in the newspaper (Trusov et al., 2009). In most cases, placing an advert on the television or on the radio is costly. Only institutions that are well established can afford those adverts. Most of the adverts do not guarantee awareness as they are supposed to. Traditional marketing offers awareness just for a short period of time. A good example is the adverts on the television (Hausman, 2000).
Most of them only last for a few minutes. It is not guaranteed that for a few minutes, the advert will be able to capture the attention of many people. In addition, only those with access to the television and the radio will be able to receive the message. WOM marketing is a modernized form of reaching out to all people, both the young and the old. The method does not limit the geographic location of potential consumers. It, therefore, can capture a large group of consumers, which is one of the main aims of marketing.
The services or goods supplied by a company should surpass customer needs. Customer satisfaction should be guaranteed. Customer satisfaction is important for every business entity engaged in the production of goods or services. Customers’ repurchase intentions and loyalty are guaranteed by customer satisfaction. It is true, as stated by the authors that a consumer cannot repeat on the purchase of the product they were not pleased with (Erdem et al., 2006). However, the consumer can find a way of launching a complaint to the company concerning the quality of the goods or services. If the consumer found out more about the product through the traditional marketing channels like the television, it would be hard for the customer to reach the producers in time.
A lot of time may be wasted when reaching the producers or the manufacturer. The main reason is that there is no interaction platform. According to the authors, and an interactive platform is very important in the process of communication; it enhances customer satisfaction (Trusov et al., 2009). WOM marketing through the internet provides an interactive platform. The platform makes it possible for the producer and the consumer to freely interact on the state of the goods or the services. Consumers are given a chance to state their grievances to the producers at no cost. It is possible for the customers to point out the areas that need improvements concerning a certain package (Kivetz & Simonson, 2002). The marker also benefits from the interaction platform as that reduces the customer churn.
Price is not a major determinant of consumer churn. The assertion is supported by a report from Accenture Global. The churn is motivated by the poor quality of the customer service, and only customer satisfaction could do away with the churn. Customer satisfaction enhanced through WOM marketing also plays a role in increasing customer lifetime value. Many successful businesses understand the importance of customer lifetime value (Trusov et al., 2009).
Satisfaction starts with how a marketer presents a commodity in the market. Negative word of mouth is very harmful to a product and to a company at large. It is true that how a product is presented in the market matters a lot. In traditional marketing ways, an advert is seriously polished before it is presented into the market. Thorough polishing does not allow any room for mistakes (Ahuja, Michels, Walker & Weissbuch, 2007). However, in WOM marketing, where the internet is used, there might be less polishing because the advert does not pass through the hands of many experts. Customers may be unhappy with how a product may be presented in social media.
It is important to do away with negative word of mouth. The objective can be achieved by assessing consumer satisfaction regularly. Measuring customer satisfaction when using the word of mouth marketing channels is a lot easy than when using traditional methods. The use of the word of mouth marketing mechanism can help in the process of retention of customers (Trusov et al., 2009). Different retention strategies applicable using this method include the use of blogs and websites in educating customers on the benefits of certain products and services. Apart from that being a way of strategies of retaining customers, it also acts as a way of promoting the value of a product or a service (Trusov et al., 2009). Special promotions about products can be sent to customers individually using emails. It is simple to view the email from time to time using the phone or any other gadgets then getting information from the traditional media like the television. From the word of mouth mechanism, it is also possible to carry out surveys where it is possible to know what consumers have to say about a certain product and its promotion (Ahuja et al., 2007). According to Trusov et al. (2009), internet entities apply various forms of WOM.
Word-of-Mouth Concepts
Viral Marketing
The viral marketing concept is a technique that uses pre-existing social networking services and other types of technologies to increase brand awareness in different areas. It is aimed at spreading information from one person to another with the aim of achieving all the marketing goals. In most cases, individuals are used to passing information from one place to another. Within a short time, the information may become trending within a certain site (Trusov et al., 2009).
Trending is another term that is used in different social media to show that information is viral. It means that people have information regarding the product or the service. Going viral of a product in a positive way is an added advantage to the marketer. The marketer is likely to get more returns from that. However, the viral marketing concept can either be successful or not. It is evident in how some companies have failed in their viral marketing campaign.
To achieve more results from viral marketing, some elements must be considered (Phelps, Lewis, Mobilio, Perry & Raman, 2004). The concept cannot be considered when using traditional methods of marketing. It is not possible to make an article in the newspaper viral. Once something is posted in the traditional media, it stays there permanently. It is not possible to transfer it to different users unless it is posted on the internet. Many people visit the internet more often, and that helps in marketing. The effects of WOM in viral marketing are more than that
Gives away valuable products and services
Giving away valuable products and services, as a form of promotion, is one of the ways of making a good viral marketing strategy. The word ‘promotion’ and ‘free’ are powerful in marketing. Attaching the words to a product attracts people to it (Trusov et al., 2009). Many consumers are attracted to free, promotional, and cheap products. According to the article, viral marketing can be enhanced through give away. Such messages of free products can be sent via the internet through the email. It is easy to reach many people who can forward the messages to their friends.
The products can be put on promotion for different seasons. The process of having free products should not be aimed at giving instant profits to the company (Verhoef, 2003). Such a promotion activity is a form of asset that the company is expected to enjoy in the future. The products to be given for free should also be high-quality ones. The fact that they are free does not mean that they should be of low quality. It is the best viral marketing technique that should be employed.
From small to large
In every marketing strategy, it is important to consider the amount to be placed for the offer. Viral marketing should start from small to large. It is important to ensure that the transmission methods are taken care of in the right way. Take an example of a mailing system. If the viral strategy is using the email, it is, therefore, important to send information that is short and precise. Information should not be boring or very long to ready. It can have animations and pictures for easier interpretation (Phelps et al., 2004). It is easy for such information to go viral because consumers can have time to read it. After creating awareness, the information can be added, but it should be exciting for the reader. Creating a viral marketing campaign using traditional methods is nearly impossible. The magazines and the radio cannot give room for the marketing concept.
The utilization of communication networks and resources
Utilizing the existing communication networks and resources is an element of a healthy viral marketing technique. Any business can apply this technique. The formation of links in different sites is a way of utilizing the communication network (Phelps et al. 2004). The different links should redirect one to the main site where the product is located. The different small links should be located in daily websites or blogs that are busy on a daily basis. It is true that many companies have employed this technique in their marketing strategy, and it has helped them increase awareness.
Easy protocols
Viral marketing strategy does not have to have many protocols. The site that contains the information to be advertised should be easy to access by all people. One of the reasons why viral marketing fails is the inclusion of different protocols in the sites. It then becomes hard for customers to access information concerning a product or a service. A good viral marketing strategy should not allow any protocols. Transfer and replication are crucial. It should be easy for copy pictures and download products from the sites without restrictions (Trusov et al., 2009). It is a good step towards viral marketing as it will allow many people to visit the site. In proper viral marketing, the cover page should not be made like a resume. Many business entities make this mistake when planning for their viral marketing (Phelps et al., 2004).
Word of mouth adverts should have a compelling summary with only the relevant keywords. Eye-catching cover images should be used as well as a standard logo. Some of these are the elements that compel the consumer to visit a particular site. Many people agree with the article that viral marketing programs act as strong pillars in WOM marketing (Trusov et al., 2009).
The Concept of Referral Programs
Referral programs also apply to WOM advertising. It is common among online businesses. Many referral programs create tools that enable consumers to refer their family and friends to a certain site after enjoying a certain product. People have the chance to purchase a product based on the opinion or influence of another person (Trusov et al., 2009). Referral programs help in a great way to increase sales and conversions. Usually, many people believe or trust the opinion of other people, thus making it a powerful marketing tool. Even though referral marketing is powerful, many companies do not know how to apply it in the right way. Several things should be taken into consideration when doing referral marketing.
Precision targeting
Precision targeting involves choosing the right target group for WOM marketing. Lack of precision can lead to the failure of a marketing campaign. People know their social friends and audiences well. When doing WOM marketing, it is important to consider these people. In most cases, these people are aware of the things being described. It is easy to convince friends to try a product or a service than unknown people (Trusov et al., 2009). That is the first step in referral. When these friends find the product pleasing and of advantage to them, they will definitely refer their colleagues and families to try it. In traditional marketing, it is very difficult. It is not possible to get a second look at the product being referred to. Precision targeting should, therefore, be highly recommended in WOM marketing.
Trust factor
The trust factor is enhanced by referral marketing. Referrals are usually made by known people. It is not like traditional marketing whereby the information about products is given by unknown people (Meuter, Ostrom, Roundtree & Bitner, 2000). It is true that not many people trust salespersons who are employed on commission when they approach them with a proposition to buy certain products. In the referral concept, the sales pinch usually comes from a person that one trusts. Incentives or rewards can help in referral products. It may be placed in such a way that one referral is equal to a certain number of points (Trusov et al., 2009). Giving of incentives is also cultivated by the trust.
Wrapping up
The entire referral program should use all the available resources. The referral program cannot work if the marketing campaign itself is poor. The site or the product that people are being referred to should be presentable. It is not guaranteed that a referral will sail through even if it is from a trusted friend (Kozinets, Wojnicki, Wilner & Valck, 2010). A good wrapping up design should ensure that it covers the tastes of the majority. An armed wrap up works best for the WOM marketing experience. The traditional way also gives rooms for polishing up the ad but does not give room for referrals.
Community Marketing Concept
Community marketing aims at engaging an audience in an active and non-intrusive customer conversation. Community marketing aims at the needs of existing customers (Kozinets et al., 2010). It is unlike marketing communication, where the adverts are aimed at capturing new customers. In community marketing, communities that share the interest of a product or a brand benefit from the manufacturer of the goods or the provider of certain services (Hennig‐Thurau, Gwinner, Walsh & Gremler, 2004). It acts as a way of appreciating the support given by the community. A community can be large or small. No matter the size of the community, communication should be strategic to ensure the expansion of content marketing. Several steps are recommended in this concept.
Identification and development of brand ambassadors
In WOM marketing, the identification and development of brand ambassadors are very important. Brand ambassadors act as agents of gathering information from the rest of the community. The ambassadors also convey messages to the brand promoters to the community (Meuter et al., 2000). It is a show that the community feels protected and respected by the brand promoter. Ambassadors make it easy for the brand promoter to know the reactions of the community towards a certain marketing campaign and a product. It is correct that many people in the community will prefer purchasing products that have on ground ambassadors (Gremler et al., 2001). In this way, the consumers can pass their complaints to the ambassadors who can later forward them to the main marketers.
The ambassadors also act as advisors in brand promotion. The promoters study the behavior of the competitors and advice on how to implement strategies that will help face the pressure. The process of communicating this information can be done through social media or through one on one (Kivetz & Simonson, 2002). It works both for a small and large business. Brand ambassadors are not necessary for traditional marketing. The success of the product in the market after a campaigning strategy is gauged by the sales. The development of promoters is also important in enhancing customer satisfaction.
Building relationships by engaging people
WOM marketing cannot pull through without engaging people and creating relationships. Marketing is a form of communication, and word-of-mouth has to ensure that a good relationship is created in passing information. Product marketing should not only aim at benefiting the producer (Gremler et al., 2001). The community should also benefit from the marketing campaign. Different brand promoters should sponsor different activities in the community. The activities could be sports, education, or even medical fees. Branding the t-shirts of the players or offering branded books to learning institutions with the logo of the product is one of the ways of promoting a good relationship with the community. Apart from creating a good relationship with the people, the company also markets its products through sponsorship and WOM advertisement.
Trade shows
Participating in trade shows is another form of WOM marketing. It allows a company to showcase a variety of products that it has. Most of the trade shows are regional. Some are also international. The trade shows help in opening up the company to the rest of the world. It also helps in interaction with the community. Apart from marketing a commodity or a service to the region, it also opens links with other companies participating in the trade shows. During the shows, the consumers are given a chance to ask questions to the producers regarding the state of the commodities and services produced.
Trade shows are a form of direct word-of-of mouth marketing. Such shows build consumer confidence. Unlike traditional methods, the consumer is able to personally meet the producer (Verhoef, 2003). The interaction can help in building consumer satisfaction. Companies and businesses that engage in trade show also show how they value their customers. It is not all about advertising products, but they are ready to meet up their customers and discuss the issues affecting the consumption of a certain product. WOM marketing in the community can be built through such occasions. In this case, WOM works better than the traditional methods of marketing.
The Concept of Buzz Marketing
Buzz marketing concept involves the creation of news, which adds fizz to the brand association whereby a product is seen sending a positive pulse to the buyer. The attempts by this form of marketing ensure that each encounter with the consumer is made unique. The exchange of information between the marketer and the consumer is made spontaneous and personal in such a way that the consumer is involved. The concept works well with word-of-mouth marketing (Ahuja et al., 2007). The Buzz marketing concept is similar to the viral marketing concept. Both create awareness of a product or a service on social media or the internet. Buzz marketing cannot work with the traditional forms of marketing. Most of these forms are not directly connected to the people, and this is the reason why they cannot support the concept.
A successful buzz marketing campaign leaves people talking about a product or a service. The concept can be applied by all sizes of business enterprises. Companies can promote their services and products successfully using the concept in many ways. In this form of marketing, it is not necessary to use the product or service to be marketed as the main theme. The product can be incorporated in other types of messages inform of pictures, animations, or short words (Ahuja et al., 2007). The idea here is to ensure that the main message in the advert is attracting people to the product. In buzz marketing, there are several things that attract the eyes of many viewers.
The message to be stated must be unusual. Many people love hearing something new. It will attract many people to the site, thus viewing the product. Apart from being unusual, it should be outrageous (Trusov et al., 2009). A message that is outrageous can be very bold and unusual. Creativity should be involved in the process. Being hilarious is also something else that many people love. The message should be fun and not bring to ensure that it captures the attention of many—consumers who are the community love to hear about secrets. Many people sign in to different social media platforms to search for revealed secrets. Revealing a secret is another way of capturing the attention of many consumers (Ahuja et al., 2007). Taboos also interest many people. Buzz marketing can apply such creativity to ensure that every consumer talks about the site. Traditional marketing cannot support this. WOM has very many ways of creating a successful marketing campaign. Many people concur with what the article states about buzz marketing. It is true that buzz marketing is one of the strongest tools that a company can use to launch a brand.
Data Collection Methods
Trusov et al. (2009) used a mixed research study method. Both qualitative and quantitative means of the study were used to come up with the above conclusions (Trusov et al., 2009). The Vector autoregression modeling approach was used in analyzing the data collected. A survey was also conducted to gather information on the effectiveness of online marketing. Different marketers were interview regarding their position about WOM marketing and the traditional form (Hennig‐Thurau et al., 2004). As shown above, the results were that many opted for word-of-mouth marketing rather than traditional.
Most of them cited the advantages associated with WOM marketing as the main reason that would allow them to apply it. The study of consumer behavior also contributed to the findings of the study. Consumers were allowed to express their feeling towards online marketing and traditional forms. Most consumers cited that most of their information on different products came from the internet. Some of them were referred to these sites by friends. The number of people visiting social media indicated that a lot of time is spent browsing.
A sampling of different sites that were engaged in marketing over the internet showed an interaction between the consumers and the marketer. Keeping in touch with consumers helped in knowing consumer behavior (Kivetz & Simonson, 2002). Marketers were able to relate with their customers on a personal level. Most consumers were satisfied with the answers and the results they got from the sites. It helped them in improving their services. The data collection methods were all successful. Each of them played a role in showing the effects of WOM marketing versus traditional marketing.
Marketing Implications
Marketing implications are the results expected from the application of a certain strategy. The two strategies, compared by Trusov et al. (2009), include WOM and traditional marketing. The authors of the article focus more on the advantages of the word-of-mouth marketing approach (Trusov et al., 2009). The implications of the strategy are more than those of traditional marketing (Chevalier & Mayzlin, 2006). As already indicated in this paper, the strategy has many benefits. They include an increase in sales, effectiveness, affordability, and reliability. The implications are some of the implications of the marketing strategy. Consumer satisfaction is also a result of the marketing strategy.
Conclusion
In this paper, a critical analysis of the article by Trusov et al. (2009) was provided. The evaluation shows that WOM is powerful than traditional forms of marketing. It is clear that marketing campaigns can succeed through the use of different social media platforms. Traditional marketing methods have been overtaken by modern strategies, which include WOM. Many people have been discouraged by the high costs associated with conventional methods. Their coverage is also less compared to that of WOM. The conclusions made by Trusov et al. (2009) show that it is possible for a marketer to gauge the right method to apply when promoting a brand. Companies should be able to compare the negative and positive implications of WOM and conventional methods before deciding on the best to employ. Marketing should exhaust all forms of communication with the consumer.
References
Ahluwalia, R., Burnkrant, R., & Unnava, H. (2000). Consumer response to negative publicity: The moderating role of commitment. Journal of Marketing Research, 37(2), 203-214. Web.
Ahuja, R., Michels, T., Walker, M., & Weissbuch, M. (2007). Teen perceptions of disclosure in buzz marketing. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 24(3), 151-159. Web.
Chevalier, J., & Mayzlin, D. (2006). The effect of word of mouth on sales: Online book reviews. Journal of Marketing Research, 43(3), 345-354. Web.
Erdem, T., Swait, J., & Valenzuela, A. (2006). Brands as signals: A cross-country validation study. Journal of Marketing, 70(1), 34-49. Web.
Gremler, D., Gwinner, K., & Brown, S. (2001). Generating positive word-of mouth communication through customer-employee relationships. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 12(1), 44-59. Web.
Hausman, A. (2000). A multi-method investigation of consumer motivations in impulse buying behaviour. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 17(5), 403-426. Web.
Hennig‐Thurau, T., Gwinner, K., Walsh, G., & Gremler, D. (2004). Electronic word‐of‐mouth via consumer‐opinion platforms: What motivates consumers to articulate themselves on the internet?. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 18(1), 38-52. Web.
Kivetz, R., & Simonson, I. (2002). Earning the right to indulge: Effort as a determinant of customer preferences toward frequency program rewards. Journal of Marketing Research, 39(2), 155-170. Web.
Kozinets, R., Wojnicki, A., Wilner, S., & Valck, K. (2010). Networked narratives: Understanding word-of-mouth marketing in online communities. Journal of Marketing, 74(2), 71-89. Web.
Liu, Y. (2006). Word of mouth for movies: Its dynamics and impact on box office revenue. Journal of Marketing, 70(3), 74-89. Web.
Meuter, M., Ostrom, A., Roundtree, R., & Bitner, M. (2000). Self-service technologies: Understanding customer satisfaction with technology-based service encounters. Journal of Marketing, 64(3), 50-64. Web.
Phelps, J., Lewis, R., Mobilio, L., Perry, D., & Raman, N. (2004). Viral marketing or electronic word-of-mouth advertising: Examining consumer responses and motivations to pass along email. Journal of Advertising Research, 44(4), 333-348. Web.
Trusov, M., Bucklin, R., & Pauwels, K., (2009). Effects of word-of-mouth versus traditional marketing: Findings from an internet social networking site. Journal of Marketing, 73(5), 90-102. Web.
Vargo, S., & Lusch, R. (2004). Evolving to a new dominant logic for marketing. Journal of Marketing, 68(1), 1-17. Web.
Verhoef, P. (2003). Understanding the effect of customer relationship management efforts on customer retention and customer share development. Journal of Marketing, 67(4), 30-45. Web.