Due to their benefits over traditional wired networks, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have enormous application opportunities for industrial applications as Industry 4.0 develops. Industrial wireless sensor networks (IWSNs) have higher requirements for high security and low latency due to completely automated mechanized activities and wireless communication environments. The response delay in IWSNs should be measured in milliseconds. Furthermore, because there are no redundant computation and transmission resources in IWSNs’ edge computing (EC) system, some sensor nodes are in entirely secure environments. As a result, lightweight authentication is critical for improving the security of IWSNs while maintaining low latency.
Due to complicated computing, the encrypted approaches are too heavy to sustain the nodes. Liao et al. performed some lightweight password processing, although their solution fails to meet several specific requirements. Other researchers suggested a rapid cross-authentication system that solves the security and latency challenges by combining non-cryptographic and cryptographic algorithms (Zhou et al., 2021). Furthermore, because of the heterogeneous nature of IWSNs, typical encryption-based authentication approaches are more difficult to establish and manage. Physical (PHY) layer solutions, on the other hand, offer some novel ways to safeguard lightweight IWSNs. For such applications, the high authentication rate and cheap cost are very important.
Background of the study
Wireless networks are recently undergoing a significant transformation. The increasing number and diversity of wireless devices, as well as increased spectrum consumption, are some of the trends that have been noted. Regrettably, radio frequency spectrum is a limited resource. As a result, certain regions of the spectrum are widely utilized, while others are neglected. Unlicensed bands, for example, are excessively overused and suffer from cross-technology interference (Zhou et al., 2021). In monitoring and tracking environments, wireless sensors are deployed at random. The sensor’s position may or may not be known. The research team must precisely determine the location of each node in the network in order to obtain the essential information about the target environment.
Aim and objective of the research
The goal of this study is to provide an overview of WSN applications and challenges, with a focus on the topic of localization. In addition, the research proposes taxonomy for classifying alternative localization algorithms. Furthermore, the paper examines many standard methods as well as their improvements using soft computing techniques. Furthermore, the study outlines the challenges of localization and identifies areas for future research.
Research question
- What kind of technology is used in the deep learning and wireless sensor networks?
- How the deep leaning-enhanced wireless sensing has been used in the past and how it will be used in the future?
- Will the deep learning-enhanced wireless sensing improve compared to how it is right now?
Literature review
Many scientists have recently focused their own research on topics such as smart buildings, sensor devices, virtual sensing, building management, Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence in the smart buildings sector, improving life quality within smart homes, assessing occupancy status information, detecting human behavior with the goal of assisted living, environmental health, and natural resource preservation. The research review’s major goal is to assess the present state of the art in terms of recent breakthroughs in combining supervised and unsupervised machine learning models with sensor devices in the smart building sector, with the goal of improving sensing, energy efficiency, and property management companies. The research approach was developed with the goal of locating, filtering, categorizing, and assessing the most important and relevant scholarly papers on the subject (Andiappan, & Ponnusamy, 2021).
In order to measure the interest in the above-mentioned topic within the scientific literature, the research team employed credible sources of scientific information, namely the Elsevier Scopus and Clarivate Analytics Web of Science international databases. After analyzing the papers, researchers were able to create a reliable, expressive, and representative pool of 146 scientific papers that the research team could utilize in developing surveys by means of the approach that was created. For academics from various domains, the research technique provides a valuable up-to-date overview, which can be useful when submitting project proposals or exploring complex problems like those discussed in this paper. Meanwhile, the new study allows scientists to identify future research areas that have yet to be addressed in the scientific literature, as well as to improve existing methodologies based on the body of information (Zhou et al., 2021). Furthermore, the performed review establishes the foundation for identifying the major purposes for integrating Machine Learning techniques with sensing devices in smart environments in the scientific literature, as well as purposes that have yet to be investigated.
Research Methodology
In the research methodology, this study uses a diagnostic research design and a deductive technique, both of which can establish a favorable relationship between an idea and factors. Secondary data sources include a number of worldwide journals and magazines, increasing the study’s useful breadth. Within the research study, which will be conducted using a secondary qualitative technique, thematic analysis will be used as a method. The primary motivation for employing these research techniques is to reduce the danger of COVID 19 exposure. Apart from the risk of contracting COVID 19, the secondary qualitative research approach saves a lot of time and is less expensive than the primary quantitative research method, thus it is suitable for this research study in the current situation.
Using a diagnostic research technique and a deductive research strategy, secondary data on deep learning on sensor networks data will be acquired from worldwide publications. The collected data will then be evaluated using a variety of literary resources. Finally, the collected data will be compared to the research objective to establish whether or not the research’s actual intent was met.
While fostering the survey system, the research team will consider the details relating to the “Writing Review” type given by Zhou et al. to be specific: the enlightening part describes “distributed materials that give assessment of later or ebb and flow writing; can cover wide scope of subjects at different degrees of fulfillment and exhaustiveness; may incorporate examination discoveries”; the quest part of the SALSA system for this kind of audit might possibly incorporate complete looking; the evaluation part “could conceivably incorporate quality appraisal”; the combination part is “ordinarily account”; the investigation part “might be sequential, theoretical, topical, and so on”. To this end, the team will utilize dependable wellsprings of logical data, to be specific the Elsevier Scopus and Clarivate Analytics Web of Science worldwide data sets, to evaluate the interest in this theme inside the logical writing and to acquire a beginning stage for building a solid, expressive and delegate information base of logical works that would be helpful for fostering our study. The picked these two information bases as there needed to ensure that the team were utilizing all around the world acknowledged wellsprings of data that unmistakably select and record their substance in a consistently steady way, upheld by many years of dependable, exact and exhaustive ordering. Besides, the team took into account the way that renowned distributing bunches order and advance their diaries by featuring the quality measurements of their diaries as given by the Web of Science Core Collection or on the other hand the Elsevier Scopus data sets. Thusly, there was contrived, in light of the scientific classification of managed and solo AI procedures, custom hunt inquiries to survey the expansive execution and to recognize which of the AI techniques from the scientific categorization addressed are generally appropriate for execution with sensor gadgets in shrewd structures with the end goal of accomplishing improved detecting, energy productivity and ideal structure the board.
The custom search queries were acquired after trying several search patterns as well as criteria, with the terms smart, sensor, and at least one of the terms machine learning, artificial intelligence, supervised learning, and unsupervised learning, as well as their associated subcategories from the taxonomy, appearing in the title, abstract, or keywords. As a result, the first two steps of our methodology are to search the two international databases using the above-mentioned search queries, yielding two initial pools of scientific works useful for conducting the survey, consisting of 1255 papers retrieved from the Elsevier Scopus database and 381 papers retrieved from the Clarivate Analytics Web of Science database, for a total of 1636 papers (with some papers being included in both databases).
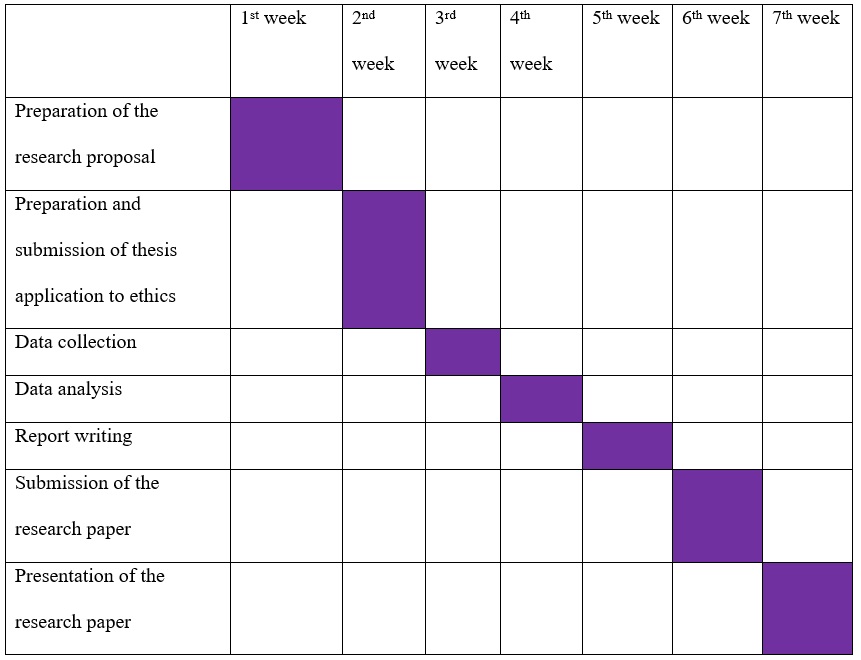
References
Andiappan, V., & Ponnusamy, V. (2021). Deep Learning Enhanced NOMA System: A survey on future scope and challenges. Wireless Personal Communications, 1-39.
Liao, R. F., Wen, H., Wu, J., Pan, F., Xu, A., Jiang, Y., & Cao, M. (2019). Deep-learning-based physical layer authentication for industrial wireless sensor networks.Sensors, 19(11), 2440.
Zhou, H., Liu, Q., Yan, K., & Du, Y. (2021). Deep learning enhanced solar energy forecasting with AI-driven IoT.Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021.