Abstract
Electronic commerce (E-commerce) is a form of trade which depends mostly on communication technology. The trade is carried out through the electronic medium (the internet) without any paper related documents.
Compared to other available markets, the net is the biggest since it has no conditions for entry and can be joined by anybody. This benefit everyone unlike other commercial online services, which have specified clients to access their services. The technology adoption has increased ability in the development of a country and as such earns most of the countries interest.
E-commerce also provides lots of benefits to consumers including the availability of products at a low cost. The aspect of ordering goods online also saves time and is much faster and preferred by many customers. Above all, E-commerce has helped a lot in the customer relation management, production and internal management.
E- Commerce in India
The growth of e-commerce in India has been largely determined by enhanced convenience and client choice. Besides, high use of internet and its accessibility have also contributed to the growth and development of e-commerce in India. The diffusion of electronic commerce has been slow among the enterprises, however, with increased globalization in money transfer and communication, the adoption of e-commerce has accelerated (Sharma & Rawat, 2014).
Majority of the Indian firms are now using e-commerce facilities to enhance their operations and increase customers’ relationships. Most of the shopping is done online by the customers due to their busy lifestyles. In 2011, e-commerce market in India was valued at 50,000 Rs. Approximately 80% of it is based on travelling. Online transactions in India cover about 15% of general money transfers (Gangeshwer, 2013).
For this reason, India has earned lots of interest from other markets as the best e-commerce market. E-commerce is not only utilized in advertising but also in enhancing business transactions. Merchandize ranging from groceries to movie tickets exchanged online. Besides, the online stock exchange has made e-commerce successful in India.
The provision of debit and credit cards by banks has also facilitated the growth of e-commerce. Banks have also availed phone banking and net banking whereby customers are able to make their bill payments instantly. Net banking is characterized by the special services including foreign exchange services and stock exchange services.
With the increased diffusion of online services, the traditional couriers have been found to be inefficient and unreliable, unlike online couriers. Besides, the advancements in computer technology has been significant in countering security setbacks experienced in the e-commerce transactions. With necessary systems and infrastructures put in place, India will be one of the major global players in e-commerce industry (Gangeshwer, 2013).
However, the growth of the industry is not uniform across the sub-continent. The industry is more developed in the south compared with the northern region. Many factors explain this variation including the internet accessibility, the level of economic growth, enterprise participation and the government policy.
The economic infrastructures as well as the internet accessibility in the southern cities have contributed to the increased growth and expansion of e-commerce industry. In fact, southern and western cities, such as Delhi have the largest share in terms of e-commerce market (Gangeshwer, 2013).
E-commerce Issues and influences in India
Consumers’ choice of product is very important in any trade. E-commerce brings changes that significantly reduce the time taken by a trader to choose products. Since e-commerce eliminates paper-based transactions, it increases business efficiency and reduces the cost of operations.
A business that embraces e-commerce has an upper hand on other market competitors. Additionally, the high efficiency brought about by e-commerce in India leads to the creation of other new distribution channels which could bring about new electronic markets. The new developed electronic markets raise competition policies. Due to this, many e-commerce companies in India face the over pricing which reduces the profits made from the transactions (Gangeshwer, 2013).
Privacy is a major concern for e-commerce customers. In fact, Indian customers may prefer having some of their possessions or information not to be shared online. The attribute has been an issue that was not curbed fully in the e-commerce industry in India. Another issue arising in the industry is the online competition between the intermediaries and the manufacturers (Lowry, Vance, Moody, Backman & Read, 2008).
The establishing of websites where customers can order their goods directly is an indication that an effort is made to eliminate the intermediaries. The access provided by the internet creation of the new websites itself is a competition. The new intermediaries are bound to sign agreements which could be restricted directly to their online buyers and sellers.
The internet cost of searching products online is relatively low in India. As a result, this restricts customers to an identified site. Such a feature leads to the switching of suppliers which will lead to a greater bargaining power (Gangeshwer, 2013).
E –commerce in China
While e–commerce has been successful in other countries, China lagged behind. However, the government has made several steps in ensuring that e-commerce easily diffuses into the commercial activities. Despite the government effort in promoting the e-commerce industry and faster enterprise adoption, the industry is still facing a tremendous regional imbalance.
Regional imbalance for the growth of Ecommerce industry is common in most developing countries. However, the reasons for the imbalance may vary depending on current level of economic development of the country.
Various factors have been identified as the main cause of this imbalance in China including the government policy, economic level and the levels of customers’ attitude. Other factors include internet penetration, credit systems, logistics, enterprise participation and talent. The factors remain critical in influencing the growth of E-commerce industry in China (Cai, Song & Zhao, 2012).
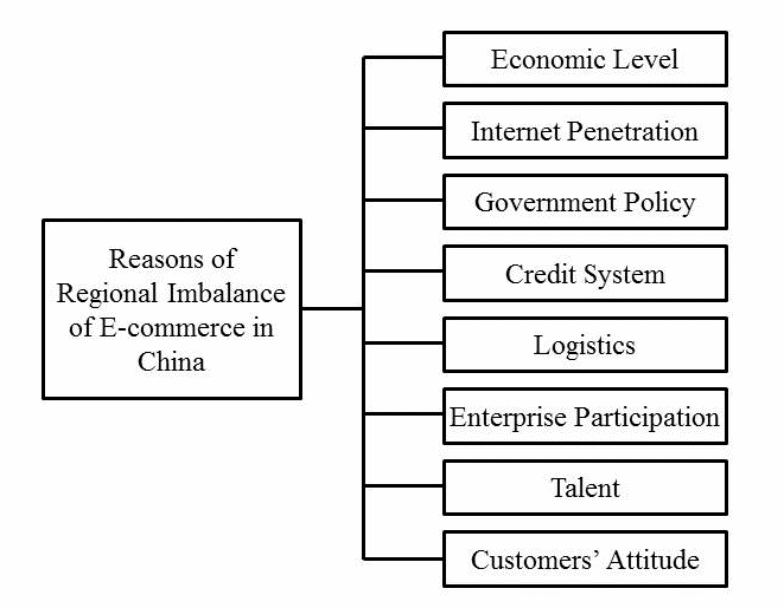
Internet penetration
The quantity and quality of the available internet determines the content usability of the websites. The accessibility to the websites remains significant in the success of the industry. As such, the success of e-commerce depends on the level of network development. The availability of network in China varies.
Besides, the online population also continues to grow differently. For instance, in the eastern region, the network infrastructure is well-developed making the great population access the internet. In Beijing, the internet penetration approximated to be about 83.3% in 2010 compared with Yunnan and Guizhou, which approximated at 45% and 45.8% internet penetration respectively.
The government policy
The government policy determines the diffusion of e-commerce. The local government policy support for the internet adoption, accessibility and usage has been diverse across the country. Such policies are the backbone of the e-commerce industry (Cai et all., 2012).
For instance, the eastern region has experienced increased local government support in planning, conducting and development of e-commerce through various policies. As such, the growth of the industry in the eastern cities is higher compared with western and central regions.
Credit system
The credibility of the system remains a determining factor for its growth and development. With increased expansion of the industry, the imperfections in the credit instruments pose a greater risk. Currently, the lapses in the security system are a major risk for online transactions.
In China, four credit models of e-commerce have been developed ranging from network ID card to third party guarantee. The development of these models also differs depending on the region. The third party systems are majorly consumed by banks that originate from eastern and central regions (Cai et al., 2012).
Enterprise participation
Enterprises are the major consumers of e-commerce. The reason is that e-commerce results in increased revenue, enhance efficiency in operations and encourage advancements in the respective industry. The number of firms participating in e-commerce determines the quantity of the market. In fact, in China, the business to business (B2B) transactions involving e-commerce vary across the country. Higher number of such transactions is found among firms from eastern regions.
For instance, the Alibaba Company in China is one of the homegrown B2B firms from the eastern region. The participation of this firm in the industry has been greater compared with foreign firms that are found in the western region of the country. The future expectation of the firm is to overtake large international retail chains and be the leader in the network retail globally (Gupta, 2013).
There are no charges in this site on transactions but the advertising brings reasonable income. The other Alibaba’s Company site is B2C which provides mall experiences for its users who have the interest to set up their own mall websites. The site earns commissions on the transactions made per individual. These two sites boom in China’s market as they deal with the sale of many products and services including shoe laces.
E-commerce Issues and influences in China
The companies in China provide the largest investors in equipment of internet infrastructure as they increase business and the flow of information through the internet. Due to the availability of the internet, it makes China the fastest growing internet economy. Besides, having access to the World Trade Organization has made China’s corporation’s operations expand massively in other countries (Qin, 2010).
There are also challenges that the country (China) faces in the e-commerce development. Many customers in China usually take orders of what they need online, but the payments are done offline using cash on delivery. Moreover, most of their websites have relations with incompetent distributors and suppliers.
On the other hand, security issues are also a problem in China. The Chinese government lacks confidence in the internet operation and the state appears to be very slow to create information resources. Besides, consumers sometimes have doubts on the electronic payment mode due to lack of automatic system of recovery. The problem gives them the reason to opt for making their payments in cash or buing things in person (Cai et all, 2012).
China’s services are not up to standard. They have incompetent prices and a small percentage of their online buyers are satisfied with their services. As a result, this lowers the e-commerce in the country as compared to other countries whose services are more exclusive.
Consumers feel the convenience of speed and the aspect of getting goods instantly. Purchases made via mobile phones and tablets have been proven to be much faster than those made on computers. Business partners found communication process without necessarily meeting in person easier. The communication is majorly done in the chatting rooms which are public or private. Not all of these rooms are easy to monitor around (Cai et all., 2012). As such, privacy is minimal and most important information included in the chats can be easily deleted.
Conclusion
Even though e-commerce has become the number one connection medium worldwide, it has its advantages and disadvantages that come along with its adoption. The creation of new business opportunities and education is a major development brought about by e-commerce. New products and services are gradually brought out by the fast growing and changing technology. Identifying these new ways soon enough can be advantageous in the selling of the newly emerging products.
One the other hand, security is being a major issue in e-commerce, better ways to improve the same should be identified and put into practice. Just as the online transaction was identified, so should the technological advancement be propped up and properly managed to warrant IT security to consumers. When the issue is solved amicably, it will also help in reducing the reluctance of online shoppers to conduct their shopping online.
References
Cai, W., Song, W., & Zhao, S. (2012). Analysis of regional imbalance of e-commerce in China. International Journal of Business and Social Research (IJBSR), 2(4), 322- 336. Web.
Gangeshwer, D. (2013). E-commerce or internet marketing: A business review from Indian context. International Journal of U- and E Services Technology, 6(6), 187-194. Web.
Gupta, S. (2013). E-commerce in Asia: Challenges and opportunities. Boston, Massachusetts: Harvard Business School Press. Web.
Lowry, P.B, Vance, A., Moody, G., Backman, B. & Read, A. (2008). Explaining and predicting the impact of branding alliances and web site quality on the initial consumer trust of e-commerce web sites. Journal of Management Information Systems, 24(4), 199–22.
Qin, Z. (2010). Introduction to e-commerce. Springer, New York: Springer Science & Business Media. Web.
Sharma, M. & Rawat, D. (2014). Evolution of e-commerce in India: Creating the bricks behind the clicks. Web.