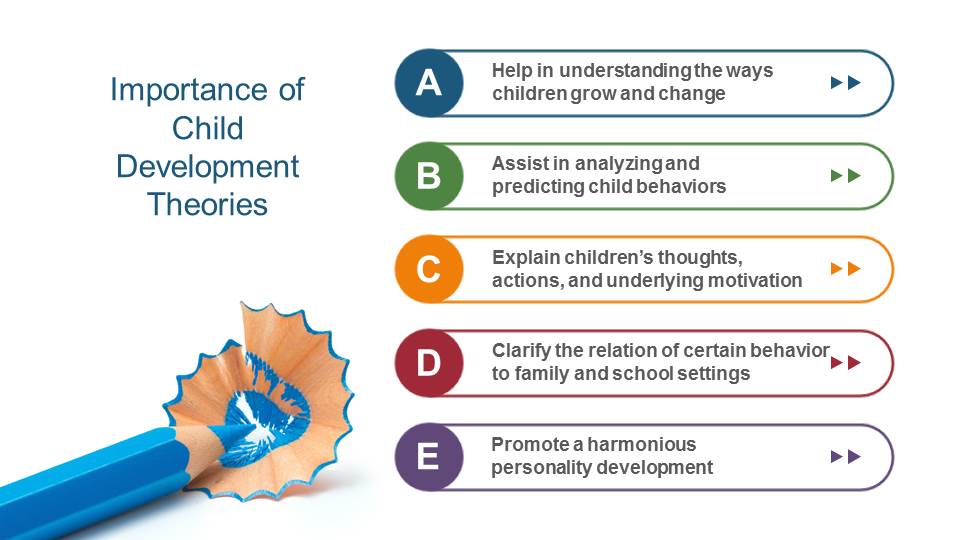
Importance of Child Development Theories
- Help in understanding the ways children grow and change;
- Assist in analyzing and predicting child behaviors;
- Explain children’s thoughts, actions, and underlying motivation;
- Clarify the relation of certain behavior to family and school settings;
- Promote a harmonious personality development.
Child development theories explain the ways children grow and change, providing a framework for learning strategies. Among the key directions, one may note cognitive, behavioral, and social theories, which help to analyze and predict child behaviors. These theories aim to clarify human development and focus on different aspects of behavior to understand what motivates one or another action and thought. While previously, children were largely considered as small versions of adults, modern researchers are especially interested in typical early childhood development. It is important to be aware of these theories for educators and parents since they help in appreciating the behavioral, cognitive, and social growth of a child.
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development
The cognitive development theory was elaborated by Piaget, a philosopher and psychologist, who worked in the field of child development. According to this theory, a child designs a mental model of the world in the process of interacting with the environment (Carey, Zaitchik, & Bascandziev, 2015). Piaget opposed the idea of fixed or innate intelligence and claimed that biological maturation lies in its foundation. Based on the systematic study of cognitive development, the identified theorist revealed that thinking patterns of children are different compared to those of adults (Ahmad et al., 2016). The cognitive theory proposes several stages of growth, including sensimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational.

Cognitive Development Theory: Classroom
- Creating an environment that encourages exploration and experiments. For example, using a method of trial and error is helpful to show that making mistakes is not bad.
- Offering problem-solving tasks: Teachers should explain various schemas to solve these tasks and facilitate student motivation (Ahmad et al., 2016).
To use Piaget’s cognitive development theory in a classroom, it is important to create an environment that promotes exploration and experiments so that children can obtain new information. For example, a teacher can explain to children that a method of trial and error is the most preferred one, which will clarify that making mistakes is not prohibited. Instead, children should understand that they are welcome to make assumptions and challenge the opinions of others. Another strategy is associated with problem-solving tasks that can be given to children to be discussed in pairs or groups (Ahmad et al., 2016). The way of organizing knowledge is called a schema, and the role of a teacher is to introduce students to and facilitate their motivation to study these units of information.

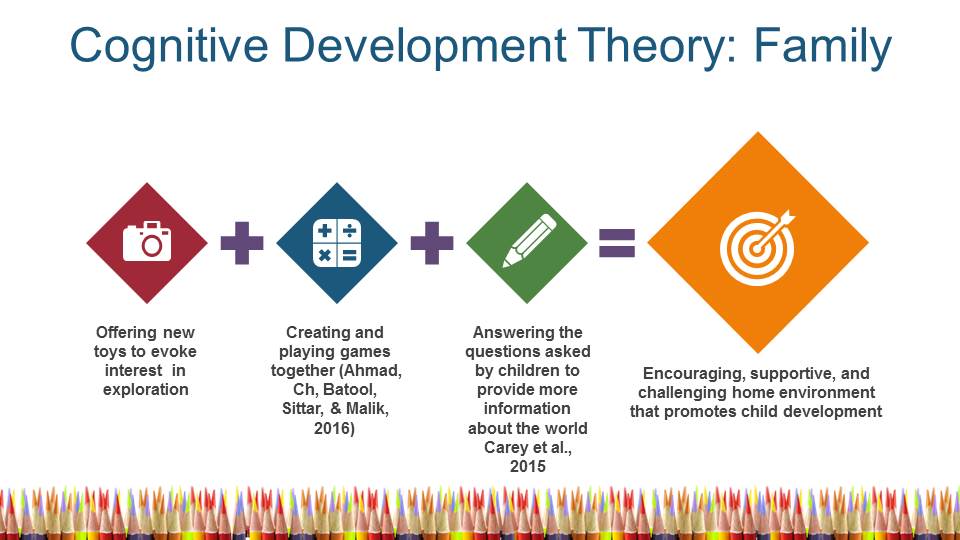
Cognitive Development Theory: Family
- Offering new toys to evoke interest in exploration;
- Creating and playing games together (Ahmad, Ch, Batool, Sittar, & Malik, 2016);
- Answering the questions asked by children to provide more information about the world Carey et al., 2015;
- Encouraging, supportive, and challenging home environment that promotes child development.
The implementation of the cognitive development theory in families is related to providing plenty of opportunities to discover the environment. For example, parents can give new toys and create new games to motivate the interest of their children in the exploration of the world. It is also critical to answer their questions about the surrounding objects, situations, and phenomena, thus stimulating their enthusiasm about learning (Carey et al., 2015). These strategies ensure adaptation that occurs through assimilation, accommodation, and equilibrium, while readiness to receiving certain knowledge should be taken into account in terms of the developmental stages.
Behavioral Development Theory
Learning occurs as a conditioned response to a stimuli (rewards, punishment, and reinforcement) (Cohen & Waite-Stupiansky, 2017).
The emergence of behaviorism led to an in-depth study of environmental influences and behavioral child development theories. Watson, Pavlov, and Skinner declared that reinforcement and association are the main processes that enable learning (Cohen & Waite-Stupiansky, 2017). According to their views, child development is a reaction to various stimuli, rewards, punishment, and reinforcement in the context of environmental interaction. The behavioral theories do not take into account internal feelings and thoughts, while prioritizing only experience.

Behavioral Development Theory: Classroom
- Token Economy System: Better emotional and behavioral outcomes in early childhood development (McLeod et al., 2017).
- Reducing Dysfunctional Behavior: Effective work with children having autism and ADHD.
In a classroom, one of the strategies to apply the behavioral theories is the use of a token system economy. It implies certain rewards (preferred items or activities) that are to be granted in response to the expected behavior. For example, students can obtain a token by listening, raising their hands to answer a question, or performing a task properly. The study by McLeod et al. (2017) shows that the token economy system allows improving emotional and behavioral outcomes in early childhood development.

Behavioral Development Theory: Family
Behavior Modification Strategy
Instead of saying that a child did “a good job,” it is significant to offer a specific reaction that promotes learning and growth, such as “the way you explained the answer is complete and I like it”.
In a home setting, families can consider a behavior modification strategy that is based on providing well-defined praise to the preferred behavior. In this case, a child’s behavior is encouraged in a positive way, and it gives the feeling that he or she is supported, which increases motivation to discover further. Also, the expected behavior should be clarified to a child in advance, including realistic consequences.

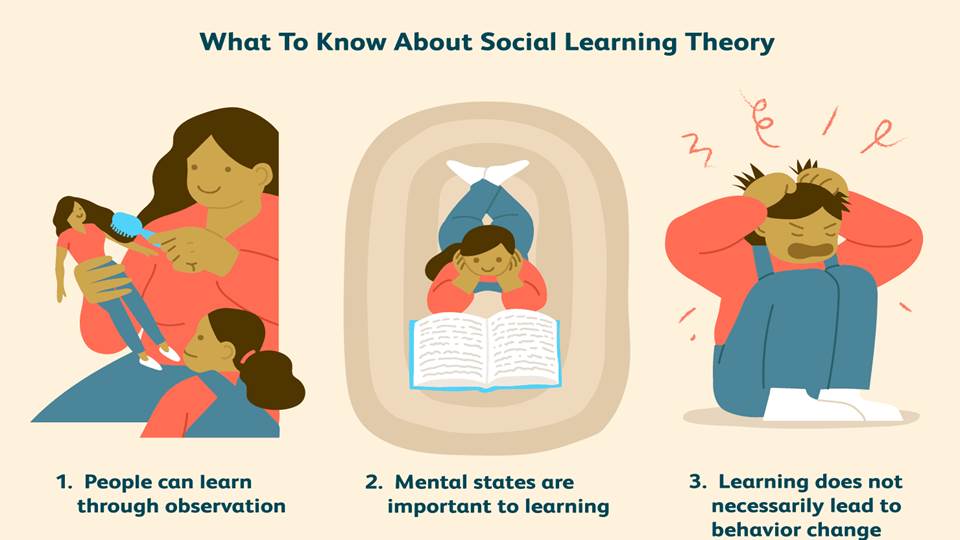
What To Know About Social Learning Theory
- People can learn through observation.
- Mental states are important to learning.
- Learning does not necessarily lead to behavior change.
The social learning theory by Bandura states that children learn through observation or based on examples. Bandura believes that mental functioning is better understood in terms of continuous interaction between behavioral, cognitive, and environmental factors. This means that behavior, personal aspects, and social influences are interdependent determinants. The environment influences behavior, but people also play an active role in creating the social environment and other circumstances that arise in their everyday interactions. Unlike Skinner, who almost always considered learning through direct experience, Bandura focuses on the role of learning through observation in acquiring behavioral skills.
Social Learning Theory: Classroom
- Role Modeling: Building Proper Relationships with Children and Fostering Learning Based on Observation.
- Personal Examples: Discussing Successes and Failures.
Since the social learning theory prioritizes examples, teachers can act as role models in a classroom. To help students with their tasks, teachers should build good relationships and ensure that children observe their performance to learn from it. It is also possible to share playing games, both physical and intellectual, demonstrating how to interact with others and act as a team. The importance of education can also be discussed by a teacher, which can be supported by personal examples, and children can learn on both successes and failures.
- Motivation is one of the key mediating processes that were distinguished by Bandura on his social learning theory.
- Children always create a link between a behavior and its outcome, also weighing the possible costs. In case the rewards are perceived as the ones that outweigh difficulties, a child is more likely to imitate the suggested role.
- Social media can be used to increase children’s motivation by engaging them in interesting activities (Deaton, 2015).
The will to complete a certain task directly depends on the potential punishment and rewards that are considered by an observing child. In case the rewards are perceived as the ones that outweigh difficulties, a child is more likely to imitate the suggested role.


Social Learning Theory: Family
For example, parents can explain to their children that good academic performance is associated with greater opportunities and improvements in social and economic spheres.
To support this idea, they can motivate children to practice everyday activities such as being responsible and concentrated on tasks (Grindal et al., 2016).
As for the strategies that can be applied by parents and caregivers at home, one should mention that children often base their behavior on the example of their parents since they perceive them as role models. ). As a result of previous experience, children can expect that certain behavior will have consequences that they value, while another one would produce an undesirable outcome.

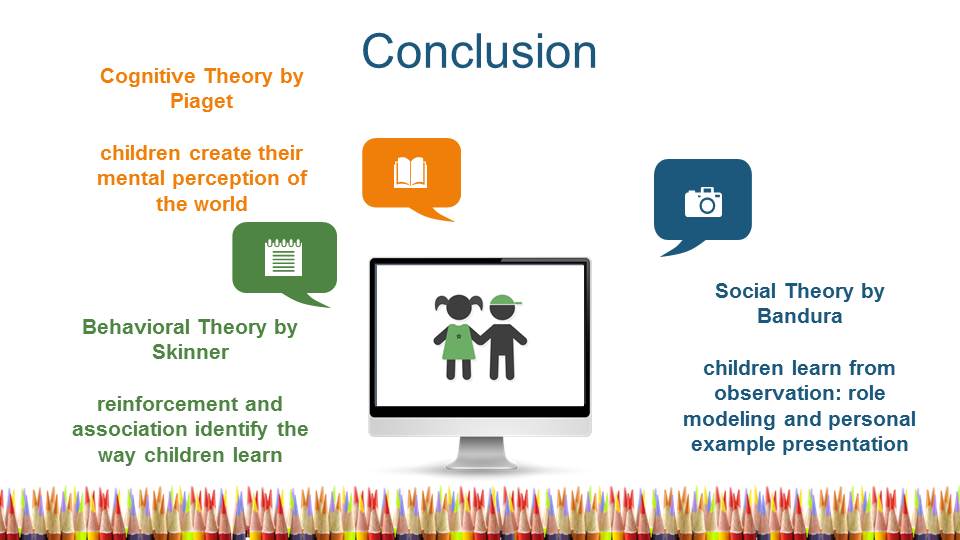
Conclusion
- Cognitive Theory by Piaget children create their mental perception of the world.
- Behavioral Theory by Skinner reinforcement and association identify the way children learn.
- Social Theory by Bandura children learn from observation: role modeling and personal example presentation.
Early childhood development theories are important to understand how children learn and how to improve this process. The social theory by Bandura implies that children learn from observation, which can be stimulated via role modeling and personal example presentation. In terms of the cognitive theory by Piaget, children create their mental perception of the world in the process of interacting with the surrounding environment. According to the behavioral learning theory by Skinner, Watson, and Pavlov, reinforcement and association identify the way children learn, which can be promoted by using the token economy system and the behavior modification strategy.
References
Ahmad, S., Ch, A. H., Batool, A., Sittar, K., & Malik, M. (2016). Play and cognitive development: Formal operational perspective of Piaget’s theory. Journal of Education and Practice, 7(28), 72-79.
Carey, S., Zaitchik, D., & Bascandziev, I. (2015). Theories of development: In dialog with Jean Piaget. Developmental Review, 38, 36-54.
Cohen, L. E., & Waite-Stupiansky, S. (2017). Theories of early childhood education: Developmental, behaviorist, and critical. New York, NY: Taylor & Francis.
Deaton, S. (2015). Social learning theory in the age of social media: Implications for educational practitioners. Journal of Educational Technology, 12(1), 1-6.
Grindal, T., Bowne, J. B., Yoshikawa, H., Schindler, H. S., Duncan, G. J., Magnuson, K., & Shonkoff, J. P. (2016). The added impact of parenting education in early childhood education programs: A meta-analysis. Children and Youth Services Review, 70, 238-249.
McLeod, B. D., Sutherland, K. S., Martinez, R. G., Conroy, M. A., Snyder, P. A., & Southam-Gerow, M. A. (2017). Identifying common practice elements to improve social, emotional, and behavioral outcomes of young children in early childhood classrooms. Prevention Science, 18(2), 204-213.