Introduction
Background
The FRBNY Company used to follow the policy of seizing monopoly over the target market as well. However, FRBNY stopped complying with the course that it had set for itself after the company experienced several problems in its functioning and the general competitiveness rate. In other words, by monopolizing the market and seizing the power in the specified environment, a company sets a trap for itself, as it designs the standards that may become too high to uphold in a complete lack of competition. Additionally, the fact that banks, when monopolizing the market, withhold information from the rest of the companies concerned, may serve as a major obstacle in promoting further development of the market.
Purpose
The purpose of the study is to prove that the monopolization of the target market by the FRBNY organization or any other company has affected the operations of other firms in the New York government securities’ market setting.
Scope
Because of the complexity of the issue and the necessity to consider a large variety of factors that can be viewed as the effects of monopolization and affect the operations of other companies in the specified area, the study scope was reduced to the observations of a particular organization. However, the effects of monopolization on the market, in general, will also be touched upon in the Literature review section.
Objectives
The location of the influence, which monopolization has on the pricing and stability of the U.S. government securities’ market through the analysis of the changes that the FRBNY underwent after the loss of its monopoly, is the prime objective of the study.
The identification of negative and positive effects of monopolization on the operations of minor companies in the realm of the government securities market can be viewed as the secondary objective of the study.
Defining the current tendencies regarding monopolization in the specified market is the third objective of the research. It is crucial that the rates of monopolization should be located and that it should be stated whether the specified phenomenon engulfs the U.S. market or is gradually subsiding.
Finally, the fourth objective of the study concerns creating a forecast concerning the future changes in the specified area and the scale of monopolization, which the U.S. government securities’ market will take, as well as the positive and negative effects that this process will have on prices and stability of the market and the companies that have entered it or are going to.
Hypotheses
- H1. It is assumed that the process of monopolization affects the U.S. Government Securities Market considerably by increasing prices for the stocks and, therefore, creating an extraordinarily competitive environment.
- H2. The monopolization of the U.S. Government Securities Market is likely to lead to a drastic drop in the stability rates, as the rapid increase in prices will affect the liquidity rates of the products and, therefore, trigger the untimely demise of new entrants, as well as SMEs.
- H3. The monopolization process also affects the companies that behold the power in the monopolized market, as the process leads to the lack of competition, poor market saturation, and the inevitable drop in the company’s productivity rates.
Literature Review
Government Securities Markets: Definition
The very concept of government security is traditionally identified as the debt securities that are “crucial for effective public debt management” (Glaessner and Kanur 21).
Government Securities Markets: Organization
Traditionally, the phenomenon of a Government Security Market is represented by the environment, in which the bonds of the United States government are sold and bought. Additionally, the concept of repayment upon maturity is typically represented in the specified market (Mankiw 22).
Monopolistic Practices: Typology
Monopolistic practices are usually characterized as the means to reduce competition in a specific market. As a rule, perfect and imperfect, private and public, discriminating, legal, natural and technological monopolies are distinguished in the contemporary market (Mankiw 321). Perfect monopolies can be defined as the phenomenon of a single company seizing the power over a certain market, whereas imperfect monopolies embrace the instances, in which other organizations also have certain competitiveness rates in the target environment and, therefore, enter the market. Private monopolies embrace the instances of private companies seizing power over a market while public ones involve the cases, in which government controls the market under analysis (Corder 38).Natural monopolies incorporate the instances of monopolies for natural resources; technological ones presuppose that a certain product dominates the market with no analogies available, while the joint monopoly occurs once two or more companies merge to create a monopoly in the target market (Mankiw 217).
Apart from affecting the competitiveness rates of small and medium entrepreneurships in the target market, monopolistic practices affect the productivity of the market and the companies that operate in it. Additionally, monopolistic tendencies in a market are known to affect the prices for products and services delivered by the corresponding organizations.
When considering the example of FRBNY, one may assume that the type of monopoly, which can be observed in the target market, can be defined as the public monopoly (Ramanadham 112) Indeed, according to the existing definition, the public monopoly is the monopoly of the government on specific assets (Corder 57). One must admit, though, that, of all monopoly types, the one in question is traditionally viewed as the least harmful. However, when it comes to a more detailed analysis of the subject matter, one will realize that the public monopoly can be replaced with private monopoly once the corresponding manipulations, such as the process of privatization (Ramanadham 78). As a recent study warns, with the transformation of the public monopoly into the private one, the prices for the target product are going to rise to the point, where no possible competition may exist and where the organization left in charge will inevitably face a failure in sustaining the required economic environment.
Government Securities’ Markets: Stability Factors
A closer look at the Government Securities’ Market will show that the balance of the specified area is disrupted very easily (Corder 24). In other words, the attitude toward the idea of introducing monopoly and public governance into the realm of the Government Securities’ market has been altered significantly after the discovery of its side effects: “Proponents of “free banking” and public choice critics of central banking claim that the monopoly on note issue creates irresistible inflationary temptations for elected officials” (Corder 72). The above-mentioned statement can be viewed as a graphic example of the fact that monopoly as a system of managing trade relations in the Government Securities’ Market cannot possibly be sustainable and, therefore, must be viewed as inconsistent and, therefore, harmful to the aforementioned environment.
FRBNY: Recent Changes
The changes, which the FRBNY organization has suffered recently, can be viewed as rather harsh given the economic environment, in which the organization has been operating. Because of the need to adapt to the requirements of the global economy, which defined the course of the American economy to a considerable degree, the company lacked the strength necessary for the enhancement of the company’s competitiveness.
Particularly, FRBNY has experienced a comparatively short period of its monopolistic revival in the mid-2000s. According to the existing reports, the company nearly collapsed under the weight of its own restrictions in terms of prices. Moreover, the company seemed to have problems upholding the standards that it set; as a result, the pricing policy, which FRBNY employed in the 2000s, proved to be incoherent and lacking efficacy (“Consolidated Financial Statements” 11).
The further introduction of monopoly for the government securities in the U.S. market only served as the means to aggravate the situation for FRBNY; according to the statements issued by the organization, the lack of competitiveness, which it can be defined by in the realm of a consistent price increase, has triggered a substantial drop in the overall quality of the organization’s performance:
An increase in isolation in either the discount rate or the property capitalization rate, which is the ratio of the net operating income produced by an asset and its current fair value, would result in a decrease in the fair value measurement. (“Consolidated Financial Statements” 47)
More importantly, the lack of stability in the target market has also affected the organization significantly. While FRBNY undermined its own financial and economic stability by forcing itself to gain monopoly over the U.S. Government Securities’ Market, it has also suffered a severe blow from the companies that gained monopoly over the government securities once the organization was out of the picture (Corder 57).
Methodology
The issue in question was researched as a case study, with a specific company as an example to consider and a model to develop a cohesive strategy on. To address the subject matter closely and have a clear example of what operating in the specified market presupposes, as well as what aberrations may emerge in the specified area and how to deal with them.
Research Method
Seeing that there is no practical need for quantifying the results throughout the research, a qualitative approach to the analysis is suggested. However, at some point, the basic statistical tools, such as the definition of the standard deviation, will have to be carried out so that the results could be compared successfully. Additionally, a correlation and regression analysis will have to be conducted to define future trends. A case study will be carried out in the environment of a Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Data Collection
The data required for the research will be collected with the help of an analysis of the company’s records. Therefore, the reports issued by the organization from 2000 to 2015 will have to be analyzed.
Data Analysis
The information processed in the course of the research will be distributed into several key groups, particularly, the group with the data indicating financial changes in the specified markets and the group that involves stability fluctuations. The information in the specified groups will be split into two key parts, i.e., the results delivered prior to the introduction of the monopolistic practices into the target area, and the implications of the specified practices. Afterward, the results retrieved in the course of the study will be compared.
To compare the study outcomes efficiently, one will have to adopt basic statistical tools, such as the location of the standard deviation of the indices obtained in the course of the study. In addition, a correlation/regression analysis will have to be conducted so that tendencies in the further development of the bank, as well as the future effects of monopoly on the entrepreneurship in question, could be located.
Theoretical Framework
The analysis of the study will be based on the tenets of the FRB/US Model. According to the standard description thereof, “The FRB/US model of the U.S. economy is one of several that Federal Reserve Board staff consults for forecasting and the analysis of macroeconomic issues, including both monetary and fiscal policy” (Brayton, Laubach, and Reifschneider par. 1). Designed as the tool for optimizing the processes that occur in the U.S. economy environment and managing the key challenges that the introduction to the global economy presupposes, the above-mentioned model can be viewed as a tool for defining the effects of changes in the specified area on a variety of levels from the level of American households to the global one.
Results Discussion
As the results of the company’s productivity rates show, the enhancement of monopoly in the realm of the U.S. Government Securities’ Market leads to a variety of negative experiences for the companies that are forced to work in the same environment (Corder 61). The quantitative analysis of the current tendencies in the designated area also shows that monopolization is likely to become an issue in the contemporary environment. Despite the tendency for most markets to globalize, the target one traditionally stays within the borders of one state and, therefore, is quite resilient to the outside factors (Mankiw 97).
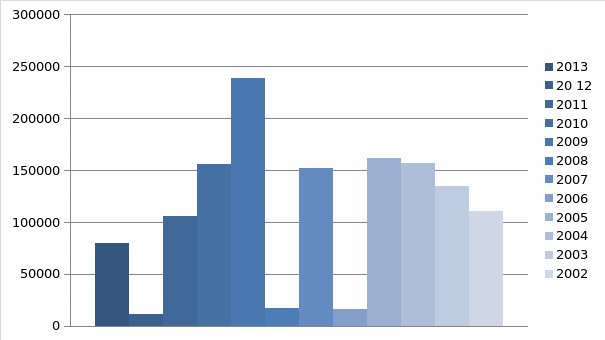
At some point, seizing monopoly over the government securities could be viewed as favorable for FRBNY: “Treasury securities originate in the primary market, where the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, in its capacity as fiscal agent for the U.S.” (Potter par. 5). The statistical data acquired in the course of the research also indicates that the organization has faced a short period of revival once it seized the monopoly in the target market (Manki2 16). However, as the further performance of the organization shows, the company started experiencing significant difficulties in maintaining its status as the leading organization and, thus, lost its monopoly over the market in question. The specified information shows that the very concept of monopoly is unsustainable in the environment of the global market; ripping other companies of the chances to survive in the U.S. Government Securities’ Market, it makes a company self-destructive.
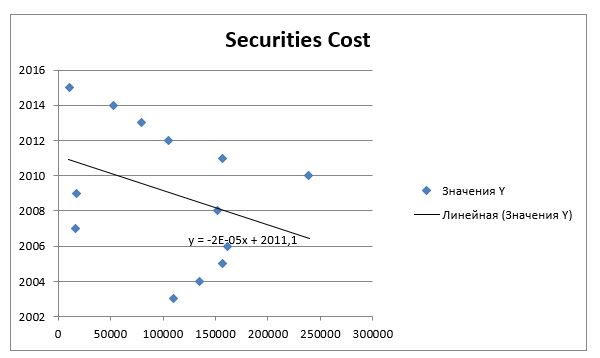
Indeed, according to the chart provided above, the process of the U.S. Securities’ Market globalization will occur at a rather steady pace in the foreseeable future. As the phenomenon in question can be considered fairly negative to the overall stability of the market and the sustainability of the organizations working in it, the forecasts for the future development of the U.S. Government Securities’ Market is rather negative. Unless the process of monopolization is discontinued, the United States may face the threat of an economic crisis in the specified area. Ousted by the companies that monopolize the U.S. Securities’ Market, SMEs will be no longer able to contribute to the economic growth; as a result, the market may face a disruption and even further demise.
Conclusion
Summary
The process of monopolization, which has captured the U.S. Government Securities’ Market, can be viewed as highly negative, as the case of FRBNY shows in a very graphic manner. While the organization can be viewed as profitable, the fact that it may develop in an unstable market shows that monopoly can hardly be viewed as a positive tendency in the Government Securities’ Market.
Implications
The study has shown that the process of monopolization of the target market is likely to lead to a no-win situation for both the company that seizes monopoly over the U.S. Government Securities’ Market and the ones that will be forced to strive in the environment of enhanced competition and increased prices.
The Lack of stability, which can also be viewed as one of the primary effects of monopolization, is also likely to shatter the U.S. economy, thus, triggering the further collapse of the market and the companies that operate in it.
Last, but not least, the fact that monopolization seems to be a self-destructing activity in the contemporary global market deserves to be mentioned. Therefore, no matter how hard an organization may try to seize monopoly over the market under analysis, it will collapse sooner or later under the weight of its own inconsistently high prices and the lack of stability and balance in the U.S. Government Securities’ Market.
Therefore, it can be assumed that no drastic actions will be required to address the problem in question. Instead, the negative aspects of monopoly should be exposed to the companies, which attempt at seizing control over the U.S. Government Securities’ Market; once understanding the implications of their choice, including the ones that affect the entire market, a company, such as FRBNY, must refrain from making the process of monopolization its next goal.
References
Brayton, Flint, Thomas Laubach, and David Reifschneider 2014, The FRB/US Model: A Tool for Macroeconomic Policy Analysis. Web.
Consolidated Financial Statements 2014. Web.
Corder, Kevin. Central Bank Autonomy: The Federal Reserve System in American Politics. New York City, New York: Routledge, 2014. Print.
Glaessner, Thomas C. and Zeynep Kanur. Two Case Studies on Electronic Distribution of Government Securities: The U.S. Treasury Direct System: The Philippine Expanded Small Investors Program. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications, 2014. Print.
Mankiw, Gregory. Principles of Microeconomics. Boston, Massaachusetts: Cengage Learning, 2014. Print.
Potter, Simon 2015, Challenges Posed by the Evolution of the Treasury Market. Web.
Ramanadham, Venkata V. Privatization and After: Monitoring and Regulation. New York City, New York: Routledge, 2012. Print.