Key Management Policy
Policy Statement
The enterprising key management policy for Slack Communications will require the company to use technologies for encrypting sensitive and confidential data for protecting the integrity of customers as well as employees. The policy will apply to all employees and affiliates to address the encryption policy and control organizational data.
Reason for Policy
The incorporation of enterprising key management policy is high on the corporate agenda as to the increase in security breaches of large corporations. In 2016 only, Centene Corporation (healthcare sector), Federal Bureau of Investigation (Department of Homeland Security), Seagate Technology, Internal Revenue Service, LinkedIn, 21st Century Oncology, Office of Child Support Enforcement, and dozens other companies and organizations reported security breaches and thefts of customer/employee information. Thus, there is a high need for Slack Communication to implement a cohesive EKM strategy for protecting its customers and employees from fraudulent security breaches and making sure that the stolen data can be recovered. Moreover, Slack communications allow users to “manage security, policy, and compliance across all of Slack” (Slack, n.d.), which is another reason for policy implementation.
Definitions
Enterprising key management (EKM) has emerged as a result of high-profile data breaches and identity thefts in large organizations. EKM is defined as a framework of efforts targeted at providing centralized management (e.g. key generation, backup, and recovery) for making sure that the lost data can always be recovered (Pate, 2009). Also, EKM is effective in helping companies manage and modify their keys in the course of the life cycle. Key management policy is defined as the secure administration of cryptographic keys. Cryptographic keys are data strings composed of binary zeroes and ones that make up cryptographic algorithms used for manufacturing “ciphertext” output from “cleartext” input (KPMG, 2002).
Responsible Executive and Office
The It department manager will be responsible for the execution of the policy since he or she has access to all procedures the department of technology implements as well as possesses knowledge and skills regarding EKM.
Who is Affected?
The IT department will experience the most impact from the policy because employees there are responsible for policy execution. Also, customers will be affected by the changes in existing policies as well as other employees that will be required to comply with the policy.
Procedures
General
- Establishment of a cohesive key management lifecycle: generation, distribution, usage, and storage (operational, backup, and archive).
- Key recovery procedures;
- Key reissuing;
- Key Escrow (BITS, 2008);
- Procedures of key retirement: replacement, deregistration, revocation, and deletion (BITS, 2008).
Rules of Behavior
- Following the established guidelines and procedures;
- Nondisclosure of the policy details to third parties;
- IT Department Manager – communicating with employees about the policy importance;
- Commitment to the policy’s success.
Training
All employees in the IT department should be trained on how to incorporate the policy. Cryptanalysis, the transformation of plaintext data into ciphertext and vice versa, verification of digital signatures, verifications of authentication codes, and decryption are all skills the department needs to learn.
Enforcement
The policy will be enforced through strict control and auditing. Two kinds of auditing should take place during EKM: the security plan and the implemented procedures monitoring for ensuring that they support the policy, and the audit of a protective mechanism for the level of security.
Response to Violations and Compliance Issues
Any violations of the policy should be monitored and controlled with the help of Slack’s IT department manager. Perfect compliance with the policy will be incentivised to motivate employees to maintain their behavior. No punishments for non-compliance will be enforced. However, the management will conduct educating discussions to help employees understand the importance of the policy.
Key Management Plan
Introduction
Data encryption is an issue that is growing at a high rate. However, it can be solved through the process of management and diversification of keys. The more different the keys are, the better is a company’s granularity and security and thus greater the complexity (Barker, Barker, Burr, Polk, & Smid, 2012). It is assumed that the implementation of the enterprising key management plan (EKM plan) will enhance the capabilities of the company (Slack Communications) to encrypt keys and be more effective in protecting data from attacks. In this plan, developers and users will be presented with choices of cryptographic mechanisms. It is crucial to note that inappropriate choices of security efforts may lead to the lack of data protection.
The integration of the plan will occur in the context of the Slack Communications software, which is a cloud-based set of collaborative tools and services such as chat rooms (public and personal), searchable content, third-party services, and interactions. The context in which Slack Communications operates calls for the enforcement of a cohesive action plan for protecting corporate and customer data.
Purpose
The EKM plan will contain recommendations for managers to address the issues associated with the lack of data protection efforts. These recommendations will expand on the processes of guidance, providing background information and developing a framework for supporting the best practices for choosing and using cryptographic mechanisms (Barker et al., 2012). The plan will address the issues associated with the modernization and updating of the main management systems, their integration into the everyday processes, maintenance, risks, benefits, and operation.
When it comes to giving advice regarding integrity and confidentiality of payments and billings, the receiving party should use the same degree of care that it uses for protecting the confidentiality of information. Furthermore, a cohesive key management strategy should account for the maintenance of appropriate safeguards (physical, administrative, and technical) for protecting the integrity of customer data. Regulations and guidelines that the plan should incorporate will relate to the existing policies regarding data protection. For instance, the plan should account for the Financial Services Modernizations Act that regulates the use, collection, and disclosure of customers’ financial information (Jolly, 2016). The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act for regulating medical information, the Fair Credit Reporting Act, which applies ti consumer reporting agencies, the Electronic Communications Privacy Act that accounts for the interception of electronic communications and computer tampering (Jolly, 2016). Overall, the plan should be aligned with the mentioned policies and regulations to ensure that customers are protected and that the company stays away from security breaches.
Workplace Scenario
Current Slack Communications key management system
Key authentication is a process used for solving the issue of authenticating keys of one person to whom another person is talking. Authentication usually occurs when a key was shared between two or more users over a secure channel of communication. In Slack Communications, key authentication takes place by using symmetric key cryptography to ensure that there is no “middle man” that is trying to get valuable data from the communication. Encryption of keys is a process of generating random strings that are created for data scrambling and unscrambling. Such strings are created with the help of algorithms used for ensuring that every key is unique and cannot be predicted. The current encryption process in Slack Communications implies the usage of symmetric forms of encryption systems that use one password to serve as both encryptor and decryptor (BITS, 2008). Although such a way of key encryption is safe, it can be improved. The current system is similar to the diagram shown below:
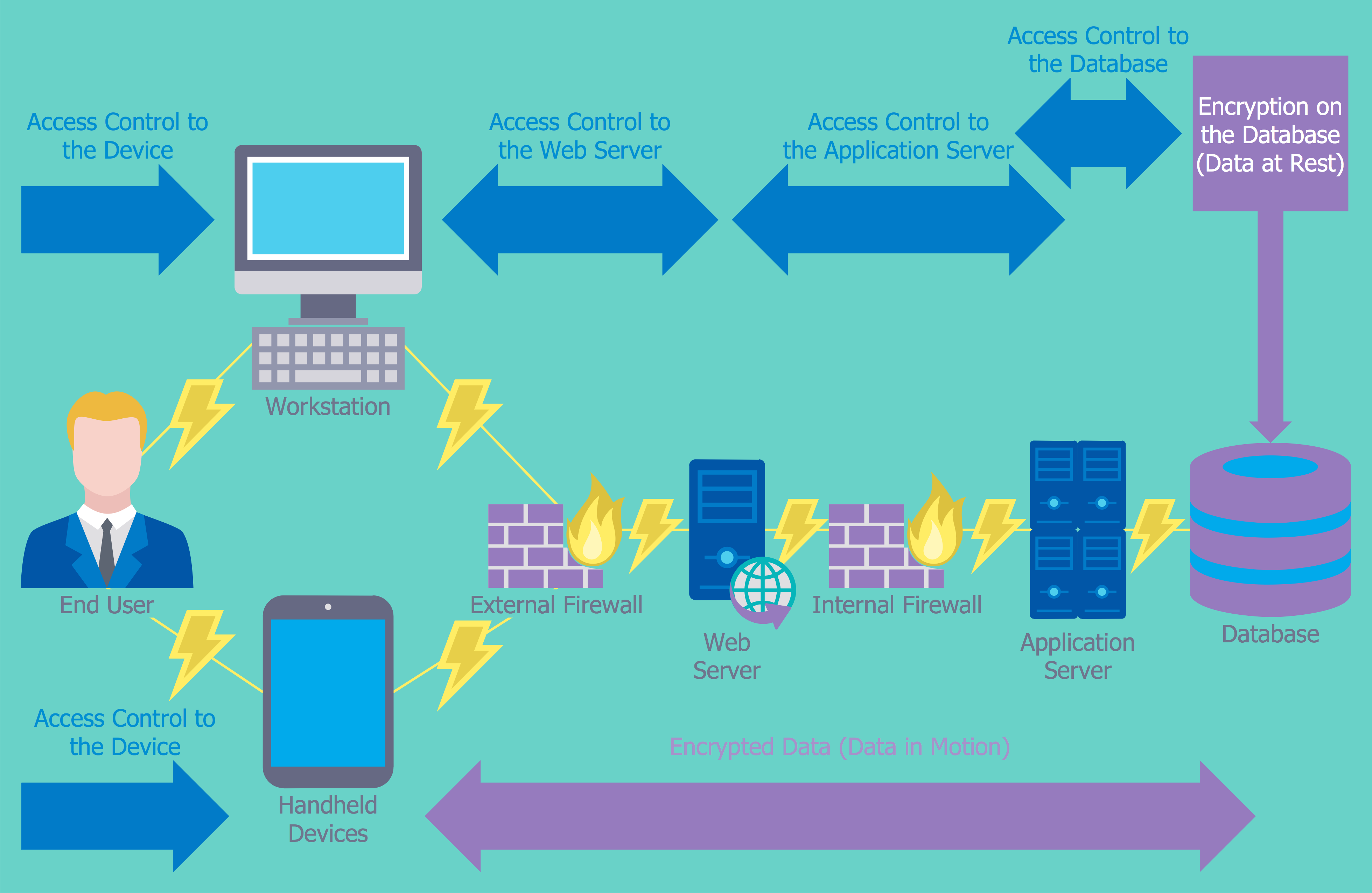
For backing up keys and protecting from ransomware, Slack Communications installed modern backup software Symantec Corp.’s Backup Exec with included snapshot management, cloud support, and VM protection. However, Symantec Corp.’s Backup Exec can only address the issue of lost data if the company is not using backups using other sites (“How to manage encryption keys,” n.d.). Disaster recovery is the most important point in key management since a company should be able to restore its operations as quickly as possible. To be prepared, Slack Communications currently has a business continuity plan that incorporates various processes that represent the state of the security at a particular point in time. The disaster recovery plan also includes specific prioritized goals and performance objectives such as:
- Protecting the safety of employees, customers, and partners;
- Minimizing the disruption of the services;
- Protecting corporate facilities and electronic information;
- Protecting the reputation and the image of the organization (Koeppel, 2016).
Locations and systems where data is:
- At rest (stored) – stored on hard drives in a relatively secure state (Raglione, 2015).
- At use – more vulnerable than data at rest since it should be accessible to those users that may need it (Raglione, 2015).
- In motion – the most vulnerable state of data; requires specific protection capabilities (Raglione, 2015).
When it comes to the identification of locations of where data is, organizations should conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify possible threats of data breaches that can occur when data is in different locations. In order to start mitigating possible risks, the management should first answer questions such as “how the data not in use is stored?” or “what mechanisms the company uses for data transportation from one location to another?”
Modernized Key Management System and System Implementation
Information for the CISO
Types of encryption: symmetric, asymmetric, hashing. In symmetric encryption, decryption and encryption occur with the help of the same key. In asymmetric encryption, a different key is used for decryption and encryption. Advantages of symmetric cryptosystems are:
- Higher speed;
- Password authentication for proving identity;
- Low chances of data being decrypted.
Disadvantages:
- Inability to provide non-repudiative digital signatures.
Advantages of asymmetric cryptosystems:
- No need in keys exchange;
- No key distribution problems;
- Ability to non-repudiative digital signatures;
- Increased security.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Speed.
Hashing is a method that helps generate fixed length value that summarizes the contents of a message or a file (“Types of encryption,” n.d.). Cryptography and cryptanalysis can be used for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality. Cryptographic systems were developed to protect information from privacy breaches during various processes. Moreover, companies can use cryptography for ensuring that their data is not altered or viewed by the third parties.
Examples and explanations of issues
With regards to gaps in key management in existing corporations, there are several issues that should be addressed. Among these issues are the increased exposure to keys, inconsistent enforcement of policies, lack of cohesive administration, encryption inefficiency, and lack of unified auditing and remediation. As results from the mentioned issues, some cryptographic risks can occur. The most obvious are the danger of losing keys, implementation bugs, misplaced confidence in the security of keys, and inefficient cryptographic infrastructure. An example of cryptographic attacks can include password, analytic, implementation, statistical, “meet-in-the-middle” attacks, and many others. For instance, an analytic cryptographic attack represents an algebraic mathematical manipulation targeted at reducing the cryptographic algorithm’s complexity (APAC, 2010). To solve the identified issues and close the gaps in key management, companies should ensure limited exposure to keys, enforcement of consistent policies, ensure cohesive administration, maintain efficient encryption as well as incorporate unified auditing procedures.
Specific plan
The overall architecture of the key management plan will rely on the centralized key management and policy enforcement. The key components of the plan should include:
- Procedures for decreasing the exposure of keys;
- Ensuring consistent implementation of policies;
- Processes for maintaining streamline administration with regards to the encryption efficiency;
- Development of a unified auditing strategy;
- Involving tokenization support (Nash, n.d.).
Among the possible solutions, leveraging purpose-built security products and services can be a beneficial solution. For maximizing the protection of key management infrastructure, it is recommended for Slack Communications to move the key management processes from the systems of general purpose. For instance, a key manager based on software usually saves keys together with encrypted data, which may pose availability risks. Instead, Slack Communications should make sure that keys are stored and managed within the framework of infrastructure that has been designed with security in mind (Nash, n.d.). Another solution may be the broad integration of services and systems across the entire organization. In this case, enterprise key management is an approach that cohesively manages all keys within an organization.
If to compare the two solutions, leveraging purpose-built security products can be beneficial for establishing a tamper-proof system of hardware security that will prevent data from being stolen. On the other hand, this may be more costly. Broad integration is a solution for the cohesive key management in a vast range of areas; however, it can be ineffective when the management pays unequal attention to each area, leading to the lack of cohesion.
The starting cost for the implementation of the solution is $150,000 that should be spent in the course of six months. The costs will include staffing, training, integration of new technologies, and paying contractors. The skills required for the plan implementation include programming, planning, decision-making, and management skills. $100,000 will be needed for maintaining the integrated solutions over the period of another six months, with the requirement for the same skills identified previously. The plan will support the Electronic Communications Privacy Act and the Financial Services Modernizations Act. In the process of development, the management plan will account for the key points of the mentioned regulations to make sure to protect the rights of customers, employees, and contractors.
Implementation
When it comes to the challenges other enterprises face when implementing key management systems, user training and acceptance, system administration and maintenance, as well as key recovery are the most prominent. To overcome the challenge of user training and acceptance, it is crucial to develop a benchmarking system that will address users’ difficulties and concerns. Second, to overcome the challenge of system administration and key recovery, the key management procedures should be aligned with the existing infrastructure (Nash, n.d.).
Operation
As found from the research, it is paramount to have CRL implanted in the management plan it is also important to make sure there is an NDA in place especially dealing with third parties. When it comes to the operation, the processes within the key management system will be as presented in the flowchart below:
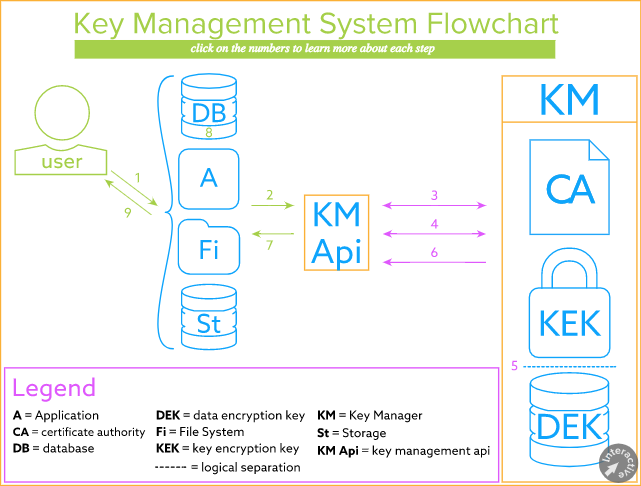
A user will request access to encrypted data, and the system will send a retrieval encryption key request to the client (key management API). Then, the client and KM will verify the certificates, and after their acceptance, there will be a secure connection created between the key manager and the key management API. Then, the key manager will decrypt the requested data encryption key with the key encryption key. The next step is sending the key to the client, who then sends it to the system.
Maintenance
As enterprise tools, Slack Communications will be required to support the following maintenance features of the key management system:
- Restorations and backups – the company will have to deal with backup and recovery procedures securely. This can be achieved with the help of encrypting the whole key database before backing it up.
- Balancing loads – it is important to ensure that key management tools should be available all the time and in high volumes, so there is a need for load balancing options for meeting the demands of the system.
Benefits and Risks
The three key benefits of implementing enterprise key management are preserving the reputation of the company, credibility, and mobility. Because the loss of information has a tremendous impact on the way a business is perceived by customers, the introduction of EKM can be a great advantage. With the protection of clients with reliable key management practices comes credibility while the convenient movement of data to virtualized environments results in immense mobility. Among the possible risks, the loss of keys and the lack of unified tools for reducing overhead are the most prominent.
Recommendations
In summary, it is crucial to note that enterprising key management is not a solution to all issues associated with security. The IT department management should be aware of the possible risks and ways to reduce them in order to be truly effective when developing an EKM plan. It is recommended for Slack Communications to follow the outlined plan for achieving the ultimate goal of securing the exchange of information within the enterprise. With the identified risks and challenges, Slack Communications will be able to become proficient in not only keeping the information encrypted but also to preserve its integrity while in use and in motion. Through the proper management of the encryption keys, the stakeholders of the company will be in full control of the data despite who is using or sharing the existing key management infrastructure. In the case when the company’s data security awareness reaches every employee and department, the enterprise will not only be successful in meeting the regulation of compliance but also become very effective in benefiting the security of data.
References
Barker, E., Barker, W., Burr, W., Polk, W., & Smid, M. (2012). Recommendation for key management. Web.
BITS. (2008). Enterprise key management. Web.
How to manage encryption keys. (n.d.). Web.
Jolly, I. (2016). Data protection in the United States: Overview. Web.
Key encryption system diagram [Image]. (n.d.). Web.
Key management system flowchart [Image]. (n.d.). Web.
Koeppel, H. (2016). A disaster recovery/business continuity plan for the data breach age. Web.
KPMG. (2002). Key management policy and practice framework. Web.
Nash, R. (n.d.). Key management challenges and best practices. Web.
Pate, S. (2009). Enterprise key management deciphered. Web.
Raglione, A. (2015). Best practices: Security data at rest, in use, and in motion. Web.
Slack. (n.d.). Let’s get to work. Web.
Types of encryption. (n.d.). Web.