Executive Summary
Zara is one of the successful fast fashion brands in the global apparel industry. The brand is dominant in European and North American markets. As a strategic move to expand its market share, it has decided to explore the Chinese market. China is home to over 1.3 billion people. With an economy that is growing very fast compared with other leading economies, it is clear that the country has a large population falling under the middle and upper-middle class.
The purchasing power of individual Chinese companies has been increasing over the past three decades. That is why many international firms are currently struggling to exploit this market. The primary goal of this paper was to analyze strategic advantages of international fashion brands – which, in this case, is Zara – and determine whether these advantages would apply in the Chinese market. The paper also looked at the risks that the fast fashion brand has to face in the Chinese market and ways in which these risks can be managed to help the organisations consolidate its advantages. The researcher collected data from various secondary sources.
Books, journal articles, and other reliable online sources proved critical for this project. Data from these sources were used to inform the discussion, conclusion, and recommendations. The paper provides a number of ways in which Zara – or any other fast fashion brand operating in China – can overcome the challenges in the Chinese market and consolidate their advantages.
The Chinese market has a number of opportunities that fast fashion brands such as Zara can tap into and achieve great success. However, the success can only be achieved if the firm’s internal strength can enable it to do so. One of the biggest advantages that Zara has over some of its local competitors is efficiency in its supply chain. In a market where competition is high, time is of the essence. The speed with which an entity can develop a new product and deliver it to the market before the concept is copied by rival firms is critical.
Zara has proven that it has that capacity. It takes the company only fifteen days to transform a good idea into a product and make it available in the market. This competitive advantage is applicable in China, especially given that a majority of the other companies are only keen on copying what the top players are doing. By the time they come up with similar products, Zara would have a large base of loyal customers earning it attractive revenues.
The company has also developed a unique ability to understand the changing market trends. In the fashion market, taste and preferences keep changing, and it is vital for firms to understand the change and act upon it in time. Zara is known to provide trendy products in line with the changing customer needs. The company has also learned how to deal with the cultural issues in China to ensure that its products remain favourable in the market.
The Chinese market presents a number of risks that the management of Zara should understand and know how to deal with in an effective manner. Competition is one of the top risks that the management must learn to manage. Zara has been facing the stiff competition in its operations in Europe and North America for decades. However, it is going to face even stiffer competition in China because of the high number of players in the industry.
The market has numerous local and international companies offering the same products. Cultural difference is another issue that this organization will face in the new market. Although globalization has helped eliminate the geographic barrier, culture is still a major issue. The Chinese consumer culture is very different from that in Europe and North America. It will force Zara to learn the local culture and adjust its operations in line with the Chinese culture.
In the discussion, it is also clear that there is the problem of rampant copyright abuse in China. Many unscrupulous individuals and firms are keen on stealing ideas from other companies and making money out of it. Others manufacture fake products and use top brands to deceive unsuspecting customers in the market. The practice can eliminate trust between a top brand and its customers when they realize that the product they bought was not of the same quality as that which they expected. If not addressed in time, it may make a successful company lose its strong base of loyal customers in the market.
To achieve success in the Chinese market, Zara will need to find ways of coping with the risks while at the same time taking full advantage over its market rivals. The study suggests that in a highly competitive business environment, creativity and innovation are one of the best ways of staying ahead of market rivals. Zara needs to have a team of highly innovative workforce in the Chinese market. It should encourage its employees to come up with new ideas on how to solve various market problems.
Having new ways of solving current problems in a cost-effective manner is important. The company will also need to understand the changing tastes and preferences of its customers in this market. Instead of waiting for other companies to come up with new products, Zara should always try to find out emerging market needs and develop suitable products that can meet these needs. It will benefit by being the innovator and market leader in the Chinese first fashion market. Instead of targeting the entire Chinese market with its products, Zara should identify market segments whose needs it is capable of meeting in the best manner possible.
The study also recommends that this company should work closely with top online retailers in China to increase its sales. A team of scouts should always maintain vigilance at this company to fight possible cases of other firms using this brand to sell their sub-standard products in the market.
Introduction
Background
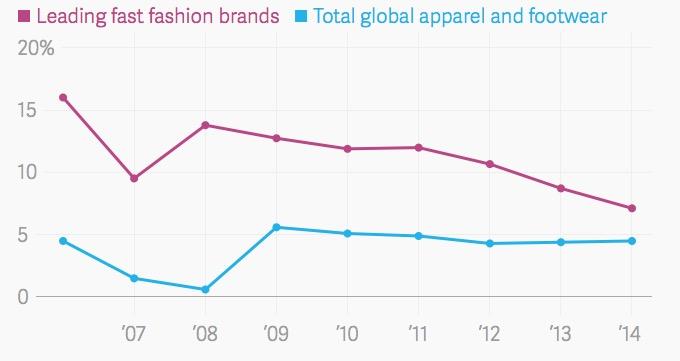
Since the international financial crisis in 2008, the global economy has been in the doldrums and the recovery is slow. Even in this context, many fast fashion brands are still stable development on a global scale, accelerate the expansion and sales continued to grow, although the growth rate slowed down. According to statistics, after the financial crisis in 2008, fast fashion brand sales growth rate remained at about 14%, while that rate of total global apparel and footwear was down to almost zero (Bain 2016). This difference shows that, whether in the fast retailing market, or clothing market, fast fashion brands’ competitiveness is could not be compared. As of 2014, the fast fashion industry sales growth rate is still higher than the global apparel and footwear overall growth rate of about 2 percentage points (Bain 2016).
Zara is from Inditex Group, which is one of the most successful fast fashion brands, the latest fashion design and the fast supply system help the company won the favour of customers. According to Inditex Group 2016 annual report, Zara’s 2016 annual net sales reached 15,395 million Euros, and opened 51new stores all over the world (Inditex.com 2017a). Moreover, Zara has also been recognized by authority agencies. In 2016, Zara ranked 27th of the Best Global Brands, ranked 53rd among The World’s Most Valuable Brands released by Forbes, and ranked 35th among Brand Z Top 100 Most Valuable Global Brands released by Millward Brown (Inditex.com 2017a).
However, with the saturation of the European and US markets, the growth of the fast fashion industry has slowed (Bain 2016). Coupled with the recent years, there are some problems shown in the European market. Both frequent terrorist attacks, and the United Kingdom departure from the European Union brought a certain of destabilizing factors to European economy. Therefore, for fast fashion brands, the expansion to the Asian market become particularly important, of which the Chinese market is one of the most promising markets.
After the financial crisis, the steady and sustained development of the Chinese market has aroused widespread concern. Chinese market’s sheer size and scale make it increasingly attractive to multinational firms, the increasing income level, risen consumer spending, continued open and friendly market environment of it presents challenges and opportunities uniquely distinct to multinational firms. Many multinational companies have entered the Chinese market, or make a plan to enter it. Japanese fast fashion brand UNIQLE enter the Chinese market in 2002, followed by Zara and H&M, respectively 2006 and 2007 (Consulting 2016).
The Chinese market has shown great enthusiasm for these international fast fashion brands. According to the data from Inditex, Zara has opened 179 stores in China (2017). According to statistics of Fast Retailing website, as of August 2015, the store number of Japanese brand UNIQLE is as high as 387 (2017). Moreover, the fast fashion brands are still in continuous expansion.
Although after repeated testing and adjusting in the local market, the excellent market strategy of these fast fashion brand guarantees its first step success in the Chinese market, but the development in the future is still full of challenges. The rapid development and changes in the Chinese market, the huge difference in regional economy is still bring a lot of issues. Fast fashion brands need to think about that whether their original strategies are applicable or not, as well as how could they adapt the Chinese market better.
Scope
The industry studied in this dissertation is the fast fashion industry; the market involved is the Chinese market. Taking Zara as an example to discuss fast fashion brands’ strategies and advantages in Chinese market. Moreover, analyze whether these advantages are still applicable to today’s Chinese market, as well as discuss the potential risks.
Research Objectives
Main points
There are three main points of this dissertation’s research objective. Firstly, take Zara as an example, analyse the strategic advantages of international fast fashion brands. Discuss whether these inherent advantages would apply to the Chinese market, and Zara made what strategic adjustment to adapt. Secondly, with the rapid development and changes in the Chinese market, discuss the possible risks for fast fashion brands’ development in this market. Thirdly, discuss the possible ways for fast fashion brands to coping with risks and consolidate or create advantages.
Necessity of the research
First of all, the Chinese market has a very important value for the global expansion and sales growth of international fast fashion brands. Next, as has been mentioned repeatedly, the Chinese market is in a period of rapid development and changes. Urban development, changes in consumer awareness, regional economic fluctuation and other factors may affect the future development of fast fashion companies.
Based on the above, it is necessary to analyse today’s Chinese market. The international fast fashion brands in Chinese market are facing challenges, and the excellent marketing strategy is guarantee for their success development. Clear the strategic advantages could help these international brands themselves to identify the future focus of development, and also could provide reference for the others brands who want to enter. At the same time, the risks in the market could not be ignored. Analyse and clear the risks are beneficial for the brands to respond positively, and also consolidate or even create advantages on this basis.
Limitation of the research
Firstly, the analysis is based on secondary data and material, which is relatively less accurate than the original data and material. The source of data and material are not unified, which result in the accuracy and reference value are not unified. Secondly, the analysis based on the current situation of Chinese market. As the purpose of this article is to provide a reference for the formulation of fast fashion brands’ future strategy, the lack of prediction and analysis of future conditions will affect the reference value of this dissertation. Thirdly, this dissertation takes Zara as an example to analyse. While, different brands have different situations, the analysis of Zara does not have universal applicability. Fourthly, there are limitations of analysis tools themselves, which would affect the reference value of the dissertation.
Literature Review
Along with the world economy continued to integrate, future growth for most companies will likely come from foreign markets, which result in more and more firms join in the overseas competition (Holt, Quelch & Taylor 2004). Among global markets, Chinese market’s sheer size and scale make it increasingly attractive to multinational firms. The higher and higher incomes, risen consumer spending, continued open and friendly marketing environment of Chinese market presents challenges and opportunities uniquely distinct to multinational firms (Hedley 2017).
This article will study the fast fashion apparel market, and Zara is one of the most representative brands. This chapter is going to introduce the key concepts of the subject, and show the development status of fast fashion industry. Next, this chapter will describe the analysis tools used in the following chapters, and describe Chinese market. At last, elaborate the relationship between risk and advantage, and prepared for later discussion.
Key concepts
Fast fashion
Fast fashion is regarded as a low-cost imitation of the current high-end fashion (Oijala 2016). High-end brands usually guide fashion trend through fashion shows, these trends change so quickly that they often become obsolete within a few weeks. Young customers tend to hold greatly enthusiastic about the fashion trend, but could not able to afford the high-end brands. Fast fashion brands are aim to target this segment market, they use relatively low quality materials to control the cost, and make their products could afford by young customers. Fast and fashion are important factors to form this industry.
Firstly, fashion is guaranteed by imitating the high-end brands. These fast fashion brand hired a lot of professional buyers with enough sensitivity for fashion, they wander around the catwalk shows and fashion conferences all over the world and give the latest information back to their company. Secondly, fast. In this case, fast refers to the ability of fast fashion brands to respond the market quickly and exactly. These brands need to maintain a high degree of sensitive about the latest fashion, and put the related fashion elements into their new design (Rosenblum 2015). The speed of production and distribution is also very important; the products should be show to customers within the shortest time.
Chinese market
Chinese market generally refers to the mainland market. The following content would introduce the basic information of Chinese market from market size and customer behaviour. First and most, size and value of Chinese market. Based on over 1.4 billion populations and growing Gross Domestic Product, Chinese has a huge garment market. According to of Industry Department of the China National Garment Association, between January and November 2015, sales of Chinese garment reached 848.8 billion yuan, showed a year-on-year growth of 9.6% (Yau 2016).While China’s demand for import clothing is also increasing exponentially.
Next, Chinese customers’ behaviour. Firstly, people’s lifestyle changed. Over the past decade, along with improved incomes and emerging affluent middle class, consumerism and the services sector in China is increasing rapidly to meet the public’s needs (Hon 2016). Consumers not only want to improving basic living conditions, and also prefer to enhancing the quality of life by elegant products, while fashion clothing is one part of the better life.
Hon’s analysis shows that, in 2015, the value generated by China’s services sector is as high as half of China’s gross domestic product for the first time (2016). Secondly, China’s online shopping is booming. According to Yau’s research, over 30% of the interviewed would like to buy clothes online, and among these consumers, 35% say they visit various online retailers for clothes at least once a week (2016).
Advantage and risk
The dictionary define advantage as ‘any state, circumstance, opportunity, or means specially favourable to success, interest, or any desired end’. In this essay, advantage mainly refers to superiorities of international fast fashion brands entering the Chinese market. Compare with local brands, the advanced part of international fast fashion brands’ market strategy. This essay will focus on analyse the advantage of Zara entering Chinese market, and discuss Whether other international fast fashion brands have these risks or not.
Risk is possibility of loss or damage the original value (Staff 2017).In this essay, risk refers to the challenge of international fast fashion brands entering China. What advantages might be lost or damaged? Whether their market strategy could adapt to the Chinese market or not? What situation in Chinese market should these fast fashion brands need to adapt and what change they should take? This essay will focus on analyse the risk of Zara entering Chinese market, and discuss Whether other international fast fashion brands have these risks or not.
Development of fast fashion brand in the global
In the past few decades, great changes have taken place in the mode of produce and consume fashion. Fashion is no longer the privilege of the elite, everyone has the opportunity to experience fashion. Firstly, the improvement in production technology brought about the initial development of fast fashion (Lejeune 2016). Increasing production speed and reducing the time from design to offering goods is the basis of fast fashion.
The product cycle is shortened with the speed increased, which makes the product update frequency greatly improved. Fast fashion brands could provide the latest fashion products for their customers within few weeks. Secondly, the increase in customer purchase frequency is related to the reduction of the price (Lejeune 2016). After the increase in production, the related company instinctively want to seek a larger consumer groups, the parity clothing market for common consumers become their target. These companies save production and time costs by using lower quality materials and imitating high-end brands.
The development of fast fashion is also facing many tests. Firstly, environment problems. Due to the huge production, there are many waste materials need to be dealt every year. Moreover, the concept of fast fashion means that related products is very easy to be out-of-date. Every year, fast fashion clothes are thrown away in large quantities, result in waste of resources and many other issues (DeHaan 2016).On the other hand, the social impact of the fast fashion brand has also been concern(DeHaan 2016). The life attitude that fast fashion shown to customers is tend to maintain the perfect looking and catch up with the latest popular trend. To a certain extent, this kind of attitude make young audience pay too much attention to appearance.
Sustainable fashion should be the future direction of fast fashion brands (DeHaan 2016).There are some problems that fast fashion brands should think about. Firstly, whether fast fashion brands should use more environmentally materials to replace some too cheap materials or not. If yes, how to balance the increase production cost and the social responsibility in environmental problem. Whether the customer would execute the idea that spending more money to buy more environmentally friendly products, or just think it is a right thing. Secondly, how to balance the contradiction between positive social influence and fast fashion concept?
Development status of fast fashion brand in China
In recent years, Chinese fast fashion industry has developed rapidly, the three most successful brands are Zara, UNIQLO and H&M. UNIQLO was the first to enter the Chinese market in 2002, followed by Zara and H&M, respectively 2006 and 2007 (Consulting 2016). Although China’s economic growth is slowing, it does not affect young people’s enthusiasm for fashion clothing and accessories. According to statistics, from 2010 to 2015, China’s fast fashion industry Compound Annual Growth Rate(CAGR) is as high as 14.5%, and in 2015 the sales account reached 542 billion Yuan, an increase of 7.4% (Consulting 2016).
At present, the fast fashion brands are looking for improvement in store productivity, actively cooperate with the e-business platform, and operating of their Chinese local social media, Weibo. Some Chinese local brands also join in the competition of fast fashion industry, such as Metersbonwe, Nuoqi and Peacebird. However, the business models and supply chain management of these local brands still need to develop, and their competitiveness is related weak.
Development status of Zara in the global
Zara Corporation is a Spanish fashion chain that established in 1975; belong to Inditex group (Inditex.com 2017b). By the end of last financial year, Zara had open 2,213 stores strategically located in leading cities across 93 countries(Inditex.com 2017b). Zara offers affordable and trendy clothing to customers across a broad spectrum of cultures and ages. According to the 2016 annual sales figures, Zara is the largest fashion retailer in the world (Heller 2017).
Compare with 2015, Zara’s net sales increased 12% year-on-year, up to 66% of total sales of Inditex (Heller 2017). Zara’s main revenue is still derived from the physical store, according to Heller’s statistics, online store sales accounted for only 6% of total brand sales (2017). Zara has benefited a lot from the effective control of each production and sales process, not only guarantees the speed and design of its products, but also establish a better brand image.
Zara also introduced advanced Radio Frequency Identification Technology (RFID) to track the location of products, ensure these products could be sent to the customers most in demanded with the shortest time (Inditex.com 2017b). Moreover, Zara would also continue underline the environment issues, they provided clothing recycling bins in the store and made plans to allowed online store’s customers use the second-hand clothing offset delivery fees (Inditex.com 2017a).
Development status of Zara in China
In 2004, Zara opened its first store in Hong Kong, China. In 2006, its first flagship China store opened at Shanghai (UK Essays 2015). The search results of Zara store information show that there are 16 stores in Shanghai, 18 stores in Beijing, 13 stores in Shenzhen and Guangzhou, 8 stores in Chengdu (Zara.cn 2017). Zara also open its online store in Tmall, which is one of the largest online platforms in China (Reuters 2014).
Its product prices ranging from RMB 29 to RMB 2799, covered women’s wear, men’s wear, kid’s wear, bags, shoes and so on. Zara has made very good results in China, however, there still some problems. Firstly, quality problems.
Shanghai daily report that the quality of fast fashion brands’ clothing is caused worrying in recent years (Yan 2014).There are total 12305 cases of substandard clothing from international fast fashion brands (including Zara) be found within 6 months (Yan 2014). Secondly, the booming of E-commerce in China would impacting international fast fashion brands (Tong 2014).Because the huge sales volume and active users of Tmall, Zara have to run its online stores in that platform, cash flow of the company would be affected (Tong 2014).
Analysis tools
STP theory
The core of STP theory is to select target customers and market through three steps: segmenting the market, targeting the market, and positioning the market (Kokemuller 2017). STP theory points out that the demands of consumers are multi-level and diversified, there is no enterprise can meet all these demands. Enterprise should analyse and categorize consumer demands. After divided consumer demands into different groups, the enterprise could select one or more group as its target market on the basis of its strategy, capability and product situation. Then, companies need to make their products as much as possible to meet the preferences of target customers.
Specific to each step, market segmentation refers to divide one particular market into some more precise groups according to the difference of customer demands. Target market is the market segmentation that the enterprise decides to enter. Market positioning is ensuring the products or services could meet the needs of target market in the process of marketing. However, in virtue of customer, demands would change with their own experience and social environment, the market is hard to correctly segmented. Moreover, company’s choice of target market is tending to limited by its strategy and actual strength, that might result in ignore of the real demand of customers (Lynn 2011).
4Ps theory
4Ps theory is a generalization of many elements of marketing into 4 categories: product, price, place and promotion (Perreault, Cannon & McCarthy 2014). Firstly, product. The formulation of product strategy requires enterprises to pay attention to the development of product characteristics, and these characteristics should be in line with the market demand. Secondly, price. The formulation of price strategy should base on the company’s market positioning and related brand value, and has a certain of attraction to target customers. Thirdly, place. Place refers to the way a company presents its products to target customers.
Fourthly, promotion. Promotion refers to the method that enterprises encourage target customers to buy their products. Such as discounts, special price and other methods. 4Ps theory is product oriented that tend to lack of thinking about market orientation and customer orientation. Agola and Hunter (2016) claims that 4Ps model is not suitable for the underdevelopment and poor markets. They believe that payment innovation should serve as a complement to the 4Ps theory (Agola & Hunter 2016).
4Cs theory
4Cs theory is developed on the basis of 4Ps theory, and is a customer oriented analysis tool (McClean 2012).The contents of the 4Cs theory include customer, cost, convenience and communication. Firstly, customer refers to customer needs. Enterprises must first understand and analyse customers, provide products based on customer demand. At the same time, enterprises should not only provide products and services, but also create customer value.
Secondly, cost refers to the cost of make customers gratified with the product. The cost also refers to the customer’s purchase costs, the ideal product pricing should be lower than the customer’s psychological prices, but also allowed enterprises to profit. In addition, the cost of customer purchase includes its monetary expenses, time costs, energy consumption and psychological costs (McClean 2012). Third, the convenience refers to that the company makes the customer to buy their goods as easy as possible. Fourthly, communication. Enterprises should establish a new type of relationship between customer and enterprise that based on common interests, positive and effective communication. It is no longer the one-way promotions or persuade customers, but find the way to realize the goals of both customer and enterprise.
However, there are some problems in customer demand orientation. For example, customer tend to hope the best quality with lowest price, this is obviously not realistic. Moreover, to a certain extent, customer orientation is an ideal state. The formulation of market strategy is tending to enslaved to various factors, such as production capacity of the company, strategy of competitors, external environment and other factors.
PESTEL analysis of Chinese market
Political factors
Political factors are about law, regulation, government policies, and other related factors, that would affect economic situation and government decision. China began economic reforms in 1978, including the reforms about foreign trade liberalization and foreign enterprise direct investment, which promoted the development of international enterprises to China (Yu 2017).
Economic factors
Economic factors directly affect businesses because they affect the availability, cost, supply and demand of capital. After China becomes a market economy, there is a huge change in economic environment, economy has grown rapidly. The government provides more self-management rights to state-owned enterprises to enhance the market competitiveness of them, and actively create opportunities for cooperation of domestic enterprises and foreign investors. As a result of the relaxation and investment in foreign trade and joining the WTO, the income of China rose sharply. China has also taken an active part in the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), which is formed with Japan, South Korea and other countries.
With its large population and cheap labour, China became the world’s manufacturing centre. Nowadays, China is the world’s second largest economy (Eckart 2016). While, along with the continuous development of science and technology, China’s manufacturing industry is now trying to change from labour-intensive to technology-intensive. At present, China’s economic growth rate is slowing down, but its development momentum is still beyond compare. Moreover, government expenditure is increasing too, which would benefit the development of economic.
Social factors
Authoritative data show that China’s population has exceeded 1.4 billion, accounting for 18.67% of the world’s population, and the growth rate of population has a certain of declined, the latest data is 3.9% (Worldometers.info 2017).
The large population provide enough labour to the market, to a certain extent, it is one of the factors promoted the rapid development of China’s economy. This also means that the amount of consumer is huge, and the market demand is remarkable. The huge population also brings many problems. Such as cities are overcrowded, per capita resource shortage, the gap between rich and poor is too large and other issues. With the economic development, people’s income and living standards generally improved. But due to slowing economic growth, employment problem becomes increasingly severe. Moreover, China has also faced the problem of population aging in recent years.
Technological factors
As mentioned, China’s manufacturing industry is now trying to change from labour-intensive to technology-intensive. Both government and industry pay a lot attention to technological development, a lot of money is used to research, innovation, develop and explore high-tech, and also speed up to technology transfer.
Environment factors
With the rapid development of China’s economy, especially the development of industry, the environment has been affected, including the reduction of natural resources, environmental pollution, as well as the waste of resources caused by underdeveloped technology.
Legal factors
All overseas business activities of transnational corporations must be bound by local laws, on the Chinese market, Shen and Tiller (2010) claim that there are eight points need attention. First, the form of representation. Foreign companies need to register a legal entity in China before they can recruit staff and carry out other business activities. Second, registration, certification and licensing requirements. Most products must be registered, certified and approved by the relevant Chinese authorities before they are sold. Third, business scope. China requires every company to have specific registered business scope, and commercial activities are not allowed to exceed this scope.
Fourth, intellectual property protection. China has established laws related to protect intellectual property rights, but there are still many problems such as illegal activities and inadequate enforcement of laws. Fifth, foreign exchange management. Chinese law requires foreign exchange enter or exit the country must go through registration, application and other procedures to approval. Sixth, import duties and value added tax (VAT).
China collects import duties and 17% VAT on all imported goods (Shen & Tiller 2010). Seventh, dispute resolution. China has signed the Convention on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Arbitral Awards. When business disputes involve two countries, they can be settled by third party arbitration (Shen & Tiller 2010).Eighth, labour law compliance. Employing employees in China is subject to China’s Labour Contract Law.
The meaning of understanding advantages and risks
Coping with risk
Only after assessing the risks, the company would be able to respond positively to risk. measures of coping with risks are divided into four categories, risk aversion, risk acceptance, risk reduction and risk sharing (Burtonshaw-Gunn, 2016). First, risk aversion, this part of the risk event was judged could be avoided. To a large extent, the company could avoid such risks by adjusting the strategy, reallocating resources, and stopping certain business activities. Second, risk acceptance, which refers to maintaining the existing risk level. Company is often willing to bear this kind of risks, in order to increase the possibility of obtain higher profits. Third, risk reduction, which refers to the use of policies or measures to reduce the risk to an acceptable level. This usually involves minimizing the likelihood of adverse events and developing strategies to deal with incidental events.
Finally, risk sharing, which refers to transfer a part of the risk to partner or independent agencies. Companies tend to share risks by cooperating or signing insurance. In this dissertation, the risk is mainly referring to the problems that fast fashion brands would face to adapt to the Chinese market. The discussion part of this dissertation will focus on the possible risks of Zara and discuss whether other fast fashion brands have the same problem.
Keep and create advantages
In general, as long as some aspect of the enterprise has a particularity, it may have an advantage from this trait. Advantages tend help companies stand out from competitors, and catch the customers who prefer these traits.
Relationship between risk and advantage
On the one hand, risks may weaken or even offset the advantages. For this dissertation, When the fast fashion brands enter the Chinese market, the geographical differences may bring a lot of risks. Such as regional policy constraints, cultural differences, different consumer preferences and other risks. The original advantages of brands may be weakened by these risks. On the other hand, Sufficient ability of risk coping is often being companies’ advantage. For this dissertation, when fast fashion brands enter the Chinese market, risks may come from many aspects. The stronger the ability to resist risks, the more likely to gain an advantage in the competition.
Methodology
When conducting research, it is important to come up with a clear research methodology that defines how data was collected, analyzed, and presented in a meaningful way that can easily be understood by the readers (Jham & Puri 2014). It is critical to ensure that the approach chosen to collect and analyze data is in line with the research goals and objectives. The approach should help the researcher to collect the needed data to help inform the study.
In this paper, the goal was to analyze the strategic advantages and risks faced by fast fashion brands in the Chinese market, and the approach that these firms should take to cope with the risk, taking a special focus on Zara’s operations in this market. The method that was chosen was considered appropriate in mining the necessary data. This section of the paper discusses the method that was used in data collection, the ethical considerations observed, and the constraints that the researcher encountered when conducting this research.
Second-hand Data and Their Relevance
According to Kaufmann (2015), many academic researches often use primary and secondary data based on a number of factors under consideration. In this research, it was decided that second-hand data would be the basis of the study. Collecting and analyzing primary data is critical in a research project. The world is very dynamic and what scholars found to be true today may not be the case after some time.
As things keep changing, it is always necessary to collect primary data from the field to get accurate information about the current state of affairs. Primary data also makes it possible for a scholar to confirm, improve, or reject the existing sources of information. However, it was not possible to use primary data in this study. The approach requires time to identify, sample, inform, and engage the respondents in a data collection process (Jham & Puri 2014).
As this is an academic research, it was necessary to ensure that the project was completed within a given timeline. As such, primary data collection was avoided because of the time needed to engage the respondents and collect data from them. The fact that the study also focused on the Chinese market made it less possible to collect data from the right respondents (Zara’s employees working in the Chinese market) within the set time.
The conclusion and recommendations made in this study, therefore, wholly relied on the data collected from secondary sources. The information from second-hand sources proved very informative in the study. The school library provided the books and journal articles needed for the project. The researcher was able to get other additional books and journals from the online platform. Electronic journals talking about the apparel industry and how it is performing in the Chinese market were readily available in various databases. Electronic newspapers and other reliable online sources were also used to collect the needed information.
Keywords such as apparel, fashion, design, risk, Chinese market, advantages, coping, competition, and top brands were used when making the online searches. As mentioned above, the changing market forces make it necessary to collect the most recent information. It is particularly important to collect recent information when conducting research in the fashion industry because of the constant changes that are often witnessed.
Change is often driven by two forces in this industry. The first force is customer driven, where their tastes and preferences change as new needs emerge. The second force is industry-driven, as individual players struggle to edge out their competitors by trying to come up with new products that meet customers’ needs in the best way possible. To ensure that the data collected was as recent as possible, the researcher made an effort to include the most recent books, journal articles, and reliable websites in this study. Some of these second-hand data were published a few months ago.
Second-hand data is very relevant in every study. Prange (2016) advises that when one is conducting a research project, it is important to come up with new information. One should avoid reproducing already existing information. The only way to avoid duplication of existing knowledge is to review what has been done by other scholars. Through the review, the researcher can get a sense of direction and purpose for the study. In a project where time was a major issue that hindered the possibility of collecting primary data, secondary data was the only source of information. That is why second-hand data was considered critical in the study. The case study discussed below was also considered part of the secondary data.
Case Study
The case study was also considered important for this research. Given the fact that the project focused on a specific company, Zara, it was necessary to use a case study in this project. The researcher looked at specific events and activities of Zara, one of the top fashion brands in the global market, in the Chinese market. The phenomenology helped in understanding specific advantages that this company is enjoying in China, challenges it has to deal with in its operations, and how it is overcoming various risks. The case study provides a practical context to the issue under investigation. Kaufmann (2015) says that when using case studies, it is possible to have a practical picture of the forces and how they affect the normal operations of a firm within the market. That is why the researcher considered case study as an instrumental approach to collecting data.
Ethical Considerations and Research Constraints
When collecting data from the respondents, it is important to observe a number of ethical considerations. Given that this was an academic project, the researcher ensured that cases of plagiarism were completely avoided. Information obtained from various sources was properly cited using Harvard referencing style. The entire project was completed by the researcher as per the provided guidelines. One of the biggest constraints faced in the study was the inability to have a face-to-face discussion with some of the employees of Zara working in the Chinese market. They have firsthand information about the advantages, risks, and the approach that the company is using to cope with the risks. Time was also an issue because the researcher needed to complete the project within a specified period.
Analysis
STP analysis
The clear analysis of the market environment and the correct positioning of market are very important for enterprises, which are conducive to enterprises to survive and achieve the sustainable development in the fierce competition.STP analysis is the process of enterprise in-depth analysis of the market, which is covered segmentation, targeting and positioning, and this three steps are sequential (Reference 2017).
Segmentation
Market segmentation refers to the division of potential customers into groups, or segments, through their common needs, similar sense of worth, same rang of consumption ability and so forth (Blythe 2006). The clothing market is often differentiating through gender, age, style, price range and other factors. Zara’s market involved the basic segments shown in the following table.
Table 1.
Among these segments, the women garment of Zara divided into three sections, woman, basic and TRF. The main customers of Zara woman are ladies over 25 years old. This section offers relatively better quality and higher prices. Zara basic offers a moderate price and relatively common style, easy to match. TRF’s main customers are 18-25 years old young girls and it is the cheapest section of women garment.
Targeting
ZARA believes that today’s clothing market cannot be simply divided into high-end luxury market and low-end cheap market. After analyse and decided by company’s top managers, ZARA positioned the fast fashion apparel market as its target market. Their target customers are fast fashion seekers who have a certain consumption capacity, while relatively do not value details and quality. Zara offers a reasonable price to target the young consumer group between 25 and 35.
This group tend to have a middle level of income, relatively have a high enthusiasm for the fashion elements and the latest popular trends. The young consumer groups in each country tend to have these characteristics, in this case, Zara could meet the customers’ needs with a minor adjustment when the company enter a new country or region. Such as, according to stature of local customers adjust the amount of stock for different sizes; according to climate adjust the time of provide new goods.
Position
After determining the target market, company tend to select the most effective marketing mix to position their product to target the valuable customers (Zia & Kumar 2016). Zara positioning its market through three main aspects: brand, product and pricing. Firstly, brand, Zara aims to be a global leader in fast fashion area. Zara hopes design and produce fashionable goods as fast as possible, meet customers’ demand, at the same time help their customers become the fashion leaders. Compare with media advertising Zara prefer to attract potential customers through unique exquisite store layout and fashion design window exhibition.
Customers could get inspiration of clothing collocation while shopping in that store. Through this way, Zara could not only show their fashion attitude and build up the fashion brand image, but also promote consumption of related tie-in products. Secondly, products, Zara hopes their products could represent the latest fashion trends. With just two weeks, Zara could fulfil the whole process of design, manufacture and market a new product.
This speed ensures that Zara will be able to incorporate the latest fashion elements into their products in the shortest possible time. Thirdly, pricing, Zara’s pricing is the middle-end price. Zara does not sacrifice sales volume to get the high profits, nor depress prices to expand the market share. Zara’s efficient distribution, logistics system and powerful supply chain greatly reduce the cost of its apparel products, and give a more reasonable price in the same quality products. This allows Zara to enter each country or region with a certain price advantage.
4P analysis
4P is the tool used to develop or evaluate the market strategy, which is include product, price, place and promotion (Bishop 2013).
Product
Zara’s product strategy is mainly embodied in two aspects: imitate the first-line fashion brand and variety of styles. Firstly, imitate the first-line fashion brand. One of the main features of fashion is changeability. In order to accurately control the current fashion trend, Zara is good at seek and imitate the fashion elements from first-line brand. Zara hired a lot of professional buyers with enough sensitivity for fashion, they wander around the catwalk shows and fashion conferences all over the world and give the latest fashion information back to the Zara design headquarter. This greatly reduces Zara’s reaction time to fashion trends, as well as the latest fashion elements can be quickly reflected in Zara’s products.
In the process of re-design the catwalk show fashion, Zara would remove the elements that not suitable for everyday wear, and too complex details, in order to make their products suits public and daily life, at the same time control production time and cost. Therefore, compared with the traditional fashion brand, Zara can grasp the trend of fashion in a faster time, cater to the needs of consumers, and establish a good brand image.
Secondly, variety of styles, Zara tends to offer more styles to customers, while the inventory of each product is relatively less. In order to meet customer’s demand for latest styles and fashion trend, Zara offers more new products than regular brands in every season, the number is as high as about 500 per month (Bhasin 2017). The relatively short product development cycle provides guarantee for more styles. In addition, there is relatively less inventory for each single item, which make Zara’s products have the scarcity characteristic. This also ensure the possibility for a faster update speed of products.
Price
Firstly, Zara sells at a relatively low price. Zara was recognized as “third-rate price” cheap labour, relatively cheaper materials and fast production speed guarantee Zara’s low pricing strategy (Yu 2016).However, relatively low prices mean that profits are squeezed, and also means pressure in sales would increase. Secondly, rather than cost-based strategy, Zara prefer to value-based pricing strategy (Ceballos 2015). The strategy focuses on the customer’s perceived value of the product.
However, customers in different regions tend to have different psychological price for the same product, that makes the original intention of value-based pricing may not be effectively reflected. Thirdly, discount strategy. Zara believes that less discount is more conducive to operation, and would achieve an efficient and fast return on investment. According to statistics in 2014, there are 3.2% of Zara’s online items have discount, while this proportion of the same kind brands, H&M, is as high as 24.2%. Moreover, there are 0.2% of items discounted by over 50%, while this proportion of H&M is as high as 9.3% (Smith 2014). However, fewer discounts would weaken the advantage of the low price strategy.
Place
Zara is a vertically integrated retailer, it controls the whole process from design, manufacture to distribution (Bhasin 2017). The distribution system allows Zara to have a good control capability in every aspect of the supply chain. This approach seems greatly benefits Zara because it has become one of the most influential fast fashion brands globally. The expansion of ZARA is underway, the company has opened stores in more than 30 countries, including China.
Zara insist on direct way to operate stores, it runs 90% of its stores itself and the rest are Joint venture franchising (Bhasin 2017). This makes customers to experience the same environment of stores in different countries, which means Chinese customers could experience the excellent storefront environment. There is no doubt that this is quite attractive. Zara also invested a lot of money to build their own factories, improve the distribution system and logistics system.
Zara hold a huge amount of its production in-house and ensure 85% of its factory’s reserve capacity could use for seasonal adjustment (Lu 2014).Zara’s powerful logistics system make sure the company could deliver products to its European stores in less than 24 hours, and to the stores in other regions within 40 hours (Lu 2014).
Promotion
Zara’s promotion strategy is unique, its marketing expenses are much lower than similar brands (Pratap 2017). Zara rarely promote itself through media magazines, most of the marketing is carried out through word of mouth. First of all, Zara tend to open stores in the prime sections of the city. Its sophisticated window design often attracts customers at the first time, and then spacious stores, diverse options and reasonable price tend to bring customers a quality shopping experience. These factors helped Zara build up an image of affordable and fashion brand. The image is actually part of Zara’s promotion strategy (Pratap 2017).
As mentioned, Zara rarely offering discount, that is because its products are often not overstock. However, when entering a new country or region, it takes time to build a word of mouth, combined with other promotion strategies is very necessary.
4Cs Marketing mix
4Cs marketing mix is the evolution of 4Ps, which is proposed by professor Bob Lauterborn in 1990 (McClean 2012).With this theory, the contemporary marketing strategy could be formulated better. It is including the transform of product to customer, price to cost, place to convenience, and promotion to communication.
Customer
From product orientation to customer orientation. Compare with product orientation, Customer orientation pay more attention to customer needs and benefits. Customer orientation believes that enterprises should profit from consumer demand and achieve win-win situation between enterprises and customers(Anastasia 2015). As mentioned, Zara’s target customers are fashionable young people aged 25-35 years’ old, based on this positioning, the company fully analyses the needs of these target customers. The following content will analyse two major demand. First demand is fashion. The precise control of the fashion trend has always been Zara’s proud.
In order to meet customer’s need for the latest fashion, ensure customers could find the season’s popular item in its stores, Zara maximize its speed from design to production, as well as from factory to store. The second need is reasonable price. The target customer is the young group, that tend to have a relatively low income, and consider with the update speed of fashion item is very fast, customers tend to have a lower psychological price for these fashion clothes. Therefore, Zara’s pricing range is on the low level. In addition, in order to ensure a lower price, to a certain extent, quality is allowed to be sacrificed.
Cost
From price to cost. On the premise of customer orientation, the cost does not mean the cost of product itself, but the price customers are willing to pay for the product. This price is determined by two factors, perceived benefits and perceived sacrifice (Mahajan 2016). How much perceived benefit greater than perceived sacrifice would determine the price customers are willing to pay. Firstly, perceived benefits, it is about the benefit from product itself, service, relationship and image. For Zara, product benefit mainly embodied in the fashion design. Service benefit is about customers’ experience in shopping.
Comfortable shopping environment, spacious fitting room and friendly shopping guide are the guarantee of Zara’s service quality. Relational benefit is about customers’ preference for the brand. The more the customer prefer a brand, he will be more pleasure when buying the product of that brand. Image benefit is about how people value the brand. For example, Zara’s brand image is fashion, when people wear Zara’s clothing, these people might be considered as a fashionable person.
If a person wants to build fashion image, then he tends to like Zara. The other aspect is perceived sacrifice, it is about monetary costs, time costs, energy costs and psychological costs. Money, time and energy are the cost that customers need to spend to obtain the good. For Zara, relatively low pricing, convenient shopping mode and efficient logistics system are all committed to reducing these costs. While the psychological cost is about the customer’s own life experience, which is uncontrollable.
Convenience
From place to convenience. The similarities between the convenience strategy and the place strategy are to provide customers with a variety of shopping channels, and to meet the customer’s needs for different channels as much as possible. the difference is that the convenience would focusing on the establishment of more efficient distribution channels, minimize circulation, reduce circulation cost. Through this way, company could provide more favourable prices and more efficient delivery to benefit customers. For Zara, convenience strategy mainly reflected in two aspects, multi-channel sales and
Efficient logistics system. Firstly, multi-channel sales. In addition to entity stores, Zara also runs online store and mobile phone App. Through the official website and phone App, customers could browse the latest fashion clothing, and the search function could help customers find what they want easily (BBC News 2010). Zara makes exquisite pictures for online store and phone App, which not only show its fashionable brand image, but also provided the tie-in reference for customers. The exquisite picture is also a marketing technique. By looking at pictures, customers can be more intuitive understanding how to tie-in these fashion items, increase the desire to shopping.
At the same time, promote the related goods, as shoes and bags, increase the amount of shopping. Secondly, logistics system. As mentioned, Zara run its own logistics system, which ensure the company could deliver products to its European stores in less than 24 hours, and to the stores in other regions within 40 hours (Lu 2014).This system also controlled the delivery fees, ensure customers get their parcel with less time and money.
Communication
From promotion to communication. Promotion focus on how to sell products efficiently, while communication not only pay attention to the process of sale, but also focus on the feedback of customers (Hanlon 2015). For Zara, the company would collect and analyse sales data of entity stores and online stores. Based on the result of data analysis, Zara could determine customers prefer to which sale channel, which type of clothing is more popular and other situations (Bhasin 2017).Zara could also use the return data to determine which clothing is popular but not practical for daily wear.
The company would adjust its marketing strategy timely according to these feedbacks and meet customer’s need better. Relative to the promotion strategy, communication strategy would help company adapt the market more flexible. Especially when the company entry a new market, the importance of effective communication will become more apparent.
Adaptive strategy of Zara in China
The distribution of stores related to economic development
As mentioned, Zara tend to open stores in the prime sections of the city. There are significant differences in economic conditions of China’s different regions, after considering many aspects of factors, Zara start its first store at Hua Hai Road, Shanghai, China in 2006 (UKEssays 2015).According to the results of the official website store search, Zara currently opened 15 stores in Shanghai, mainly distributed in Jing’an District, Huangpu District, Xuhui District and other bustling area (Zara.cn 2017).According to the statistic of the official website store search, So far the number of Zara store in most parts of China is shown in the below table (Zara.cn 2017).
Table 2.
Note. Number of stores in different cities.
Zara stores are mostly concentrated in the eastern region, the proportion up to about 65%.As can be seen from the table, Shanghai, Beijing, Jiangsu and Guangdong have the largest number of stores, while many provinces and cities in the central and western regions have only 1-2 stores. This distribution is positively related to regional economic development.
Cooperation with Alibaba
Other than physical stores, online store is the most important selling channel for Zara. Normally, Zara prefer to operate its own official website, which is conducive to the company to establish a unified brand image. While, in order to adapt to the shopping habits of Chinese consumers, except of run its own official website, Zara also cooperate with China ‘s largest e – commerce platform, opened its Tmall flagship store in 2012 (Reuters 2014).
Tmall is operating by Alibaba, it has a very important position in China’s online market. Tmall has more than 230 million active users and generates over £150 billions of transactions (Marketing to China 2014).The decision of open the Tmall flagship store is very wise, Chinese customers’ purchases amount at the online store is very impressive. The best selling goods of Zara Tmall flagship store received over 15000 customer reviewers (Appendix I).
Provide special products in Asia
People in Asian countries, including China, often have different shape and clothing preferences from people in Europe and America. This is one of the challenges for Zara to enter the Chinese market. First of all, in order to solve the problem of shape differences, Zara need to adjust the stock of clothing’s different size. In Europe and American, Zara’s stores tend to store more clothing of large size, while in Asia, Zara’s stores tend to store more clothing of small size (Anderson 2015).
Secondly, in order to solve the problem of clothing preferences, Zara would estimate customers’ preferences based on the feedback from customers’ purchase data. According to this feedback, Zara would decide to offer different styles of clothing for different countries and regions, or make adjustments in the amount of supply. For example, sling is one of the ordinary lady wear in Europe and American, while it is not that common in Asia lady’s daily life.
Zara would offer more styles of sling for Europe and American, while offer relatively less styles for Asia. Moreover, Zara provides some clothing only in Asia, this is one of the strategies to adapt the Asia market, including China, and attract customers in these countries (Anderson 2015).
Discussion
The fast fashion industry has been growing rapidly over the recent past as countries all over the world continue to register impressive economic growth following the end of the global economic recession of 2008/9. Many countries are recovering from the recession to the benefit of the fashion industry. One of the countries that have registered impressive growth since the recent recession ended is China. According to Prange (2016), China currently has the largest middle class in the world.
The country is home to over 1.3 billion people, most of who are employed in various industries. Many companies have been targeting this huge market with various products specifically because of the growing purchasing power of its people. The fashion industry is flourishing in this market because of its huge size and the increasing purchasing power of the individual customers. In fact, reports indicate that the fashion industry in China was not significantly affected by the recent recession that hit the global market. Some of the top fashion companies in the global market have found their way into this country as they seek to grow their market share. Zara is one of the apparel firms that are offering various fashion products in the market.
The rivalry is increasingly becoming stiff, but companies are keen on coping with these challenges to ensure that they remain sustainable in the market. In this section of the paper, the researcher will focus on three areas. First, the researcher will look at the advantages that the Chinese market has to offer fast fashion firms such as Zara. It will help in understanding why companies are keen on finding their way to the Chinese market. Secondly, the section will discuss specific risks that the fashion industry faces in the Chinese market.
Rivalry is one of the biggest risks that these companies face in China. However, Prange (2016) notes that other than competition, numerous other challenges exist that fast fashion companies in the Chinese market must be ready to handle. Failure to understand these risks may force an entity out of the market. The third section will look at how to cope with these risks. New competitors will continue to emerge in this market. New challenges will keep on rising, some of which may be worse than the current problems. The worth of a firm is defined by its ability to deal with these challenges in the most efficient way to ensure that its operations are not jeopardized. Successful firms know how to manage each challenge in a way that may not be a threat to its survival.
Advantages in Chinese Market
According to Zhu, Pickles, and He (2017), for a long time, the United States was the most attractive market that every global company was keen on operating in, especially because of the considerably high population and a very strong purchasing power of its people. The consumer culture in that market also made it the most attractive market in the world. Studies suggest that it is still an attractive market for fashion products.
However, China is also emerging as one of the critical markets that global fashion companies cannot ignore. With a population four times larger than that of the United States and a rapidly growing size of the middle class, China is currently a very lucrative market that many fashion companies are targeting. It is important to look at the specific advantages that it offers to fashion firms such as Zara. It is important to understand that China, as a market, has a number of benefits that Zara can take advantage of in its operations here. The growing purchasing power, the huge market size, low production cost, and improved infrastructure are some of these pros (Ni & Wart 2016).
However, the focus at this stage will be to determine the advantages that Zara has over its market rivals in the local Chinese market. The superiority of Zara as a fashion firm is known in the Western markets, especially in Europe and North America. However, the study will look at whether they are applicable in the Chinese market. The study will look at what is making Zara more competitive in the market.
Efficient supply chain
In a market where competition is high, companies often try to find ways of improving their performance to cut down costs, improve their revenues, and win customer loyalty. Zara is known to have one of the very efficient supply-chain management systems in the fashion industry (Ni & Wart 2016). The good control of fashion and efficient supply are important factors that make Zara become one of the best fast fashion brands in the world.
It has properly coordinated departments that help to make sure that the raw materials arrive at the production plants promptly. The company has also developed an efective system that ensures that the finished products are delivered to the customers at the right time and in the right manner. The products are always available at its designated outlets, eliminating any possible cases of customer dissatisfaction that may be caused by the lack of availability of the products in the market.
Zara understands the market demand, always making available the quantity needed by a customer. It helps in avoiding overproduction that may lead to an oversupply of products in the market. The strategy ensures that the organisation is always in control of the pricing of its products. This capability offers the company a competitive edge over its rivals, which have a problem when it comes to managing a lean and efficient supply chain.
The ability to understand the changing trends
According to Information Resources Management Association (2018), the fashion industry is one of the most dynamic industries in the world. As explained above, changes in the industry are pushed by the industry players and changing customer tastes and preferences. Successful organisations understand that these changes are regular and must be managed to protect a firm from its negative consequences. As Prange (2016) says, timely tracking the fashion trends and accurate use of fashion elements is important. Zara has always known how to track the changes in the industry and act upon them in a way that can help it achieve the desired result in the market.
It is one of the leading change agents in this market. It has perfected the art of understanding the changing market forces and acting upon them in a way that yields the desired outcome. It is seen as a firm that understands the needs of its customers. This unique ability has been critical in enabling it to achieve success in the Chinese market. Its products are always considered superior to that of competitors, a very important characteristic of products in the fashion industry. It is making it an industry leader in this huge market.
Cultural exchange
The world is increasingly becoming a global marketplace where values and culture is easily shared among people of various countries. With more cultural exchanges between China and western countries, the fashion culture from west is also increasingly recognized by Chinese consumers, and the young people’s fanaticism to the latest fashion is regardless of national boundaries. Moreover, among the multitudinous popular trends, Zara’s fashion is found to be the most likely sought after brand by public. Zara’s designer also would exclude the elements that not suitable for everyday wear and too complex details, in order to make their products suits public and daily life.
The popularity of the Zara brand in the international market, especially in the western countries, has given it an edge over its local rivals in China. The Chinese consumers trust the brand partly because it is trusted in the developed economies. It is viewed as a unique brand that comes with prestige. Most of the local competitors in China have weak brand that is not even known properly in the local Chinese market. With that strong brand, Zara has found it easy overcoming stiff market competition in the Chinese market.
Rapid production
In a market where competition is very stiff, the speed with which a firm is capable of producing and delivering products to the market is very important, especially when dealing with a new product that is just launched in the market. The production system that Zara has been using in its European and North American markets has been introduced in the Chinese market. The company has invested heavily in developing a system that is efficient and effective.
The rapid production and distribution system is giving it an added advantage. Zara only takes 15 days to design and produce one new product, and could deliver to the stores in China within 40 hours (Lu 2014). It makes Zara occupy a great time advantage, when a new popular trend or fashion elements are released. China’s competitors tend to use much longer time to respond to the new fashion trend. Zara has often already sold a lot before the Chinese brands offering the similar products.
It means that even if the rival firms intend to produce similar products in the market, it will take them long time. It gives Zara a considerably time to enjoy the benefits of the newly introduced products. As an innovator in this industry, the speed of developing new products is delivering it to the market has made it stand out as a unique brand in the Chinese market. it has helped it expand its market share over the recent past.
Target positioning
Fashion industry requires a thorough understanding of the targeted market. Successful firms know that they need to target a specific segment of the market with very specific products instead of generalization. Demographical factors such as age, gender, social status, race, and religion all play a critical role in defining the purchasing pattern of customers (Ni & Wart 2016). Given that customers have several options to make when planning to make their purchases, they often opt for products that meet their specific needs. That is why targeting a specific market segment and positioning the products in the right manner is critical in achieving success.
Zara’s products target people of varying demographical classes, from youth, the middle-aged, and the elderly, to Muslims, Christians, and people of varying skin colour. The company often tries to ensure that it is as specific as possible when meeting the needs of its customers. This approach of operation has enabled it gain competitive advantage over its rivals in the Chinese market. Irrespective of one’s unique tastes, this firm always tries to meet the needs.
Reasonable expansion
As mentioned, Zara insist on direct way to operate stores, it runs 90% of its stores itself, and the rest are Joint venture franchising (Bhasin 2017). Therefore, in China, the number of Zara stores is not large, only 179 (Inditex.com 2017a). Relative to China’s local fast fashion brand, this is a very small number. Metersbonwe, once the largest Chinese local fashion brands, had more than 5000 outlets in 2013 (Schuman 2013).
Fewer shops are conducive to the brand image of the shape and unified management. Zara is very strict about choosing a store address. Its stores are often in the downtown area and next to the luxury brands, which create a better brand image. According to Frynas (2015), operating many stores inflates the cost of operation. It forces a firm to have a large size of workforce that requires regular training. In China, Zara has maintained a manageable size of the workforce trained to handle customers is a proper way. Its management maintains that it is important to have a reasonable expansion instead of growing rapidly without understanding the market forces.
Choosing the location is critical when it comes to long-term operations. Due to the unpredictability of China’s urban development planning, the original bustling area may become deserted. There is one flagship store has been closed in Chengdu, China because of the reducing revenues. Although relevant person in charge said that this is only normal, adjustment for the outlets of Chengdu area, the impact of store address change cannot be ignored (Retail News 2017). It is a clear warning that this firm must take strategic steps when it comes to expansion.
Risks
Cultural difference
It is important to appreciate that Zara faces a number of risks in its operations in the Chinese market. One of the risks is cultural difference. Due to cultural differences, the customer’s understanding of fashion and the demand for clothing would be different. For example, Western consumers tend to wear a fashion dress only once. Although a waste of resources, but greatly driven the market demand.
Relatively, Chinese consumers tend to wear a dress repeatedly. The requirements of the clothes tend to look good and suitable wear, while the enthusiasm to the latest trend relatively not that high. That situation to some extent affected the sales. It forces the firm to find a way of understanding the local culture and adjusting its operations in line with that culture. As Frynas (2015) says, a failure of an international company to understand the local culture may affect its ability to achieve success in the market.
Stiff market competition
The level of competition in the Chinese market is an issue that Zara may have to deal with in its operations. China is home to numerous local and international companies all of which are keen on tapping into the opportunities that the market has to offer. Sayle (2012) says that numerous international firms, especially from North America, have moved their production to China because of a relatively cheap labour and low cost of energy.
It costs less to produce in China, a benefit that is now turning out to be a problem because of the number of companies in the local market. Local brands such as Helen Lee, La Vie, Josie Chen Range, and Nicole Zhang are some of the top local players controlling significant proportion of the market. Top international brands such as Louis Vuitton, Dior, Burberry, Prada, and Gucci are also active players in the Chinese market.
They are established brands, with strong international image that the locals appreciate within the Chinese market. Competing against these brands may sometimes pose serious risk to a firm. Frynas (2015) notes that when dealing with luxury products, price ceases to be a competitive advantage that an organisation can use. In fact, an attempt to lower price in such a market may mean that the quality of products is compromised. On the other hand, when a company increases its product price, it will be hard-pressed to justify reasons why the price had to be increased.
Rampant cases of copyright abuse
According to Liti, Prostitis, and Tulip (2014), one of the biggest risks that international companies operating in China face is copyright infringement. It does not depend on the industry in which a firm is operating. Numerous unscrupulous companies exist in this country, which are very likely to steal ideas from other reputable companies. The country’s copyright laws are weak and do not effectively protect foreign firms.
The problem becomes worse when some local organisations develop their substandard products and use the brand name and logo of reputable companies. The problem is that when customers purchase these products, they will be dissatisfied because of the low quality they offer. It takes a long time, hard work and many resources to create a pool of loyal customers in the market. When a company loses such customers because of an imposter, it becomes a major problem. Zara is faced with this problem, although it has not affected it directly. It will be necessary to have a plan on how such a major risk can be dealt with in case it emerges in the market.
Recommendations
The Chinese market remains a very attractive destination for Zara and other fast fashion companies keen on tapping into the opportunity it offers. As the economy keeps growing, it is clear that the size of the market targeted by Zara will also continue to grow. It will need to continue taking advantage of the benefits available in the market. However, it is important to note that this company can only take advantage of the market opportunities if it has the capacity to cope with the risks in the market.
Its sustainability in the Chinese market will depend on its ability to take full advantage of the opportunities in the market while at the same time guarding itself against various risks that may emerge from time to time. The following are the recommendations that the management of Zara should consider to ensure that it remains sustainable and competitive in the Chinese market.
Partnering with top online retail outlets locally
China is home to a number of top online retailers. Molenaar (2016) says that the middle class all over the world have limited time that they find the idea of visiting brick-and-mortar stores a waste of time. They prefer making their purchases on trusted online platforms. Zara should find a way of collaborating with these top retailers to increase its sales within the Chinese market. The company has already ensured that its products are now available on Alibaba.
It should also target Baidu, Alipay, Amazon China, and Weibo among others to help it reach out to more customers in the market. Selling of products on e-platforms is a concept that is becoming very popular in China, and Zara should be keen to adopt the new trend. This strategy will help it take advantage of the opportunities available in the Chinese market.
Targeting specific market segments
Zara should ensure that its products target specific customers. Instead of releasing products that target general customers in the market, it should identify specific segments based on age, social class, gender, and any other relevant demographical classification. The organisation should avoid segments it considers less attractive. The attractiveness of each segment should be defined by its size and purchasing power. In each of the segments, this company should ensure that it provides high-quality products at all times. This strategy will help it cope with stiff competition in the market.
High level of vigilance in the market
One of the risks that were identified in the section above is possible cases of copyright infringement or theft in the local Chinese market. This is a serious threat to the firm’s ability to survive in the market. It is the responsibility of the management of Zara to deal with this problem in an effective manner. It should put mechanisms that will ensure that counterfeiters and individuals or corporate keen on stealing from this company are identified as soon as possible and are dealt with before their activities can affect this entity. It should have scouts capable of protecting the Zara brand and all its products.
Maintaining the spirit of creativity and innovation
One of the most important recommendations that the management of this company should take seriously is the need to maintain the spirit of creativity and innovativeness in all its operational activities. The market is increasingly becoming competitive and new challenges continue to emerge that this organisation must know how to overcome. On the other hand, opportunities will continue to arise in this market. The only way through which Zara can become one of the most successful fashion companies in China is to embrace creativity and innovation. It should always come up with new ways of operating in this market.
Molenaar (2016) suggests that a firm operating in the fashion industry should ensure that it is capable of coming up with new products more often to ensure that it can meet the changing customer needs and preferences. It should be seen as an innovator in the market not only in terms of delivery of new products on a regular basis but also in terms of using lean and efficient production systems. If the management of Zara takes into consideration these recommendations, it will be able to register impressive performance in the Chinese market.
Conclusion
Fast fashion brands such as Zara have enjoyed a long period of market growth as the number of the middle class continues to increase all over the world. These top brands are finding it increasingly important to expand their market share as a way of remaining sustainable in the market. One of the common strategies they are currently using is to explore international markets away from their home countries.
As new rivals emerge in their traditional markets, these firms find it necessary to operate beyond their home country markets. Zara is one such company that has considered operating beyond their home country borders. It has made entry into the Chinese market as it seeks to ensure that it becomes one of the dominant companies in this sector. The decision to move to the Chinese market was motivated by a number of factors.
It is important to note that as it moves to this new market, this organisation is exposing itself to a number of challenges. Indeed, the management weighed the challenges against the benefits and concluded that it was more beneficial to move to the new market than to avoid it. However, success can only be achieved if this company can effectively manage the risks it faces in this market while at the same time taking full advantage of the opportunities that the market presents. The study shows that successful firms in this industry have learned the art of defending their market share while at the same time acquiring new clientele base in the market. It is important to start by looking at the advantages and risks that this organisation should be aware of while operating in China.
Zara has a number of factors that make it stand out among the rest as one of the dominant players in the fashion industry globally. As discussed in this paper, the speed with which this firm is capable of producing new products and delivering them to the market is unmatched. Every time the company sees an opportunity to come up with a new product, they take the shortest time possible to develop it and make it available in the market before its competitors can steal the idea. By the time its rivals come with the same product, they find that Zara has already developed a pool of loyal customers and is making very attractive sales.
The supply chain at Zara is also superb. The management has developed a system that enables it to get the needed materials for production reliably. The company has established systems and structures that enable it to penetrate the Chinese market. It has a number of retail outlets strategically located across the major cities in China. It is also using a number of trusted online platforms to reach out to more customers.
It is currently using Alibaba.com to help it expand its market share beyond its brick-and-mortar stores. It is also clear that this company understands how to deal with the changing market trends. Fashion keeps changing, and it is critical for individual entities in this business to understand these changes and act upon them accordingly. Zara has been perfect at this, and it is considered one of the main change agents in this sector.
Competition comes in as a natural risk in this fashion industry. China is currently home to the highest number of the middle class. Over the past three decades, the country has experienced a consistent growth in its economy. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, most of who fall under the middle class, China is one of the top market destinations for the top brands in the fashion industry. The country has experienced an upsurge in the number of companies in the apparel business. Most of these entities are local while another significant proportion includes the top global brands.
Although the market is relatively big, these players are keen on dominating it as they try to outsmart their competitors. Another major problem in this market is the possible copyright abuse by some unscrupulous individuals and entities. They always target top brands such as Zara because they want to benefit from the huge trust and loyalty that these companies have created. They not only steal the concepts developed by these top brands but also the brand itself by selling fake products under a false name. Multinational corporations such as Zara also have to deal with the cultural differences in the market. Although globalization has helped in eliminating the geographic barrier, it is important to appreciate that the culture in China is significantly different from that in other western countries.
The management of Zara must understand how to cope with the challenges in the market while at the same time using its competitive advantages to strengthen its position as a dominant player in the Chinese fashion market. One of the major recommendations made is that the company should embrace creativity and innovativeness. The top management should encourage its employees to be creative in every activity they undertake.
They should be able to understand the emerging challenges and come up with creative solutions. They should work as a unit when trying to find a common way of addressing a given task. Creativity will help this firm to remain at the top of the industry in terms of delivery of quality products in a timely and reliable manner. It is also recommended that this organisation should target specific segments of the market that it feels are the most attractive.
By selecting specific market segments, it will be able to provide products that meet their needs in the best way possible. To help increase sales volume, it is suggested that Zara should collaborate with various online retailers in the market. It is less costly to sell on an online platform than to set up brick-and-mortar stores. The management should also be vigilant in terms of protecting its brand and products. It should have a team in the local market that will monitor any unscrupulous individuals or entities trying to sell their fake products under its brand name.
Reference List
Agola, N & Hunter, A 2016, Inclusive innovation for sustainable development, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Anastasia 2015, Understanding the 4C’s of marketing mix. Web.
Anderson, E 2015, Zara owner Inditex reports sales jump on Asian growth. Web.
Bain, M 2016, One chart shows how fast fashion is reshaping the global apparel industry. Web.
BBC News 2010, Zara launches online retail store. Web.
Bhasin, H 2017, Marketing strategy of Zara – Zara marketing strategy. Web.
Bishop, E 2013, What is the 4P marketing matrix. Web.
Blythe, J 2006, Marketing, SAGE Publications, London.
Burtonshaw-Gunn, S 2016, Risk and financial management in construction, Routledge, New York, NY.
Ceballos, F 2015, Zara: worldwide pricing strategy revealed by study. Web.
Consulting, D 2016, Fast fashion industry in China dresses a new mix & match generation. Web.
DeHaan, E 2016, ‘Fast fashion and its environmental and social impact’, The Eco Guide. Web.
Eckart, J 2016, ‘8 things you need to know about China’s economy’, World Economic Forum. Web.
Frynas, J 2015, Global strategic management, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Hanlon, A 2015, ‘The 4Cs marketing model – smart insights digital marketing advice’, Smart Insights. Web.
Hedley, M 2017, ‘Chinese market entry: b2b international’, B2B International. Web.
Heller, L 2017, ‘Why Zara is the most exciting retailer today’, Forbes. Web.
Holt, D, Quelch, J & Taylor, E 2004, ‘How global brands compete’, Harvard Business Review. Web.
Hon, J 2016, ‘How to break into the Chinese market’, Minutehack. Web.
Inditex.com 2017a, Zara – inditex.com. Web.
Inditex.com 2017b, Inditex annual report 2016. Web.
Information Resources Management Association 2018, Fashion and textiles: breakthroughs in research and practice, Business Science Reference, Hershey, PA.
Jham, V & Puri, S 2014, Cases on consumer-centric marketing management, Business Science Reference, Hershey, PA.
Kaufmann, H 2015, Handbook of research on managing and influencing consumer behavior, Business Science Reference, Hershey.
Kokemuller, N 2017, Cite a website – cite this for me. Web.
Liti, S, Prostitis, P & Tulip, M 2014, Central themes in business studies, EDUCatt, Milano.
Lu, C 2014, Zara supply chain analysis – the secret behind Zara’s retail success. Web.
Lynn, M 2011, Segmenting and targeting your market: strategies and limitations. Web.
Mahajan, G 2016, What is customer value and how can you create it. Web.
Marketing to China 2014, Zara decides to develop a more refined strategy in China – Marketing China. Web.
McClean, R 2012, The C’s and P’s of marketing: what’s the difference. Web.
Molenaar, C 2016, Why customers would rather have a smart-phone than a car: relationship retailing as an opportunity, Routledge, New York, NY.
Ni, A & Wart, M 2016, Building business-government relations: a skills approach, Routledge, New York, NY.
Oijala, L 2016, What is fast fashion. Web.
Perreault, W, Cannon, J & McCarthy, E 2014, Basic marketing, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New York, NY.
Prange, C 2016, Market entry in China: case studies on strategy, marketing, and branding, Springer Science and Business Media, London.
Pratap, A 2017, Marketing mix and marketing strategy of Zara fashion. Web.
Reference 2017, What is STP analysis. Web.
Retail News 2017, Zara China closes giant flagship store in Chengdu. Web.
Reuters 2014, Zara owner Inditex to join Tmall to reach more Chinese shoppers. Web.
Rosenblum, P 2015, Fast fashion has completely disrupted apparel retail. Web.
Sayle, S 2012, Cam & Zara the travel bugs – China, John Wiley & Sons Publishers, Hoboken, NJ.
Schuman, M 2013, Never heard of metersbonwe: well, you will soon. Web.
Shen, F & Tiller, L 2010, Top eight legal issues regarding entering the China market. Web.
Smith, K 2014, Zara vs H&M: edited compares the apparel retailers’ strategies. Web.
Staff, I 2017, Risk. Web.
Tong, F 2014, ‘Zara expands in China via Alibaba’s online marketplace’, Digital Commerce 360. Web.
UKEssays 2015, ZARA in Indian and Chinese market. Web.
Worldometers.info 2017, China population (2017, 2018) – world meters. Web.
Yan, P 2014, Zara, H&M in quality safety scare – China.org.cn. Web.
Yau, P 2016, ‘China’s garment market HKTDC’, China-Trade-Research. Web.
Yu, C 2016, ‘Zara’s secret to success retail – its pricing strategy’, T1 2016 MPK732 Marketing Management. Web.
Yu, K 2017, What political reform looks like in China. Web.
Zara.cn 2017, Zara shop in China. Web.
Zhu, S, Pickles, J & He, C 2017, Geographical dynamics and firm spatial strategy in China, Springer, Berlin.
Zia, M & Kumar, N 2016, ‘A three dimensional vertical differentiation model: implications for segmentation, targeting and positioning’, SSRN Electronic Journal, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 55-76.