World Economy and France
The recent global financial crisis, also considered as the credit crunch, is a dilemma that almost collapsed the majority of the world’s leading economies. Fears of another Great Depression loomed as financial experts became divided on whether the economy can still regain its momentum or not. Some experts say that the recession that began in 2008 was worse than what happened since the Great Depression of the 1930s when the economies in Europe went stale after the effects of the First World War, affecting even the commerce of the United States. But during the Great Depression, the financial crisis was mainly concentrated on the United States and Europe In the recent financial crisis, however, the recession has affected even the strongest economies like Germany and Japan, sweeping even to the Asian region.
The recent financial crisis is a worldwide phenomenon that almost collapsed the entire financial system. Because the world markets are interconnected with each other via trade partnerships and credit, the collapse of one financial institution would result in a domino effect on other financial systems. Now, the term financial crisis is normally used to describe an event where a financial institution or a set of assets suddenly drop in value. Often, it also refers to the bursting of a bubble, a crisis in currency, a market crash, or a nation that defaults in its foreign debt. A financial crisis leads to difficult economic consequences, but it is manageable if suffered only by a single institution or asset, which, in such a case, can be considered a banking failure. However, in this recent crisis, analysts consider it a systemic financial crisis because the entire financial system is in trouble.
Macroeconomics Indicators- Banks and funds across the world have been negatively impacted by the adversities arising from the sub-prime crisis, primarily because borrowers had bought bonds and risks that were directly linked to sub-prime loans. The collapse of the home market highlighted the weakness in different ways because such debt had been framed, especially in regard to the massive risk associated with inaccurately selected risk assessment. The collapse of the US banks in the year 2008 – beginning especially with the Lehman Brothers bank – had a critical impact in triggering an era of crisis that quickly spread into the other parts of the globe as well. As a result of this crisis inter-banking market across the world has quickly dried out. this was added with the additional factors like subtler and more difficult lending conditions, higher prices of borrowing for companies to accumulate capital assets, expand and/or maintain their existing business volumes and constant collapses suffered by the stock markets. The markets reacted swiftly after the collapse of Lehman Brothers and there was large-scale redemption of asset-backed securities within a week of the collapse. Financial institutions could not provide for the over $2 trillion worth of credit that they had extended, thereby leading to problems of refinancing by wholesale funding institutions. Conventional sources of funding were not available and banks aimed at improving their financial position by reducing lending. Therefore it became very difficult to borrow across the entire world, which further led to the decline of real estate markets.
The slumping confidence of consumers, which is reflected in the business sectors as well, has become a major factor behind the consistently declining rates of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The net results of these events have been a more than a noticeable decline in the investment areas of the corporate sector in addition to a major restocking and a compressing experience in the world trade segments as also threatening levels of deterioration in the labor markets across the world – this has been particularly true in the case of property industrial workers
Brief History on BNP
BNP is a financial institution with its headquarters in France and among the fifth largest banks in the world. They offer various products and services which include car loans, consumer loans, housing finance, educational loans, credit cards, Retail Banking, Corporate, Investment, Treasury and Wealth Management. These products and services are offered for individuals, corporate institutions and for government entities both locally and internationally. Retail banking includes a comprehensive range of financial products viz. deposit products, residential mortgage loans, credit cards, auto finance, personal loans, consumer durable loans, loans against equity shares, loans from subscribing to Initial Public Offers, debit cards, bill payment services, mutual funds, investment advisory services. These products provide an opportunity for banks to diversify their asset portfolio with high profitability and relatively low NPAs. Today, the most proactive banks have entered the retail banking segment and have identified it as a principal growth driver. They are slowly gaining market share in the retail space. For several years now, banks viewed consumer loans with skepticism. Commercial loans dominated the bank’s portfolio as they generated high net yields with low credit risk. Consumer loans in contrast involved smaller amounts, large staff to handle accounts and high default rates. They were considered substandard by the banks. Even the regulators across the globe have not encouraged consumer finance till very recently. However, over the recent past, fierce competition among the banks lowered the spreads and profitability of commercial loans. With deregulation and an increase in consumer loan rates, the risk-adjusted returns in the retail sector have exceeded the returns on commercial loans.
Competition, securitization, automation and regulation are the major forces that are driving and shaping consumer lending. Net banking, phone banking, mobile banking, ATMs and bill payments are the new facilities that banks are using not only to lure customers but also to help them reduce their total operating costs. For example, if we look at the Indian Retail Banking market, it is dominated by consumer credit. Even nationalized banks, which control more than two-thirds of the banking business in the country, are tapping retail lending with great vigor. The enormous competition has led to innovative retail banking products that are extremely customer–friendly.
The growth in retail banking has been facilitated by the growth in banking technology and automation of banking processes that enable the extension of reach and rationalization of costs. ATMs have emerged as an alternative banking channel, which facilitates low–cost transactions vis-à-vis traditional branches. It also has the advantage of reducing the branch traffic and enabling banks with small networks to offset the traditional disadvantages by increasing their reach and spread.
The retail banking industry is diverse and competitive. In addition to checking and savings account service, banks offer brokerage and insurance capabilities to manage all aspects of a customer’s financial portfolio. Attracting profitable customers from competitors is essential for long-term success. Retail banking has both pros and cons. In the present situation, the bankers have very little option, but to chant the ‘retail mantra’. Banks today face complex challenges on multiple fronts. Customer expectations are higher than ever, with growing demand for more rapid service delivery and more flexible, personalized interaction.
The bank is owned by many shareholders including AXA, SFPI, Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg, employees, corporate officers, treasury shares, retail shareholders, institutional investors, socially responsible shareholders, Europe.
Board of Directors
- Baudouin Prot- Chief Executive Officer
- Michel Pébereau- Chairman
- Claude Bébéar
- Jean-Louis Beffa
- Suzanne Berger
- Patrick Auguste
- Georges Chodron De Courcel- Chief Operating Officer
- Jan-Laurentonaf- Chief Operating Officer
- Miclonczaty- chief K Ffice
- Frédéric Lavenir – head Of Group Human Resources
- François Villeroy De Galhau- head Of French Retail Banking
- Janamon -managing director, Head of compliance and internal Control coordinator
- Philippe Bordenave -Senior Executive Vice-President, Chief Financial Officer
The Competitive position of BNP
The bank’s bank rating is among the best in the banking sector. The bank has many competitors in the international market. In France, the banking sector has been intensely competitive, but the landscape had somehow changed because of the economic problems that hit the world. However, the race is still on for who can offer lower financing, preferred rates and investment services. Because of this, it is imperative that the new executives act on behalf of the customers’ interests because the future of the bank is in the continued patronage of these customers. It is safe to assume that these new managers are aware of their beneficiaries’ expectations because these are the reasons why they have been hired for their new positions. The following is the rating of the bank
Ratio Analysis
Return on Asset- This measures the amount of profit made per value of assets that they own. It gives an idea as to how efficient management is at using its assets to generate earnings. This rate has increased from 2009 due to an increase in the total assets.
Net Interest Margin- Net Interest Margin not only indicates the profitability of the bank but also gives more detailed knowledge about risk management by the bank. The bank would want to keep this ratio high to be able to show they are good risk management. Whereas, Net Interest Margin could be valuable in measuring the success of its risk management in terms of managing people’s money.
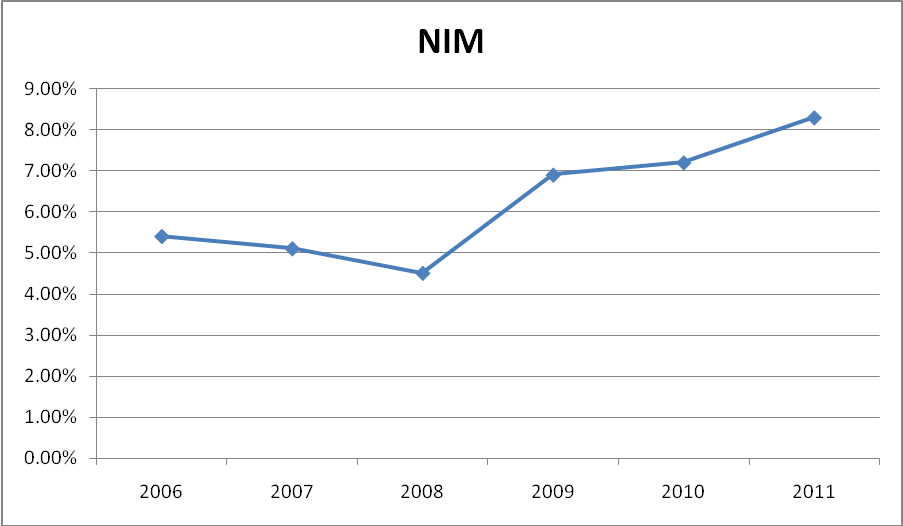
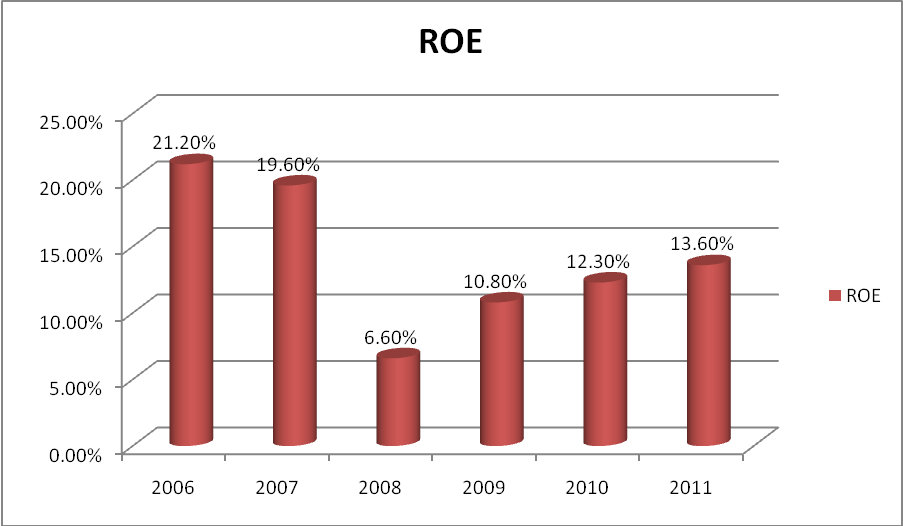
Return on Equity- Return on equity measures a corporation’s profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested. The graph shows the performance of the ratio;
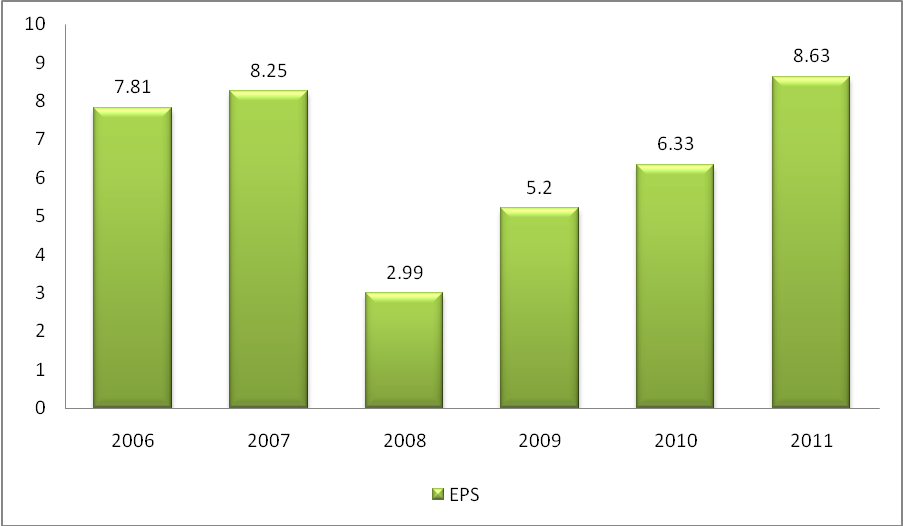
Earnings Per Share -The portion of a company’s profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. Earnings per share serve as an indicator of a company’s profitability. The ratio indicates how profitable a company is by comparing its net income to its number of shares outstanding. the performance of this ratio was as shown in the graph below;
Risk Management
Net Interest Margin not only indicates the profitability of the bank but also gives more detailed knowledge about risk management by the bank. The bank would want to keep this ratio high to be able to show they are good risk management. Whereas, Net Interest Margin could be valuable in measuring the success of its risk management in terms of managing people’s money. This ratio is for the bank was decreasing meaning that the risk of the bank was decreasing annually as shown in the excel appendix. The trend curve below shows how the bank was fairing.
This ratio is important in indicating whether a company has sufficient cash to finance its debt. This ratio is, however, limited in that it does not guarantee that the cash flow from operating activities will increase and this is the main concern for the investor.
From excel it can be observed that the bank is very conservative in nature in dealing with risk. However, that attitude might cost any organization a lot of opportunities in return. Bank manages its credit risk exposure by implementing diversification in every business that they do. Their investments, capital markets, and lending and financing activities are diversified to avoid undue concentrations of risks with individuals or groups of customers in specific locations or businesses. It also obtains collaterals when appropriate. The types of collaterals obtained include cash, treasury bills and bonds, a mortgage over real estate properties and a pledge over shares. The group uses the same credit risk procedures when entering into derivative transactions as it does for traditional lending products. The bank is also involved in hedging foreign exchange risk.
Liquidity is the risk that the group will encounter difficulty in meeting obligations associated w/ its financial liabilities. Repayments, which are subject to notice, are treated as if notice were to be given immediately. The group expects that customers will not request repayment before the contractual repayment date. They maintain a portfolio of highly marketable and diverse assets that could be readily liquidated in the event of an unforeseen interruption to cash flow.
Forecasting the Balance Sheet 2012
The excel file shows the forecasted financial statement of the company:
Forecasting the Income Statement 2012: