Abstract
This report examines the performance of Foodco in the last two fiscal years. It determines the company’s ability to meet its obligations, profitability level, and solvency. It also examines the company’s strategies using Michel Porter’s five forces model. It concludes that the company is financially healthy but needs to focus on its business strategies.
Introduction
Foodco Holding is one of the companies under the banner of UAE’s Abu Dhabi National Foodstuff Company (Foodco), a public shareholding company established in 1979. Foodco is involved in importing and distributing household items and foodstuffs in the UAE, packing, repacking, importing, exporting, distribution, and sale of food products.
Purpose
The purpose of this report is to develop a comprehensive analysis of the company’s performance (based on ratio analysis) and business strategy based on the five forces analysis.
Business strategy analysis
A business strategy is an initial step in determining the profitability of a proposed venture. The Michel Porter model is a framework that examines five forces that influence an industry.
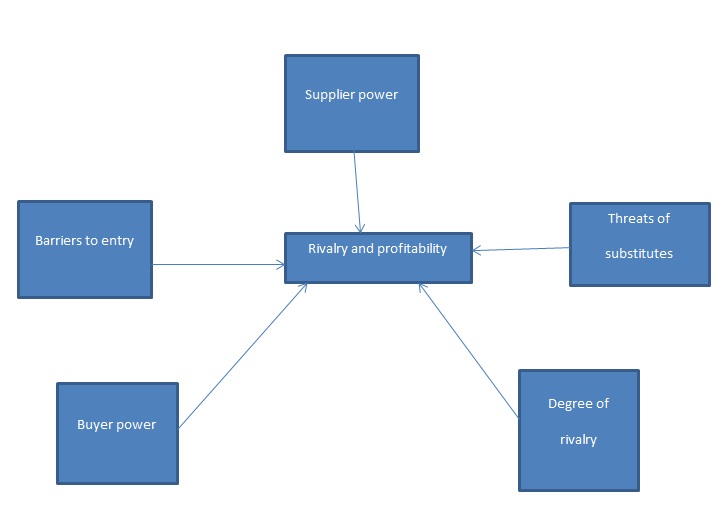
Rivalry
Foodco faces strong competition from rival corporates in the food distribution industry in the UAE. The international and regional firms that are involved in the foodstuff business, including distribution, importation, exportation, packing, repacking, and processing activities, dominate the UAE foodstuff industry. Among other companies, Alma Foodstuff, the Gulf International, Jaleel General Trading, Belselah Foodstuff, and Food Center are the major rivals in the industry. Nevertheless, Foodco is able to fight rivalry through working with subsidiaries and providing them with the appropriate backing in order to achieve the core objectives.
Threats of Substitutes
Substitute products are the products and services in other industries that have the capacity to satisfy the same need (Kevin, 2007). In the UAE, the foodstuff industry does not have substitutes, which means that the company does not have concern for substitutes.
Buyer power
The presence of many suppliers and few buyers means that buyer power is strong (Triantis, 2009). In the case of Foodco, the number of foodstuff suppliers in Dubai is relatively large due to the presence of local, regional, and international competitors.
Supplier power
The power of suppliers in an industry is the impact that suppliers of goods and services or raw materials have in an industry (Porter, Argyres & McGahan, (2006). In the UAE foodstuff industry, the number of suppliers is relatively large.
Barriers to entry
In the UAE, the government regulates the foodstuff industry through laws and food safety regulations. In addition, the government has a strict tax policy that demands heavier taxes from foreign companies than local companies. However, the industry’s profitability is relatively high, which encourages foreign companies to enter the market.
Generic strategies to counter the five forces
Foodco has been using a strategy that involves working with subsidiaries in order to counter the competition and rivalry, expand the market, and increase sales. This means it has differentiated its business in order to counter these forces.
Foodco Introduction
Mission
The company’s mission is to provide all of its subsidiaries with the appropriate backing in order to achieve their core objectives and ensure that they are resourced and managed appropriately.
Ratio analysis
Liquidity ratio
Liquidity ratios describe the company’s ability to meet its short-term liabilities, such as debts and loans. Foodco has high current, quick, and operating cash flow ratios. The ratios are non-negative, which means that it can repay its short-term debts using short-term assets.
Solvency ratios
The debt ratio of more than 40% and a cash-debt ratio of 0.14 are enough to explain that the company has a sufficient cash flow that can meet its obligations.
Profitability ratios
Profitability ratios measure the ability of a firm to reap from its activities by making gains. In this case, Foodco’s gross profit ratio, ROA and PMR increased significantly in 2013.
Conclusion
This analysis shows that the company is a strong destination for investors to make gains from their investments because the profitability ratio is high. In addition, it is able to meet its short-term and long-term obligations. Moreover, the company does not face serious threats of new entrants, while consumer power is not a major threat. Nevertheless, all its strategies must consider the evidence of heavy competition in the industry.
References
Kevin, P. (2007). Coyne and Somu Subramaniam, “Bringing Discipline To Strategy”, The Mckinsey Quarterly, 12(4), 14-25.
Porter, M., Argyres, N., & Mcgahan, A. M. (2006). An Interview With Michael Porter. The Academy Of Management Executive 16(2), 44-46.
Triantis, J. E. (2009). Navigating Strategic Decisions: The Power Of Sound Analysis And Forecasting. New York: CRC Press.