General Motors Corporation has Toyota Motors and Ford Motors at present as main competitors. Both of them are multinationals. General Motors is headquartered in USA was founded in 1938 by William C. Durant. In the year 2008, General Motors stands as the world’s largest automaker firm according to industry statistics around the globe. (Bunkley) it is present in around 35 nations and has 284000 people at present. The brands sold by the firm are Buick, Chevrolet, GMC, Opel, Pontaic, Saturn, GM Daewoo, Cadillac, Holden and Saab. (About GM) As a publicly traded company it is the fifth largest in the world as ranked by Fortune Global 500.
General motors at the moment have reached level of maturity in the business cycle. This cycle is called election cycle at this level the firm has borrowed more or credit than they use equity shares this cycle in the business requires reinvention and reinvestments in order to remain competitive if the firm does not take care they will find themselves closing the shop because of credit facilities that they took this cycle of bankruptcy under which general is at with makes them loss a lot of business because customers will not willing to transact business with a bankrupt institutions. However, most firms in the united states of auto industry are facing similar circumstances what it means is that the automobile industry in the United States has reached this bankruptcy level.
When the firm reaches this level it starts experiencing diminishing returns if technology and competitiveness is not embraced. The cause of diminishing returns for firms such as general motors is inability to use factors of production well the share holders of the company should inject new capital, to inject liquidity and remove some unwanted debt.
Ratios Analysis
Liquidity
On short term financial stability, the current ratio indicates that the firm is not financially stable since in 2005. This ratio was 0.87:1 in 2005 it improved to 0.93:1 in 2006 before slighting back to 0.86:1 lower than the two previous years while the industry average is 1.06:1. As a result of the company’s fluctuating current liabilities, decreasing current assets and decreasing performance in has lead to poor liquidity. Its quick ratio has fluctuated from 0.58:1 to 0.64:1 before settling at 0.57 in years 2005, 2006 and 2007 respectively while the industrial average is 0.85:1. The cash ratio is also having the same trend.
Although these ratios improved in year 2007 but the performance was not as in year 2005. This current ratio means that for every dollar the company owes in short term liabilities, it has 0.87 dollars, 0.93 dollars and 0.86 dollars in current assets for years 2005, 2006 and 2007 respectively. The current ratio indicates that the firm is not financially stable as it is less than the recommend ended average although the auto is performing poorly. Current liabilities may or may not include short-term borrowings.
Creditors consider current assets as a buffer for current liabilities and hence they prefer a higher ratio. However there is an increase in the ratio. This is due to an increase in investment in debt securities and decrease in accrual expenses. The quick ratio indicates how able the firm is in meeting its financial obligations from the most liquid assets. It shows that the firm is strong in it liquidity.
Should be there Technical default then the company will not be liquidated as liquid assets are enough. The recommended ratio should be 1:1. The Quick Ratio shows that the liquidity position of the firm gone down in terms of its ability to meet short-term obligations. The reason why these are so high is due low investment in debt security which the company then increases steadily in the subsequent years.
Working capital amount is quite adequate which increase consistently during the past three years. It shows that company is in good position to finance its short term financial needs. In terms of liquidity the company is performing than industry as it can be depicted by the industry average of 1.06:1 and 0.85:1 for the current ratio and quick ratio.
Profitability ratio
From its fiscal years ending December 31, 2005, 2006 and 2007, general motors showed fluctuating net income figures available to common shareholders. From a loss of $10.567 billion in fiscal year ending December 31, 2006 to just $1.978 billion in the fiscal year ending December 31, 2006 while 2007 the loss increased to 38.732 billion decline of more than 100 per cent for that period: 72.39 per cent in 2005, 36.35% for 2006 and 104.42 per cent in 2007.. The decline in profitability was exacerbated by a non-parallel decrease in selling, general and administrative expenses which resulted to a decline in operating income.
Return on Assets is also used for the same purpose of measuring the overall performance. However to be meaningful to calculate the ROA it should be adjusted for implicit interest which is difficult to estimate and hence makes the process unnecessarily complicated. The figures show that performance is lower in 2007 than in 2006 and the performance ratio is 0.60% and 5.79% respectively while the industrial average was 4.25%. this means that the company is doing poorly than the industry.
The return on owner’s equity also shows a downward trend through the periods 2005 to 2007. From the period 2005 to 2007, it was below the industrial average which is 12.1%. However in 2006, the ratio improved. However, there exists no record of the industrial average to compare with.
As to the ability of the company to continue showing profitability in the next three years or so, that depends on how fast the US economy will recover from the economic crisis. After all, general motors business is strongly dependent on the economy. Therefore it is difficulty it is difficult to say that the performance of the company itself has increased.
Market price
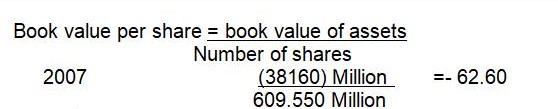
The decline in profitability of the company and the worsening situation of the US economy was eventually reflected into the price of general motors stocks as they traded in the stock exchanges: from a price high of $31.189 in the fiscal year ending December 31, 2007 to just $3.18 in the fiscal year ending, 2008.
This decline resulted to a price earnings ratio of -0.49 times from -1.15 times in December 31, 2007 and 2005, respectively which is below rhe industrial average0.17. This and other factors such as earnings yield, made the company’s total investment return to its shareholders for the period ending December 31, 2005 at a negative 64.39 per cent. This means that if an investor invested $1,000 in General Motors stocks on February 1, 2005, that investment is only about $204 at the end of the period – December 31, 2007.
However, the market estimated that General motors earnings per ordinary share in the next fiscal year, December 31, 2008, is actually higher than their estimate of this year’s earnings per ordinary share last year. The estimate for the price earnings multiple, on the other hand, is lower than this year. Market price to book value also went down from 1.6 to -0.5 in years 2005 to year 2007 while industrial average was 0.17. earning yield also show the same trend go on that is industrial average is more favorable as compared to the three year company rates.
Leverage ratio
Interest coverage ratio improved from times 3.5 in the year 2006 to 4.3 in the year 2007 as well as 2008. What it means is that interest coverage ratio improved and credit providers will be confident with the profitability of the company. Cash coverage ration also improved from 2.5 to 2.6 before coming back to times 2.5. It means that some expenses in the company were affected by inflation tendency due to financial and at the same time the management was unable to convert receivables into cash.
Asset utilization
Despite the declining net income and net margin figures reported by General Motors, the company showed an improvement in its asset turnover ratio from 0.405 times to 1.11times for the fiscal years ending 2005 and 2006 respectively. While in the year 2007 it was times 1.22.
An analysis of the company’s balance sheet, on the other hand, shows that current assets, total assets, current liabilities, long term debts, total liabilities and total shareholders equity all declined at the end of 2007. However, due to lower sales and slower inventory turnover, the company’s total inventory by 2006, as a proportion of total assets and all the rates are below the industry of 0.62 which is an average for 5 years.
The company’s Inventory turnover is 8.4 times in 2007 which is the higher turnover than 2006 that is times 6.16 meaning that the average stock was turned 8.4 times in 2007. It shows that company declined in its performance in terms of converting its inventory into sales resulting in higher sales figure during the year 2006 and 2007. the industry has an average of 7.23. this means the company manages stock better the other players industry.
The rate at which the company converts debtors/receivable into cash in 2007 is times 30 days which are higher than the figure of 2005 and 2006 of times 30 and 32 respectively while the industry average is 8.43. It means that the efficiency with which the firm is utilizing its debtors to generate cash is improved.
Sales to account receivable is has fluctuated over the three years showing that company is rapidly converting its receivable into cash. Same is the case with inventory. The company is converting its inventory into sales rapidly over these years resulting in higher sales. It shows that company is converting its inventory into receivables and receivable into cash quite efficiently.
Valuation
In valuing this company dividend growth model will be used as well as earnings per share. Using published financial statement, capital pricing model will be used to arrive at the cost of equity for the firm which in turn will be used to determine the value of the company. This company has a beta of 1.77 as at 26th November
The cost of equity will be calculated as follows through equity,
Ke = Rf + β(Rm –Rf)
whereas;
- Rf is the risk free rate
- Rm is the market rate
- While β is beta.
From the information available, risk free rate is the American Treasury bill rate which is 4.23%. the market rate is 11% and β is 1.77. Therefore cost of equity is
4.23+ 1.77(11-4.23) = 16.21%.
Using the dividend growth model which is

Wheres:
- Ke is the cost of equity,
- Div is dividend one year from now
- While g, is growth of dividend
In this case growth of dividend will be measured by measuring the growth in net income available to common holders.
Therefore the value of the share is
0.41
0.1621
=2.53
Recommendations
From the calculations carried out I can conclude that the shares of this company are overvalued in the market therefore I will advice an investor not to purchase the share since the intrinsic value is lower than the market value. Overall, the market’s outlook on General motors is a hold.
In order to achieve better future results, better or close to industrial average, the firm needs to cut down its operating expenses. This would considerably improve the profitability ratios. They also have to review their policy on capital management and keep optimal levels of various items of current assets.
This would improve the firm’s liquidity position. In order to improve the return on owner’s equity ratio, the management should invest in viable projects that would yield positive NPV’s. This has the effect of maximizing their wealth. To improve on the financial ratios, the firm would ensure that it has more liquid assets and also resort to internal sources of finance as opposed to external ones.
Based on the debt ratio, and if the restaurant is to finance the operations , it is should not be through external borrowings (debt), then it would be advisable to do so. This is because Blue Ribbon’s debt management is efficient as shown by the declining trends of debt. However, the management of the restaurant is not efficiently utilizing the current equity as shown by a decline in the return to equity over time.
If additional borrowings would however adversely affect the restaurant’s balance sheet position, they should withdraw the expansion plan. Additional borrowings can increase the restaurant’s gearing hence subjecting it to financial risk.
Work cited
Brown, Philip George foster , and eric Noreen, security analysis multi-year earnings forecast and capital market. Sarasota, FL: American accounting association.1985.
Cohen, Jerome B.,Edward D. Zinbarg, and Arthur Zeikel, Investment Analysis and Portfolio management, 5th ed. Homewood, IL; Richard D.Irwin, 1987.
Davis, H.Z,. and Y.C Peles , measuring equilibrating forces of financial ratios , the accounting review ( 1993)
Fama, Eugene and Kenneth French, the CAMP is wanted, dead or alive, working paper, graduate school of business, University of Chicago, 1995.
Largay, James A III and Clyde P. Stickney, cash flows, ratio analysis and the W.T Grant Bankruptcy, financial analysis journal (1980)
Saunders, Anthony, financial institution management: a modern prospective 2nd ed. (Chicago, IL: Richard D Irwin) 1997.
Train, John, Money masters. New York: Harper and Row 1987