Executive Summary
This is a risk assessment report for Global Finance Inc. (a fictional institution) The company has serious security issues, which affect its assets and have severe consequences on its reputation, finance, and operations. The report shows risks associated with GFI assets and possible mitigating approaches.
The report identifies and describes GFI authentication technology and network security challenges. It also shows both internal and remote access points of the company’s network. The report also has a design of secure authentication technology and network security for GFI. Moreover, it provides assumptions for any unknown facts identified in the process. The report identifies all known vulnerabilities in the GFI system and then proposes a new design.
The use of combined technologies is important in this case for enhancing authentication and network security measures. In addition, the report also addresses the CEO’s concerns about the mobility security and design for secure mobile computing for portable devices with regard to authentication technologies and protection of data.
The report also contains areas of wireless vulnerabilities and provides recommendations for protecting the network against security breaches. Finally, it shows a cloud computing system for GFI, which has secure ways of data protection under different situations.
The report also shows security risks and identifies them with severity as critical, high, medium, or low with associated impacts to GFI.
The report highlights information security challenges at GFI. It is important for the CEO, COO and other senior executives to take part in formulation of security policy to protect GFI from both internal and external threats. The security policy must account for prevention, detection, and response.
Risk Assessment
Risks assessment is critical for GFI. The process identifies threats and vulnerabilities that GFI has suffered from its vulnerable information technology (IT) environment. Risk assessment shall allow the company to detect, avoid, and minimize threats and fix all discrepancies in its policies and procedures in an effective way.
The aim of the risk assessment at the company is to avoid possible monetary losses and damages to its reputation. Threats have caused damages to GFI in the past. In addition, attackers have exploited its system vulnerabilities to gain access to confidential information of clients.
The scope of Risk Assessment at GFI
The risk assessment scope for security and GFI system vulnerabilities covered the following areas:
- Networked servers, such as Web, e-mail, application
- Desktop and mobile devices used by staff members
- Network devices, such as firewalls, switches, routers
The scanning tools have the ability to detect any known security breaches or bugs in the IT infrastructures. The tools can also determine if the GFI systems are prone to known attacks and exploitation by hackers. In addition, they can show vulnerabilities with software and hardware in terms of setting and determining flaws in security policies (US Department of Commerce, 2011).
Scanning of GFI systems focused on critical areas like servers and the networked equipment. Some key departments and administrative areas were also potential areas for scanning. The approach was suitable for understanding attack trends on the system, avoiding intrusive and disruptive scanning of the entire assets. GFI system scanning had clearly defined goals.
- Identify various securities issues at GFI, analyze tools, procedures, and processes in use with aim of improving security features of the company network. Risk identification and quantification of their potential impacts on the business was to allow management to understand and prioritize risks and conduct cost-benefit analysis of risk mitigation at GFI.
- Understand the extent of risk impacts from threats and vulnerabilities, and their abilities to harm the company in case of an adverse attack. It is also important to assess consequences of damages in terms of legal implications, relationships with customers, other partners, and accessibility of sensitive information.
- Identification and recommendation for enhancing security policies of GFI networks
- Show recommendations for all threats and vulnerabilities discovered during risk assessment of GFI assets
Risk Rating
The report assigned specific risk based on a risk rating metric. Risk rating depended upon the severity of the threat or system vulnerabilities. We defined risk rating for GFI security situation as follows:
- Critical – extremely severe damages to the bank in case of security breaches. The impacts were immediate with massive financial losses to GFI and legal action from clients. The bank lost ability to conduct its business. The situation could lead to imprisonment of perpetrators and other life-threatening damages.
- High – the situation leads to severe damages in cases of breaches on confidentiality and integrity of the system. The effect can impair core operations of GFI. Consequences can lead to imprisonment, financial loss, loss of life, and may need legal action as a remedy to the situation.
- Medium – GFI may suffer serious damages because of breaches on confidentiality and integrity of the system. It could suffer financial losses, legal implications, and damage to the systems. However, the situation may not cause loss of life or imprisonment and other life-threatening outcomes. In addition, GFI will be able to perform its core operations, but at reduced standards. The situation may also require a legal action to correct.
- Low – the compromise of GFI’s network has minor repercussions to the bank. The damage has minor financial losses, harm to people, and minor damages to the company’s assets. The damage affects effective delivery of services. Correctional measures require administrative intervention.
A list of access points internal and external (remote)
- Wireless access points or Wi-Fi
- Internet
- Local and remote workstations
- Intranet Web servers
- A SUS server
- File servers
- The trusted computing based (TCB) internal network
GFI Security Risks and levels of severity
Access Control
Access control only allows users to gain access to resources, which match their roles at GFI. Access control also focuses on gaining physical access to GFI servers, workstations, devices, and other hardware, as well as complex network systems and passwords.
- Users have weak passwords, which attackers can easily guess (Critical)
Attackers have gained access to GFI network for few years because of possible weak passwords. They can easily generate such passwords by using different techniques. This is a critical issue for sensitive data security. Such passwords are short, default, or common names. Users must change their passwords to complex ones, which have combinations of characters.
Corrective action – the IT department must introduce a complex password policy, and users must create complex passwords.
- User passwords do not expire after a given period, and users fail to change their passwords regularly (Medium)
Prolonged usages of the same passwords make them weak and vulnerable. Passwords lack expiry dates scheduled in the user profile. This is a risk to the company.
Corrective Action – the company should schedule password expiry after 30 days. The system will automatically prompt users to change their passwords.
Security Designs or Architecture
These are the standards, principles and designs, which network engineers use in network configuration in order to develop secure networks for protecting information assets. The IT department must focus on network diagrams, virtual local area network (VLAN) configurations, virtual private network (VPN) devices, instruction-detection systems (IDS), and network-monitoring tools.
- System relies on non-real-time analysis and detection only happens after the intrusion has taken place (Critical)
The security systems cannot detect intrusion on real-time basis.
Corrective Action: the IT department must review security architecture.
- Lack of regular updates for the network-based IDSs, VLAN, and VPN (High)
The network may lack effective intrusion detection systems because the IT department cannot block, identify, or keep log of all threats on the network.
Corrective Action: GFI must implement IDSs.
- GFI lacks firewall policy (Medium)
GFI has no policy on firewall to show traffic in the company network. Thus, GFI cannot determine whether safe users or attackers are gaining access to the network. The abnormal traffic may be originating from potential attackers. Firewall must guide the use of all communication platforms.
Corrective Action – formulate and implement firewall policy for the following areas:
- Network categorization based on risks
- Vulnerabilities
- Follow industry best practices on intrusion detection
- Exception policies on access
- Network traffic matrix
- Firewall policy document and corrective action upon detection of threats
Network Security
The aim of effective network security is to ensure integrity, availability, and confidentiality of data. Several attacks on the GFI network show that the company lacks effective network security. The IT department must review all access points on the network.
- No patch management for third party programs (Critical)
Patch management on third party software may not be active. The IT department should know the condition of patch management, including those of third parties. Vulnerabilities could have also originated from outdated versions of third party patches.
Corrective Action – update patches on the network and acquire applications that can manage third party patches.
- The network has outdated and unreliable software (High)
Vulnerabilities of the GFI network may originate from outdated OS and software. Such OS and software no longer have updates because there are new versions. GFI should update its OS and software to new versions.
Corrective Action – the IT department should review current OS and software, and recommend for new updates as soon as possible.
- Wireless networks lack protection, are not encrypted and prone to attack (High)
There is no policy on wireless devices. Thus, there is no integrity, availability, and confidentiality of GFI data. The system cannot guarantee confidentiality of customers’ sensitive data. Thus, wireless devices may provide the easiest options for attackers to the entire network. The default settings are not effective for such confidential information.
Corrective Action – develops and implements wireless network policy using latest secure Cisco platforms. The IT department should encrypt data in the network and improve authentication and access controls.
- GFI does not conduct a regular scan for vulnerabilities to identify outdated applications and network issues (High)
A lack of regular scanning can lead security threats on the system. Scanning helps the company to detect threat and initiate corrective actions. The company should conduct regular scans in order to detect threats and vulnerabilities within the network.
Corrective Action – introduce regular scanning of systems in order to identify threats and take corrective measures, including updates for outdated applications.
- Network security lacks intrusion prevention features, antivirus, and anti-spyware (High)
Antivirus and antispyware are effective for blocking viruses and malwares. The antivirus must block, scan, and delete all detected threats.
Corrective Action – the IT department should adopt antivirus software that can detect, scan, and delete threats automatically. Critical risks may need Internet security for maximum protection.
Security Management
This entails all initiatives, which GFI takes in order to ensure confidentiality, availability, and integrity of its data. Thus, no asset should suffer damages under effective security policies, standards, and procedures.
GFI has weak security management procedures, which make the network vulnerable (Critical)
Security management at GFI is not clear. The company should adopt a new security management policy for its vulnerable network. The policy must be clear for employees on usages of personal devices on the company’s network and devices. Such personal devices may introduce virus and other threats to the company’s network.
Corrective Action – GFI must adopt a new policy for security management in order to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data. Users must also authenticate access to the network.
- Sudden spike in traffic from unknown source (Low)
There is unknown increment in traffic, which the IT department cannot determine its source. This shows poor tracking of threats on the system.
Corrective Action – implement security features and firewalls to block suspicious traffics.
Operations Security
This involves controlling usages of hardware, points of access, people, and usages of media on the company’s resources.
- Concerns from the interrelationship between data and operations (low)
GFI has noted that demands for data do not meet operation requirements. The system is slow in generating required data due to growth in the company. Poor speed in generating required data may result from poorly implemented features, viruses, and other threats, which may slow the system.
Corrective Action – review network configurations for data generation, conduct scheduled maintenance, upgraded software, antivirus, review security features.
- Remote sites have been reporting significant problems with network latency, slow performance, and application time-outs against the Oracle database (Medium)
The company lacks regular or scheduled system maintenance. Thus, core access points and other network devices may be outdated. It is important for the IT department to conduct regular maintenance, upgrade patches, and review network security features.
Corrective Action – the IT department should develop and implement a program for system maintenance and updates.
No documented change management in the system (Low)
The company seems not to have any records of changes made to the system. Thus, it is difficult to determine previous or current software configuration.
Corrective Action – GFI requires change management approach for the network.
Business Continuity
Some events may disrupt business operations. This makes preservation of business activities important for continuity of the business. Major attacks have paralyzed GFI operations for some days. The company has to rely on other partners to restore its operation.
- Attacks leave GFI vulnerable (High)
Past attacks have left the company vulnerable and unable to operate. It is important for the company to create and maintain a recovery plan for continuity after an attack. The company can determine the frequencies and common attacks from its recovery plan. This can allow GFI to respond effectively to subsequent attacks. Currently, GFI has no recovery plan and must rely on other service providers to restore its database.
Corrective Action – GFI should develop and implement a recovery plan for its network once an attack has taken place. There should be backups. Thus, it would be important if GFI can rely on such data to provide estimate of time needed to restore the operation. The plan must account for any required hardware or software based on the nature of the attack.
Ethics, laws, and investigation
There should be regulations, laws, and ethical issues, which concern methods of using the system, collecting data, and using gathered data.
No existing procedures for responding to attacks (Medium)
GFI does not have any documented approach of responding to attacks and conducting investigation. Thus, it is difficult to determine sources of attacks or abnormal traffic in the network. Moreover, the company cannot determine motivation for the attacks. At the same time, GFI lacks any policy on handling internal issues, which may relate employees’ inappropriate usages of network resources.
Corrective Action – it is important for the company to create and implement a record for all attacks, which have taken place on the network.
Aims of intervention
The intervention shall treat system vulnerabilities as follow:
- Removing vulnerabilities from the network through updating security features or improving on security architecture
- In case of difficulties in removing vulnerabilities, the approach would be mitigating effects of such vulnerabilities on the assets
- The IT department may decide not to take any action against residual risks. However, it would be important to follow procedures and policies before declaring any vulnerability as residual.
The CEO, COO, and the IT department must understand that the level of interventions may have different impacts on the company. For instance, some security issues may be simple to fix through updates or by adjusting security settings. However, others may require overhaul of affected parts, replacing software, and installing new features. This may require adequate resources before implementation of the intervention begins.
A secure authentication technology and network security for GFI
Authentication is a verification process, which rely on distinctive credentials of users in order to identify their identity. These distinctive user credentials are usually what the user has, knows, or what the user could be. GFI can use different authentication credentials like “shared secrets, tokens, or biometrics” (FFIEC, 1999). In some cases, firms with critical cases of threats and vulnerabilities like GFI should use more than a single authentication technology in order to enhance security of assets. Multifactor authentication has strong protection relative to single-factor authentication. Through effective authentication, GFI shall be able to enhance confidentiality, accountability, security, and availability of its valuable data.
GFI needs effective authentication technology based on a multifactor approach because of critical risk levels it has experienced in the past few years. All authentication approaches must consider past attacks, vulnerabilities, and risks to assets.
GFI has recognized that multifactor authentication must be suitable for its network. Moreover, multifactor authentication has become common among financial institutions (Tiwari et al., 2007) that engage on electronic transactions. GFI must also implement an encrypted system for transmission and storage of all verification credentials.
Authentication has been a challenge to GFI. In some instances, GFI cannot control actions of all users who visit its network. Thus, a single-factor authentication is not appropriate for GFI because of customers’ data and the nature of transactions. An effective authentication approach must be able to mitigate potential risk that GFI may face in its network.
Authentication technology will maintain “confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data security” (Columbitech, 2008) for GFI. The company shall rely on cryptography for network authentication and access control.
The best approach will consist of a combination of several measures, such as passwords, security token, and in some cases, the use of some features like fingerprint. Strong authentication is mandatory for GFI for protection of sensitive data in its network.
All known vulnerabilities identified in the GFI environment and the proposed new design with a combination of technologies to harden authentication process and network security measures
GFI has a number of vulnerabilities in its network environment. Thus, its network security needs effective control mechanism that can control gaining access to customers’ information. GFI must evaluate its network complexity and implement network control mechanisms that meet its complexity. GFI has a complex network system because of the growth, increased demand for data, and computing systems. GFI experienced confidentiality loss and security breaches because of poor controls in its technology environment. The following is a list of vulnerabilities in the GFI network.
- Optical and electronic media – malicious users can collect data from such devices. Effective security policy should focus on disabling USB ports and CD or DVD ROM drives within the workstations.
- Wireless technologies – employees and other people in nearby buildings can connect to the GFI’s unsecure network by using Wi-Fi. The company must provide secure Wi-Fi access on its network through multifactor authentication, network access control, VPN, encryption, and effective firewall policy. GFI should provide Active Directory lockdown for Smartphone systems. The controls should have password authentication and data wiping technologies.
- E-mail and messaging systems – these forms of communications within or outside the company may be sources of virus and malware. GFI should implement anti-malware, antivirus, and anti-spam. The company should control messaging and transfer of sensitive files across departments or to external clients. The system should have logging controls and disable all messaging options by default. System logins, system configuration, and access controls can protect the company.
Instant messaging should be within GFI only, and any instant messaging to external clients should be on a secure instant messaging platform.
- Internet usage – the Internet provides several access points to the GFI networked environment. GFI should introduce Internet usage policy to regulate users’ access to the Internet. GFI must control users’ access to the Internet during business hours. Browsers patch management should be a high priority for GFI. The company must control Internet usages and services such as file transfer, DNS, remote access, Web mail, streaming media, downloads, and other Internet services.
- Virtual Private Networks – GFI must control usages and monitor access controls. The company should apply encryption to the network and introduce lockout controls and expiration of authentication. The network should have certification alongside granulated access to GFI assets.
- Mobile devices and telecommuter systems – GFI must introduce security policies on laptops and desktops. It should use thin client access and disable all shared access of the remote systems by other users and nearby buildings. The company should apply patch management controls and anti-virus controls and updates. It must apply the entire disk encryption policy and control the use of optical and electronic media.
- Network access – GFI must introduce penetration testing policy and controls of internal and external evaluation security programs. All in-house Web systems should undergo security reviews and codes analysis for vulnerabilities.
GFI must secure access to its computer network by using several layers of access controls and multifactor authentication technology in order to control unauthorized access to the network. GFI must control network servers, VPN, data access, implement user security domains for external clients, internal customers, and rogue external networks.
In addition, GFI must establish the necessary access controls within and between network access points. The network environment must have suitable access technological controls, which can mitigate potential threats consistently. Finally, GFI must audit its network, monitor access at various points, cross-domain access and apply security policy, detect violations, spikes in access, and take appropriate action.
The CEO’s concern over the mobility security and design a secure mobile computing (smart phones, tablets, laptops, etc.) in terms of authentication technologies and data protection
The CEO has noted that mobile computing shall provide flexibility and productivity to GFI. Employees can work at any place or time. As a result, the CEO has thought of introducing the Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy to GFI.
However, given the security situation at GFI, personal devices can also contribute to vulnerabilities of GFI network system. Poor configuration and management of such devices can result in security breaches, loss of confidentiality, integrity, availability, and damages to assets.
The CEO’s concerns about mobility programs and GFI security are real. Any instance of negligence can lead to serious damages. Thus, secure company mobility is mandatory for GFI. The IT department must design mobile security measures, which are cost-effective, user-friendly to employees and facilitate GFI productivity.
It is important for the CEO, COO, and other executives to note that mobile security must reflect security challenges at GFI, and upon the introduction of the BYOD policy, all devices must operate within the company’s security policy. If the IT department follows some basic principles on access controls and authentication technology, then GFI can have secure mobile devices for employees mobility needs.
The CEO must recognize that the IT department requires adequate resources in order to develop a secure mobile computing for the company. This process is comprehensive, and it will reflect the security needs of GFI and data sensitivity as a financial institution. The IT department shall concentrate on seven issues of security concerns for GFI mobile devices.
- Data encryption – GFI can develop its own encryption solution or obtain the same from vendors. However, encryption of mobile devices must not affect usability of mobile devices. Encryption must provide adequate protection from hackers. This will ensure that GFI’s data have adequate protection, whether users store them in their mobile platforms or stream and share across the network.
- Password enforcement – the IT department must ensure that all devices have appropriate password for protecting and controlling access to stored data in the mobile device. Password must be complex enough in order to ensure effective protection. The IT department can propose the standard length, a combination of characters (alphanumeric symbols) and regular changing of passwords. Such passwords must reflect sensitive of GFI data.
- Device management – the company must consider fail-safe approaches of locking down or erasing data in case such devices are lost or stolen. The IT department must introduce device management service, which can wipe out business data and keep personal data for employees who will leave GFI.
- Compliance and configuration management – the IT department must evaluate all mobile platforms in order to ensure that personal devices are not threats to GFI network and its data. The system should identify and block sites, which are sources of security threats to GFI.
- Data access – GFI must define levels of network access based on the user’s profile, job title, or roles. The system must also compel employees to reveal what they intended to do with the retrieved data.
- Trust and confidence – the department must install applications, which do not inhibit employees from using their personal devices.
- Enable and ease of use – the focus should be on positive aspects of security measures and outcomes from the devices rather than negative consequences.
Wireless vulnerabilities and recommended safeguards, authentication technologies, and network security to protect GFI data
- Accidental association – threats from overlapping wireless networks
- Malicious associations – cracking laptop to gain access to the network
- Ad-hoc networks – peer-to-peer that lacks access point
- Identity theft (MAC spoofing) – the attacker monitors traffic of the network to identify MAC address
- Man-in-the-middle attacks – “de-authentication attack” by using soft computer access point
- Denial of service – constant attacks on the target network with unrealistic requests and messages
- Network injection – takes place in non-filtered network traffic
- Caffe Latte attack – the attacker aims at the wireless stack
Recommendations for Secure Wireless Networks
The BYOD policy will present new risks to GFI. Thus, the IT department must address these issues to protect assets from damages, which result from breaches of confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the network. It is necessary for the IT department to evaluate wireless network risks, test the system, and improve security features frequently.
- GFI must conduct regular risk assessment, implement security policy, and identify security requirements for wireless devices
GFI must not use default settings on wireless technologies. It must control access points, develop and implement security architectures, and implement security options for the system.
The company must block all unnecessary ports in the system alongside cryptography. The network must be vigorous and secure.
The IT department must determine “wireless threats and vulnerabilities prior to implementation of the BYOD policy” (Radack, n.d). The company must consider current security policy, ethics, legislation, network performance on increased demand for data, and other technical requirements for data protection.
GFI should integrate “wireless protection in its System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)” (Radack, n.d).
- GFI must be aware of security and technical challenges of mobile devices
GFI must recognize that wireless technology is an evolving system, which has inadequate security standards, implementation challenges, end user challenges, and low-levels of administrative and security policies. The company must monitor the distance due to wireless eavesdropping. It must also provide suitable wireless antennas for the system.
- The IT department must plan installation of wireless technologies in its network
GFI must consider security of wireless devices from “the beginning because it will be difficult to address security challenges after implementation of the policy” (Radack, n.d). It is important to focus on configuration and infrastructure of wireless devices.
- GFI must recommend effective security management policies, practices, and controls for a secure wireless network for data protection
The IT department must identify all assets and propose standard policies that shall ensure “confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information system resources” (Radack, n.d). NIST has proposed the following for financial institutions:
- The policy must address usages of “Bluetooth, 802.11, and other features of wireless technologies” (Radack, n.d).
- Regular security updates, configuration, and controls for enhancing security features and new patches for new vulnerabilities
- New configuration must take into account security demands for GFI data, policy, and change all default settings in the devices
- End users must undergo training in order to develop their awareness about threats and vulnerabilities that concern wireless technologies
- The department must create effective cryptography for data protection during transmission
Physical controls for protection of devices and information
The company must introduce access barriers, control mechanisms, and guards. This can eliminate cases of device thefts, tampering with network equipment, or inserting devices in access points or network devices for retrieving data.
Mobile devices are prone to getting lost, theft, or misplacement. Physical controls for mobile devices must be effective more than desktop or workstation equipment controls.
The IT department must conduct a routine test on security features, threats, and vulnerabilities. In addition, it must review authentication and encryption technologies for wireless devices. The company must introduce firewalls for access point protection.
There are built-in security components for wireless devices. The IT department must activate these features for protection against unauthorized disclosure, access, and attacks on the network.
The company must provide firewall filtering, good access points, and antivirus. This is an appropriate way of eliminating residual risks, which cryptography and other security measures may fail to address effectively.
The network may cross other networks. Thus, the IT department must introduce end-to-end cryptographic network protection.
The IT department must:
- Have full knowledge of the wireless network typology
- Keep all records of wireless devices
- Perform data backups regularly
- Conduct regular tests in order to determine security status of the network
- Random audits of all wireless devices in the company
- Enhance network patches and security features
- Keep track of developments in the wireless technologies and security applications
- Review the system for new threats and vulnerabilities.
Design of a cloud computing environment for the company with a secure means of data protection at rest, in motion and in process
GFI must switch to a secure cloud computing in order to achieve security benefits and other cost-effective advantages. Customers will also save on the costs of business transactions while cloud providers have recurring sources of revenues. However, adoption of cloud computing will have significant security threats and vulnerabilities to GFI. Thus, the IT department must have a robust cloud computing security for the network.
Cloud computing requires authentication technology and access control like other areas of the network. Thus, the IT department must focus on access control, encryption, user’s identity verification, secure deletion of data, user integrity verification, and data masking.
The company can also adopt cryptography for protecting data in the cloud computing system. GFI can protect its data when it transfers data across the cloud. It will lessen vulnerabilities and threats. Cryptography shall guarantee data encryption and create a secure connection for data movement.
Thus, encryption is the best approach to protecting all in data in the cloud. Encryption of data ensures that data remain of no use in case of theft or leakage. However, GFI must note that data encryption will make the system to be slow in performance. This is also the case during decryption (the process of turning data into their useful forms).
Authentication technology and secure network for cloud computing focus on a secure browser for gaining access to the user portal and transmit encrypted data. The IT department must develop Security protocols Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for safe communications over networks. TSL and SSL are critical in secure web browsing (HTTPS) technologies.
Data in motion requires security features for protecting data, which are in transmission across the network. The IT department must monitor the network in order to identify cases of mismatch in the channel and data sent. This could mean a possible security breach in the network.
The IT department focuses also on data at rest. Attackers may scan all stored data and repositories for data in order to identify where GFI may be storing its sensitive customers’ information. Any attempt to store data in a wrong repository normal alerts the user, and he must initiate a corrective action.
Authentication and access control technologies also protect data in use. The system must monitor how users access and transfer data. The system can detect and lock any attempt to transfer data to a wrong destination.
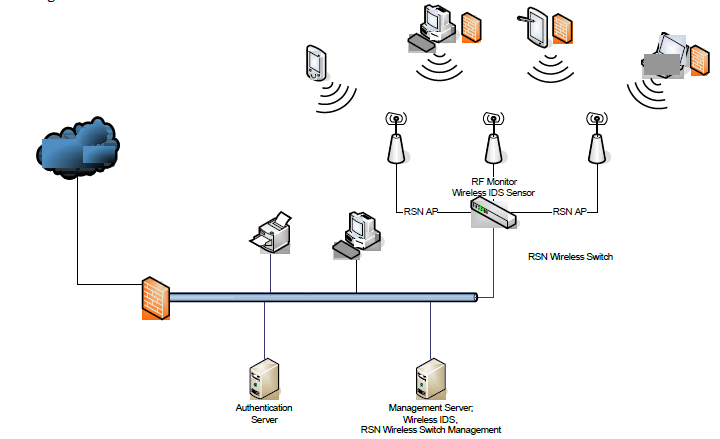
Figure 1: A secure wireless network based Cisco products or equivalent (Courtesy of Jason Meyer)
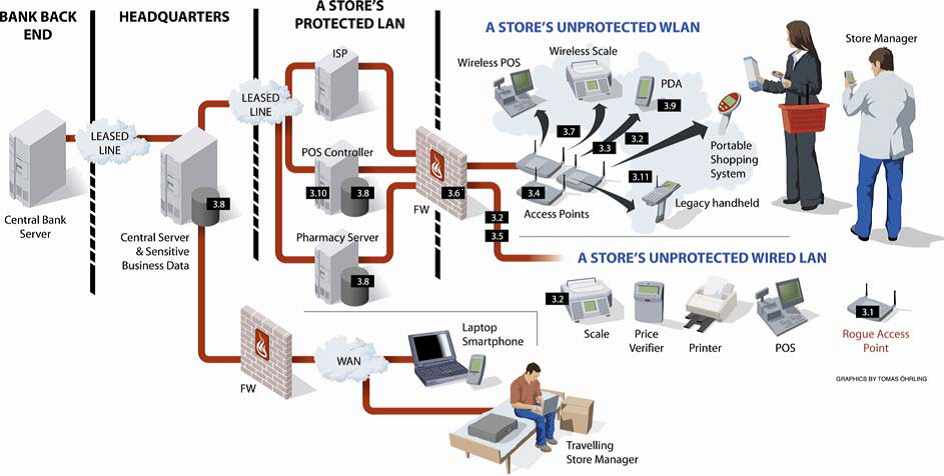
Figure 2: Protected and unprotected Bank networks (Columbitech, 2008)
References
Columbitech. (2008). Security Threats and Risk Mitigation in a Retail Network Environment. Web.
FFIEC. (1999). Authentication. Web.
Radack, S. (n.d). Security for Wireless Networks and Devices. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/publications/security-wireless-networks-and-devices
Tiwari, A., Sanyal, S., Abraham, A., Knapskog, S., and Sanyal, S. (2007). A Multifactor Security Protocol for Wireless Payment- Secure Web Authentication Using Mobile Devices. IADIS International Conference Applied Computing , 160-167.
US Department of Commerce. (2011). Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments. Washington, DC: NIST.