Introduction
Google Company is a multinational company which came into existence once there was a strong need among internet users to find a search engine. Since its inception, Google has made remarkable progress in the corporate map because its popularity has tremendously soared over the years.
Currently, Google is deemed the world’s most used search engine and its usability has penetrated to the core of English language since the word “Google” has been incorporated into the English dictionary and even informally, if one wants to find information about a person, one would often say “Google the guy” (Hill 2009, p. 1).
Until the year 2008, Google did not command the huge market share it enjoys today since its market share was only estimated to be about 45%, while other search engine companies such as Yahoo took the rest of the share (Hill 2009, p. 1).
However, after the year 2008, Google has commanded a strong market presence of about 61% in its primary market (US) while other search engine companies trail behind. For instance, yahoo is estimated to control only about 20% of the market share and Microsoft is estimated to account for less than 10% of the market share (Hill 2009, p. 1).
This huge market share has seen Google enjoy huge profits which have also tremendously grown over the years as more advertisers pay for advertising space in the company. Google’s business model has been a simple one, in the sense that, companies pay for every click customers make to their company’s websites. This is done in an online bidding manner where the company with the highest bid is given priority in the search engine website (Hill 2009, p. 1).
Currently, Google has grown to add more product features to its company and at the moment, it has developed auxiliary products such as Google maps, Google mail, Google desktop and the likes. This growth has pit Google on the collision course with its competitors since it is said that, the company is adopting a business model which is beyond its search engine core business line.
With this fact ascertained, Google’s competitors have gone all the way to expand their market share because to them, Google seems to be expanding into business ventures that have been predominantly the preserve of a few other companies (Hill 2009, p. 1). For instance, through Google’s online word processing program and spreadsheets, the company has come very close to Microsoft’s word and Excel programs and this has threatened Microsoft’s share of software application in the information technology world.
As a result, Microsoft has tremendously increased its investments in search business to measure up to Google’s dominance in the industry. Yahoo has also adopted the same strategy. This trend provides a problem for Google because it is feared that Google may have bit more than it could chew.
The greatest challenge the company now faces is the competitive strategy its competitors have adopted and it is yet to be determined if the competitive pressure will have an impact on the company’s future sustainability. This study therefore seeks to explore the future sustainability of the company, in light of these developments but to do so; we will analyze the company’s internal and external strengths and weaknesses; business mission and goals and existing strategies.
Business Mission and Goals
Google’s mission and goals have recently been threatened by the company’s expansion and more so, the company employee growth. This growth prompted the company’s founders to redefine the company’s mission and goals because there was a strong need for the company to stay true to its initial mission and goal, as opposed to fragmenting under the effects of market growth.
In this regard, Google’s mission is defined as “organizing the world’s information and making it universally acceptable and useful” (Hill 2009, p. 3). Alongside this mission is Google’s goals which from a general perspective, act as the guiding principle behind Google’s operations.
One main goal is to satisfy its clients’ needs and therefore, every other activity the company undertakes will be channeled towards satisfying this goal. This goal is translated towards ensuring the company’s user experience is according to the customer’s satisfaction. In this regard, the company focuses more on improving the usability of their web pages and much effort is directed towards satisfying the company’s experience as opposed to reflecting the principles or goals of the company.
Secondly, Google aims to undertake its activities to always meet perfection. In this regard, the company prides itself in undertaking few activities that it can accomplish to perfection, as opposed to carrying out several activities which may not be done to perfection. In this regard, the company has been able to solve some of the most difficult problems envisioned in the search engine industry and the company has so far managed to stay above its competition in this regard.
Hill (2009) explains that “Through continued iteration on difficult problems, we have been able to solve complex issues and provide continuous improvements to a service that already makes finding information a fast and seamless experience for millions of people” (p. 4)
Google’s third objective is to develop the fastest online search engine to maximize the client’s time. This aim is motivated by the company’s acknowledgement that, its customers value their time and one company employee is quoted joking that, “Google is probably the only online search company which strives to get its clients out of its homepage fast as possible” (Hill 2009, p. 4).
It is also a strong aim of the company to uphold democracy in online experiences as much as possible. In other words, the company prides itself in letting its clients know which websites have been ranked the best and consequently, it is able to rank websites in this regard. The company also upholds democracy in terms of programming because it believes that, through the input of many programmers, the company is able to enjoy increased innovation among its staff.
Making the company’s online services available to the users at their own convenience is also a major objective of the company because it believes the world has increasingly become mobile and many of its users want to get information wherever they are and whenever. This is the major motivator for Google’s venture into the mobile industry so that its users can be able to access its services from their mobile (Mobile Beyond 2011).
Google also prides itself in making money through legitimate and good ways, as opposed to making money out of evil activities. For instance, in the advertising scene, the company aims to undertake user-friendly browsing, such as preventing pop-ups in advertising because it believes this interferes with the user’s browsing experience (Hill 2009, p. 4).
Also, this is the reason why the company always registers its advertising spaces as “sponsored links”. Google also believes that, there is an abundance of information out there and in this regard, it aims at providing access to such information to the clients at whatever cost.
This, the company believes is a simple procedure where the company has to integrate information relating to specific website links and as a result, consumers would have an incredible browsing experience. Close to this aim is Google’s belief in providing information to its users across all borders. This is the reason why the company has in the recent past made its services available in over 130 languages and opened offices in more than 60 countries across the globe (Hill 2009, p. 1).
Google also aims to develop new ideas by nurturing unconventional talent from its employee pool. In other words, the company’s founders believe that, one need not be serious (say, dressed in suits and working in offices) to come up with brilliant ideas that can be tested and applied.
Lastly, the company’s aim is to transcend the notion that “great” is good. In other words, the company aims at being better than its previous success and in the same regard; the company believes that, it cannot be able to stay above its competitors if it is satisfied with being “great”. This aim has therefore prompted the company to look for new grounds where it can make a difference.
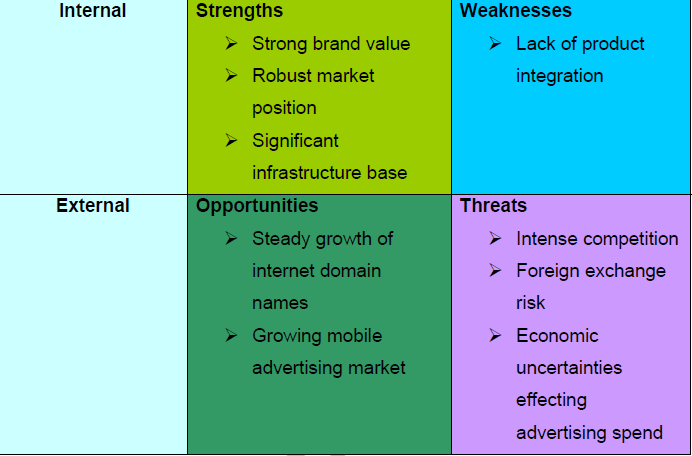
Internal Strengths and Weaknesses
Google brands itself in being a strong brand in the online search industry. Besides distinguishing the company from its competitors, Google’s strong brand poses a lot of advantages to the company (Collier 2011). First, it gives the company an indelible position which is uniquely indistinguishable from its competitors because Google’s strong brand name prompts online search engine users to think of the company first, before any other.
This is the reason why many online users undertaking research activities, or who want to look up certain information on the internet normally think of Google first. This is also the reason why many people normally refer to looking up something online as “Googling it”. In fact, often, the brand Google is often envisioned as the only solution existing in the market, despite the presence of other online search engines.
Due to Google’s strong brand presence, the company enjoys a strong individuality and separateness in the marketplace because its online clients are able to distinguish the company from other competitors. Also, the company’s clients are able to establish the company’s unique features and characteristics which enable them to prefer using Google as opposed to other competitors existing in the market. Moreover, from the Google brand, the company is able to reflect its personality.
This refers to the company culture, say, of doing no evil and therefore, this process seeks to create a brand personality for Google which ultimately helps it command a stronger market share in the online search engine market. In other words, the company is able to express what it stands for in the corporate world. Collier (2011) further explains that, the brand Google “is what the company’s opinions, values, beliefs and moral character stand for. It’s not just what they say but what they do” (p. 3).
Through the positive brand image that Google has, the company is able to control people’s perception of the company. Through a positive brand perception, the company is able to attract clients and professionals without even putting much effort towards it. In a way, the popularity of the Google brand has even elevated the company’s founders to a near celebrity status.
Another internal strength Google enjoys is its robust market position. This robust market positioning is part of Google’s market strategy because it has been able to appeal to the minds of its customers as a result; thereby strongly maintaining its high market share.
Because of the robust market positioning, customers are able to appreciate the attributes related to Google and how such attributes can be of benefit to them. Moreover, the positioning strategy enables Google to cut a mark above its competitors because it is able to stand superior to its market competitors as a result.
Lastly, Google’s main strength lies in its infrastructure base because it enables it to come up with innovative products which set it above its competitors. The good infrastructural network of the company also enables the company to facilitate employee performance in the organization but monetarily, the infrastructure base of the company has attracted investors and advertisers to bank on the company’s success in remaining a leader in the online search engine industry.
In other words, the company has been able to enjoy considerable levels of success because Google’s competitors have not been able to match up to the level of infrastructure-sophistication Google enjoys (because no investor would like to invest their money where they cannot make money). Google has so far provided a good infrastructure for investors to make money.
However, despite these strengths, Google bears one major weakness – its lack of product integration. Its lack of product integration has seen Google experience a lot of market problems with regards to existing competitive forces because the company is perceived as a search engine company, but in recent times, it has developed products which cannot be associated with its core business model.
Such is the case evidenced with its development of Google spreadsheets and the likes (which are software applications) (Hill 2009, p. 5). There is therefore a strong need for the company to enhance its product integration to merge its business interests and align its strategies for growth.
External Strengths and Weaknesses
Google’s external environment poses several strengths for the company because of the nature of the operating environment. For instance, the growth of internet domain names has increasingly posed a growth opportunity for the company because with an improvement in the company’s online infrastructure, Google can be able to handle the high traffic of the increased domain names.
However, there is bound to be a resultant competition for existing domain names and Google needs to brace itself for such a challenge, in light of such increased competitive pressures. With a growth in domain names, Google anticipates that, the market share is bound to increase as a result and consequently, this is likely to result in more revenues for the company because advertisement revenues and investor growth will be evidenced as well.
Also the growing market of internet mobile is also spurring more growth for online internet search companies because internet mobile increases the accessibility of users to Google’s services (Mobile Beyond 2011).
More importantly, internet mobile is increasing the company’s chances of developing a new market share of lower income customers. In fact, this anticipated growth is likely to increase the company’s advertising revenues because many companies are now acknowledging that most internet users are currently moving to internet mobile because of its portability and easy access.
Moreover, the development of mobile phones which access the internet has tremendously increased, and consequently, the penetration of internet services has increased worldwide. This is because users who cannot afford computers, especially in the Asian and African markets, can now access the internet through their mobile phones and this increases the market for internet services (Mobile Beyond 2011, p. 3).
It is further estimated that in the coming years, many internet users will be using mobile internet as opposed to desktop internet. This fact is affirmed by Mobile Beyond (2011) that: “The mobile Internet is growing faster and will be bigger than the desktop Internet did, due to five converging technologies and social adoption trends: 3G, social networking, video, VoIP and impressive mobile devices” (p. 4).
In the year 2010, it was estimated that, mobile internet devices were not less than ten billion; meaning that, internet mobile is quickly overtaking desktop access to internet because the latter does not show the same growth levels.
However, Google also faces several weaknesses emanating from its external environment, like the intense competition it faces from its competitors (Buzzom 2011, p. 2). Google’s competitors are however not confined to the search engine field but also to other core areas the company operates in; especially with regards to the products and services it has come up with over the past decade.
For instance, in the recent past, the company has experienced a stiff competition from Apple co., regarding the development of Smartphones and the development of various mobile applications it seeks to enjoy with the emergence of the internet mobile market. However, in the search market, Microsoft poses the stiffest competition for the search engine giant and observers are keen to see how the competition plays out because Microsoft probably has the greatest impact in the information technology field.
Amazon is also in competition with Google regarding cloud computing because there is a similar feature for both companies where clients can create web applications and run it in the infrastructure of both companies (Buzzom 2011, p. 2).
There is also increased competition between Google and Facebook regarding the future of search engine companies because there is an overwhelming move towards social networking and Google is worried that Facebook may eventually pose a threat to its future sustainability in this regard (Buzzom 2011, p. 2). The same is true for similar social networking companies such as twitter.
Google also faces several risks regarding its international market ventures, in terms of foreign exchange risks, but this weakness is not only unique to the company alone but also other companies operating under the same circumstances. It is therefore important for the company to hedge such risks. Finally, Google also faces significant challenges with regard to its business model in the sense that, its advertisement revenues dwindle periodically due to the uncertainties in advertisement revenues.
For example, the recent 2008/2009 global economic slump translated to decreased advertisement revenues for the company because there was reduced business. Nonetheless, this market weakness is also not only unique to Google. The following diagram summarizes the analysis of the internal and external strengths and weaknesses of the company:
Company Strategies
Google’s strategy revolves around innovation, to be ahead of its competitors and to provide customers with the best online experience. The move towards spurring innovation is fronted on the employee’s point of view because the company tries to provide a conducive environment where employees can be able to come up with new ideas and products which can be tested for future use.
This is one primary strategy the company uses to come up with a good product development strategy. As part of the strategy, the company’s employees are expected to spend about 20% of their time on something that they like. Hill (2009) explains that, “seemingly based on 3M’s Famous 15% rule, Google’s 20% rule is designed to enhance creativity” (p. 7).
To compliment this strategy, the company has established a forum where employees can share their ideas with others and ultimately realize product improvement as a result. If the projects are considered viable, they definitely receive funding after they are approved by the top managerial committees. The policy of coming up with new ideas spread throughout the organization; meaning that anyone within the organization can come up with interesting ideas on product development.
The company also strongly believes that with regards to its product development, focus should always be made on the customers and not the money that is going to come as a result. This strategy guides the company’s activities because it is in their belief that, money and advertisers follow consumers and therefore if the company is able to attract a lot of consumers, it will be able to attract a lot of advertisers and consequently, a lot of money (Hill 2009, p. 7).
The company also acknowledges that, innovation is the bedrock of coming up with good products and by no means is the project instantaneous. In other words, the company acknowledges that, it is patient while developing new products because through constant improvements, a product can achieve perfection.
Due to the fact that, Google relies a lot on its product development strategy, the company has in the recent past focused on developing the right human resource team for this purpose. Its human resource strategy is focused on its hiring strategy because the company has embarked on an effort to hire only people with the highest IQs (Hill 2009, p. 8).
The prospective employees also go through a vigorous hiring process. However, there are concerns that Google’s hiring strategy is not as efficient as it should be because employee turnover is said to be increasing.
Recommendations and Conclusion
Since Google is majorly run by two individuals, it is important for the company to adopt a bottom-up approach to management because in the past, the company has always relied on its founders to make important decisions regarding the future of the organization.
Also, all ideas which come from the employees are most likely passed by the founders and an approval is made, or a rejection of the idea is registered. Focusing a lot of power on the founders of the organization is likely to inhibit the company’s sustainability into the future but most importantly, it is essential to acknowledge that, best performing companies have a decentralized power where employees feel part of the team and not subjects to a few individuals.
Factoring the analysis of the company’s external and internal strengths and weaknesses, it is important for the company to adopt product integration to develop a strong business competency. To achieve this objective, it is important for the company to concentrate on developing products that match the company’s online search specialization.
In other words, they should focus more on the company’s ability to provide users with an unforgettable online search experience and develop products which focus on this objective. From this point of view, the company can reduce competition from other entrants who are venturing into the online search industry where Google’s specialty lies.
With regards to the company’s risks (like foreign exchange risks and uncertainties regarding advertising revenues), Google should adopt prudent hedging strategies to ensure its future financial standing. These recommendations should be observed alongside capitalizing on the company’s strengths. These recommendations are bound to guarantee the future sustainability of the company.
References
Buzzom (2011) Toughest Competitors of Google in 2010. Web.
Collier, O. (2011) Advantages of a Strong Personal Brand. Web.
Hill, C. (2009) Google in 2008. Washington, University of Washington.
Mobile Beyond. (2011) Mobile Internet Research Report Reveals Massive Growth. Web.