Introduction
History of Health, safety security & environment management
Health and safety management is a relatively young phenomenon established out of the industrial revolution. During this time, the industry went from hand production to more complex production methodologies such as heavy machineries, chemical manufacturing among others. Notably, there were no efforts made to improve neither environmental issues nor implement health and safety standards for the existing workforce.
The expanding economy during this historical period required a huge workforce; this resulted to harsh working environments since there were no regulations to protect the workforce. After some major incidents like the Monongah Mine disaster in the US 1907, the federal government developed some agencies to improve labour safety, which were under the department of labour (“Mining Disasters”).
However, it took almost another 60 years until Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) was created in the US. In Europe things where developed earlier. The Institute of Occupational Safety and Health was created 1945. It was developed to create professional standards and give advice on health and safety issues.
Health and Safety ensures that workers are protected at their workplaces thus preventing harm and accidents. Some activities like mining and loading of ships and fishing boats are risky adventures that require adequate protection. Others are steel, chemical, and loading industries; the emissions from the chemical industries are extremely harmful and can lead to loss of lives.
In addition, cement firms can cause asthmatic conditions to employees. Therefore, employers should ensure that the safety of their workers is paramount by following all the provisions of OHS acts (“Occupational health & safety” par. 7). The OHS act upholds high level of mental and physical well-being of workers when at the workstations.
In addition, there are psychological and social issues such as bullying, work-related stress, sexual harassment, and burnouts. These situations lead to stressful life; it becomes dominant when the management postpones decision-making activities. Employees who are tasked with decision-making should ensure that they do it within the shortest time possible. This will help to avoid procrastination in decision-making.
HSSE background information
Globalization over the past decade has intensified over the past decade and many organizations are spread across the globe. This went hand in hand with the development of new information and telecommunication technologies that has changed how the society runs.
Organizations and companies have spread over the globe leading to new & different management structures. Health safety security and environmental management has new challenges in a globalized world focusing on a global standard.
An organization that fails in managing Health and Safety risks meeting more cost than getting it right at the initial stage. In Canada, the Canada Labour Code Part II (CLC Part II) has set out policies and standards that give all departments the responsibility to manage their Health and Safety requirements (“Health and Safety Boards – Background” par. 1).
The employees must be able to access all information concerning health and safety. For that matter, the policies require employers to post such pieces of information in accessible regions. It was the responsibility of the Health and Safety Committee to ensure that all departments comply with the requirements of the OHS at the workplace.
Exposures in the fishing, transportation, metalworking, construction, lumber, aviation, and mining industries are exceptionally dangerous. For instance, in the United States, injuries from the construction industry were three times the injuries from all the remaining industries (“Occupational Health & Safety” par. 6).
On the agricultural sector, there are skin diseases, ear problems due to noise from machines, and certain cancers. Farm workers can also get fatal injuries from tractor rollovers and drowning.
To mitigate these complications, industries should have a properly laid down safety policy and insurance policies like workers compensation. The construction industry, for instance, should use proper safety equipment to avert impeding risks. Further, there should be clear health and safety regulations that the Construction Design Management Coordinator must ensure that all the workers follow.
The OHS professionals ought to evaluate all working environments to certify if they conform to the required standards, inform employers to develop measures that will minimize injuries and carry out OHS awareness among workers so that they can raise the alarm in case of disobedience by employers (“Who we are – IOSH”).
In OHS, risk assessment procedures include hazard identification, identification of those affected by the hazard and to what extent, evaluating the risk and, then, identifying and prioritizing control measures. This process is done in a practical manner. OHS remains an essential health concern since human being must work to earn a living.
Labour standards
This defines the general condition of occupational safety and health in the workplace. The objective in harmonizing this type of standard is to prevent ‘social dumping’ that is to prevent the comparative advantages that are derived from lower production costs at the expenses of inferior working conditions in a company.
Harmonization of these standards seeks to achieve social integration within the process of economic integration and liberalization, in such a way that social progress accompanies the economic growth.
The International Labour Organization (ILO) on its part has designed a system that promotes equality, freedom, and dignity across the workforce since 1919. Moreover, it has promoted gender equality by providing opportunities for both men and women (“Labour standards” par 1). The international labour standards have formulated a framework that ensures that the global economic growth benefits all.
The advent of globalization has made labour standards highly significant. The Philadelphia Declaration of 1944 recognized that labour is part of everyone’s life; therefore, it is essential to the development and well-being of human beings.
The Declaration altered the medieval perceptions of viewing labour as an object to a crucial factor of production. In addition, these standards have created a-levelled playing field such that governments and employers cannot attempt to alter the labour standards.
Product safety
The World Trade Organization (WTO) instituted the elimination or reduction of tariffs among its member states. It is currently occurring due to the signing of multilateral trade agreements by the regional economic integration or blocks.
People must be confident that the products they use or consume safe and do not present any danger to their health and physical safety, therefore product safety standards are crucial. Although OSH does not directly deal with environmental issues, they will have a positive impact on the management of OSH, as there is a link between work environment and environment in general.
In Australia, a product safety website guides consumers on the conditions that they should check in order to avoid illness and death that can results from unsafe products. Some of the acute diseases include diarrheal diseases and different cancerous diseases. These diseases have caused enormous threats to human lives until they have become a public health concern.
The WHO through its vision and mission is helping Member States to identify and prevent various causes of food borne diseases. This program helps to ensure food safety from the production point to the final consumption point (“Labour standards” par 1). In ensuring continuous food safety among the public, the WHO in 2010 launched a new resolution on food safety dubbed Advancing food safety initiatives.
The resolution was to put a strategy that could survey food borne diseases and efficient exchange of information among Member States, especially the developing nations that have poor nutritional status.
The initiative notes that product security has been a perennial problem in the third world countries; therefore, food safety and nutrition should be essential in malnutrition and hunger eradication. Product safety requires risk assessment techniques in order to avoid numerous infections that come as a result of mishandling of foods.
Environment
Following the success of the ISO 9001 (international organization of standardization) (9001 –quality standard) the ISO has developed a series of environmental management standards (ISO 14000). Although there is no “physical security standard” as such, ISO has developed an information security standard ISO 27000 what is a best practice recommendation on information & risk management.
What is a management system
“Management is the process of setting policy, organizing, controlling, monitoring, and reviewing the effort of an organization and of using all other organizational resources to achieve stated goals.” First, it must be understood what a management system is.
A management system is a framework for your organization to enable it to achieve certain tasks or objectives. For example – your organization has to build a house. Without a checklist, this would most likely end up in chaos. With an adequate management system, you would have to write a policy what specifies. (The policy is your business plan for managing a task.)
- Problem identification.
- Policy Formulation.
- Adoption.
- Implementation.
- Evaluation.
After writing the policy, the work task will be executed.
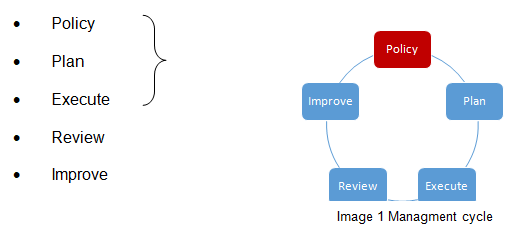
Once the task is completed, the outcome will be reviewed. If there are some improvements, in the work cycle, this can be added or corrected into the policy and the cycle begins from start.
The most common management system in the industry is ISO 9001 (quality management) Lots of the big corporations see the ISO 9001 as requirement for their supply company’s and contracting organization.
“The ISO 9000 family of standards is related to quality management systems and designed to help organizations ensure that they meet the needs of customers and other stakeholders while meeting statutory and regulatory requirements related to content the product. The standards are published by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization, and available through National standards bodies.”
However, the industry has adopted these management systems into the specialized fields of
- Health & Safety.
- Security.
- Environment.
Successful businesses work in unity towards achieving their vision. In the management process, they have to share information, engage in environmental forecasting and benchmarking, and even engage in teamwork. Management systems lay strategies that assist businesses go through numerous challenges in the 21st century.
If a business implements an effective management system, it will be able to promote innovation, manage its financial risks, raise customers’ satisfaction, and reduce cost. Moreover, an environmental management system assists firms to improve their environmental performance.
Health & Safety
The definition of Health & safety according to ILO (International Labour Organization):
„Occupational health should aim at the promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social well-being of workers in all occupations; the prevention amongst workers of departures from health caused by their working conditions; the protection of workers in their employment from risks resulting from factors adverse to health; the placing and maintenance of the worker in an occupational environment adapted to his physiological and psychological capabilities and; to summarize: the adaptation of work to man and of each man to his job.“
Therefore, as you can see Health and safety management deals with:
- Protecting people from injury and ill health (both – employees and non-employees).
- Complying with legal requirement.
- Managing health and safety in a cost effective way to achieve business goals.
To identify possible risks an easy tool can be used. The so-called Risk matrix – more of this will be explained in the Risk section. Same as the ISO standard this will be integrated into a managing cycle (see Image 1– management cycle).
Health and Safety in Employment Act of 1992 (HSE Act) in New Zealand promotes protection of people at their places of work. The act emphasizes a systematic health and safety management.
Security
Organizations operating either in there conventional business settings and in new or unique environments will be presented with a wide scope of foreseeable and unforeseeable risks.
Security management deals with Risks (Risk = Threat to an organization + Vulnerability + Impact on the organization)
Same as the ISO standard this will be integrated into a managing cycle (see Image 1 – management cycle) including prevention measures to keep the risk as low as possible.
Security Risks can include
Nonphysical risks:
- Commercial Espionage.
- Information Technology (Computer Virus, etc.).
- Liability Risks (Employees seek compensation through failure of organization).
Physical risks: (especially in high risk areas)
- Armed attacks on facility’s (BP in Algeria 2013).
- Improvised explosive devises (Iraq from 2004-now).
- Kidnapping (South America, Somalia, Nigeria etc.)
Environmental
“Environmental Management offers research and opinions on use and conservation of natural resources, protection of habitats and control of hazards, spanning the field of applied ecology without regard to traditional disciplinary boundaries”
In most industries such as mining or oil & gas the environmental damage are huge and can result in unrepeatable damages to nature. Environmental management tries to keep these damages to a minimum regarding the country specific regulations or the organizations policy.
Environmental risks can include:
- Reducing oil spills.
- Waste management.
- Drilling mud disposal.
- Hydrocarbon contaminated wastewater.
- Water dry out areas.
Environmental protection involves practices that human beings can institute to lower environmental degradation. The current environmental challenges like global warming, water pollution and massive soil erosion. Human activities like improper land usage can lead to soil erosion; for instance, continuous soil tillage and ploughing across the contours facilitate soil run off (“Environmental Protection Plan Guidelines” par. 8).
In addition, cutting down of trees in the environment exposes soil to wind, thus removing the top fertile soil. When this happens, crop productivity also goes down thereby setting up food insecurity. On the other front, lack of the forest will lead to low rainfall in that area since there will be no rainfall catchment region.
Define Risk & Hazards
Hazard
A Hazard is anything that has the potential to cause harm. (E.g. chemicals, electricity)
For example:
- a container of gasoline is a hazard.
- Smoking next to the container would be a risk.
Risk
Is the probability of a specific occurrence happening that reduces the value, reputation, or outcome of your organization.
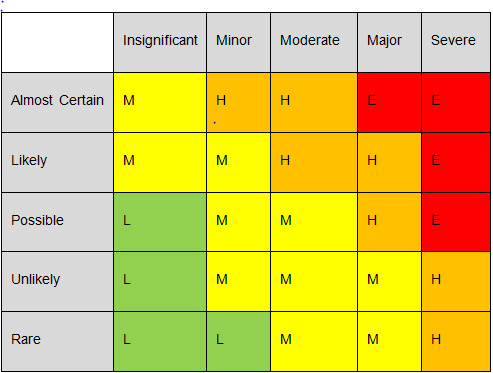
The risk matrix fulfils the purpose of categorizing, ranking, and quantifying risks. This can help to identify which risks are most prevalent in terms of likelihood, impact and counter measures effectiveness. It also provides an easy way to be incorporated into the HASP or HSSE plan.
Auditing
The origin of environmental auditing can be traced from the beginning of 1970 in Western Europe and USA. Health and safety audit assess risk and contingency planning to prevent hazards in the environment (Holbrook par. 5). Auditing entails statistical verification that occurs within a given period following a relevant environmental legislation.
Why is HSSE important for an organization?
Risk varies depending what work environment or surrounding an organization has. From a small business with mainly office work with no health and safety requirements up to the oil and gas industry or the mining industry with a huge requirement of an health and safety system and professionals.
It is important within an organization that management gives a clear direction towards HSSE and that enough resources are available for implementation.
Works Cited
Environmental Protection Plan Guidelines. National Energy Board Site | Site de l’Office national de l’énergie. N.p.. 2011. Web. ”
Health and Safety Boards – Background. Health and Safety Boards – Organizing Your Workplace. Health and Safety Boards, 2005. Web.
Holbrook, Julian. “An introduction to environmental auditing.” Scottish Natural Heritage – Home. Environmental Audit Branch, n.d. Web.
Labour standards. International Labour Organization. International Labour Organization (ILO), 2004. Web.
Mining Disasters – An Exhibition 1907 Fairmont Coal Company Mining Disaster Monongah, West Virginia. Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) – Home Page. U.S. Department of Labor, n.d. Web.
Occupational Health and Safety. Human Services – Alberta Human Services. Government of Alberta. 2006. Web.
Who we are – IOSH. Home Page – IOSH. Institution of Occupational Safety and Health, n.d. Web.