Introduction
The embracement of healthy living habits contributes greatly to the improvement of a person’s well-being. In particular, proper dietary habits and exercising have been identified some of the factors that improve the health status of an individual. However, the contemporary lifestyle exposes people to detrimental dietary habits that undermine their well-being. Notably, the consumption of junk food has become one of the major health issues that destabilize the health of individuals and groups in contemporary societies. In this respect, there is a need to establish strategic mechanisms that encourage people to overlook fast food, owing to their adverse health effects. In this concern, this paper identifies and discusses the various health effects associated with the consumption of junk food.
Literature Review
The junk food issue is a major one in contemporary settings. Notably, children, adolescents, and adults continue consuming more unhealthy foods today compared to the situation in the past. As such, the growing consumption rates predispose consumers to health threats that have a negative effect on their well-being. Various studies show that junk food meals lead to the emergence of health issues that undermine the functionality of the digestive and cardiovascular systems, the respiratory system, the central nervous system, the reproductive system, and the skeletal system (McCarthy, 2013). In this respect, there is a need for reviewing relevant literature that uncovers detrimental health outcomes related to the consumption of junk food.
Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
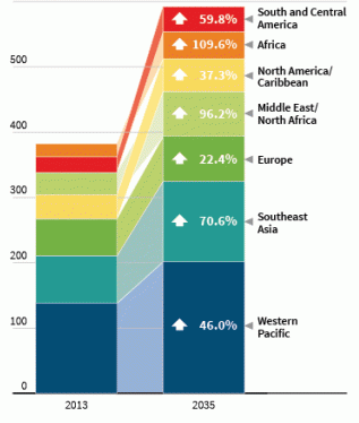
The consumption of junk food is connected to increasing a person’s risk of acquiring Type 2 diabetes. Notably, poor dietary habits trigger an increase in diabetes cases in the world. In this concern, McCarthy (2013) projects that at least 10% of the world’s population will acquire diabetes by 2035. The health trend may be a direct long-term outcome of behavioral factors, especially unhealthy dietary practices. As such, as shown in Figure 1, different regions globally will record a 55% increase in the prevalence of diabetes, thereby undermining the overall wellness of various societies.
In a study to investigate the extent to which junk food leads to the development of Type 2 diabetes, Lazarou, Panagiotakos, and Matalas (2012) provide reliable contributions regarding the public health issue. Particularly, the intake of fast food gradually triggers insulin resistance that eventually results in the development of Type 2 diabetes. Eating fast food reduces the ability of insulin to regulate blood sugar in the system. Important to note, fast foods such as potato chips have considerable levels of carbohydrate and individual fatty acids that undermine the performance of the insulin hormone.
In another inquiry, Naeem (2012) underlines that the consumption of fast foods such as pizza, chips, burgers, and fried chicken exposes Saudi Arabians to an array of health problems, including Type 2 diabetes mellitus. In addition to its contribution to the development of the health issue, junk foods undermine the health status of the Saudi Arabian population by heightening the risk of developing complications such as obesity, hypertension, heart attack, and cancer of the colon.
In this respect, Saudi Arabian health agencies have put in place measures that seek to cut cases of Type 2 diabetes. The recommended approaches to mitigating the emergence of Type 2 diabetes from the consumption of fast food meals in Saudi Arabia include the establishment of programs that seek to control children from consuming junk foods, conducting education initiatives on nutrition, and advocating for a habit of consuming healthy foods (Naeem, 2012). In this regard, owing to the increasing consumption of junk foods, Saudi Arabia is witnessing an upsurge of cases of people diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes. As such, the interventions put in place by the government are expected to mitigate the witnessed adverse outcomes of eating unhealthy foods.
The Risk of Developing Obesity
In recent years, concerns have emerged over the increasing cases of severe obesity. The United States (U.S.) population acquires almost 29% of calories from the consumption of junk food (McCarthy, 2013). Health issues associated with the consumption of junk food range from exposing an individual to the risk of developing obesity to the acquisition of diabetes among other ailments.
In a bid to influence individuals to avoid the consumption of junk food, concerned parties, including public health agencies, engage in programs that seek to raise awareness regarding the risks associated with unhealthy eating. Nonetheless, amid having awareness about the health risks posed by junk food, 80% of the U.S. population frequents fast food joints at least once every month (McCarthy, 2013).
To understand the triggers of obesity, scholars have identified the consumption of junk food as one of the leading factors of the health issue. Popkin, Adair, and Ng (2012) assert that the consumption of junk foods emerged in the 1970s when people started increasingly opting for processed foods, sugar-sweetened beverages, and edible oils. Such dietary behaviors marked a shift from the conventional use of healthy foods and beverages to junk foods that exposed them to an array of health concerns, including obesity.
Apart from obesity, other health issues such as hypertension and diabetes started manifesting at a greater scale during the 1990s, thereby denoting the detrimental effects of using unhealthy foods (Popkin et al., 2012). Furthermore, Finkelstein et al. (2012) uncover that the problem of obesity and overweight affects individuals in various income levels and regions. Thus, low-income earners in regions such as South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa, as well as high-income earners in Europe and North America, among other regions, report heightening instances of obesity and overweight as an outcome of poor dietary habits.
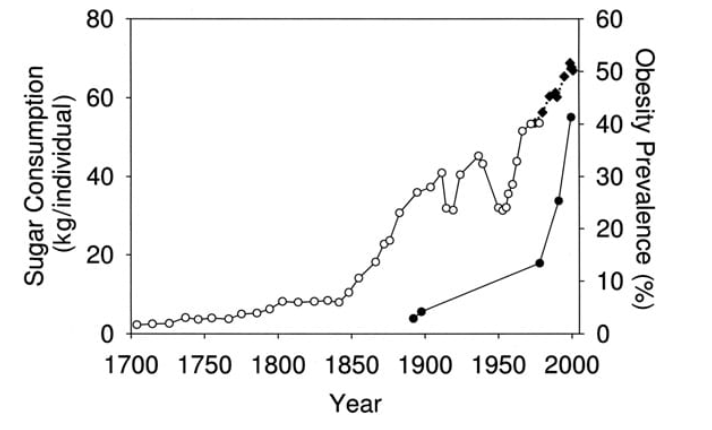
Projections show that the prevalence of obesity is on the verge of increasing significantly, owing to poor dietary habits embraced by individuals in modern societies. Gunnars (2017) posits that the past 160 years have witnessed a skyrocketing rise of the total sugar intake, a situation that had led to increased cases of obesity globally, as shown in Figure 2. People in western countries mainly consume significant quantities of sugars averaging 500 calories on a daily basis. The calories come from the intake of junk foods that have exposed consumers to health risks such as obesity.
Studies that use the linear time trends predictions indicate that obesity will remain unabated in the next decade, owing to the prevalence of unhealthy eating habits (Finkelstein et al., 2012). Nonetheless, the authors predict that the occurrence of severe obesity will reach lower levels than the currently reported rates if people acquire healthy dietary habits. The integration of nonlinear regression models into a study reveals that the prevalence of moderate as well as severe obesity will reach rates of 42% and 11%, respectively, by 2030 (Finkelstein et al., 2012).
The study uncovered that amid linear models predicting that obesity will rise over the 50% rate by 2030, there is still hope that such cases will reduce because of effective and efficient public health interventions. Nonetheless, failing to put in place the required interventions has the possibility of seeing moderate and severe obesity reaching prevalence levels of 33% and 130% correspondingly (Finkelstein et al., 2012). In this regard, the junk food consumption trend has the potential of worsening the health position of the global population by 2030, given that the dietary habit is associated with the development of obesity.
In a study, Garcia, Sunil, and Hinojosa (2012) underscore that the regular consumption of fast food is one of the leading behavioral factors attributed to the prevalence of obesity in modern settings. The alarming issue is that severe obesity in on the rise compared to moderate obesity. As such, Garcia et al. (2012) note the need for advocating for the integration of public health measures that can facilitate the reduction of the rates of morbid, as well as super morbid obesity. Importantly, the authors identify the strategy of discouraging individuals from consuming junk food as one of the effective ways of combating the severe obesity menace.
Mental Health Risk
The consumption of junk food affects the effective and efficient functionality of the central nervous system. In the end, the use of fast food, as well as processed pastries, may result in the development of mental health issues. Various inquiries reveal that junk food consumption is linked to the development of depression. Notably, poor dietary practices such as the intake of commercially baked foods, sweetened beverages, and sweets raise consumer’s risk of encountering depression by 51% (Zahedi et al., 2014). As such, the emotional imbalance manifested by depression negatively affects the overall well-being of a person. Thus, depression is one of the long-term adverse effects of junk food consumption.
In a study, Zahedi et al. (2014) sought to investigate the degree to which the use of junk food increases the threat of developing mental health problems among Iranian children and adolescents. The study uncovers that the regular intake of fast food increases an individual’s chances of experiencing psychiatric distress in the end. Notably, psychiatric distress manifests in the different forms of violent behavior demonstrated by children and adolescents consuming foods such as fried chicken, chips, burgers, and sweetened beverages regularly (Zahedi et al., 2014).
Psychiatric distress portrayed by violent behavior among regular consumers of snacks and sweetened beverages also affects other aspects of a person’s well-being. Zahedi et al. (2014) uncover that violent behavior has the potential of undermining an individual’s cognitive and social development. Particularly, children and adolescents consuming junk foods to the frequency of a daily basis engage in violent conduct such as physical fights and bullying. They also demonstrate irregular levels of confidence.
In a similar undertaking, O’Neil et al. (2014) find a close association between the unceasing intake of junk food and depression among children and adolescents. The research reveals that proper dietary habits during the early stages of an individual’s lifespan considerably affect their mental health in the long term. As such, failing to embrace quality dietary practices from an early age heightens the chances of individuals experiencing mental problems, especially depression (Jacka, Rothon, Taylor, Berk, & Stansfeld, 2013).
Thus, mental or psychological issues arising from the use of unhealthy meals undermine the well-being of individuals, especially children and adolescents. As such, mental health imbalances that result from unhealthy dietary behaviors may inhibit the proper growth and development of children and adolescents.
Discussion
Over the centuries, the world has witnessed a substantial rise in sugar consumption. In the recent past, most of the sugars the global population consumes emanates from junk foods that people take regularly. Adversely, high-calorie levels acquired from unhealthy diets result in a skyrocketing rise of diabetes and obesity prevalence in the entire regions of the globe. For this reason, projections presented in the literature review show that the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes is on the brink of realizing a 55% increase by 2035.
Shockingly, populations in developing countries in regions such as Sub-Saharan Africa reveal greater tendencies of reporting significant cases of Type 2 diabetes in the next decade. In this view, junk food menace cuts across geographical regions since demographic factors have been presented to expose individuals to health risks of consuming junk food.
Obesity is a public health concern that continues to undermine the well-being of the global population. The literature reviewed confirms that indeed poor eating habits play a part in increasing the prevalence of moderate obesity and extreme obesity globally. Given that obesity is linked to comorbid conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension, it poses a great threat to public health. For this reason, the prevalence of obesity may remain unabated if the global population fails to abandon poor dietary ways.
The need for educating the public and raising awareness regarding the obesity issue is crucial towards improving the health of the overall global population. In this view, in addition to advocating the need for individuals to engage in physical activities, discouraging them from consuming unhealthy foods will go a long way in alleviating health issues associated with such dietary customs. Thus, effectively combating obesity will also reduce the chances of related health issues such as diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, and stroke, among other complications. These outcomes imply an improvement in the public health position in various regions.
The intake of junk foods, sweets, and sweetened beverages is identified as one of the factors that contribute to the rise of mental health issues globally. As noted in the literature review, the unceasing cravings for junk food leave individuals depressed as they seek to satisfy the urge to eat such meals.
In this respect, as companies continue to advertise various types of junk foods that they offer to consumers in the market, they may successfully pursue more individuals to consume such products, thus increasing their chances of experiencing depression. In this respect, various interested parties agitate for the establishment of measures that facilitate the regulation of junk food intake to improve the mental well-being of the global population.
The rising consumption of fast foods among children and adolescents is also regarded as one of the major triggers of psychiatric distress. As such, after consuming unhealthy meals, the occurrence of violent behaviors by young people increases, thus denoting the mental health issue triggered by junk food consumption. Consequently, depressed individuals undergo difficult processes of development, owing to their unbalanced mental well-being. The scenario implies that over 50% of the world’s population has the potential of experiencing poor psychosocial development if the regular intake of unhealthy foods continues.
Moreover, as noted in the literature review, the unceasing consumption of junk food in the contemporary settings exposes individuals to health issues such as diabetes, obesity, and depression. For this reason, there is the need for individuals to acquire positive behaviors that foster their well-being. One of the practical ways of improving the status of the society’s population is the embracement of quality dietary customs. As such, people need to consider eating more vegetables, fruits, grains, and healthy beverages, as opposed to commercially baked pastries, sweets, and sweetened beverages among other unhealthy foods.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, individuals who consume junk foods on regular intervals subject themselves to an array of health risks that undermine their well-being. The notable health complications associated with poor dietary ways include diabetes, obesity, and depression. Shockingly, alarming instances of severe obesity raise concerns, owing to the contribution of the health issue to other conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
As such, there is the need for combating obesity as a way of mitigating the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes, a notable detrimental outcome of unhealthy eating. Moreover, adolescents engaging in the consumption of unhealthy meals have the potential of experiencing psychiatric distress denoted by violent behavior. Therefore, it is crucial to change the current dietary trends to adopt eating approaches that improve one’s well-being.
References
Finkelstein, E. A., Khavjou, O. A., Thompson, H., Trogdon, J. G., Pan, L., Sherry, B., & Dietz, W. (2012). Obesity and severe obesity forecasts through 2030. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 42(6), 563-570.
Garcia, G., Sunil, T. S., & Hinojosa, P. (2012). The fast food and obesity link: Consumption patterns and severity of obesity. Obesity Surgery, 22(5), 810-818.
Gunnars, K. (2017). 11 graphs that show everything that is wrong with the modern diet. Web.
Jacka, F. N., Rothon, C., Taylor, S., Berk, M., & Stansfeld, S. A. (2013). Diet quality and mental health problems in adolescents from East London: A prospective study. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 48(8), 1297-1306.
Lazarou, C., Panagiotakos, D., & Matalas, A. L. (2012). The role of diet in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes: Implications for public health. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 52(5), 382-389.
McCarthy, R. (2013). The global diabetes epidemic in charts. Web.
Naeem, Z. (2012). Increasing trend of junk food use in Saudi Arabia and health implications. International Journal of Health Sciences, 6(1), 5-5.
O’Neil, A., Quirk, S. E., Housden, S., Brennan, S. L., Williams, L. J., Pasco, J. A.,… Jacka, F. N. (2014). Relationship between diet and mental health in children and adolescents: A systematic review. American Journal of Public Health, 104(10), 31-42.
Popkin, B. M., Adair, L. S., & Ng, S. W. (2012). Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutrition Reviews, 70(1), 3-21.
Zahedi, H., Kelishadi, R., Heshmat, R., Motlagh, M. E., Ranjbar, S. H., Ardalan, G.,…Qorbani, M. (2014). Association between junk food consumption and mental health in a national sample of Iranian children and adolescents: The CASPIAN-IV study. Nutrition, 30(11), 1391-1397.