Abstract
The United Arab Emirates pay much attention to its foreign policy because it provides the country with the opportunity to develop and maintain the positive relationship with other countries. The humanitarian assistance plays a vital role in this perspective, as its allocation ensures that the United Arab Emirates is ready to support the vulnerable representatives of the general public regardless of their location. The leaders of the country conduct such actions because they want to emphasize the culture and ideological values, ensure security and enhance interactions with the rest of the world for business purposes.
Introduction
The United Arabian Emirates (UAE) developed its foreign policy in order to follow a particular guideline when interacting with other countries and improve its position in the global perspective. Its purpose is to reach enhancement for the UAE with the help of proper utilization of governmental, organizational and individual resources. Of course, the majority of the countries all over the world have the same objectives. Still, the UAE policy is influenced greatly by the size of the territory, its location, available resources, and population. In the last several decades, the leadership of the UAE implemented a lot of changes connected with its foreign policy in order to meet country’s and people’s interests. In this way, the defense received more funding, economy streamlined its development, and new approaches to dispute resolution were undertaken.
In the framework of the UAE foreign policy, the country is willing to ensure its security and stability. The tension that exists between Iraq and Iran that are rather close makes the UAE focus on the neighborhood. The UAE provides humanitarian assistance to these countries because it is likely to ensure safety. Except for that, the UAE wants to have close ties with other regions. Thus, it can be able to cope with occurred challenges in different spheres with the help from the outside. The Arab and Muslim identity, in its turn, focuses on the assistance and protection of human rights, which motivates the country to support others and allocate aid, especially humanitarian one (Abed & Hellyer, 2001, p. 163).
Even though some scientists and researchers still argue whether moral or materialistic considerations made the UAE focus on the provision of humanitarian assistance to other countries in the framework of its foreign policy, some conclusions can be made on the basis of the available information. Thus, this paper will try to prove that the humanitarian assistance is emphasized in the foreign policy of the UAE because it reveals the culture and ideological values, provides an opportunity to ensure security and enhance interactions with the rest of the world for business purposes.
The UAE as a Donor
The UAE is a country which recently became widely known due to its enormous development in various spheres. Even today it does not stop and is targeted at becoming a world leader in various industries. Such goal presupposes expansion of the companies and their appearance in the world market, which presupposes tight interaction with foreign organizations. Realizing such tendency, the former president of the country, Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, paid much attention to the foreign policy. He emphasized the necessity of becoming a good global citizen, which involved the improvement of diplomatic relations, negotiations with other assistance to other countries. In this way, the UAE promotes partnerships and shows tolerance and respect for others. It does its best to ensure regional peace and stability to on its territory and on the foreign ones with the help of various approaches, including political, developmental and humanitarian mechanisms. Thus, humanitarian assistance is seen as a vital element of the country’s foreign policy (Gibbons & Heintze, 2015, p. 12). The leaders of the UAE consider such support to be their primary duty, as it is what Islam taught. One more reason why aid is provided is not religious but moral.
They believe that as the UAE is a wealthy country, it is right for it to help those who did not turn out to be so fortunate. In support of such explanation, Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, once said that those advantages that were obtained by the UAE and its population from God should not be utilized only by it and are to be shared with others. Today, humanitarian diplomacy is one of the driving sources that support the UAE foreign policy, revealing its efforts to help others when they suffer from disasters and require assistance. According to the special report, which was prepared in 2015, the country spent more than Dh170 billion since the 1970s on the foreign aid. This financial assistance was received by almost 200 countries and turned UAE into one of the most generous donors (UAEinretact, 2016, para. 3). Bhattacharya (2010) mentions that it is on the 7th place of the top humanitarian aid donors (para. 2).
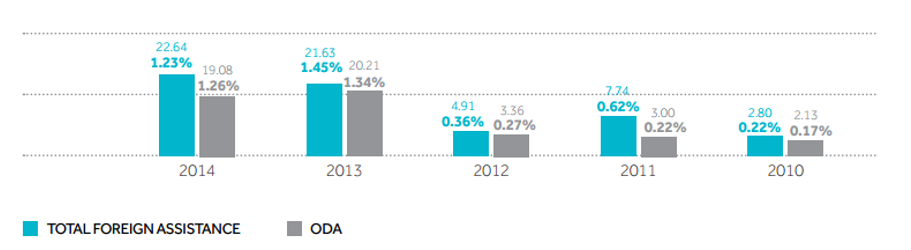
Of course, humanitarian assistance provided by the UAE differs every year because it is not predetermined. Professionals define the amount of aid taking into consideration the needs of the vulnerable populations as well as the connection and cooperation of their country with the UAE that tends to provide assistance to those recipients that can reveal their loyalty later and benefit it. Figure 1 shows the findings of the research study that was conducted by UAE Ministry of International Cooperation and Development (MICAD). It represents both aid provided to foreign countries in total and those distributed as official development assistance (ODA). A dramatic increase of the foreign aid volume ODA disbursements per the gross national income (GNI) can be observed during 2010-2014. For example, initially AED 2.80 billion (about US $763 million) were allocated to assist other countries while four years later this amount exceeded AED 22 billion (more than US $6 billion). UAE ODA/GNI, in its turn, increased from 0.17% to 1.34% (MICAD, 2015, p. 112). Thus, it cannot be denied that the UAE is one of the main world’s donors that pay enormous attention the interactions with other countries.
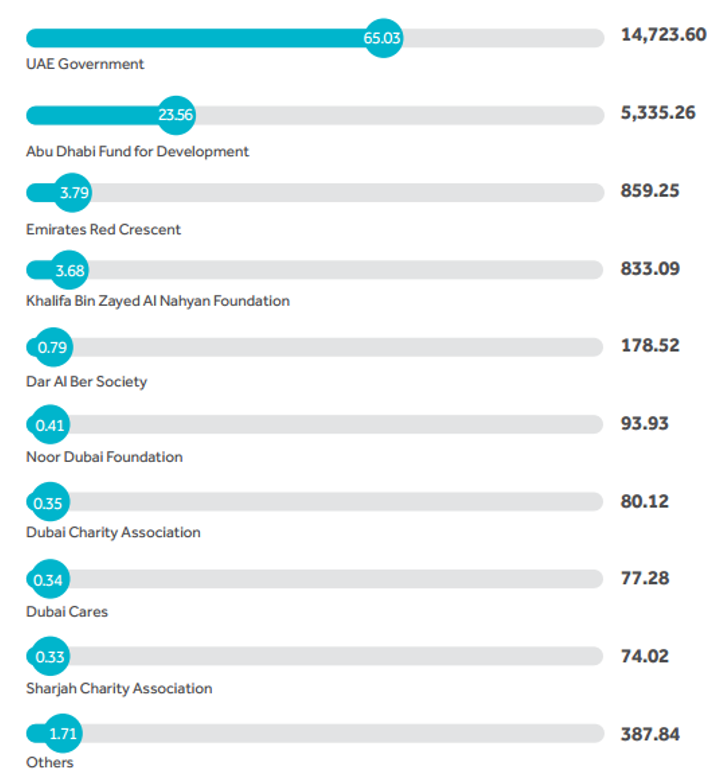
assistance provided by the UAE comes from the contribution of different donors. The main one is the government of the country. For example, just in 2014, it allocated almost AED 15,000 million to foreign aid, which is more than a half of the total sum. Such statistics allows to claim that the further distribution of funds depends greatly on the governmental decision that is based on the foreign policy of the UAE. The second largest donor is the Abu Dhabi Fund for Development. It provided about 20% of funding the same year, which equaled more than AED 5,330 million. The Emirates Red Crescent and Khalifa Bin Zayed Al Nahyan Foundation provided almost 4% of total aid each, while other parties did not reach the line of 1% (MICAD, 2015, p. 7). These results do not minimalize their contribution but prove that they are less involved in decision-making processes.
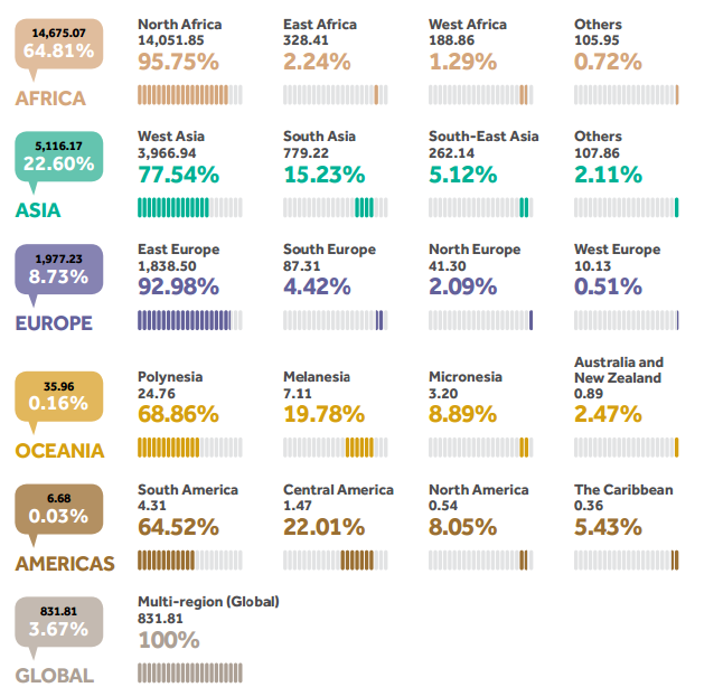
Foreign aid is distributed to different locations all over the world depending on the need of assistance and the UAE views on it. As it can be seen in the Fig. 3, the largest part of funds is allocated to Africa, especially its Northern part. Almost 65% of the total amount of aid was donated to this continent in 2014 so that it received an opportunity to restore after disasters and improve health and the quality of life of its population. Asian countries received 22.6% of all funding to fulfill its needs, which equaled more than AED 5 million (MICAD, 2015, p. 7). Other recipients also received substantial amounts of foreign aid, which gave them an opportunity to strengthen their position. All in all, it can be claimed that the UAE distributed money globally to reach diverse populations and support them.
Taking into consideration those enormous findings that were allocated for the humanitarian aid, it can be stated that the UAE turns out to be an outstanding global humanitarian player. It did not only provided large amounts of money to those countries that were in poor condition but also affected the policymaking procedures. As a result, the UAE started to be called a global donor country. It cannot be denied that after obtaining such status, other donor countries started to be interested in the cooperation with the UAE.
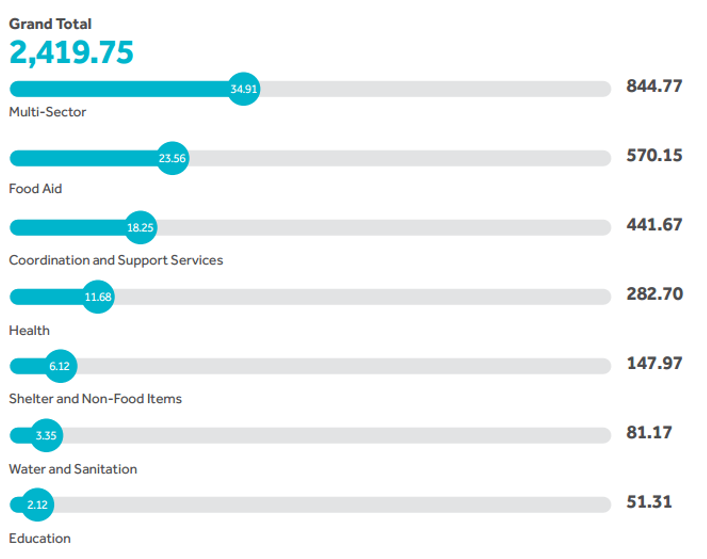
Humanitarian assistance requires substantial funding. As a donor, the UAE is willing to appeal to as many populations as possible. That is why it is critical for the country to ensure that it pays attention to different categories of humanitarian aid. In 2014, 10.7% of all funding allocated to foreign assistance was distributed to the humanitarian aid sector (see Fig. 4). As a result, AED 2.42 billion (almost US $659 million) were spent to meet the needs of the most vulnerable populations. The majority of these funds received the multi-sector aid. As a result, different relief items and services were provided to the recipients all over the world. For example, assistance was received by Syria (that had to support its refugee camps), Malaysia (as it suffered from flood), Gaza (that required reconstruction), Tunisia and Lebanon (that were affected by the cold wave), Badakhshan and Afghanistan (that had to cope with the consequences of mudslides). The second largest category focused on food aid. Almost 40 projects received funding so that countries that suffered from floods could restore and get back in the swing. Among the beneficiaries were “Jordan, Somalia, Syria, Yemen, Pakistan, Palestine, Indonesia, Lebanon, Malawi, Libya, Chad, Myanmar and a multi-country program supported by the World Food Program (WFP) in Africa” (MICAD, 2015, p. 49).
The last type of assistance in the top three sectors is coordination and support services. More than 25 projects were sponsored by the UAE so that a lot of recipients had an opportunity to benefit from them. For example, the UAE allocated funds to support the Abu Dhabi Fund for Development (ADFD) program focused on the provision of aid to Syrian refugees in Jordan. It focused on the operations, administration and logistic of their camps. In addition to that, a lot of grants were allocated to Afghanistan so that it received emergency relief assistance. The situation in Syria was also considered by the UAE. Provided aid supported humanitarian coordination and advocacy inside the country. Substantial amounts of money were also distributed to the health sector, which allowed many recipients to enhance overall health condition of their countries. Shelter and non-food items, including clothing and bedding materials, enhanced the quality of life. The similar contribution was made due to the improvement in the framework of water and sanitation. Finally, the UAE funded education aid, which proved that it supported future generations (MICAD, 2015, p. 49). On the basis of this information, it can be stated that the UAE does not simply provide some humanitarian aid that can be used in any way the recipient wishes. The donor pays much attention to the events that happen all over the world and defines those that are the most critical. Then, it refers to its foreign policy and identifies those recipients that tend to be connected with it more than others (for instance, due to the geographical location). Supporting them, the UAE also ensures its security and stability.
Of course, it is not surprising that the majority of the official humanitarian aid that was provided to Arab and Islamic countries that have more in common with the UAE than others (Kroessin, 2007, p. 36). These countries are said to have together the “brotherly relationship”, which reveals their tight connection and readiness to help in a difficult situation (Korany & Dessouki, 2010, p. 465). This tendency was also supported by the domestic factors. The government of the UAE was rather concerned about the condition of the large migrant communities that had to move because of the disasters (Korany & Dessouki, 2010, p. 465).
The UAE assisted various countries with the help of charities. Different government entities in the individual emirates also have a say in humanitarian aid decision-making. A lot of attention is spent by the UAE to the various aid agendas. The country mainly focuses on the humanitarian and development ones in the global perspective. About ten years ago it became a part of the Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs Donor Support Group and later joined the Western United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees Donor Support Group, which enhanced its relations with other members greatly.
Trying to organize aid delivery and make this process more efficient, the UAE established “the UAE Office for the Coordination of Foreign Aid (OCFA)” (Al Mezaini, 2012, p. 98). It provided an opportunity to unite different charities and organizations that would gather the information about the past foreign aid activities for them to be properly organized. In this way, then also started to coordinate the humanitarian funding, making it more substantial. Except for that, this organization conducted a search for charities, which ensured that they allocated aid to those most in need. The company is claimed to be connected with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which supports the idea of the humanitarian assistance being critical for the foreign policy. OCFA tries to cooperate with different organizations that share its ideas. Thus, today its colleagues include the US, Sweden, and other countries.
Motivations and Purposes
The UAE turned into a global donor and a great source of the humanitarian aid as it improved its financial condition due to the discovery of oil. Its significance can be observed due to the economic and geographical peculiarities. However, the leadership is also of great value. It is affected by security and national concerns as well as cultural factors. For example, ideologies determine a lot of activities that are maintained by the country. In this way, it was already mentioned that the leader of the UAE consider that it is supposed to share its wealth, which was obtained by fortune.
There are two main opinions regarding the motives different countries, including the UAE, have when they cooperate with others. In the framework of international relations, constructivists are sure that cultural norms and values determine what is done and why. Still, it seems to be rather naïve to consider that the aid provided by one country to another is given just to reach its moral goals. The thing is that the UAE’s desire to ensure others that it will provide required humanitarian aid should be also discussed in the framework of political considerations, and rationalists are sure about the UAE’s material self-interest. However, it would be unfair and unreasonable to claim that such actions are conducted only because of self-interest and profit because both parties have reasonable claims. Just the adaptation of the foreign policy to the provision of aid is not likely to ensure support from other countries and future transition into a global leader. Thus, it can be said that the UAE provide humanitarian aid using it as a foreign policy facility as well as moral and cultural one. It is willing to improve its economic and political position but also tries to follow those ideas that are spread due to the religion and national identities.
According to Lancaster (2007), in general, all countries make a decision to provide aid considering four main objectives; these are “diplomatic, developmental, humanitarian relief, and commercial” (p. 13). Diplomatic purposes deal with political considerations. They depend on the relationship between different countries and their governments as well as influence them greatly. Developmental goal deals with the desire to streamline the progress made by the country. Humanitarian relief objectives are focused on the intention to assist individuals who are in need and refer to vulnerable populations. In their turn, commercial purposes are connected with the intentions to expand the business and improve imports. Still, the fact that some countries provide aid just to achieve one of these goals is not really true to life. Humanitarian aid can be used to meet not only humanitarian but also commercial and diplomatic goals.
When paying more attention to the rationalist perspective of aid-giving, Al Mezaini (2012) claims that the UAE’s initial purpose pursued self-interest and concentrated on security and survival (p. 49). At that time, the UAE was focused on the desire to be globally recognized, so during the first decade of its existence, the country wanted to show its solidarity with the Arab world and allocated the largest volume of humanitarian aid to it. What is more, even with the course of time when the country turned into one of the leaders in the global market, it did not shift its focus. Still, some new implications occurred as well. The UAE develops its foreign aid policy so that it helps the country to spread its ideas all over the world. It is believed that foreign policies can reveal particular ideas and form the behavior of recipient countries so that it benefits the UAE. For example, they can become more loyal and offer some beneficial trade contracts. Even though there is no necessity for the country to use foreign assistance as a tool to enhance economy because of its dependency on oil, the UAE can enhance its leadership position in this way. Even the operations of the charity organization tend to be connected with the enhancement of the recognition of governmental and non-governmental institutions. Having an opportunity to analyze the effectiveness of humanitarian assistance in the framework of foreign policy during almost 50 years, Al Mezaini (2012) concludes that the UAE successfully achieved good reputation and prestige among other countries (p. 50).
Needless to say that various countries tend to have different reasons to allocate humanitarian aid, as they do not exist in the same environment. The UAE is located on a relatively small territory, which has a great influence on its foreign policy and objectives of aid provision. It is a reach country that continues to develop rapidly. The UAE depends on non-renewable sources, such as oil. In addition to that, it operates under the US security umbrella, which ensures its safety (Al Mezaini, 2012, p. 2). As a result, the country can be likely to base its decisions related to the humanitarian aid on those gains that are not diplomatic. It seems to be rather reasonable that the assistance is provided just with the desire to help vulnerable populations and streamline development of other countries. Even though the focus on moral and humanitarian obligations is often made by small donors, it is believed that those dependent on oil are looking for economic profit obtained in return. Moreover, they tend to think that rich countries are obliged to help poor ones.
The provision of humanitarian aid by the UAE in the framework of its foreign policy is discussed by those parties that operate in this sector, both local and international. Existing research studies and analysis maintained as a part of this assignment reveal that the country allocates humanitarian aid considering not only political motives but also moral ones. In this way, such assistance looks like a part of the foreign policy and a tool that can help to improve relations with other countries as well as like an action maintained under the cultural and religious influence. Such conclusions can be made because the attention was paid to both cultural and political aspects of cooperation and assistance among the countries.
Conclusion
Taking everything mentioned into consideration, it can be claimed that the foreign policy influences the development of the UAE and its interaction with other regions enormously. As the donor of humanitarian assistance, it spent hundreds of billions of dollars to support almost 200 countries from all over the world. The leaders of the country did it because the cultural factors that affected their decisions and value-driven motivations. In addition to that, the UAE was willing to ensure national security that was at risk because of the problems that existed between the neighboring countries. Moreover, it hoped to gain economic profit from such relationship. Being fortunate enough to become wealthy, the UAE considered that they need to share with others and help them. Humanitarian assistance became emphasized because it revealed non-material triggers more than other types of aid, which allowed the country to show that its actions are not only economically-driven. It was allocated to support the representatives of the general public mainly after the disasters that took place in different regions. As a result, the UAE became known as a donor of aid even though its purposes remained rather vague.
References
- Abed, I., & Hellyer, P. (2001). United Arab Emirates: A new perspective. London, UK: Trident Press Ltd.
- Al Mezaini, K. (2012). The UAE and foreign policy: Foreign aid, identities and interests. New York, NY: Routledge.
- Bhattacharya, S. (2010). UAE in top 10 donors of humanitarian aid. Web.
- Gibbons, P., & Heintze, H. (2015). The humanitarian challenge. New York, NY: Springer.
- Korany, B., & Dessouki, A. (2010). The foreign policies of Arab States: The Challenge of globalization. Cairo, Egypt: American University in Cairo Press.
- Kroessin, M. (2007). Worlds apart? Muslim donors and international humanitarianism. Forced Migration Review, 29(1), 36.
- Lancaster, C. (2007). Foreign aid: Diplomacy, development, domestic politics. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- MICAD. (2015). United Arab Emirates foreign aid 2014. Web.
- UAEinretact. (2016). Foreign aid. Web.