Company Description and Market Analysis
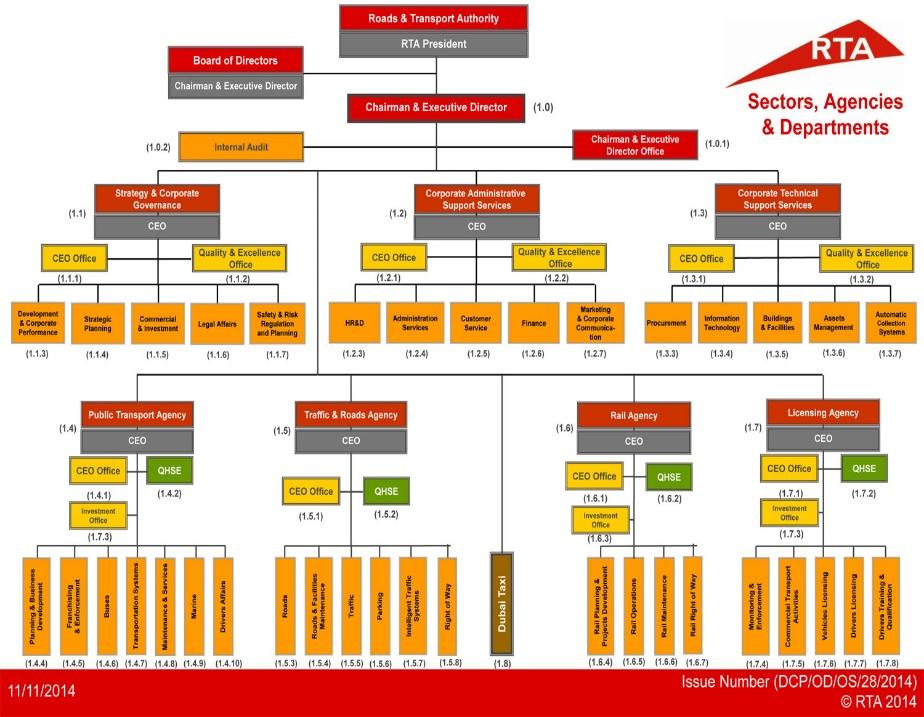
Also known as the Road and Transport Authority, RTA is an organization responsible for not only planning but also providing necessities of transport in Dubai and the neighboring cities. The primary objective of this organization is to provide reliable, efficient, and integrated transport systems that will help Dubai to achieve its vision of serving significant interests of the UAE (Smith 2010). Formed through the 2005 declaration number 17, RTA believes that since Dubai is among the world’s fastest-growing cities, there is a need to provide high-quality infrastructure. Through Dubai’s government agenda of improved transport, RTA embarked on a mission to provide not only smooth but also safe roads for UAE. RTA’s main competitors are the Public Transport Agency (PTA) and the Transportation Systems Department (TSD). The organization has adopted a matrix organizational structure (Kamoun, Werghi & Al Blushi 2010). Through this structure, the organization’s management team can achieve concrete results through its team of experts in the various functional areas. (See fig. 1)
In 2014, alongside other awards, RTA received the ISO certification in the Energy Management system award. Visits to the company’s website (www.rta.com) has continued to increase over the years. With over 2million visits in 2009, the organization’s website has made up to 117 percent increase. After introducing Salik toll gates in 2007, RTA was able to raise 1.658 billion Dirham. Although the organization’s revenue was 1.2 billion Dirham in 2007, it is expected to increase to about 5 billion Dirham by the year 2016. With its headquarters at Marrakesh Street Umm Ramool, RTA is a government agency within the Government Administration industry. RTA is a public company with about 1001 to 5000 employees. Through its mission of developing an integrated transport system that will provide notable services to all stakeholders, RTA promotes growth initiatives in Dubai. The organization motivates its employees through the formulation of friendly legislations and policies, utilizing innovative strategies and technologies, and adhering to the global demands and practices (Edquist 2010). Primary roles of RTA include providing intercity transport, maritime transport, vehicle registration, road beautification, and rail and road projects.
Innovation Policies and Strategies at RTA
Since its inception, RTA has actively taken part in adopting policies and strategies that foster innovation. The main source of innovation for this organization is effective leadership. According to Mattar Al Tayer, the executive, and chairman of the RTA Executive Committee, RTA takes part in initiatives and programs that promote innovation. Addressing the issues of innovation at RTA has come as a result of the directive from the President of the United Arab Emirates, His Highness Sheikh Khalifa. RTA has put in place a standing committee that monitors its innovative strategies and policies. Also, the standing committee has put in place an innovation incubator that ensures that the current innovative procedures meet global standards (Rad & De Moraes 2009). The global strategies at RTA have been in line with the creation of innovating technologies and materials such as the rail vibration sensors and the heat-resistant asphalt.
Through its rewarding approach, RTA has continued to motivate its customers and employees in contributing ideas that will promote business processes. Also, RTA has assigned more financial resources to research awards. In line with comments made by RTA’s president, this move has stimulated employees to take part in innovations (Smith 2010). In line with these insights, the organization has effectively utilized Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. Marlow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs suggests that when an employee’s needs are met, they will be motivated to perform.
There are many strategies RTA uses to promote innovation. At the beginning of this year (2015), RTA embarked on research on the use of driverless vehicles. This research aimed to deploy the autonomous cars in Expo 2020. In the same spirit of innovation, RTA will complete the ongoing makeover to the Smart Government Project (Rad & De Moraes 2009). In line with SGP, RTA will introduce innovative, smart, and user-friendly applications to meet its consumer’s needs. Presently, RTA smart services have scored above 90 percent when compared to other smart applications. According to the president, RTA will soon start an electric bus test run. The electric buses will be powered by rechargeable batteries and will have the capability to travel up to 200 km and speed of 100 km/h (Kamoun, Werghi & Al Blushi 2010). As highlighted in the Dubai Metro Projects, the 75 km stretch mass transit systems and the spanning roads have proved a successful invention of driverless cars. Build on the Artificial Intelligence skill, these innovative strategies have proved to be successful. Furthermore, the floating bridge projects have made residents to travel with ease. These strategies have proven a successful application of RTA’s innovative strategies and policies.
Recommendations, Suggestions, and Conclusion
While innovative practices at RTA have made traveling efficient, there is a need for other countries to adopt such innovation strategies. One of the most remarkable strategies to be incorporated at RTA is the use of research in advancing the existing business practices. Through forming institution-based research teams, RTA can utilize research to promote innovation (Dubai Award for Sustainable Transport: RTA Portal 2015). These teams should be evenly distributed throughout the organization’s agencies and sectors. The organization should take part in the detailed evaluation of its current suggestion system to improve innovation. In conclusion, this paper has provided a set of not only useful but also practical recommendations and insights that can be used to foster the enhancement of public sector innovation (Smith 2010). Therefore, the collected information on Road and Transport (RTA) is significant to the developing transport field. Since innovation strategies and policies have been successful in other countries, RTA must establish and exploit a connection mechanism. This connection will help RTA reduce effort duplication and the waste of useful synergies between the various national strategies.
Brief Summary
Innovation in the public sector involves the formation and application of new processes, services, products, and method deliveries resulting in enhanced effectiveness and efficiencies of the outcomes (Rad & De Moraes 2009). In line with an understanding of this term, innovation in the public sector facilitates the application of new concepts in producing better results. Innovation has taken place across the spectrum of the United Arab Emirates government public sector entities. This paper discussed strategies and policies that support the management and commercialization of innovations at the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA). Alongside how the organization protects its IPR, it also discussed the processes and sources of innovation at RTA. On understanding the nature of these strategies, this paper also discussed the appropriate recommendations, suggestions, and conclusions on the unitization of innovation in UAE.
Reference List
Dubai Award for Sustainable Transport. 2015. Web.
Edquist, C 2010, ‘Systems of innovation perspectives and challenges’, African Journal of Science, Technology, Innovation and Development, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 14-45.
Kamoun, F, Werghi, N & Al Blushi, M 2010, On the Appropriateness of Incident Management Systems in Developing Countries: A Case from the UAE, Journal of technology management & innovation, vol. 5,no. 4, pp. 57-69.
Leonard, V & LeBrasseur, R 2008, ‘Individual assignments and academic dishonesty: exploring the conundrum’, The Australian Educational Researcher, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 37-56.
Smith, D 2010, Exploring Innovation, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill Education, Europe.