Introduction
A jet engine is an engine that propels the body by expelling the mass against which it operates to produce acceleration. The engine works in line with Newton’s law of motion (Mattingly, Heiser & Pratt 2002). The law states that: “the rate of change of momentum of a body is proportional to the resultant force acting on it and takes place in the direction of that force” (Ellse & Honeywill 2003, p. 12).
The engine has the ability to move the aircraft forward at a high speed due to the propulsion, making a plane move very fast. Jet engines are mostly internal combustion engines, although it is possible to find a non-combustion engine. The engines have a fan at the front for sucking air. Once the air has been sucked there is a compressor inside the engine that increases the pressure of the air.
The compressor has blades that are connected to the shaft. The shafts are used for compressing the air. Fuel is then sprayed into the compressed air, resulting in an electric spark that produces light from that mixture of fuel and air.
The gases start burning and eventually blast out via a nozzle that is located at the rear side of the engine. The backward shooting of this gas is what in turn propels the airplane forward and at a very high speed (Mattingly, Heiser & Pratt 2002).
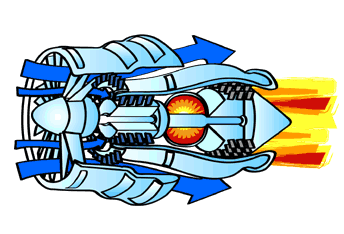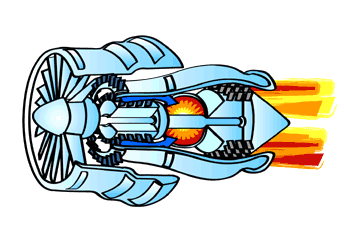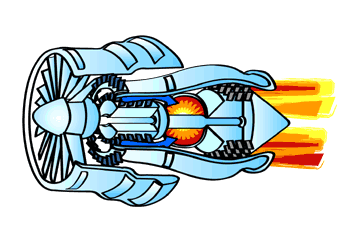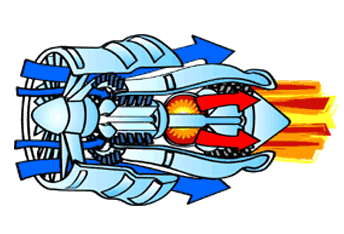
Figure: Jet engine showing combustion process
Source: Mattingly, Heiser and Pratt (2002)
The introduction of this kind of an engine was a great revolution in the aircraft industry. It increased the efficiency of air transportation. The engine had numerous implications on the industry regarding airline regulatory issues, commercial, as well as legal and network issues. The purpose of this essay is to evaluate the impacts of the jet engine development on the air transport industry.
Significance of Jet engine to air transportation
There was a slow development of the air transportation industry after the first aircraft was established by the Wright brothers in the year 1903. It took over ten years before the first passenger service was introduced. The first flight for paying passengers took place in the year 1914 on January 1st in Florida. The first ever international flight took place in the year 1919, and it was between France and England.
Since then there have been numerous developments in the industry, with efforts being put to develop a more efficient aircraft in terms of speed and cost. The introduction of the jet engine aircraft was first witnessed in the year 1958 when Boeing 707 became the first successful commercial jetliner flight (Mattingly, Heiser & Pratt 2002).
The introduction of the jet engine in the air transport industry brought great improvement on the performance of aircraft. It brought improvements in terms of economic efficiency. It also improved on environmental pollution by aircrafts. Its reduced fuel consumption meant that there was less emission of carbon dioxide gas, which is known to be among the most dangerous greenhouse gases.
The jet engine increased productivity of airlines and led to reduction of flight fares (Ali & Dapoigny 2006). The following is a discussion of some of the implications that the jet engine brought to the air transportation industry.
In the 1980s, there was a necessity for reforming the airline regulation. In 1987 an announcement of the basis of a deregulated domestic aviation market was made. Deregulation led to the construction of more hubs in different nations to facilitate travel in different regions across the world. This helped in increasing the frequency of services.
It, in turn, helped to lower the costs incurred by customers per every kilometer travelled. Deregulation also facilitated the development of technology in the air transport industry. As a result of hub-and-spoke networks, computer systems as well as other flyer programs were developed to increase the quality of services. Technology is meant to increase the quality of services.
In a business organization, technology improves the level of customer satisfaction. Introducing computer systems in the air transport industry was a great stride that helped to further lower the overall cost incurred by customers and travel efficiency. This was coupled with further development of low cost carriers that were flying across Europe and America (Abeyratne 2011).
As mentioned earlier, there is an increase in ‘per unit production’ of aircraft influenced by the jet engine. The ratio of ‘power to weight’ has increased greatly. Airplanes can now cover longer distances in much less time, and at the same time carry heavier weights than before. The sector that has benefited most from this development is the military sector.
Economically, this has also been of much benefit. Military equipment has big masses and might be required urgently at a given destination. Jet aircraft are the most efficient for such transportations (Abeyratne 2011). The military has become more mobile as they can even use tactical air power. Jet engine has improved the sales of aircraft since more of the aircraft are being purchased due to their increased effectiveness in transportation.
Fighters prefer the jet engines since they enable them move fast and they can even attack using the planes. Fighters can carry heavier weights, meaning they can carry more equipment to use in war. This capability has also facilitated the development of communication equipment, as well as navigational equipment.
In terms of technology, the development of jet engines was characterized by high levels of innovation. This was the major factor that led to the success of this new development. People were actively trying to find ways in which they could reduce environmental pollution and improve safety in transportation in terms of ecosystem preservation. Jet engine is designed in such a manner that it consumes less fuel compared to other engines.
It is estimated that the development of jet engines has led to reduction of fuel burns and a consequent reduction in the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by about 70%. In addition, emission of NOx has reduced by 90%. Further, organizations have taken advantage of technology to improve on the jet aircraft.
For instance, the most successful organization in the industry has been McDonnell since the 2nd World War (Mattingly, Heiser & Pratt 2002). The company was established in the jet era. Other companies such as the Boeing were established in the piston era, although they were able to master the technology used to manufacture jet engines.
It is important to note that no company, especially in the seventies, were able to master the technology used in the development of jet engines. Out of the twelve big companies at the time, only eight of them were able to master the technology. It was a technology that brought a big revolution to the companies in terms of performance and innovation.
Human factors are those factors that have the ability to influence the behaviour and activities of human beings. The evolution of the jet engine had much influence in the way human beings behaved. Some of the human behaviors that were influenced by the development are performance, cognitive factors, dimensions, as well as industrial design. Development of the jet engine had an impact on the performance of human beings.
For instance, it requires more experience to operate the jet aircraft. Jet engine aircrafts require more kills and knowledge to fly compared to the rest of the aircrafts. Human beings, therefore, had to find ways of acquiring this knowledge and skills through training or experience.
Human performance is usually improved either through training or through experience. Prior to jet engines, pilots and managers working in the air transport industry had no experience on how to operate the engines; therefore, the only way to improve their performance was through training (Council of Europe: Parliamentary Assembly 2007).
Another significant issue that is associated with the development of the jet engines is that they are highly automated. Jet engines facilitated the development of technology and innovation in the air transport industry and the consequent automation of most operations in the aircraft. The effect of these developments on human behaviour is that workload was greatly reduced.
It is a good thing when the workload is reduced, but at the same time there is the risk of the pilot being bored since he or she is under loaded. In addition, there are chances that if the equipment fails to function, the workload might increase dramatically and overload the pilot. When one is overloaded, he or she is likely to perform a shoddy work due to exhaustion or inability to handle the workload appropriately.
The chances of errors increase, and errors might lead to bigger and more serious mistakes (Abeyratne 2011). There are chances that errors may occur as a result of failure of pilots to pay attention or be vigilant. For one to be attentive, in most cases there should be a stimulus. This will relay information to the brain.
Due to the fact that the brain may not be in a position to process all the information that it receives, the effect will be that poor decisions will be made or errors will arise.
This is an important effect on human behaviour in the air transport industry resulting from the development of jet engine. Errors might lead to accidents or other negative results. However, it is important to note that the number of accidents in the industry has reduced significantly with the development of jet engines.
The air transport industry has grown rapidly, especially since the development of the jet engine about 40 years ago. On top of economic influence, the development has had an influence on the legal and political environment. There are legal regulations that are put in place to control environmental pollution (Bartsch 2013).
Aircrafts use fuel as a source of energy; therefore they produce carbon dioxide which is greenhouse gases. The aircraft industry violates the laws that are meant to prevent production of carbon dioxide. Different nations have different regulations regarding carbon dioxide emission. Any company or industry whose operations emit carbon dioxide is required by the law to pay a certain amount of tax depending on the country.
When the jet engine was introduced, it partially solved the problem of carbon dioxide emission. As stated earlier, the engine consumes much less fuel and less carbon dioxide is emitted. The effect of this to the laws regulating environmental pollution is that the laws were made less strict. The fact that jet engines emit less carbon dioxide means that the laws do not have to be very strict on companies that use jet aircraft.
On the other hand, jet planes are likely to trigger insecurity since they are favourable for military use. Laws, therefore, had to be tightened to ensure that jet engine aircrafts are used for peacekeeping rather than for causing havoc and insecurity.
The engines have been developed in a period when the political scene is changing rapidly and insecurity has become rampant. They can, therefore, be used to enhance security worldwide (Abeyratne 2011).
Conclusion
The history of jet engines can be traced back to about 40 years ago. There was slow development in the air transport industry following the invention of aircraft by the Wright Brothers, although this took about ten years before air transport started being commercialized. Innovation continued until a jet engine was invented. The jet engine had the ability to travel at a higher speed, consume less fuel and emit less carbon dioxide.
Consequently, the jet engine improved the economies in the air transport industry, air travel fares were reduced and passengers could be offered improved services. It also facilitated technological enhancement, thus more innovations were made and services became much better.
The jet engine made a significant impact on the efforts of the aviation industry to reduce environmental pollution. Generally, the jet engine has been advantageous to the air transport industry.
Reference List
Abeyratne, RIR 2011, Strategic issues in air transport: Legal, economic and technical aspects, Springer, Heidelberg
Ali, M & Dapoigny, R (Eds) 2006, Advances in applied artificial intelligence:
19th International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems, IEA/AIE 2006, Annecy, France, June 27-30, 2006: Proceedings, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Bartsch, RIC 2013, International aviation law a practical guide, Ashgate Publishing, Ltd, London
Council of Europe: Parliamentary Assembly 2007, Documents: Working Papers, 2006 Ordinary Session (third Part), 26-30 June 2006, Vol. 4: Documents 10868, 10886, 10893, 10903-10950, Council of Europe, London.
Ellse, M & Honeywill, C 2003, Mechanics and radioactivity, Nelson, Cheltenham
Mattingly, JD, Heiser, WH & Pratt, DT 2002, Aircraft engine design, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Reston, VA