Executive Summary
Leadership is an important concept in an organizational setting because it defines the level of motivation of employees and their output. There is a distinct difference between leaders and managers. Leaders are visionary people who can positively influence people within an organization to take a given course without using any form of coercion. Managers on the other hand issue instructions and expect the given objectives to be achieved without trying to understand how they are achieved.
It is emerging that in the United Arab Emirates, there are more managers than leaders in most of the organizations. Instead of working alongside the junior employees and sharing their vision with them, these managers sit in their offices and issue orders that they expect to be followed strictly. Any failure to follow these directives often results in punitive measures. This has created a feeling among many employees that they are exploited and forced to work under pressure. This study recommends that managers working in various Emirati organizations should re-think their strategy and embrace leadership in their management.
Introduction
Background
The United Arab Emirates has experienced massive economic growth, especially following the decision of the government to invest in other sectors to reduce the country’s reliance on oil exportation. The country is currently boosting of a diversified economy that is attracting both foreign and local investors. This impressive growth may be hampered by the feeling among the working class that many organizations lack leadership at the top management and instead they have managers who only know how to direct.
Recent studies have confirmed that one of the most prominent management dilemmas within organizations in the United Arab Emirates is lack of leadership (Adetule, 2011). Specifically, management tends to consist of ‘managers’ rather than leaders.
This can result in de-motivated employees and low morale, which affect the company’s productivity and performance. It is worth noting that leadership helps employees grow, building a stronger community and nation. It is important to investigate and determine if this claim is true and how the problem can be solved as a way of having a pool of highly motivated employees within the local organizations (Aquinas, 2006). In this study, the researcher aims to determine if the problem exists in the United Arab Emirates and the measures that can be taken to deal with it.
Problem statement
According to Small and Rentsch (2010), Leadership is a very important concept that helps in creating an enabling environment where employees can easily interact with their superiors in finding solutions to common problems within an organization. It is worrying that most of the employees in various local firms in this country feel that they have to deal with managers who care less about the employees’ motivation and are only interested in output (DuBrin, 2011).
Such a feeling may result in having a local workforce within these organizations that feel stressed, pressured, and lack proper motivation. Managers of various organizations in this country need to understand how leadership can add value to organizations in the United Arab Emirates. This research will help in enlightening them so that they can embrace various leadership concepts in their management.
Research objectives
The study seeks to explain the difference between leadership and management in an organizational context. It will help managers to understand that it is not enough to be in the management position (Valdiserri & Wilson, 2010). One needs to be a leader, a visionary person who can influence others positively to act in a given way without using coercion. The study will help in creating a leadership culture in Emirati firms.
Research Questions
When conducting a study, it is important to come up with several questions that will help in data collection. The following are the specific research questions that will be answered in this study using both primary and secondary sources of data.
- What is the difference between leadership and management?
- How important is leadership to the success of an organization in the United Arab Emirates and across the globe?
- How is a lack of leadership hindering the growth and effectiveness of Emiratization?
Methodology
This section provides a detailed description of the approach that was taken to collect data from the field, how the data was analyzed and presented to specifically answer the research questions, and to meet the set objectives.
Secondary sources of data
Secondary data including newspaper articles, interviews, and journal articles are crucial in defining the above items and developing in-depth research. For instance, I had a very general idea of the difference between leadership and management. Through research, I was able to better understand the two concepts separately. More than that, secondary data helped me determine that leadership is crucial in the motivation of employees, allowing them to be more productive.
According to an article published by Forbes, “Management and managers are human inventions that were designed with a single purpose in mind, to enforce controls and protocols. The role of a manager was to make sure that employees showed up on time, did their jobs, didn’t cause any problems, and showed up the next day to repeat the process. There was no emphasis on creativity, innovation, engagement, empowerment, or the like.
However today we live and work in a very different world where all of these things are essential. This means that managers must be leaders” (Morgan, 2015). In addition to that, secondary data helped me infer specific consequences of management in the United Arab Emirates. Through conducting research, I learned more about ‘Emiratization’ – a government plan to ensure that jobs are provided for United Arab Emirates nationals, both in the private and public sectors.
One of the many aims of Emiratization is to help the Emirati youth grow and develop, strengthening the nation’s community by empowering the youth and equipping them with the knowledge and skills they need to excel. This is where leadership plays a crucial role. Leaders are seen as role models and mentors rather than superiors. They help those around them grow and develop, rather than merely caring about the bottom line, as managers do. For that, leadership is crucial in the effectiveness of Emiratization. By placing young Emiratis under leaders, rather than managers, the UAE government ensures that these youngsters are learning rather than merely performing meager jobs.
Through secondary data, I was able to learn that leadership is crucial for the growth of the United Arab Emirates through the empowerment of its youth. In conclusion, secondary data is important as it helps one further develop initial ideas. My initial idea was that a lack of leadership in the United Arab Emirates has negative effects on organizations. Through research and secondary data, I was able to look into real-life examples, such as Emiratization, that are relevant to my research. Secondary data supports primary data.
Research Design
Question crystallization. When considering question crystallization, my study is classified as an exploratory study. When I commenced my project, I did not have a concrete structure and hypothesis. Rather, as I began studying the organization, I gained information that helped me develop a hypothesis about the management problems and dilemmas plaguing the organization. The study began as an exploration of the organization. With increased observation, data collection, and interactions, my study was steered in a clear direction with a solid hypothesis as well as conclusions and recommendations.
Data collection method. When considering the data collection method, my study is classified as both a communication and monitoring study as it comprised both interactions with employees as well as monitoring them during their usual workdays. This helped me gain two different perspectives for my research. The first one consists of employees’ opinions, suggestions, and complaints. This perspective was somewhat subjective. The second perspective was objective as it was my take of what employees went through – this information was gained through monitoring. Both perspectives were extremely valuable and insightful.
Experimental effects. When considering the experimental effects, my study is classified as an ex post facto study. As a researcher, I did not have the power to produce effects in the variables under study. Rather, it was an after-the-fact report on what happened to the measured variable which was the lack of leadership in the organization.
Time dimension. When considering the time dimension, my study is classified as a cross-sectional study as it consists of a snapshot of one point in time. The study focused on the leadership and management dilemmas faced by the organization during one period of time. Changes were not studied over time.
Topical scope. When considering the topical scope, my study is classified as a case study. Firstly, my study is qualitative rather than quantitative as it relies on a deep and detailed analysis of the organization and its management dilemma. Secondly, multiple sources of information were used to gather data for this study. Case studies focus on a contextual analysis of events/conditions as well as their interrelations. My study focused on an analysis of the conditions within the organization as well as their interrelations. The problem within the organization (lack of leadership) was studied by its effects and causes.
Research environment. When considering the research environment, field condition is the best option to describe my research which was conducted under the actual conditions of the organization. While conducting my research, I observed and monitored employees to go about their normal workdays to gain an objective perspective on the conditions in the organization.
Purpose of the study. When considering the purpose of the study, my study is classified as casual-explanatory. My study attempts to learn how one variable produces a change in another. Specifically, the lack of adequate leaders and role models in the organization has led to demotivated employees, lack of teamwork, and low morale as well as productivity.
Perceptual awareness. When considering the perceptual awareness, there was no deviation perceived as employees were encouraged to go about their daily tasks and routine. This helped me gain an objective understanding of the company as well as its problems and potential solutions.
Type of the study
Theory Building/Theory Testing. My research is classified as qualitative as it relies on theory building rather than testing. Theory building in qualitative research relies on understanding through a detailed description. This was the case with my project as it relied on developing my initial theories by gaining more information about the organization and its employees. By doing so, I was able to definitively pinpoint specific problems that were affecting the organization and its performance.
Focus of research. My research is classified as qualitative in terms of focus as it depends on understanding and interpretation. To successfully identify the problems faced by the organization, I needed to understand how the organization operates and how employees interact with their managers. Using this information, I was then able to interpret management issues within the organization; specifically, a lack of leaders as opposed to managers who were ineffective in motivating employees and guiding them.
Researcher involvement. My research is classified as qualitative in terms of my role as a researcher, which was crucial. When conducting my study, I interacted with employees, asking about their relationships with their managers and leaders. For that, my involvement in the study is can be described as extensive.
Time duration. My research is classified as both qualitative and quantitative in terms of time duration. Firstly, my research is quantitative as it is cross-sectional. As mentioned before, this means that the study captures a snapshot of time i.e., it describes the conditions of the company during one point of time rather than changes over time. Secondly, my research is qualitative as it involved different methods of acquiring information including observation, interaction, communication, and research.
Sample design and size. My research is classified as qualitative in terms of sample design and size as only a small sample size was used. Qualitative studies typically involve a sample size of 25 people or less. During my research, I was able to gain information through interactions with less than 10 employees at the organization. Each employee was selected based on his or her particular opinions, attitudes, and experiences.
Turnaround. My research is classified as qualitative in terms of a turnaround as the research was fast due to a limited sample size. As mentioned before, my research involved interactions with less than 10 employees. For that, the research was not time-consuming. However, making use of the information gained from interviews was time-consuming. The information acquired from interviews and monitoring were tied back to my ideas and hypothesis.
Data Collection and Analysis. My research is classified as qualitative in terms of data analysis as it involved my perspective and judgment coupled with facts and evidence.
Preparation of participants
Pre-tasking is not suitable for any of the data collection methods identified above for my research. Qualitative studies depend on the researcher’s judgment as well as facts. By deliberately preparing participants, I would not be able to gain an objective perspective on the issues plaguing the company. Employees’ answers to interview questions would be rehearsed rather than genuine. This would negatively affect the outcome and reliability of my research.
Findings
This section summarizes data that was collected through the survey.
Question 1: Number of companies worked.
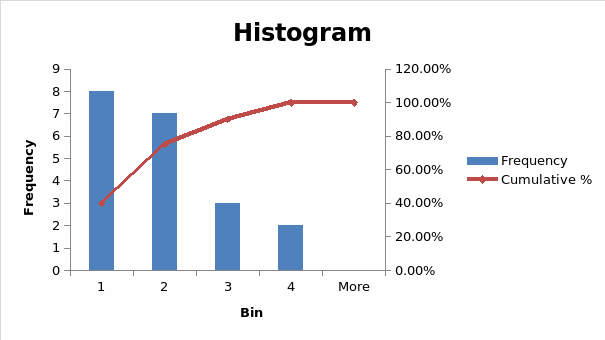
The results show that a large percentage of the population has worked in one company.
Question 2: Number of years worked.
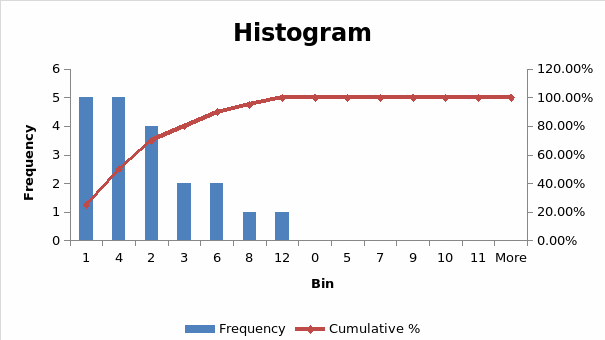
The outcome shows that the most frequent number of years worked are 1 and 4.
Question 5: Values that are demonstrated by leaders.
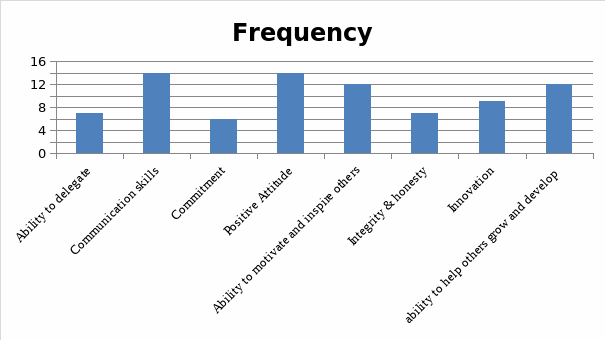
The results show that the most important values that are demonstrated by leaders are communication skills and a positive attitude (Arslan & Staub, 2013).
Question 9: Factors to consider when deciding on workplace.
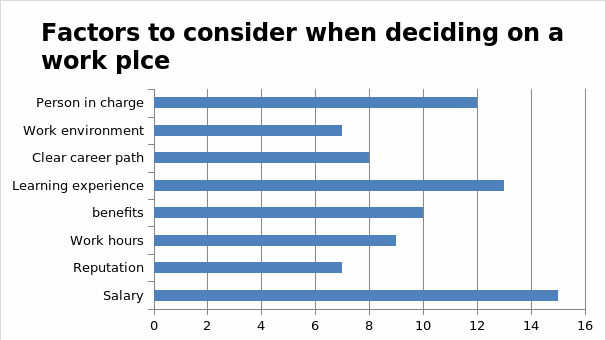
Question 10: Reasons for leaving a workplace.
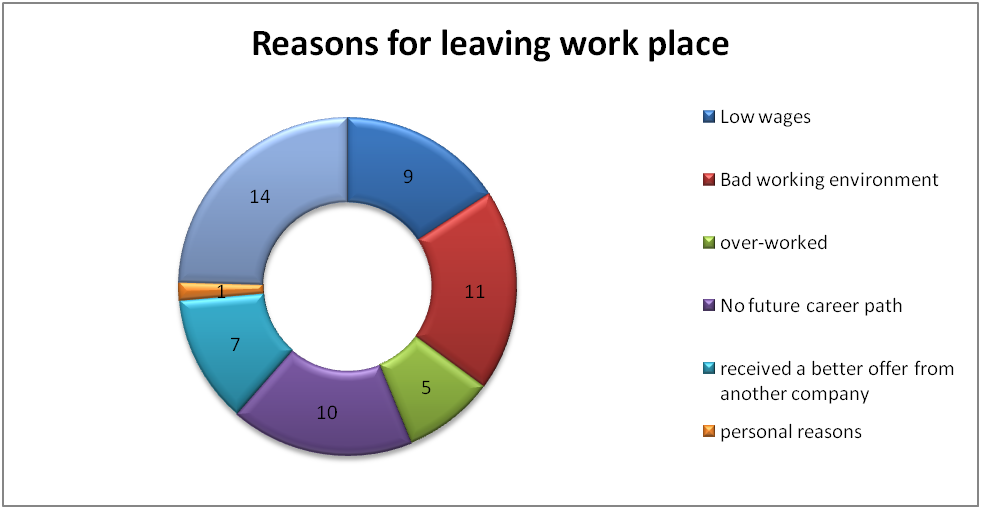
Research Questions
The difference between leadership and management
The data show that most respondents understand the difference between management and leadership. The results are summarized using the pie chart presented below.
The results of question 4 show that most employees feel like they report to managers and not leaders (Bloom & Reenen, 2010). The results are summarized in the table and the chart below.
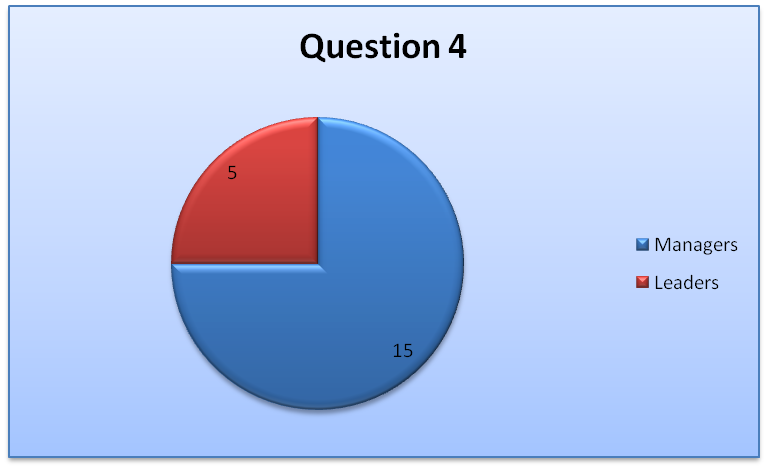
This shows that the number of managers in the organization exceeds that of the leaders. Thus, organizations in the UAE have more managers as compared to leaders.
The importance of leadership to the success of the organization
The outcome of question 17 will be used to answer the research question. The results of the question are summarized in the table below.
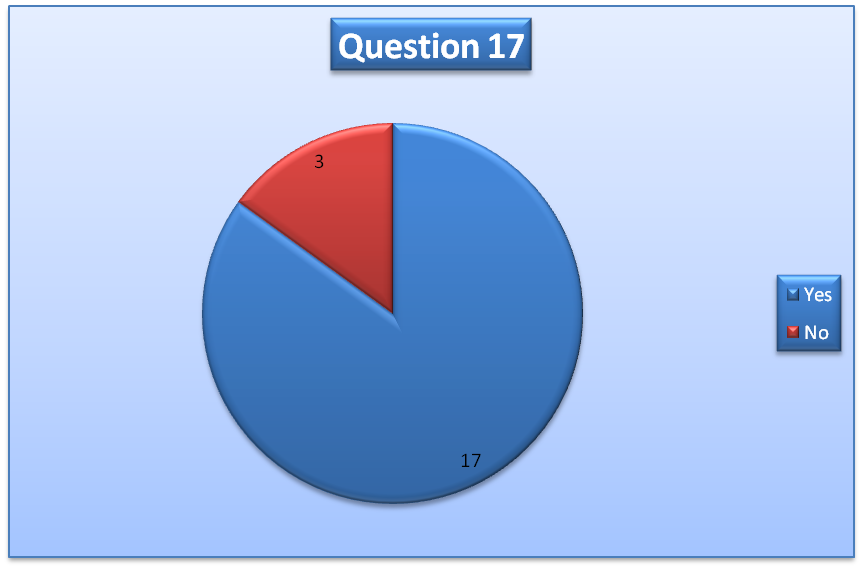
The data show that a significant proportion of the respondents have the opinion that leadership, as opposed to management, would improve the performance of an organization. If the results are extrapolated, it implies that the leadership can contribute immensely to the success of organizations in the UAE (Bloom & Reenen, 2010).
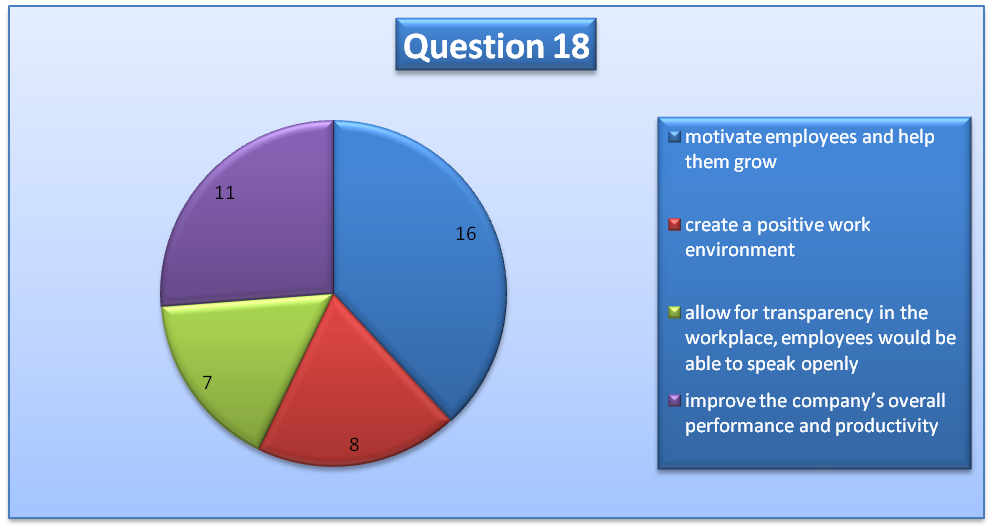
Also, question 18 gives more highlights on how leadership will improve the company. 16 respondents thought that leadership motivates employees and helps them grow, eleven thought that it improves the company’s overall performance and productivity, eight believe that it creates a positive work environment while seven believe that it allows for transparency. Thus, leadership in an organization is significant because it contributes to the overall growth of employees and the organization (Baxter, 2014). The results are summarized in the pie chart below.
Lack of leadership hinders the growth and effectiveness of Emiratization
The results of question 20 will be used to answer this research question.
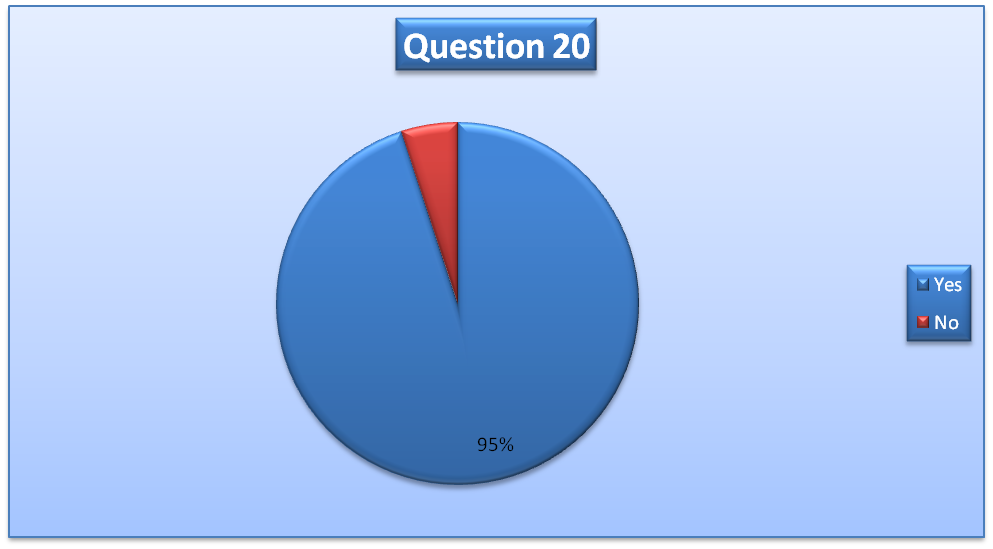
The mean number of respondents who think that lack of leadership hinders the growth and effectiveness of Emiratization is 1.95. The median and the mode are 2. This implies that a large percentage of the sample size believes that a lack of leadership hinders the growth and effectiveness of Emiratization. The standard deviation is 0.22 (Arslan & Staub, 2013).
Determinants of leadership
A regression analysis will be used to evaluate the determinants of leadership in an organization. Therefore, the outcome of question seventeen and five will be used in this analysis. The dependent variable will be leadership while the independent variables will be the determinants listed in question five (Andreadis, 2009). The regression results are presented below.
From the t-test, the p-values of the coefficients are greater than the alpha (0.05). This shows that all the indicators are not statistically significant determinants of leadership. Also, the F-significance of the ANOVA test is greater than 0.05. This shows that the overall regression line is not statistically significant. Finally, the value of R-square is 26.53%. This coefficient is low and it indicates that the explanatory variables do not explain the variations in the dependent variables. It measures the goodness of fit (Aamir, 2008).
Discussion
From the findings, it is apparent that the functionality of a service organization in the UAE is determined by the efficiency of different leadership styles applied, especially in managing the relationship between managers and subordinates. Leadership and motivation in the workplace are two concepts that are intertwined since they operate concurrently to create an environment of inspiration and emotional stability in an organization as observed by the respondents.
Proper integration of the two concepts is instrumental towards a health inter and intra interaction while maintaining professionalism and focus towards organizational goals and culture with the UAE. As observed by the respondents, the main impediments to stable leadership and performance organization are excessive work pressure, low compensation, poor learning structures, and limited space for a consultative approach to performance review.
As a result, organizations may have employees who are poorly motivated due to constant fear of the weak systems that are not friendly to their personal growth and development in the work environment.
Conclusion
The primary principle of sustainability and the ideal model of leadership in an organization incorporate different rules that steer management and subordinates towards efficiency and general success. In most cases, the principle is in the form of a properly structured hierarchal ladder in the decision system and response channels for the management and subordinates as observed by the respondents. The discussion above shows that there is a lack of leadership in most organizations in the UAE since most employees feel like they are reporting to the management and not leaders. Also, the results show that leadership contributes immensely to the growth of employees and the entire organization.
Finally, the lack of leadership has hindered the growth and effectiveness of Emiratization. Therefore, the leadership team in an organization should be empowered by the authority and influence ladder to dispense duties and present solutions to different challenges within a consultative matrix.
Recommendations
Based on the conclusion made after the analysis of the data, the following are the specific recommendations that should be observed by Emirati firms to promote the growth and effectiveness of Emiratization.
- Top managers in various Emirati firms should understand and embrace various concepts of leadership when handling employees.
- There should be employee engagement when developing new organizational structures and systems.
- The management of the Emirati firms should ensure that there is effective communication between the junior employees and top managers.
- Views of the junior employees should be taken into consideration when coming up with new policies within these organizations.
References
Aamir, C. (2008). Impact of job involvement on In-Role performance and organizational citizenship behaviour. Journal of behaviour and applied management,9(2), 3-8.
Adetule, J. (2011). Handbook on management theories. London, England: Author House.
Andreadis, N. (2009). Learning and organizational effectiveness: A systems perspective Performance. Improvement, 48(1), 5-11.
Aquinas, P. (2006). Organisational behaviour: Concepts realities applications and challenges. New York. NY: Excel Books.
Arslan, A., & Staub, S. (2013). Theory X and Theory Y Type Leadership Behaviour and its Impact on Organizational Performance: Small Business Owners in the Şishane Lighting and Chandelier District. Procedia-Social and Behavioural Sciences, 75(1), 102-111.
Baxter, J. (2014). Who Wants to Be the Leader? The Linguistic Construction of Emerging Leadership in Differently Gendered Teams. International Journal of Business Communication, 3(4), 23-41.
Bloom, N., & Reenen, J. (2010). Why Do Management Practices Differ across Firms and Countries? The Journal of Economic Perspectives, 24(1), 203-334.
DuBrin, A. (2011). Leadership: Research findings, practice, and skills. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley & Sons.
Small, E., & Rentsch, J. (2010). Shared Leadership in Teams a Matter of Distribution. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 9(4), 203–211.
Valdiserri, G., & Wilson, J. (2010). The Study Of Leadership In Small Business Organisations: Impact On Profitability And Organisational Success. The Entrepreneurial Executive, 15(5), 47-66.