Introduction
Mobile Computing technology can be defined as technology that make it possible for people to access network services wherever they are and at whatever time they want (Helal, 2002). Mobile computing has grown immensely in recent years and it is projected that in the future, mobile computing will control almost all technological activities in the world.
This will be projection will be looked at in this research paper. Mobile simply describes a computing device that is not restricted. Mobile devices include personal digital assistants, smart cell phones or web phones, laptop computers, tablet PCs or any other devices that allow users to complete computing tasks without physical connection to a network.
Most mobile computers are equipped with a wireless connection to a fixed network and then connected to other mobile devices. This results in a computing environment, referred to as nomadic or mobile computing which enables unrestricted mobility (Mallick, 2003).
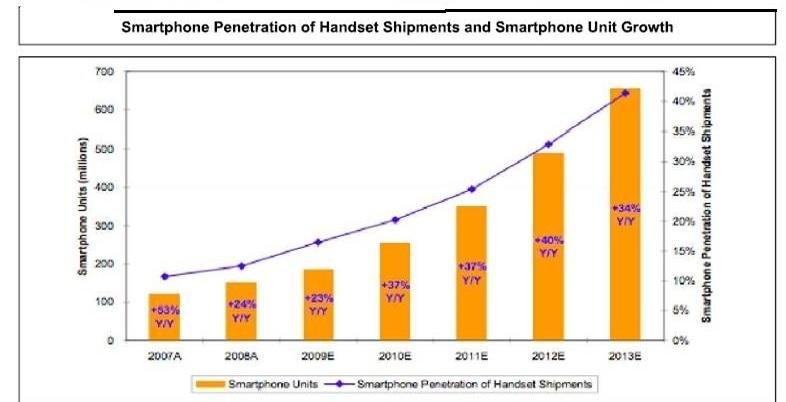
A graph showing estimated growth of smart phones shipment from 2007 to 2013.
Mobile communication, mobile hardware and software are the main concepts in mobile computing. Information is made available and accessible any place and any time due to the fast expansion of communication technology.
Mobile communication
This is the infrastructure created to ensure flawless and reliable communication. It is more radio wave oriented. Signals are transmitted through the air to devices that are capable of receiving and sending similar kinds of signals (Kwok and Lau, 2007).
Mobile hardware
These are the devices that enable reception or access to mobile service networks. They include Portable laptops, Smart phones, Tablet Pc’s, Personal Digital Assistants. They are basically the tangible and visible parts of the mobile computing system.
Mobile software
Mobile software is the engine of the mobile device. This is the program that actually operates the device hardware. It can also be defined as the operating system of the mobile device or gadget
Mobile Computing Classification
Mobile computing gadgets are classified in the following categories:
Personal Digital Assistant (PDA)
This device acts as a portable easy to use electronic organizer, capable of sharing information with a computer system through a process known as synchronization (Agrawal and Zeng, 2006). Synchronization operates on infrared rays and Bluetooth technology.
Smart phones
These devices combine features of a PDA, and a mobile phone. Smart phones can run several programs concomitantly. Their features include high-resolution touch screens, fast data access via Wi-Fi, web browsers, and high speed cellular broadband.
Some of the Operating systems used by smart phones include Android, iOS, Symbian, BlackBerry OS and Microsoft’s Windows Mobile.
Tablet PC and I-Pads
They are larger than mobile phones or personal digital assistants. They are operated by touching their sensitive screens. Examples would include; Ipads, Galaxy Tabs and Blackberry Playbooks.Tablet PCs and I-Pads function as portable computers. They are superior mobile computing devices with enormous processing power.
Advantages of Mobile Computing
Mobile computing appliances can be used in any place as long there is connection to a network. It saves time; Mobile computing has enhanced telecommuting. This reduces time wasted on travelling as users can access files and documents from anywhere over a secure portal. Enhanced productivity; Productivity is boosted due to the fact that users can choose to work from whichever location they feel comfortable.
One doesn’t have to work from an office. Ease of research; In terms of easing research, users can collect data and feed them into the system from wherever they are. Unnecessary trips from the field to an office to feed data into a system are avoided. Informative materials can also be easily accessed from the Internet.
Entertainment; Mobile computing has made it easy to access a variety of entertainment which include, music, movies. People with mobile devices can watch news, movies, and other entertainment as long as they can access networks. This was not possible before mobile computing was introduced to the computing world.
Reorganization of Business Processes; Transactions can nowadays be done through secure mobile network connections. Business information sharing and business deals can be done through secure connections (Reza, 2005). Innovations like video conferencing have greatly reduced the need for lengthy travelling to attend meetings hence cutting down on expenditure and travel time.
Limitations to Mobile Computing
Security: The major issue affecting mobile computing is security. It is hard to supervise safe usage of mobile computing because of its mobile nature. Several cases have been reported worldwide about improper, criminal or unethical usage of mobile computing technology. For example, online fraud and system hacking.
Another problem affecting mobile computing is proper user verification. At times a user’s password is leaked and it can be used by anyone who comes across it. This big threat to security has made many companies be wary of implementing mobile computing. The problem is intricate and hard to effectively deal with. Unauthorized access to data and information by hackers is an issue (Schiller, 2005).
Resource constraints: most of these devices have a rechargeable battery. Interference: there is no shielding to protect Radio transmission against interference and this result in high rates of loss of transmitted data. Low Bandwidth: compared to desktop systems, transmission rates for wireless devices are still very low. Researchers look for more efficient communication protocols with low overhead. Other limitations include network issues and interoperability issues.
Mobile Computing Trends
Smart phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), tablets and other mobile devices currently being used in the world have made mobile computing exceptionally handy. The mobility of these innovative gadgets enables their users to access almost all computer based services.These advanced technological devices can create or upload files, browse the internet, stream live videos at high speeds and also do video or voice conferencing.
The exponentially increasing demand for better and quality devices has been as a reason for market growth. Manufacturers of these devices are having sleepless nights seeking to get their own big share of the market.
The market share for the various companies is constantly being jostled for. An example is Microsoft Windows Mobile makers and Apple’s I phone OS makers who are continuously trying to out do each other by improving on their products every now and then.
The demand for standard, portable, affordable, and quality devices has also made the vendors to continually be creative. An example is the latest Motorola device which is a real-time hands-free mobile computing Wearable Terminal. The Motorola device gives a user excellent and accurate efficiency.
Motorola’s integrated voice and data mobile computing gadgets have flexibility that enables their users to capture and exchange important data depending on their individual business needs. Recent researches have revealed an increasingly growing demand to buy and utilize these devices. Due to the fact that technology is determined by current and future market or user demands, companies come up with innovations suited for current and futuristic use.
This has also led the companies to ensure better service delivery on their products to ward off competition. This they can do by providing superior services like higher speeds for internet and data access in comparison to their competitors. Other device manufacturing companies may attract prospective users by offering free data and roaming services if a user buys their device.
The objective of mobile computing is to be able to work from anywhere. People of the world today need devices that will easily enable them to do their work from the confines of their current location. The devices are programmed to access, process and store large sizes of data.
Chief Executive Officers and other high ranking officers can make decisions based on mobile computing information without having to go to the office (Russell, 2011). For example, a C.E.O can access sales reports of his company through such devices and a do review or remark of the same report.
Conclusion
Today’s mobile computing technologies have gone notches higher in comparison to yester years. Users can nowadays work comfortably from any location as long as they are connected to a secure network. Mobile computing has become a major part of Information Communication and Technology world.
Mobile functionality is available now, but performance remains an issue that will need to be addressed. It is certain that mobile computing will control the world’s economies in the near future. There is still much room to grow and much work to be done to get technology to the desired heights.
References
Agrawal, D.,& Zeng, A. (2006). Introduction to Wireless and Mobile Systems, 2nd edition, Hampshire, UK.Thomson Learning.
Helal, A. (2002). Anytime, Anywhere Computing : Mobile Computing Concepts and Technology. SECS 522. Kluwer Academic. EBook. Web.
Kwok, Y., & Lau, V. (2007). Wireless Internet and Mobile Computing: Interoperability and Performance. New Jersey. Wiley-IEEE Press.
Mallick, M. (2003). Mobile and Wireless Design Essentials. New Jersey. Wiley Publishing.
Reza ,B. (2005). Mobile Computing Principles: Designing and Developing Mobile Applications with UML and XML. Cambridge, UK. Cambridge University Press
Russell, J. (2011). Mobile Computing. Internal Auditor. Aug 2011, Vol. 68 Issue 4, p40-43. 4p. Web.
Schiller, J. (2003). Mobile Communications. 2nd edition. New Jersey. Pearson Education.