Summary
- Background: In this paper, attention is paid to the discussion of nitrous oxide and its benefits over general anesthesia in dentistry in the United Arab Emirates. Pediatric patients experience anxiety and fear when they have to treat their caries or other dental problems. Therefore, the goal of healthcare workers is to reduce the level of pain and panic among children and improve the quality of dental care. Nitrous oxide is discussed through the prism of three items – the level of care quality, implementation costs, and patient satisfaction.
- Methods: A scoping review of 20 peer-reviewed articles is used to gather the material and analyze recent findings. The initial number of the articles found was 2,527; after the removal of duplicates and exclusion of non-eligible articles, 5 primary studies and 15 review articles were chosen.
- Results: Overall satisfaction and the possibility to control pain during dental services with the help of nitrous oxide inhalation sedation with or without ketamine is proved to be an effective treatment modality compared to general anesthesia for pediatric patients.
- Conclusion: Nitrous oxide inhalation has its advantages over general anesthesia, and modern UAE dentists find it effective to choose this modality regularly to enhance patient satisfaction and positive attitudes toward dental care. Increased care quality and patient satisfaction are the two key benefits of using nitrous oxide sedation in pediatric patients. The potential reduction of care costs is likely to be achieved due to lower levels of complications and faster recovery.
Introduction
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has one of the best health care systems in the world. The country has achieved in reforming private health insurance and care services (Koornneef et al., 2017). Dental caries is one of the most critical public problems that influence the health of the population (Elamin et al., 2018). Children are in need of regular and safe dental care services. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (2018) defines nitrous oxide inhalation as a safe technique to reduce anxiety among children and establish communication between a patient and a medical worker.
Considering that anxiety and pain are the key concerns faced by many pediatric children, proper sedation serves as a viable solution to the identified problem (Gazal et al., 2016). In this connection, the importance of the chosen topic is associated with understanding the current sedation practices in pediatric dentistry and revealing any tendencies and opportunities for its further improvement.
This paper aims at reviewing current academic resources to understand the worth of this practice for children with dental problems of different levels. A scoping review is a research strategy to analyze the effectiveness of nitrous oxide in UAE dental hospital management. PICOT and research are discussed in Section 2, Sections 3 and 4 explain dental services, and Section 5 evaluates three items about nitrous oxide (quality, satisfaction, and cost). Section 6 concludes that compared to general anesthesia, nitrous oxide inhalation has its benefits, threats, and impact on care quality, patient/staff satisfaction, and cost policies.
Methods
To investigate the impact of nitrous oxide inhalation sedation, a scoping review is chosen as it allows gathering and analyzing national and international sources from different perspectives. In this paper, several guidelines, scholarly articles, and books will be found via Google Scholar and PubMed databases and used to answer the main research question about the worth of the chosen intervention. The following keywords will be used: pediatric dental services, nitrous oxide inhalation sedation, general anesthesia, care quality, patient satisfaction, and care costs.
The search results revealed 2,527 articles, of which 2,321 were considered as potentially relevant, but only 20 articles met the eligibility criteria and were included in the review (Figure 1). The exclusion criteria involved adult participants, uncovered methods, not hospital-based settings, and non-academic type of publication. There were 15 review articles and 5 primary studies, the outcomes of which are presented in the Results section of this paper.
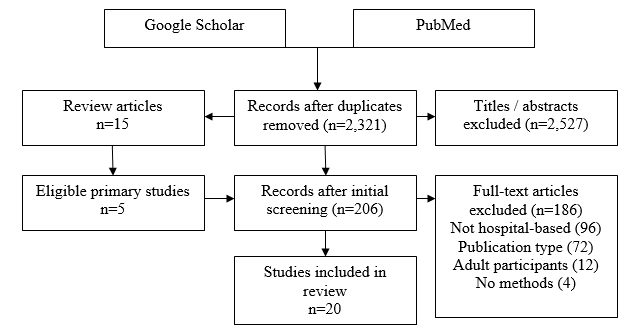
The PICOT of this scoping review is, “In pediatric dental patients (P), would nitrous oxide inhalation sedation (I) compared to general anesthesia (C) lead to increased patient/staff satisfaction, cost reduction, and care improvement (O) within one (T)? The worth of the chosen topic depends on how well nitrous oxide inhalation may be implemented not only in minor oral surgical procedures but in complex services that include the extraction of several teeth. Some patients expect to receive professional medical help without anxiety or fear of being interrupted in their conditions, and nitrous oxide is one of the options modern UAE dentists are free to use and combine with other techniques.
Results
Pediatric Dental Services and Hospital Management in the UAE
The development of high-quality dental services is a priority of many countries and their healthcare systems. The government pays much attention to how hospitals are managed to make sure pediatric patients have access to counseling and treatment. For example, in the United Kingdom, one-third of children are diagnosed with dental caries, and more than 621 million children have similar problems worldwide (Knapp et al., 2017). In the UAE, specialized conferences and international meetings are organized to prove the importance of dental care for children and the evaluation of available treatment options.
Many researchers admit that fear and anxiety are the common emotions among pediatric (and even adult) patients at dental clinics (Sampaio et al., 2019; De Stefano et al., 2019). Taking into consideration the necessity to control mental and dental health among pediatric patients, the medical staff is obliged to identify the most useful means to help their patients and avoid unnecessary complications. In the majority of cases, dentists prefer to use general anesthesia to perform regular dental services like extraction, whitening, implantation, and restoration. However, nowadays, nitrous oxide inhalation sedation is frequently recognized as a solid anesthetic alternative.
In the majority of cases, pediatric dentists frequently choose general anesthesia to manage their services. However, according to Galeotti et al. (2016), there are several reasons for considering nitrous oxidant as a better alternative, including higher mortality risks associated with general anesthesia, discomfort, and unpredictable costs. Nitrous oxide is a “colorless and odorless gas, hardly visible and with a sweet taste, which presents a low tissue solubility” (Bonafé-Monzó et al., 2015, p. 64). General anesthesia is defined as a “controlled state of unconsciousness in which protective reflexes is lost” (Lee et al., as cited in Ramazani, 2016, para. 5).
Compared to nitrous oxide that is frequently recommended to young children with emotional or cognitive immaturity, general anesthesia is not the best modality for the same candidates (Ramazani, 2016). Researchers explain the worth of general anesthesia for adult patients with one prevalent health problem, and the minimization of psychological traumas remains poorly investigated (Galeotti et al., 2016; Lim & Borromeo, 2017; Ramazani, 2016). Today, access to different techniques, services, and treatment methods is available in the field of dentistry, and general anesthesia is chosen when patients totally lack cooperation and understanding.
Table 1. Results of the reviewed studies.
Discussion
This scoping review revealed several studies that examined nitrous oxide sedation in pediatric children in terms of care quality, patient satisfaction, and costs. The majority of studies addressed the dimension of care quality, stating that this intervention allows dentists to focus more on the treatment process, which positively affects patient outcomes. The findings of this review are consistent with previous research, yet it was discovered that nitrous oxide inhalation is more beneficial to use compared to general anesthesia.
Impact of Nitrous Oxide on Care Quality
During a long period, sedation is defined as one of the appropriate pharmacological techniques to facilitate dental care in pediatric patients and enhance quality and safety. To enhance the success of dental services for pediatric and anxious patients, Nelson and Xu (2015) introduce a nitrous oxide nasal hood that is modified to be used with “an end-tidal carbon dioxide sampling line” (p. 98).
Along with simulation training, this mechanism is proved to be effective in improving health care quality and patient safety at the same time. The contributions of nitrous oxide to human health are remarkable among British and American patients as people find this laughing gas working and not harmful in treating mental health disorders and neurodegenerative disorders (D’Angelo et al., 2017). The study proves the enhancement of cognition, motivation, and creativity among patients who use nitrous oxide as one of the lifestyle drugs (D’Angelo et al., 2017). If care quality is improved in different healthcare fields, its effectiveness in pediatric dentistry cannot be neglected and must be thoroughly evaluated.
Comparing nitrous oxide sedation and local anesthetic with general anesthesia, it should be stated that the former is the most preferred option (Adewale, 2012). Inhalation sedation turns out to be a safe method that is applied by many dentists to enhance communication and cooperation with patients and increase tolerance for new appointments. In addition, nitrous oxide may be combined with such drugs as melatonin (3 mg), ketamine (0.25-50 mg), midazolam (0.005-05. mg), or trilofos (70 mg) (Corcuera-Flores et al., 2016).
This sedation type is proved to be less harmful in comparison to general anesthesia in terms of its postoperative care and reactions among children aged 3-10 years (Ilasrinivasan & Shyamachalam, 2018). If patients need to undergo such procedures as multiple extraction or pulpectomy, nitrous oxide inhalation in combination with ketamine (preferably) can be applied to pediatric patients.
Impact of Nitrous Oxide on Implementation Costs
Regarding the experiences of people and their attitudes toward pain associated with dental care, the question of cost is not significant when the necessity to calm down and control anxiety occurs. In the majority of cases, people pay about $200-300 for nitrous oxide for one procedure and $400-600 for general anesthesia for one hour. Sometimes, insurance plans could cover the costs, but the prices for dental services remain high.
The investigations by Burgette and Quiñonez (2018) show that the cost-effectiveness ratio is about 953 for conscious sedation and about 803 for general anesthesia in 2015. The benefits of nitrous oxide are evident, and one should admit the length of the recovery period for both options. If general anesthesia may need hours in a recovery room to obtain normal physical qualities, nitrous oxide administration is characterized by rather short recovery periods – from 12 to 26 minutes after a procedure (Lyne et al., 2019). Hospitals obtain certain benefits when the length of recovery is shortened, and more patients could be served instead of observing patients after general anesthesia or making some preparations before the procedure (required for general anesthesia).
Impact of Nitrous Oxide on Patient/Staff Satisfaction
Local sedation that has no color or odor is an offer pediatric patient, their parents, or other caregivers could receive from dentists. Laughing gas to control anxiety and reduce the level of pain satisfies patients and makes them free, relaxed, and protected. Its anxiolytic and sedative effects are discussed by healthcare experts to prove the effectiveness of the chosen modality (Appukuttan, 2016).
Modern dentists continue investigating their opportunities to understand what kind of services are less damaging and more preferable to children (Bonafé-Monzó et al., 2015). Their anxiety and fear could influence their further visits and the inability to support dental care. Caries can be prevented, and if a pediatric patient is satisfied with dental services, there is a good chance to cooperate with families (Pasarón et al., 2015). Therefore, nitrous oxide that is free from needles and other fearful devices is chosen by parents to protect their children. Both patients and dentists find nitrous oxide as a predictable way to achieve necessary sedation during dental treatment and various specific procedures to prevent referrals to general anesthesia.
Limitations
Although this scoping literature review allowed understanding the role of nitrous oxide sedation in treating child patients, some limitations should be mentioned. First of all, the search was restricted by the English language and academic sources; no grey literature was included. Second, the eligibility criteria may be excessively stringent since only several relevant articles were found. Accordingly, important information may be missing, which limits the generalization of findings. The consultations with stakeholders, which are characteristic of scoping review, were not performed due to the small sample size of this paper.
Conclusion
To conclude, the chosen research method of scoping review proves that many modern dentists prefer nitrous oxide inhalation sedation to general anesthesia due to a number of reasons. Regarding the fact that the UAE strives to create the best healthcare services for patients, the analysis of an international perspective helps recognize the best options. First, it turns out to be beneficial for health to work with nitrous oxide and ketamine to reduce the number of negative outcomes and long recovery periods.
Second, implementation costs of the intervention deserve attention because general anesthesia usually requires additional pre-operative assessments and postoperative care. Even the costs of nitrous oxide are proven to be lower compared to other options. Finally, patient satisfaction and an overall positive attitude towards laughing gas contribute to the establishment of trustful and friendly relationships between patients and dentists.
References
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. (2018). Use of nitrous oxide for pediatric dental patients. Web.
Adewale, L. (2012). Anaesthesia for paediatric dentistry. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia, Critical Care & Pain, 12(6), 288-294. Web.
Appukuttan, D. P. (2016). Strategies to manage patients with dental anxiety and dental phobia: literature review. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry, 8, 35-50. Web.
Bonafé-Monzó, N., Rojo-Moreno, J., & Catalá-Pizarro, M. (2015). Analgesic and physiological effects in conscious sedation with different nitrous oxide concentrations. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 7(1), 63-68. Web.
Burgette, J. M., & Quiñonez, R. B. (2018). Cost-effectiveness of treating severe childhood caries under general anesthesia versus conscious sedation.JDR Clinical & Translational Research, 3(4), 336-345. Web.
Corcuera-Flores, J. R., Silvestre-Rangil, J., Cutando-Soriano, A., & López-Jiménez, J. (2016). Current methods of sedation in dental patients-a systematic review of the literature. Medicina Oral, Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal, 21(5), 579-586. Web.
D’Angelo, L. S. C., Savulich, G., & Sahakian, B. J. (2017). Lifestyle use of drugs by healthy people for enhancing cognition, creativity, motivation and pleasure. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(19), 3257-3267. Web.
De Stefano, R., Bruno, A., Muscatello, M. R., Cedro, C., Cervino, G., & Fiorillo, L. (2019). Fear and anxiety managing methods during dental treatments: A systematic review of recent data. Minerva Stomatologica, 68(6), 317-331. Web.
Elamin, A., Garemo, M., & Gardner, A. (2018). Dental caries and their association with socioeconomic characteristics, oral hygiene practices and eating habits among preschool children in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates – The NOPLAS project. BMC Oral Health, 18(1). Web.
Galeotti, A., Garret Bernardin, A., D’Antò, V., Ferrazzano, G. F., Gentile, T., Viarani, V., Cassbgi, G., & Cantile, T. (2016). Inhalation conscious sedation with nitrous oxide and oxygen as alternative to general anesthesia in precooperative, fearful, and disabled pediatric dental patients: A large survey on 688 working sessions. BioMed Research International, 2016. Web.
Gazal, G., Fareed, W. M., Zafar, M. S., & Al-Samadani, K. H. (2016). Pain and anxiety management for pediatric dental procedures using various combinations of sedative drugs: A review. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 24(4), 379-385. Web.
Ilasrinivasan, J. V. S., & Shyamachalam, P. M. (2018). A comparative evaluation of the sedative effects of nitrous oxide-oxygen inhalation and oral midazolam-ketamine combination in children. International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry, 11(5), 399-405. Web.
Lyne, A., Johnson, J., & Baldwin, D. (2019). Reaction times of children having nitrous oxide inhalation sedation for dental procedures. European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry. Web.
Knapp, R., Marshman, Z., & Rodd, H. (2017). Treatment of dental caries under general anaesthetic in children. BDJ Team, 4(7). Web.
Koornneef, E., Robben, P., & Blair, I. (2017). Progress and outcomes of health systems reform in the United Arab Emirates: A systematic review. BMC Health Services Research, 17(1). Web.
Lim, M. A. W. T., & Borromeo, G. L. (2017). The use of general anesthesia to facilitate dental treatment in adult patients with special needs. Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 17(2), 91-103. Web.
Nelson, T., & Xu, Z. (2015). Pediatric dental sedation: Challenges and opportunities. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry, 7, 97-106. Web.
Pasarón, R., Burnweit, C., Zerpa, J., Malvezzi, L., Knight, C., Shapiro, T.,… Velis, E. (2015). Nitrous oxide procedural sedation in non-fasting pediatric patients undergoing minor surgery: A 12-year experience with 1,058 patients. Pediatric Surgery International, 31(2), 173-180. Web.
Ramazani, N. (2016). Different aspects of general anesthesia in pediatric dentistry: A review. Iranian Journal of Pediatrics, 26(2). Web.
Sampaio, M. M. D., Valadas, L. A. R., Neto, E. M. R., Gimenez, T., Imparato, J. C. P., Calvo, A. F. B., & Lobo, P. L. D. (2019). Sedation in pediatric patients: Assessment of pediatric knowledge. Journal of Young Pharmacists, 11(4), 382-385. Web.