Executive summary
Operations management is a tool that the UAE could use to create a framework for installing a nuclear facility in the country, which acts is a clean, cheap, and safe source of electricity for industrial and domestic purposes.
However, several issues, which include the safety of the facility, its closeness to Iran, natural disasters, unanticipated threats, the cost of installation, reliability and efficiency of the technology, and international concerns about nuclear technology underpins the need for the government to develop a program implementation strategy to achieve its goal.
Operation management deals with the best practices for developing policies to manage the installation and operations of the nuclear facility and provides the right steps necessary to evaluate the future of nuclear energy in the UAE. The paper recommends the country to develop policies to peacefully use the technology and comply with the non-proliferation standards to achieve long term stability and sustainability.
Introduction
The purpose of this report is to describe and analyse the operations management issues related to the installation of the nuclear facility in the UAE (Park & Chevalier 2010).
The elements of concern include construction issues, quality assurance issues for ensuring that the facility is protected from various threats and vulnerabilities associated with nuclear facilities, the best method to alleviate international concerns, and operational policies that could underpin the development and operation of the facility in the UAE (Wheelen & Hunger 2004).
Operations management is based on transforming inputs into outputs in an efficient and effective manner, which in the context of the nuclear facility implies converting uranium into fissile material to generate electricity. Proponents of the project propose a number of issues and practical examples such as the Chernobyl nuclear disaster to oppose the installation of the facility.
However, Australia has shown that the project is feasible based on the policies in place to ensure that the country does not engage in large scale construction of nuclear reactors, but generates enough uranium to be the major supplier of the yellow cake.
Scope
The scope of the proposed study will be to examine the relevant approaches of developing a strategy for the installation of the nuclear facility in the UAE and covers issues related to the strategy. The main areas to focus on include understanding the three levels of operations strategy, which include cooperate, business, and operations program strategies, which are necessary for developing the strategy.
Methodology
The methodology of conducting this study is based on the desk top literature review of secondary sources of information on the operations management concepts and how to apply them to develop the operational strategy for installing the nuclear facility. The secondary and primary sources of information will be journals, online databases, and academic journals on various areas of operations management and nuclear energy.
Assumptions
The main assumptions are that the literature on nuclear safety in the context of operations management is readily available and any information required to conduct the study to its conclusive end will be made available upon request.
Limitations
The main limitations include the inability to provide the correct estimates of the effects associated with the installation of the program.
Background
This section takes us through the background history of the construction of the nuclear facility in the UAE based on the assumptions that nuclear power is reliable, safe and clean for use in the UAE (Park & Chevalier 2010). In April 2008, the UAE decided to install nuclear reactors for the purpose of providing nuclear energy to her population for industrial and domestic use.
The installation was to take place according to the plan and nuclear policy developed in 2008. The project started in 2006, when the plan to install the nuclear reactor was completed (Park & Chevalier 2010).
The plan was the prerequisite to the development of the nuclear policy of the UAE in 2008, which was followed by the development of the appropriate infrastructure to accommodate the construction of the nuclear facility (Nuclear Power in the United Arab Emirates: World Nuclear Association 2014).
Vision & Mission
The mission is outlined in the statement which says that country wants to “deliver safe, clean, efficient and reliable nuclear energy to the United Arab Emirates grid by 2017 and beyond”
The vision statement says that the “country will provide the people and the entire population of the UAE electricity for “powering the future growth and prosperity of the United Arab Emirates through a safe, clean, efficient and reliable civil nuclear energy program”
The core mission and vision statements provide direction for the UAE to provide the people and the nation with clean and safe energy to address the energy needs of the country.
Discussion and Analysis
Structure
The following diagram shows the structure of the nuclear energy process and shows that.the head of the nuclear installation program is the prime minister to whom all parties involved in the installation of the program give account (Nuclear Power in the United Arab Emirates: World Nuclear Association 2014)
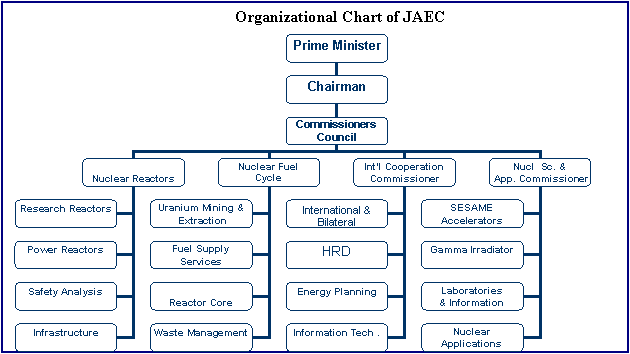
(Source: Van Goethem, 2010, p. 7)
The nuclear energy department
The nuclear energy department of the UAE consists of the executive board, the internal audit department, the chief executive officer, and other departments, which function under the chief executive officer as shown in the diagram below.
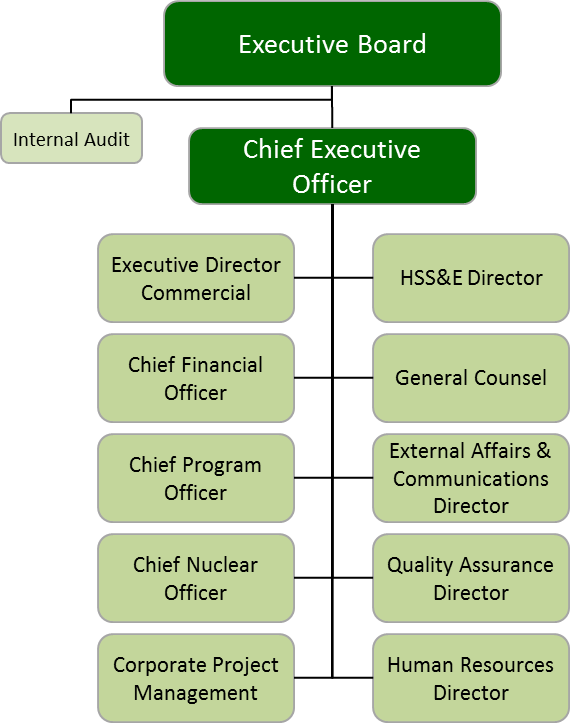
(Source: Van Goethem, 2010, p. 7)
The departments which operate under the chief executive office include HSS & Director, executive commercial director, the chief financial officer, the general counsel, the chief nuclear officer, the quality assurance director, the cooperate project management, and the human resource director department (Kumar & Van Hillegersberg 2000).
Define and Understanding the Problems
The strategic goal is to install a nuclear reactor to provide the people with clean, efficient, and reliable electricity for industrial and domestic use.
The strategic initiative faces a number of criticisms because of the closeness of the UAE to Iran, potential disasters associated with nuclear reactors such as the Chernobyl nuclear disaster, and other natural disasters, which the UAE does not have the infrastructure and disaster management response programs to deal with.
Levels of Strategy
An assessment of the three level of strategy will provide the country with the most appropriate strategy to install the nuclear facility in the UAE. The strategic process involves the people at the top level of the management hierarchy.
The next level is the business strategy, which deals with the financial transactions or the money required to purchase the facility and train personnel to manage the nuclear facility (Abusharekh & Shamisi 2011).
The third strategy is the business strategy, which shows business need to install the facility and includes safe, clean, and efficient source of electricity. The last strategy is the operations strategy, which deals with the hiring and training of skilled personnel to operate and maintain the facility and the technical operations of the facility.
The concept of Operations management
Operations management is responsible for managing the transformation of processes, which deal with the planning and organising the provision of value to the services in the production of goods for the purpose of fulfilling the needs of people in a cost effective way by avoiding waste, during the transformation process of converting inputs into outputs.
Here, efficiency and effectiveness underpin the functions of the operations manager (Van Goethem 2010). Efficiency means doing the right things and effectiveness means doing the things right. Typically, operations management provides guidelines for the management of an organisation to address managerial issues to ensure that quality of services and products are achieved within the organisation at each level of operation.
That makes operations management a critical component of any organisation in managing the resources of the organisation, which includes the people, money, and other primary and secondary assets and support activities.
Operations management Issues
The operations management issues, which are consistent with the installation of the nuclear reactor in the UAE, which are discussed in the paper include ensuring that the UAE, through the commission responsible for the installation of the nuclear facility, is able to provide systematic solutions to the problems, which will face the UAE in implementing the nuclear plan.
In addition, the commission and the nuclear department are able to address various issues such as infrastructure development for the implementation of the program (Stewart, Milford, Jewels, Hunter & Hunter 2000).
Operational policies for long term operations
According to Schwalbe (2007, p.3), the operational polices of the UAE to sustain the nuclear facility should direct that the facility should include regular safety assessment of the facility, management of the regulatory competence of the nuclear department, continuous assessment of the safety of predisposing of nuclear waste, using an up to date and secure information system to run the facility, and formulating the polices which underpin the assessment and compliance with the IAEA policies on the safety of nuclear wastes (Kumar & Van Hillegersberg 2000).
The policy is to offer ““continued education and training, which constitutes a cornerstone of the critical infrastructure necessary to sustain a nuclear power program” (Kumar & Van Hillegersberg 2000).
Burying nuclear waste and other storage alternatives
The people in the region could refuse the dumping of nuclear waste because they are aware of the consequences of radiation leaks from nuclear wastes. One alternative is to store nuclear wastes in proof containers and bury them under the ocean, and away from human habitats. Most of the containers will have rusted in 1000 years and that will not guarantee the children and future generations their safety.
Deficiencies in the Current Operations management strategy
A detailed study shows that the current strategy, which underpins the installation of the nuclear facility, is deficient of certain ingredients to ensure a successful implementation and fulfillment of the strategic objective of generating power from a nuclear reactor (van Weele 2010). The main weaknesses of the current strategy is that it lacks the operations component to enable the management achieve its strategic objectives.
Developing Operations Strategy
The nuclear department will conduct an analysis of the perceptions of the people of the UAE, surrounding countries, international atomic energy agencies and bodies, and other nations to develop the right strategy to address the concerns in each area.
It is important to ensure that the strategic process of implementing the nuclear facility is done at three levels, which have been discussed above, based on the elements discussed below (van Weele 2010).
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis provides the nuclear department with the fundamental understanding of the forces, trends, and factors, which will affect the implementation of the program at the organisational level, business levels, and operational level in the installation of the nuclear facility. A SWOT analysis shows the strengths (critical success factors) show that the country has already well trained personnel to install and maintain the facility.
In addition, the country has the economic ability to purchase the facility, which has a great potential of contributing to the energy needs of the economy. The country has already built an infrastructure to accommodate the implementation of the facility.
The weaknesses include lack of experienced personnel, exposure to the use of the technology, and the huge financial investments, which could take the country a significant amount of time to earn. On the other hand, the opportunities include a new learning experience on the use of nuclear technology, the use of clean and safe sources of energy, the availability and high demand for electricity in the Middle Eastern countries.
The threats include natural disasters, the proximity of the UAE to Iran, and the potential threat of a nuclear accident, which can be very disastrous to the people and the country.
Evaluating Alternative Business Strategy
The nuclear facility, when compared to hydrocarbons, which when burned produce greenhouse gases, which pollute the environment is reliable, clean and safe. The strategy can be achieved by installing the nuclear facility. Another alternative strategy is known as the focus strategy for the UAE.
The strategy can be achieved by concentrating on buying the technology from one source, which has a proven track record of no accidents (Park & Chevalier 2010).
The last strategy is known as the differentiation strategy, which allows the government to focus on the special features of the technology such as the ability of the nuclear reactor to produce yellow cake uranium, which is in demand in the market, without raising eyebrows from other countries (Park & Chevalier 2010).
Formulating &Implementing Operations Strategy
The key elements to consider include the quality of the technology and quality management issues related to ensuring that the technology is safe. That is in addition to installing a technology, which has every aspect of control and safety and the provision of leadership to implement the strategy at all levels of the strategy.
The quality assurance, control, and planning components should form part of the strategy to ensure that the cost of quality is within the projected budget (Park & Chevalier 2010).
Information Technology & Operations Management
Information technology comes in handy for the implementation of the strategy because it underpins the effective and efficient management of different activities, operations and the coordination of the departments, which are critical for the operational efficiency of the company (Abusharekh & Shamisi 2011).
The departments to coordinate include the nuclear department, the human resource, financial, and quality assurance departments.
Designing and Developing New Services
The approach of designing and developing new services, which are specific to the installation of the nuclear facility in the UAE, will be based on the use of information technology (Abusharekh & Shamisi 2011).
Process Management
The core processes will be done within the facility subject to the availability of skilled technicians and other trained personnel to handle the issues. Non-core activities will be outsourced to reduce the costs associated with employing personnel to carry out the activities (Park & Chevalier 2010).
Calculation based on the following formula, will provide the basis for making the right decision on the value of outsourcing certain services and carrying them within the facility.
Q = (P+FC)/ (p-v)
From the above equation, Q is the quantity of units produced (electricity, etc), p is the profit, v is the variable cost, and f is the fixed cost. The formula translates to the following equation:
Total costs (TC) = fixed costs (FC) + vQ
Quality Management
An organisation, which implements the strategy very well, finds that the issue of quality is one of the fundamental elements underpinning the delivery of services and effective implementation of operations management.
To ensure that the strategy works well, the operations manager must ensure that a number of elements which define the strategy have to be factored into the process. The operations manager has to ensure that they are able to address the issues related to the installation of a nuclear reactor to generate electric power for domestic and industrial use.
Quality Frame Work
The quality framework for the strategy and the nuclear facility will be based on the fitness for use of the nuclear facility, user satisfaction who are the people and the government of the UAE, the quality of the design of the nuclear facility to ensure accidents do not happen in the event of threats, the quality of conformance to ensure that the facility conforms to international quality standards of nuclear facilities, availability, which is a key component to ensure that the facility makes its services available to the users, reliability and maintainability to ensure extra costs do not increase out of proportion, and field service to ensure the facility is up to standard (Park & Chevalier 2010).
The key components of quality the quality framework include quality planning, control, and assurance.
Forecasting and Capacity Planning
The operations management concept underpins the ability of the management of the nuclear department to forecast and provide capacity planning for the country to evaluate its resources to purchase and install the facility (Park & Chevalier 2010).
The nuclear department will have to forecast and predict the demand for additional needs for energy, assess the cost of the facility and determine the likely behavior of other countries, which have shown a lot of concern on the safety of the nuclear facility in the UAE.
The key tools the organisation will use to assess the nuclear facility for compliance to the quality standards include Pareto analysis, statistical sampling, and inspections by qualified personnel. The six sigma steps and the Seven Run Rule of quality management will underpin the quality framework.
Recommendations
A close investigation of the issues related to operations management in this study show that the implementation of the facility is economically, technologically, and socially feasible. However, there is a need to seek for public opinion on their perceptions, which an issue not exhaustively covered in this paper.
In addition, there is a need to assess the nuclear awareness level of the citizens of the UAE and the need to assess and create policies, which deal with nuclear nonproliferation treaties to make the UAE compliant with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and other treaties to could remove any suspicion that the UAE may go in the way of processing uranium for military use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study has established that the UAE is prepared to install the nuclear facility amid the international concerns related to the safety of the facility from external threats, which include natural disasters such as earthquakes, the country’s closeness to Iran, the need to comply with nuclear nonproliferation treaties, and other international bodies, which control the sale of nuclear technology.
To address the concerns, the government of the UAE through the department of nuclear energy can adopt the operational strategy and integrate the elements into its nuclear installation strategy to implement the program successfully.
The strategic elements include quality management at different levels of the strategy and the use of information technology as a tool to implement the strategy. It is however, recommended that further studies on the UAE’s nuclear policies and the public perceptions about nuclear energy be conducted to clarify the issues related to the public’s overall perceptions about nuclear energy.
References
Abusharekh, RN & Shamisi, AS 2011, ‘Organisational Culture and its Effects on Innovation within ERP Systems’, Open Innovation at Firms and Public Administrations: Technologies for Value Creation, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 14–16.
Ahearne, J F 2011, ‘Prospects for nuclear energy’, Energy Economics, vol. 4, no. 33, pp. 572-580.
Kumar, K. & Van Hillegersberg, J 2000, ‘ERP experiences and evolution’ Communications of the ACM, vol. 1, no. 43, pp. 23–26.
Nuclear Power in the United Arab Emirates: World Nuclear Association 2014, http://www.world-nuclear.org/information-library/country-profiles/countries-t-z/united-arab-emirates.aspx
Park, KC & Chevalier, F2010, ‘The winning strategy of the late-comer: how Korea was awarded the UAE nuclear power contract’ International Review of Business Research Papers, vol. 6, no.2, pp. 221-238.
Schwalbe, K 2007, Information Technology Project Management. Thomson Course Technology, New York.
Stewart, G, Milford, M, Jewels, T, Hunter, T & Hunter, B 2000, Organisational Readiness for ERP Implementation. Paper presented at the AMCIS 2000, Long Beach CA.
Van Goethem, G 2010, ‘From knowledge creation to competence building Euratom education and training activities in nuclear fission and radiation protection’ In IAEA Int’l Conf. on Human Resource Development for Introducing and Expanding Nuclear Power Programmes, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 14-18.
van Weele, AJ 2010, Purchasing and Supply Chain Management 5th edition. Singapore: Cengage Learning.
Wheelen, TL & Hunger, D J 2004, Strategic Management and Business Policy 9th edition. Pearson Prentice Hall, NJ.