Abstract
Factory efficiency is characterized by its solution based on improving labor productivity and reducing the duration of the production cycle and the cost of products. Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) increase factory efficiency. This is possible due to advancements in the manufacturing sector’s digitalization process and the associated data availability. AI applications in the industry are becoming increasingly significant, as it has a high potential for reducing the impact of industrial outcomes on the environment. However, its effects on industrial efficiency have not been studied yet. Therefore, this report aims to analyze the advantages of using AI in factories and suggest using AI technologies to optimize factory productivity.
Introduction
Until recently, the adoption of integrated automation systems was the primary trend in industrial output growth. Powerful and distributed computing technologies have been used by large businesses to implement solutions. They allow enterprises to control the entire production cycle, and the close integration of production and computing systems ensures the flexibility of technological processes and the ability to change the types of products. It would seem to be the best decision to optimize factory efficiency.
However, the development of systems based on AI technology has facilitated the creation of automation systems at a structurally new level. This leads to the purpose of this paper, which is to answer the question of how the modern industrial sector put into practice the technologies generated by the fourth industrial revolution.
The limitations of the research lie in the fact that multiple developments are currently not yet described by their creators or are limited in the description due to corporation privacy policies. As a result, some innovations might be defined less thorough. Nevertheless, the paper is intended for the general public and researchers that want a quick overview of the problem so that the level of detail might suffice their needs.
The link between AI and Factory Efficiency
Artificial intelligence
AI is a system that can do specific tasks and learn from the data it receives over time, replicating human behavior. A typical example of AI can be the Google search engine, which is used to search for websites and return a list of those that include the searched request (Kowalczyk & Dunajko, 2021, para. 6). It has been changing, attempting to answer inquiries directly, hence, behaving humanly. AI is dramatically changing the performance of product development and production (Wizata, 2021, para. 3). People make decisions based solely on their senses and thoughts, while AI makes decisions based on data. It finds patterns in large amounts of data, identifies weak places, and proposes better solutions.
Factory efficiency
Factory efficiency is one of the most significant concepts deserving attention when discussing AI. Factory efficiency is the ratio of beneficial results to the use of resources necessary to reach them (Waltersmann et al., 2021, p. 2). For an enterprise in the industrial sphere of activity in the conditions of uncertainty of the external environment and a continuous increase in competition, one of the most critical concerns is the evaluation of industrial effectiveness. This is necessary to identify shortcomings in their use and focus the financial resources of the enterprise on much more essential elements of information and communication technologies.
Factory Inefficiency
The common cause of factory inefficiency
One of the costliest problems a manufacturing company might face is production inefficiency. And because the building design was not focused on your specific process production requirements, these inefficiencies were incorporated into plant improvements, resulting in years of extra avoidable costs. Every step of the production cycle is susceptible to inefficiencies in the processing sector. They include issues with food safety, material damage, energy waste, and even production processes that do not perform correctly. Statistics show that the length of offering, staffing, corporate governance, liquidity ratios, and high-technology production all have an impact on the profit and commercial efficiencies of manufacturing enterprises (Anh & Gan, 2021, p. 19). Even though technology might not be able to eliminate every inefficiency in a production process, it is imperative to identify them.
The demand
The current global market has a demand for various types of AI. As such, many large enterprises now use traditional object-oriented systems, which can provide some flexibility in managing production processes. Still, they cannot control the conditions in which the solution of the task is performed and vary the use of resources in real time. That is, they cannot use resources for solving, as well as a list and modes of operation of heterogeneous systems in real time. The tasks of optimizing the technological process are most in-demand for continuous production, for example, in the oil refining, metallurgical, and chemical industries. Predictive equipment maintenance systems are the most implemented for discrete industries, such as mechanical engineering. IDC (2021, para. 1) states that the global market for solutions based on this technology will grow by 16% in 2021 to $327.5 billion. With a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.5 percent and total revenues of $554.3 billion, the market is predicted to surpass $500 billion by 2024 (Figure 1).
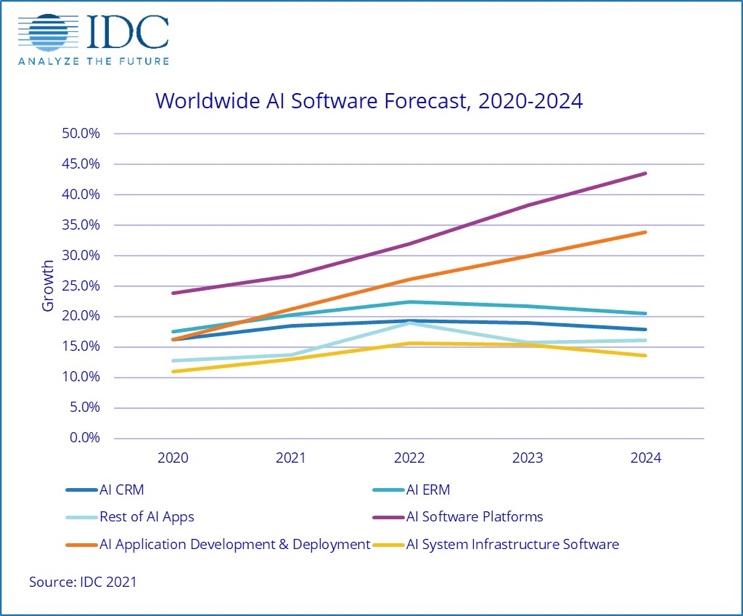
The need for modernization
The existing AI does not suffice the needs of its users, which raises the question of modernization. According to Buła & Niedzielski (2021, p. 117), most modern industries could still require an improvement in the optimization of production process control, reduction of waste generated in production, reduction of supply chain errors, design of machines, and identification of the reasons for failures during production. Weichert et al. (2019, p. 10) also support the idea that factories are much ineffective due to high production time and energy loss. At the same time, manufacturing workers will not fix these problems since they are more concerned with completing jobs than with enhancing overall efficiency. When the industry needs to switch its priorities or adjust the manufacturing according to the state of the business, manual workers may not be able to modify the operations correspondingly.
AI As A Solution For Factories To Increase Efficiency
The benefits of AI in increasing efficiency
AI technologies are actively used in industry and energy complexes to increase factory efficiency. For example, AI provides solutions for ensuring industrial safety, controlling the availability of personal protective equipment and technological processes, and predicting possible risks and accidents at work (Wizata, 2021, para. 15). First of all, such technologies can reduce the risk of equipment failure. Regardless of the specific tool, the goal is to catch potential problems early to resolve them before a failure leads to disaster or costly production downtime. In addition, AI can fully take over the functionality of managing technology and business processes. After training on the relevant data, the algorithm can detect technological defects, deviations in the stages, and completeness of the methods being executed. This allows for increasing the final efficiency of the business, minimizing the human factor. Modern industrial enterprises are facing several issues, which are not solved, which can lead to hazardous consequences like high risk of human errors, climate change, and long production time.
Effects of AI on Production
Which enterprises need to use AI
AI in manufacturing can be implemented in almost any business vertical AI’s main task is to employ machines for choice- and decision-making based on the input visual information. For instance, at the design level, it can be applied for a significant increase in efficiency of new product development, automation of supplier assessment, and selection while analyzing the need for spare parts and parts (Wizata, 2021, para. 9). Meanwhile, at the production level, it can coordinate the improvement of business processes and administer various manufacturing systems. The use of intelligent assistants allows a reduction in the rates of human errors, simplifying the production process and reducing downtime during process changes. According to Industrial Automation (2021), the development of AI technology is expected to increase. The level of rise is expected to be at least 40% by 2035 (Figure 2).
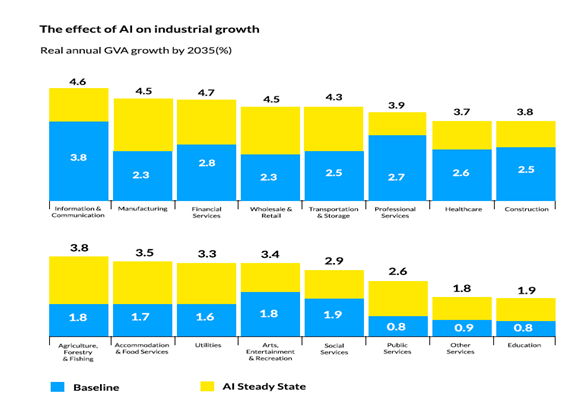
How AI can be used in factories
At the promotion level, AI can predict support and service volumes, manage price, and analyze customer satisfaction with product quality. The occurrence of potential component failures can be expected since there is an opportunity to input asset usage data into machine learning models in prognosis maintenance (Savjani, 2020, para. 13).
Moreover, introducing AI does not require a sharp restructuring of the enterprise’s business processes. The solutions currently on the market are reasonable because they allow the factories to achieve a new quality by optimizing the operation of existing systems. The enterprises can gradually introduce new elements of production processes into the monitoring and control loop and coordinate them, increasing the degree of process controllability.
Because of advancements in the manufacturing industry’s digitalization process and the accompanying available data, much attention is paid to implementing machine learning and optimization to enhance production processes (Weichert et al., 2019, p. 10). Furthermore, a lack of resources encourages new methods like machine learning to reduce and avoid waste while saving energy, time, and resources.
Eco-friendly production and sustainability
Integration of sustainability into company operations is becoming increasingly crucial for firms and a key competitive advantage in addressing climate change and pressing environmental concerns such as biodiversity loss. Following the era of economic prosperity in which industrial pollution was commonly tolerated as a side effect, the effect of production and industrial outcomes are becoming a threat to ecological sustainability. The industrial developments produced by using resources during the production process are one of the primary causes of greenhouse gas emissions (Waltersmann et al., 2021, p. 10). Reducing energy and material resources could lead to considerable improvements in the manufacturing industry’s environmental effects. However, environmental protection through the use of green and renewable energy may impair production rates. This is because the power might come from different sources; it may be unsteady and negatively affect the industry.
AI technology is one of the ways to efficiently solve the issue of excessive resource use and increase overall industry stability and sustainability. It can balance the need for supply and account for storage while detecting possible drawbacks in production and calculating a better plan in real-time (Waltersmann et al., 2021, p. 9). Additionally, AI can adjust energy use in case of instability without decreasing manufacturing rates (Weichert et al., 2019, p. 1). Therefore, with AI technology, a factory would have an opportunity to use a variety of resources. As such, it is tackling existing environmental issues and maintaining production that can combine while avoiding a reduction in factory efficiency with the help of AI technology.
Recommendations
AI can help systems self-regulate to reduce downtime, maximize asset usage, and predict faults. With an AI-enabled modern factory, manufacturing can be run at high speed and vide the opportunity to lower costs and improve customer satisfaction. AI’s use in manufacturing is leading to the improvement of efficiency and quality:
- Businesses may prevent machine downtime by anticipating malfunctions.
- Businesses may use inventory better by keeping track of stockpiles.
- Businesses can predict and estimate delivery times and work on dispatching the finest quality products.
- AI can digitally duplicate a complete manufacturing system, allowing businesses to conduct numerous simulations to observe how the real-world counterpart might react.
Conclusion
Fully autonomous operation of production and processes is yet to come. However, AI systems can serve as an auxiliary adjustment tool for process control operators, technologists, and engineers, helping them make informed decisions to maximize productivity. The ability to remotely monitor and speed up the troubleshooting process improves factory efficiency, while condition-based repairs optimize maintenance schedules and increase profits. The manufacturing industry can significantly benefit from using cyber-physical systems to improve the efficiency of production lines.
References
Anh, D. L. T., & Gan, C. (2021). Inefficiency causes and resolutions toward financial success of Singapore manufacturing enterprises.The Singapore Economic Review, 1–23.
Buła, P. & Niedzielski, B. (2021). Management, organizations and Artificial Intelligence: Where theory meets practice. Routledge.
IDC. (2021). IDC forecasts improved growth for the global AI market in 2021. Web.
Industrial Automation. (2021). The Future of Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing industries.
Kowalczyk, T. & Dunajko, M. (2021). Artificial Intelligence uses in production process optimization.
Savjani, R. (2020). 5 ways AI can optimize the efficiency of your production line.
Waltersmann, L., Kiemel, S., Stuhlsatz, J., Sauer, A., & Miehe, R. (2021). Artificial Intelligence applications for increasing resource efficiency in manufacturing companies – A comprehensive review.Sustainability, 13(12), 6689.
Weichert, D., Link, P., Stoll, A., Rüping, S., Ihlenfeldt, S., & Wrobel, S. (2019). A review of machine learning for the optimization of production processes. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 104, 1889-1902.
Wizata. (2021). How to optimize production line with artificial intelligence.