The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipids by-layer that selectively allows substances in and out of the cell. The movement of substances in and out of the cell is a function of various transport mechanisms. The type of transport employed is in turn determined by the type of substance transported (Chiras, 2010).
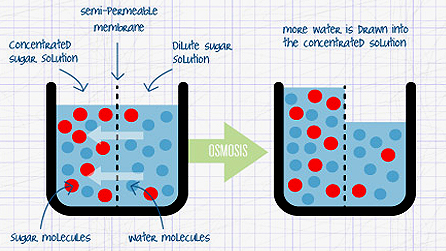
Osmosis is a form of transport that occurs across a cell membrane. The process involves migration of water molecules from an area of elevated water concentration to an area of decreased water concentration via a semi-permeable membrane (Audesirk, Audesirk & Byers, 2008). The cell membrane acts as the semi-permeable membrane as it allows only the small water molecules to move across it while preventing movement of the solutes that are big in size.
The process of osmosis does not need energy to take place. It is the difference in concentration of water across a semi-permeable membrane drives the process. The process of osmosis is regulated by osmotic pressure that is defined as the force per unit area needed to stop the absolute movement of pure water into aqueous solution through a semi-permeable membrane (Khurana, 2008).
Osmosis is an essential process that is required for the survival of living things. It is involved in processes critical to life in both plants and animals. Such processes include water re-absorption in the proximal convoluted tubule in humans, absorption of water by the cells in the roots of plants and absorption of water across the small intestine in human
Examples of molecules transported across the membrane
Water molecules are main molecules transported across the semi-permeable membrane by the process of osmosis. The process is facilitated by the disparity in potential of water across the semi-permeable. As a result, there is migration of water molecules from an area of elevated water concentration to an area of decreased water concentration via a semi-permeable membrane.
References
Audesirk, T., Audesirk, G., & Byers, E.B. (2008).Biology with physiology: life on earth (5th ed.). San Francisco, CA: Benjamin Cummings.
Chiras, D.D. (2010). Human biology. Sudbury, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Khurana, I. (2008). Essentials of medical physiology. New Delhi: Elsevier.