Provide a Brief History of the Company
The development of PETsMART Company can be traced back in the 1860s when James Spratt invented the first dog biscuit in England. However, pet industries grew slowly until a decade later when the interest of domesticating pet animals sprouted in many parts of the world, leading to the expansion of pet industries and diversification of pet products and services. Jim and Janice Dougherty conceptualized the idea of adopting pet animals in 1986 before its implementation kicked off a year later (Reference for Business par. 1).
Initially, they operated two warehouses for pet food under the name PetFood Warehouse in the Phoenix, Arizona area in North America. The purpose of the business was to provide specialized foodstuffs for pet animals. However, the name of the company changed from PetFood Warehouse to PETsMART in 1989 owing to the growing demand and care for pets in the region. To gain a competitive advantage over other pet markets, PETsMART Company had to strategize on the provision of quality products and services to pets and pet customers.
In 1993, PETsMART offered shares to the public at a rate of approximately 10 US dollars per share, which elevated the company sales. In 1994, Jim and Janice founded PETsMART Charities, an independent non-profit animal welfare organization, to help the control of pet populations and cases of euthanasia that were on the rise (Reference for Business, par. 3).
However, PETsMART encountered financial instability between 2000 and 2002 that led to decrement of market stock. The elevated market pressure and increased demand for quality pet services led to the emphasis of the “Smart” rather than “Mart” in the name of the company. As a result, the company rebranded its name to PETsMART in 2005 as an implication of commitment to the provision of “Smart” products and services.
Under the new name, PETsMART expanded businesswise to offer numerous products and services such as pet salons, equine department, pet clinics, and the adoption centers among other pet places. These services included dog training, grooming, and daycare among other pet services. Owing to diversification of services and continued expansion of client base, the company opened its 1000th store in 2007 (Reference for Business par. 5).
List the top management of the firm and note what experience and leadership skills they bring to the firm. If a large conglomerate, list both corporate and business managers
David Lenhardt heads PETsMART as the president and chief executive officer. He joined PETsMART in 2000 as a senior vice president of services, strategic planning, and business development (PETsMART Inc. 11). At the dawn of 2007, the company selected him to assume the place of a chief deputy president of store tasks and services. The company chose him as the leading deputy president of go down procedures and human capital at the start of 2009. The dawn of 2012 saw him become PETsMART’s principal commissioner.
However, in June 2013, the company announced David Lenhardt as the new business leader. To reinforce David’s role as the fresh head of the PETsMART Inc., the company appointed him to assume the responsibilities of both the president and the chief executive at PETsMART in April this year. David acknowledges the need for customer satisfaction and selfless provision of premium products and services. His leadership strategy focuses on both the customer needs and profit maximization.
Matt McAdam is the Executive Vice President of merchandizing and real estate at PETsMART. He became the vice president of Hard Goods Merchandizing in 2008. The company promoted him to head the merchandizing department in January 2012. In April this year, he assumed the office of the docket of the executive vice president in the merchandizing and real estate section.
McAdam has a vast experience on retail merchandizing techniques that have improved PETsMART’s sales volume. He has practiced merchandizing for over twenty years prior to joining the pet company (Knight 18). The author reveals that McAdam had previously worked for other retail merchandizing companies such as Kohl’s and May Department Stores. Matt is a role model and a champion for the provision of good life to pet animals.
Carrie Teffner serves the company as the executive vice president and the chief financial officer. The company employed Carrie as the head of this docket in June 2013. However, during PETsMART’s reorganization in April, she became the executive vice president and chief financial officer. Carre has practiced management for over two decades. She has worked for Weber-Stephen Products LLC in a similar position. She has also worked for The Timberland Company as the chief financial officer. Furthermore, she has also assumed various leadership roles in related financial management positions at Sara Lee Corporation.
Bruce Thorn is the executive vice president of store operations, services, and supply chain. With his vast experience in diverse occupations, Bruce joined PETsMART in 2007 to serve as the vice president of Supply Chain Solutions. Two years after the endorsement, the company elevated him to become the senior vice president of Store Operations and Services.
During the reorganization in April this year, Bruce assumed the roles of PETsMART’s executive vice president of store operations, services, and supply chain. In addition to working for the United States Army, Bruce has gained experience from diverse leadership positions in companies such as LESCO Inc., John Deere, Gap Inc., and Cintas Corporation.
John Alpaugh heads PETsMART’s marketing section as a senior vice president and the chief marketing officer. PETsMART Company absorbed him as the vice president of specialty merchandizing before he became the vice president of strategic planning and business development. In February 2010, the company appointed John to become the senior vice president and the chief marketing officer.
Prior to joining PETsMART in 1999, John had played numerous leadership roles in a number of specialty merchandizing companies as a marketing officer. In addition to working for IBM as the Financial Planning and Analysis Officer, John has also served in the area of brand management for Procter and Gamble Company in Europe.
What is the principal business model of the firm? (How does the firm make most of its profits?
PETsMART seeks to deliver superior and differentiated products and services to increase the client base thereby increasing its profit margins. The business model enables different business segments to retail the company’s consumables, hard goods, pets, and pet services (Mules 5). PETsMART Inc. sells its products and services through its stores and websites. The arrangement or location of PETsMART stores provides convenience for pet clients to navigate from one store to another.
Each store has a grooming section, Banfield pet hospital, boarding, and daycare facilities. The uniqueness of the individual pet sections distinguishes between the services that PETsMART offers for the pets. According to Mules, PETsMART has expanded enormously during the last decade (6). The author reveals that the company’s pet service revenues rose to over 10-percent of the total revenues. Rego, Morgan, and Fornell unveil that company derives about 90-percent of its revenues from the sale of its merchandise while pet services such as grooming and training services give rise to the remaining 10-percent (11).
Search a Mission Statement
PETsMART’s mission statement is “To provide Total Life Time Care for every pet, every parent, every time – which means that we have to offer solutions, unmatched services and superb customer service” (PETsMART 88). PETsMART leaders recognize the importance of providing superior services to both pets and pet clientele.
The company is dedicated to fostering the safety and health of pet animals with an aim of stimulating the best relationships between them and human beings. At the PETsMART Company, leaders believe that pets make people happier (La Monica 47). The company strives to make its mission a reality through charity events and the creation of public knowledge about the need for fostering the wellbeing of pets.
Identify the major goals of the company
PETsMART is the largest specialty pet supplier in America. PETsMART Company has moved from the goal of providing mere pet foodstuffs to the provision of pet clothing and administration of high-end healthcare services to domestic dogs and cats. In the modern world, there is an increased demand for specialized pet services and products.
The emergence of “pet parents” has changed the attitude of people towards companion animals. Consequently, this trend of market demand has led to the establishment of PETsMART’s key goal of offering a range of products and services for dogs, cats, reptiles, and birdies among other pet animals. PETsMART targets to model the perceptions and attitudes of people towards pet animals by placing a significant emphasis on the health of pets (La Monica 48)
Does the firm seem to have any longer-term challenging or stretch goals that would serve as its strategic intent?
PETsMART seeks long-term management strategy objectives that align with its mission and goals to foster the wellness of pets whilst acquainting pet parents with the necessary knowledge that pertains to the care and health of companion animals. PETsMART deems the provision of valuable information to clients a first step towards an effective strategy for reaching the company’s targets. The company aims at providing the best pet stores that satisfy their clients’ demands. To achieve this objective, the company frequently addresses its long-term stretch goal of evaluating its store formats to assess for any required in-store design upgrades.
For instance, Moloughney reveals that the company finalized the upgrade of an in-store design package with a view of initiating a highly distinguished training for PETsMART’s clients in 2011 (62). Within the in-stores, the company has continuously maintained exemplary PetsHotels and Doggie Day Camps that facilitate pet training and grooming services. Perhaps, the overall objective of the PETsMART is to differentiate itself through effective brand management strategies. The company’s brand management strategy focuses on the creation and development of an identity for its products and services.
Trace any changes in strategy that you can identify over time. Try to determine whether the strategy changes of your selected firm are because of intended strategies, emergent strategies, or some combination of both.
PETsMART has performed a series of dynamic structural and organizational changes to develop into a highly differentiated product and service provider with the view of delivering assorted and innovative supplies for its clients. Since the company’s establishment in the late 1980s, it has expanded dramatically and extensively through the acquisition of regional chains and diversification of pet foods and hard goods (Alldredge, Eastman, Lynch, Sharma, and Sivaeva 5).
However, PETsMART has undergone an operational shift in structure and logistics due to the need to balance customer demands, working costs, and market forces. As a result, the company’s strategy has shifted from pet supply to the provision of standards to premium pet products and services (Acito and Williams 34). The retail strategy has led to further establishment of both multi-store and single-store units. The plan is to provide clients with diverse products and services that range from standard to premium quality while sustaining high profits and good customer relations.
PETsMART continues to expand its business while offering superior customer services. Regularly, the company evaluates the store formats to provide the right structural design that meets the needs of pet customers. Today, PETsMART offers an assortment of specialized pet products and services that match the increasing ownership of dogs, cats, birdies, reptiles, and other pet animals (Acito and Williams 37).
Are any changes taking place in the macro environment that might have positive or negative impact on the industry in which your company is based? Apply the PESTEL framework to identify factors, which may be the most important in your industry. What will be the effect on your industry?
The prevailing political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal (PESTEL) factors have had varying impacts on the pet industry. Changes in political and economic environment have not had significant effects on the PETsMART market. For instance, Kortis reveals that the pet industry in America has rapidly undergone an unprecedented expansion from 25 to over 45 billion dollars within the last decade, despite the consequences of the periodic fluctuations on the American economy (11).
However, social and technological factors have favored the growth of PETsMART. As a result, the number buyers for both pets and pet products and services have notably turned out to be greater than before. A research conducted by the American Humane Association revealed that approximately 40 million households in the United States own a cat as compared to 47 million homesteads that own dogs (4).
Socially, most researchers agree that pets have increasingly become part of families in many parts of America, especially in the United States, Puerto Rico, and Canada. Interestingly, consideration of pet expenditure in the family budget has become a common phenomenon amongst pet owners. Kortis attests that some organizations have used laws that relate to health and environment to comment on the functionality of the pet company (12).
Apply the Five Forces Model to your industry. What does this model tell you about the nature of competition in the industry?
The five forces model can be applied to develop a viable strategy for PETsMART to remain competitive in the American pet industry. PETsMART Inc. exists in a competitive market that is influenced by five interdependent forces, which include the supplier power, entrant threats, buying power, substitute threats, and degree of rivalry (Dobbs 36; Aldrich 164).
The degree of rivalry that exists between PETsMART and competitor companies determines the behavior of other forces. Undoubtedly, the increased ownership of pets, particularly in America, has elevated the demand for pet products and services. As a result, numerous pet companies and stores have sprouted in PETsMART’s markets such as the United States, Puerto Rico, and Canada. These companies and stores have posed entrant threats for PETsMART Inc., prompting change of production and marketing strategies to maintain their supply power. Consequently, competition in the pet industry has tremendously increased (Dobbs 37).
Identify any strategic groups that might exist in the industry. How does the intensity of competition differ across the strategic groups that you have identified?
Furthermore, more companies that supply similar products and services have emerged in the America’s pet industry. The growing industries have placed PETsMART Inc. at a competitive edge due to the availability of similar and cheaper pet products in the market. Statistical findings have indicated that the company has lost some of its clients to the smaller pet companies that offer equivalent products and services. Although these companies may be small, their numbers and diversification of cheap products in the specialty market have stalled the demand for PETsMART’s premium products and services (Knight 18).
The company also faces significant competition from big-box merchandisers and supermarkets such as PetCo and Target, which offer a sizable range of moderately priced pet products and foods. The author reveals that the economic downturn in the past five years, especially in the United States, has led to consumer trade-down that has had profound implications on PETsMART’s market.
Despite the economic downtown, the pet industry has indicated a growth due to the establishment of small pet businesses. The ever-increasing number of pet owners necessitated the demand for pet products and services. This situation has elevated the stiffness of competition amongst the pet retail stores whilst maintaining high revenue returns for the overall industry (Dollinger 339).
How dynamic is the industry in which your company is based? Is there any evidence that the industry structure is reshaping competition, or has done so in the recent past?
Generally, the pet industry is dynamic due to the need for new products and incorporation of new technology in the pet industries. Competitiveness requires pet companies to maintain high quality products and services to meet the needs of consumers. By virtue of PETsMART’s net sales, the company is the leading specialty provider for pet services.
Nevertheless, the company faces inflationary pressures due to dramatic changes in the specialty market. Market fluctuations affect the purchasing choices of pet owners. Rego, Morgan, and Fornell note that the influence of buying decisions on the specialty market has led to decreased demand for pet products and services (14).
A research conducted by Moloughney to evaluate the market trends in the pet industry indicated that the demand for standard pet products at PETsMART exhibited a gradual decrease in the fiscal year 2013 (63). Absolutely, dynamism has reshaped the competitive nature within the pet industry. Regardless of the size of the retail stores, they have to emphasize the quality of products and services rather than the quantitative value. PETsMART is one of those companies where quality has turned out to be the key driver of customer attraction and the construction of the company’s reputation.
A good place to start with an internal firm analysis is to catalog the assets a firm has. Make a list of the firm’s tangible assets in the firm. Then, make a separate list of intangible assets that you can identify
PETsMART Inc. has a variety of tangible and intangible assets as listed below:
Tangible assets
Property Plant and Equipment
Attractive real estate locations
Talented employees
Quality Control Systems
Strong Distribution Networks
Intangible Assets
Goodwill
Inventories
Accumulated amortization
Net Receivables
Valuable Brand Name
Customer Loyalty
Now extend beyond the asset base and use the VRIO framework to identify the competitive position held by your firm. Which, if any, of these resources are helpful in sustaining the firm’s competitive advantage?
PETsMART operates under an archetypal VRIO (Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization) framework that has enabled the company maintain a competitive advantage over other pet companies in America. The company has realized the value of its products and services through its wide customer base. Pet products and services have turned out to be valuable items for the owners of pets in America. PETsMART seeks to offer the best pet supplies for its clients. PETsMART focuses on both regional and global markets that have proved the value of its products and services by the strengthening the company’s distribution network (Cardeal and Antonio 10162).
The company’s distribution framework is crucial to compete with other giant pet companies such as PetCo and Target. The company has achieved rareness through venturing into highly differentiated markets. PETsMART offers a variety of unique products and services such as personalized dog baths and “Look Great Guarantee” grooming services.
The fact that PETsMART delivers pet products and services to a sizeable number of customers in both regional and the international scale distinguishes its operations from those of competitors. As a result, PETsMART Inc. has sustained a competitive edge by developing key business relations that are vital for the company’s distribution network (Oliveira 356).
Although many pet companies and stores that offer similar products and services have sprouted in the American pet industry, PETsMART’s distribution channels are far-reaching and uniquely structured. Consequently, it has become a difficult task for competitor companies to imitate the overall structural design of PETsMART’s business framework (Cardeal and Antonio 10165). The company is organized to exploit its potential of delivering standard premium products and services to home and foreign markets. For instance, PETsMART Inc. has its headquarters at Arizona, with its branches in Canadian and Puerto Rico regions.
Identify the core competencies that are at the heart of the firm’s competitive advantage. (Remember, a firm will have only one, or at most a few, core competencies, by definition.)
PETsMART’s core competency is the treatment the company offers to its clients. The increased treatment of pets, especially family dogs and cats as family members, has compelled the company to treat pet owners as ‘pet parents’. Unlike competitor companies whose focus is on the products, PETsMART Inc. has gone beyond delivery of pet supplies to the provision of premium pet service at specialized pet areas such as Doggie Day Camps and PetHotels. This diversification of products and services has led to the establishment of a production line for premium pet goods.
The aim of the company is to create the closest relationship between pet owners and pets (Pathfinder Report 5). Many families, especially in the United States and Canada, appreciate the treatment of pet animals as members of the family. This phenomenon reveals why PETsMART Inc. has acknowledged the need to provide specialized services and premium products for pets. PETsMART’s business trend has maintained the company’s reputation regionally and internationally whilst preserving its competitive advantage in these markets.
Perform a SWOT analysis for your firm. Remember that strengths and weaknesses (S, W) are internal to the firm, and opportunities and threats (O, T) are external. Refer to Small Group Exercise 2 earlier for an enhanced version of the SWOT analysis.
In spite of the company’s reputation, it has its areas of weakness and strength. A SWOT analysis of the company reveals that it has various strengths that earn it competitive advantage in the pet market. A research conducted by Beaurline revealed that the company receives strong support from the community because of the exemplary corporate moral principles that are held by the company (23).
Furthermore, PETsMART has well-defined human resource policies that align employee professionalism with specified performance goals and objectives. PETsMART’s work environment promotes broadened experience for its employees. This strategy has created diverse workplace efforts that have developed socially responsible workers. However, some of the PETsMART’s staff members display some questionable characters that depict less motivation. Beaurline reveals a huge wage disparity amongst PETsMART’s workers (23).
Perhaps, this fact reveals the reason behind some employees’ low self-esteem at PETsMART. Moreover, some of the company’s major stores have less distribution centers that are prone to severe weather impacts, a situation that distracts accessibility, which leads to postponement of some dog services. Nevertheless, the company has many opportunities for expansion (Company History Index par.3). Statistical findings indicate that the rising number of pet owners and the need for first-hand services and products may necessitate the company to offer more holistic products than it offers.
The company has also initiated plans to promote local pet retailers as a way of fostering pet ownership in its areas of operation. Nonetheless, the company faces some potential threats from the local pet retailers who deliver pet products and service offerings at comparatively lower prices than PETsMART. Apparently, some authors have predicted the possibility of losing some workers owing to the underprivileged work conditions and unmatched benefits (Sweeney 65).
Based on the information in the annual reports or published on the firm’s website, summarize what the firm views as the reasons for its successes (either past or expected in the future). Search both quantitative and qualitative success factors provided in the report.
There are varieties of quantitative and qualitative reasons that explain the success of PETsMART Inc. One of the key factors that have led to the success of PETsMART Inc. is the ever-increasing number of pet parents in America. The rising number of pet owners has led to increased purchase of pet products and services from the company (Ferrara 22). Pet owners have expressed their willingness to spend huge sums of money on buying pet foods and as a payment for pet recreational and boarding facilities at PETsMART stores.
As a result, the company has reaped huge revenue from payments that are made for pet services and products. In addition, the love for pets has led to the development of cozy PetsHotels that offer standard premium accommodation services for family pets. The prices of the accommodation are relatively high. However, they depend on the class of the accommodation facility. Definitely, the sizeable number of pet owners has created a clear path for PETsMART’s success (Wong and Tein 201).
Does the firm seem most focused on the economic, accounting, or shareholder perspective of its competitive advantage? Give quotes or information from these sources to support your view.
PETsMART focuses most on the shareholder perspective of its competitive advantage. The company follows a corporate organizational approach that focuses on the value of the stockholder. The plan is to create a long-term shareholder value whilst maintaining worthwhile profit margins and the utmost sense of customer satisfaction.
PETsMART has moved from being a mere supplier of pets to provide highly differentiated products and services (Global Pet Food Trends 4). The need to satisfy consumers has compelled the company to stock standard premium pet products whilst maintaining first-class pet services such as grooming and daycare facilities. Therefore, development of the shareholder value is critical for the maintenance of adequate market and profitability of the business (Ferrara 81).
Many firms are now including annual corporate responsibility (CSR) reports on their websites. See whether your firm does so. If it does not, are there other indications of a triple-bottom-line approach, including social and ecological elements, in the firm’s strategies?
PETsMART includes annual corporate social responsibility (CSR) reports on its online websites. The company runs a variety of programs that encourage the protection of homeless pets. Kotler and Lee reveal that the company has adoption centers and stores where it conducts in-store campaigns to encourage customers donate for homeless pets (59). The company has posted this information on its online platform to create prior awareness before clients reach the stores for purchases.
With the assistance of the website, the company conducts wired fundraising to promote homeless pets. The company also runs online campaigns to encourage people and companies embrace environmental sustainability. The company serves as a role model by building on unpretentious means of waste management practices such as recycling of water bottles (Yokoyama 353).
Does the selected business have differentiated products or services? If so, what is the basis for this differentiation from the competition?
PETsMART Inc. has differentiated products and services. The key drive for shifting from a pet supplier to a highly differentiated provider of pet products and services was the focus on need to unify the vision of client whilst maintaining unique customer services. For PETsMART, this strategy will open new markets and development areas.
Owing to the initial fragmentation of PETsMART’s stores that led to inefficiencies in its pet services, there was an emerging desire to differentiate the company’s business from other competitor stores such as Wal-Mart, Target, and Big-Box Retailers (Rego, Morgan, and Fornell 17). Consequently, PETsMART began to offer diverse and creative pet services and products to meet the need of the growing number of “pet parents”, especially in the United States, Canadian, and Puerto Rico regions.
Does your firm have a cost-leadership position in this business? If so, can you identify which cost drivers it uses effectively to hold this position.
PETsMART has a cost leadership position to ensure the delivery of acceptable products and services to its clients. Its cost leadership strategy enables the provision of both standard and premium products at prices that create value for customers. To build on a sound cost reduction, PETsMART has established efficient-scale pet facilities through examination of sales, operational ability, and satisfaction of customers. For instance, the company’s PetsHotels provide a full-service boarding for dogs and cats. This section provides convenience for travelling clients who leave their pets under the care of PETsMART (Jackson 47).
What is your firm’s approach to the market? If it segments the market, identify the scope of competition it is using.
The business seeks constant market competitiveness through regular revision of its merchandizing approaches in an attempt to sustain a sound business-level strategy. PETsMART has a high priority for products and services that serve to satisfy the company’s clients. The company’s leaders seek effective customer relations by effectively managing strong interactions. To increase the client base, PETsMART trades products from both trademarked manufacturers and its own private label merchandise.
In addition, the aforementioned business segments form a strategic framework for conducting product and service sales. A survey that was carried out Beaurline to examine PETsMART’s business segments indicated that the consumable merchandise sales accounted for 54-percent of the company’s profits (23). The company provides specialty products such as premium pet food, treats, and litter. Alongside these products, the company trades first-class dog and cat foods. Owing to the rarity of the products, most supermarkets and big-box retailers in America do not stock premium products.
The unavailability of premium products in other stores places PETsMART at a competitive edge for rare pet products. The company also trades hard good merchandize that includes a collection of pet supplies such as collars, leashes, healthcare supplies, grooming and beauty aids, pet toys, pet beds and carriers, and pet apparels among other products (Jackson 49).
The author reveals that the hard good merchandize contributes to 33-percent of the overall revenues. In addition, PETsMART Inc. also stocks pets such as fresh-water tropical fish, birdies, reptiles, and small pets that contribute to about 3-percent of the overall revenue. The last business segment deals with the provision of pet services such as grooming, training, boarding, and day camps.
Using the answers to the preceding questions, identify which generic business strategies your firm is employing. Is the firm leveraging the appropriate value and cost drivers for the business strategy you identified? Explain why or why not.
PETsMART has adopted various generic strategies at different stages of development in an attempt to sustain consumer confidence and satisfaction (Stokes and Lomax 18). For instance, PETsMART used a differentiation strategy to distinguish the company products and services from competitor companies. This strategy necessitated the need to rebrand the name of the company from PetsMart to PETsMART to emphasize the value of products and service delivery (Creating a Smarter Pet Parent 6).
This strategy focused on satisfaction of pet parents and the provision of superior services to cherish the lives of pets. As a result, the company has realized an increasingly large number of pet parents in its area of operation. The number of pet animals that are owned by families has turned out to be the main driver of demand for both standard and premium pet products and services. Apparently, this increase in pet ownership in America has reflected an elevated consumer spending trends.
As noted in the chapter, each business strategy is context-dependent. What do you see as positives and negatives with the selected business strategy of your firm in its competitive situation?
The selected business strategy does not guarantee effective management of PETsMART’s inventory records. The business strategy does not adequately capture important aspects of retail merchandizing such as seasonality, emergency of new products, and consumer behavior. The pet industry, as well, experiences market dynamics due to the changing consumer tastes and establishment of new brands (Kuczmarski 8). However, PETsMART’s inventory records fail to determine precise selection of merchandise and future demand for pet products and services.
In Chapter 3, we identified strategic groups in the industry relevant to your firm. Review the firms listed in the same strategic group as your selected firm. See if there is a similarity with the generic business strategy used by each. In most strategic groups, there will be market and some strategy similarities across the firms.
PETsMART’s operates under a similar generic business strategy with most pet companies in America such as PetCo and Target. These firms offer nearly the same products and services as PETsMART. However, PETsMART’s differentiated market makes it difficult for the firms to match its competitive edge. Statistical findings have indicated that the pet industry in America is booming. Pet babying has become a common phenomenon amongst pet parents across the entire pet industry (Brennan 3).
Most companies have evolved from the provision of modest pet food and grooming services to delivery of inventive and specialized superior products and services. The provision of first-class products and services is a priority need for consumer satisfaction has become the norm for giant companies such as PetCo, Target, and Big-box Stores. The similarity between these pet companies has stiffened the competition gap in the pet markets.
What suggestions do you have to improve the firm’s business strategy and strategic position?
The business should heighten its focus on the development of stronger customer strategies by creating personalized interconnections. PETsMART can personalize consumer relationships by incorporating cell phone technology in areas such as pet food selection and stocktaking. The company should encourage customers to order online and/or offer door-to-door product and service delivery where applicable (Lee 350). Additionally, PETsMART should ensure the adoption of apt business strategies that account for market dynamics, the changing consumer tastes, and the emergence of new pet products and services (Rothaermel 302).
Where is your firm’s industry on the life cycle as shown in Exhibit 7.2?
According to the Company History Index, the pet industry has reached the mature stage in its lifecycle (par. 3). However, the industry’s performance does not mean that it has stagnated in growth. In fact, Beaurline reveals that the industry has the possibility of growing at an average rate of over 3-percent in the next decade (23). Nevertheless, the growth of the pet industry is at the same level as that of the overall American economy.
What is the dominant technological design of the industry in which your firm is primarily located?
Computerized Point-Of-Sale (POS) technology has dominated the pet industry. Pet parents have increasingly shown great compassion for their pets by providing them with services that generate the best experience for them. The POS technology has incredibly increased the rate of production due to value-added and efficient processing of information that has reduced the number of human-related mistakes during transactions in pet firms such as PETsMART Inc. (Dollinger 338).
Did this dominant technological design develop quickly or more slowly? Can you identify what influenced the speed of diffusion?
Dollinger reveals the computerized Point-Of-Sale technology has developed slowly in the pet industry (339). The pet industry has exhibited a sluggish rate of adopting technology for many years. Despite the limited advances in technology, the industry has experienced various improvements in some technologies such as computerized cash registers, bar code scanning, and inventory records over the last decade. The prevailing competition in the pet industry and the desire for quality pet pampering have forced pet firms such as PETsMART to adopt the technology to improve service delivery to pet parents.
Where is the dominant technology on the S-curve in your focal industry? What alternative technologies can present a paradigm shift as shown in Exhibit 7.10?
The Point-Of-Sale technology has advanced to the inflection point on the S-curve. The diffusion rate for the POS technology has become relatively high in the pet industry. With the installation of numerous Point-Of-Sale terminals in strategic locations, many pet companies, including PETsMART Inc., have adopted the technology to improve customer services. The robust sales system has ensured better product placement in pet stores. Besides, it has incredibly incentivized the sales personnel in the entire industry. An alternative technology to the POS technology is the use computerized card-based financial systems to enable pet clients to process transactions at strategic places.
What is the role of standards in the focal industry?
The role of maintaining standards in the pet industry is to guarantee the safety of pets by ensuring that the production process uses proper ingredients that have expressive nutritional functions in the pet food. Standards also ensure general care of pet animals whilst boosting the prevention of special infection risks that accompany human-animal interactions. PETsMART has maintained reputable brands by delivering quality products to meet the health demands of pets across its regions of operation.
From a marketing perspective, what attributes describe the current major customer segment for your firm?
PETsMART’s customers have proven their loyalty to the company by their repeated acquisition of pet products and services. However, the company has strived to build customer loyalty through recruitment of experienced workers who guarantee attractive product presentation and effective quality control. A study conducted by the American Humane Association indicated that PETsMART’s clientele find the totality of the experience gained from the pet store (par. 4). The firm has focused on providing its customers with first-hand experience by offering high-end products and services.
Are the intellectual property rights important for your firm? Can you find the strategies the firm is implementing to protect its proprietary?
Cardeal and Antonio posit that PETsMART Inc. values intellectual property rights since they are vital for its merchandizing and marketing strategies (10164). As a result, the company has implemented strategies to safeguard its proprietary position in the pet industry. The company’s intellectual properties include a variety of service marks and trademarks. The company has registered PetSmart®, PetPerks®, PetSmart.com®, PetSmart PetsHotel®, All You Need For The Life Of Your Pet®, and Where Pets Are Family® among others with the United States Patent and Trademark office (USPTO) in an attempt to safeguard its intellectual property.
Draw out the vertical value chain for your firm’s industry. List the major firms in each important activity along the chain (see Exhibits 8.4 and 8.5 as examples). Note that a firm’s name may appear multiple times in the value chain. This indicates some level of vertical integration by the firm. If your firm is in many industries (e.g., GE), then choose the dominant industry or the one that intrigues you most and use only that one for this analysis.
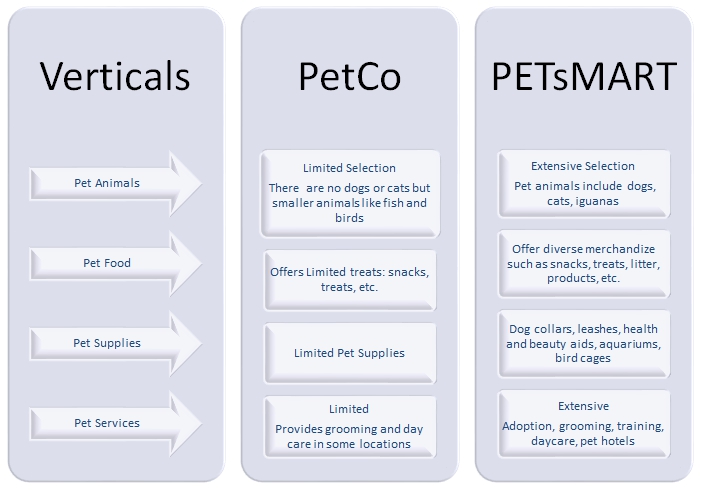
Is your firm highly vertically integrated? If yes, does it also employ taper integration?
An analysis of the PETsMART pet firm indicates that the firm is not vertically integrated since it purchases cheap pet products from production companies. Buying or running individual production companies might be expensive for PETsMART since the firm will require restructuring and acquisition of production knowledge and techniques that may result in the delivery of substandard products. The firm’s major focus is on the provision of services to pets. This strategy has created a source of recurring revenue as repeat customers bring back their pet animals for more services.
Are any of the vertical value chain operations off-shored? If so, list some of the pros and cons of having this part of the value chain outside the home country.
PETsMART has numerous vertical chain operations off-shored. Despite having its main stores at Phoenix, the firm runs various stores in other localities in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico (Lee 368). The author posits that the company has achieved numerous pros from its off-shored investments such as entry into new and international markets.
To a greater advantage, the company has experienced expansion in offshore markets owing to the delivery of differentiated merchandize that has attracted many pet clients. Nevertheless, PETsMART has also experienced significant competition from smaller chain stores that offer similar products at favorable discounts. This situation has hindered the realization of its anticipated potential in the international arena.
Use the preceding vertical value chain to identify the corporate strategy of the firm. In other words, where within the industry has the firm chosen to compete? Based on where it competes, describe what you know see as its corporate strategy?
The firm has committed its efforts to compete in the pet industry by offering highly differentiated products and services. In addition, the firm offers competitive prices on products and services to compete with retailers such as Wal-Mart and Target that offer considerable discounts on similar products. For instance, Oliveira posits that PETsMART’s prices are approximately 9-percent higher in relation to those offered by discount retailers (357). However, in average, PETsMART’s prices are13-percent less the prices offered in grocery stores.
The firm has strived to become the lowest price provider in the pet industry by ensuring regular price evaluation in the entire pet industry. In addition, the firm’s vast range of services such as training, grooming, veterinary care, doggie day camps, and overnight boarding among other services has set a strong customer loyalty whilst increasing the competition gap for other pet companies. The firm’s wide range of products and services culminates into its corporate strategy to be the preferred provider for the lifetime need for pets (PETsMART 89).
In Module 2, you were asked to identify the mission and major goals for your selected company. Go back to that information now and compare the mission and goals to what you have found as the corporate strategy. Are the mission, goals, and corporate strategy in alignment? Do you see any holes or conflicts among these three elements? Can you relate the performance of the firm to this finding in any way? (If all three are consisted, is this a well-performing unit?) If there is a conflict between the corporate strategy and the mission, does this lack of alignment contribute to performance problem? Why or why not?
PETsMART’s has aligned its mission, goals, and corporate strategies in a manner that has driven the company to achieve effectiveness and consistent client experiences (Ferrara 65). The firm’s corporate strategy has enhanced the company’s operating excellence. The firm has increased its shares in the existing multi-store markets by establishing more multi-stores as well as single-stores in it areas of operation. This strategy has amplified PETsMART’s operating efficiency.
Moreover, the alignment of mission, goals, and the corporate strategy has improved the company’s economies of scale in business segments such as supply systems, information channels, procurement, store processes, and marketing (Ferrara 66). Generally, PETsMART has worked towards minimization of possible conflicts that may arise due to misalignment of its mission and goals by devising a sound corporate strategy. For instance, in 2010, PETsMART planned to slow its development of stores by about 20-percent in an attempt to balance future investment whilst getting the most out of quality customer delivery.
Has your firm participated in any mergers or acquisitions in the past three years? What was the nature of these actions? Did they result in a consolidation of competitors?
PETsMART has not participated in mergers and acquisitions in the last three years. Although the management is aware that the firm’s shareholders will benefit highly from mergers and acquisitions, especially with a large competitor such as PetCo, PETsMART has failed severally to sign into merger and acquisition deals. Jackson predicts that the company would have elevated its overall number of chain stores across the American markets if it had signed into mergers and acquisitions with its major competitors (48).
Research what strategic alliances your firm has entered in the past three years. If there are several of these, choose the three you identify as the most important for further analysis. Based on company press releases and business journal reports for each alliance, what do you find to be the main reason the firm entered these alliances?
PETsMART has engaged in several strategic alliances in the last three years that have enabled it gain a competitive advantage over other pet companies such as PetCo (Alldredge, Eastman, Lynch, Sharma, and Sivaeva 7). In 2011, PETsMART Charities entered an agreement with Humane Alliance to ensure the availability of affordable neuter services in an attempt to regulate the number of pets across the United States.
In addition, PETsMART collaborated with Banfield alliance to increase its hospital services for improved health pets in its power stores. Furthermore, PETsMART Charities teamed up with Boulder Human Alliance in July 2011 to open more pet shelters in Westminster in an attempt to increase the number of pet homes and/or control pet overpopulation in the area.
Do you think each of the three alliances achieves the original intent, and therefore is successful? Why or why not?
Each of the above-mentioned alliances has achieved its original intent of collaborating with PETsMART. For instance, Boulder Humane Alliance has dramatically enabled PETsMART Charities reduce dog overpopulation by transferring adoptable dogs and puppies from overcrowded shelters to their new homes at Boulder Humane.
A recent study conducted by Global Pet Food Trends indicated that the alliance between PETsMART and Boulder Humane Alliance saved approximately 55,000 dogs and puppies from being euthanized (4). Banfield Alliance had strategically located pet hospitals and veterinary clinics in PETsMART stores and around the neighborhoods where pet parents could access pet health services easily.
Does your firm have an identifiable alliance management organization? Can you find any evidence that this organization improves the likelihood of success for these alliances? What responsibilities does this alliance-management organization have in your firm?
Presently, PETsMART does not have an alliance management organization. However, the company has deployed strong teams in its operational areas that make sound strategic decisions that pertain to purchasing, store location, and engagement in alliances. The firm’s teams maintain strong corporate relationships and enhance sustainable enterprises within PETsMART’s areas of action (PETsMART 89).
The enhancement of strong corporate relationships has improved the competitive landscape for PETsMART during the last five years. Furthermore, the firm has increased its sensitivity to protect the company from revenue volatility by making sound investment decisions that can affect long-term investment plans. As a result, its business leaders prefer management of their own decisions rather than engaging in alliance management organizations.
Go to LinkedIn (www.linkedin.com) and see what executive officers or groups your firm may have set up on the professional networking site. Next, look to see if the firm has a “fan page” on Facebook. Is there also a “detractor’s page” for your firm? How would you assess your firm’s use of web networks and social media for its business?
Numerous profiles of PETsMART’s associates on LinkedIn have widened the size of the company’s professional network. Moreover, the company has also created fan pages and advertisement banners on Facebook and several other social sites such as Twitter. Generally, the company has developed a number of conventions and protocols around web services and social media to market its pet business.
The firm has exclusively implemented the use of web services and social media by distributing adequate and reliable information about its merchandise on the online platforms. According to the Global Pet Food Trends, PETsMART has created also created an events page on Facebook where pet clients can acquire information about the firm’s programs. The company has a plan to start a question-answer forum with its clients on social media to improve its connections with clients.
Is your company varying its product or service to adapt to differences in countries? Is the marketing approach different among the involved nations? Should it be?
According to the Global Pet Food Trends, PETsMART has proved its active involvement in international activities through the maintenance of membership and establishment of various office branches in international localities (par. 4). Conventionally, the international trade activities of PETsMART remain accounted for only at the manufacturing level. A recent report published by the American Humane Association indicated that pet parents in both local and international market zones have increasingly heightened the care for their pet animals (5).
As a result, PETsMART has remained on the forefront to offer tailored pet diets that have created a potential niche market, especially for consumers who seek vigorous diets for obese pets. Sweeney confirms that PETsMART’s marketing approach is varied amongst its areas of operation (68). The author posits that the firm’s extensive production has out powered other firms that offer similar pet products and services. Moreover, the fact that the firm’s stores serve as one-stop-shops for localized products make PETsMART significantly different from smaller firms that offer considerably a narrow range of merchandize.
Is your firm working internationally to access larger markets? To gain low-cost input factors? To develop new competencies? To develop new competencies? Is its approach in all three areas appropriate?
Jackson reveals that PETsMART has worked towards accessing larger markets in the international arena (28). The firm has established numerous pet infrastructures in a variety of strategic locations in countries such as the United States, Puerto Rico, and Canada among other countries in North America to venture into the international market. The author confirms that PETsMART possesses and operates approximately 1200 pet stores in the United States and Canada only.
Throughout its regions of operation, PETsMART has rolled out PetsHotels in selected PETsMART stores that arrange for overnight lodging services for pets, especially for travelling pet parents. The firm has established a measurement framework that defines a fair value with regard to the nature and type of input in use. The purpose of this framework on the international markets is to capitalize on the utilization of low-cost inputs whilst lessening the use of high-cost inputs (Jackson 29).
Despite the increasing fragmentation and encroachment of the pet market by big-box stores, warehouse clubs, and supermarkets, PETsMART has developed and maintained a high competency both in regional, national, and international markets by ensuring the delivery of highly differentiated pet products and services. Nonetheless, the firm’s participation in global pet activities has further strengthened its brands. The situation has earned it a competitive advantage over other pet companies in the international arena (Alldredge, Eastman, Lynch, Sharma, and Sivaeva 8).
Which of the four global strategies is the firm using? Is this the best strategy for it to use? Why or why not? (Exhibit 10.7 provides a summary of the four global strategies).
PETsMART uses the localization strategy to maximize market responsiveness to pet products and services (Aldrich 165). The author posits that the company has strived to meet special needs of its pet clients in different countries by adopting the localization strategy that has resulted in the delivery of highly differentiated products and services in both local and international markets.
The localization strategy seems the best for PETsMART since the firm’s pet customers have appreciated the availability of different products under one-stop-shops. Aldrich reveals that the firm has realized an increasing number of clients ever since the establishment of additional one-stop-shops in areas such as the United States and Canada (169).
Works Cited
Acito, Frank, and Theresa Williams. Positioning the Retail Firm for Future Value: Recognizing and Measuring Intangible Assets. 2014.
Aldrich, Greg. Rendered Products In Pet Food. 2014. Web.
Alldredge, Kari, Jayne Eastman, Brian Lynch, Alok Sharma, and Tanya Sivaeva. Value management beyond pricing and promotions. 2014.
American Humane Association. Keeping Pets (Dogs and Cats) in Homes: A Three-Phase Retention Study, 2013.
Beaurline, Andrew. “Guest Article: Outlook for Pet Industry M&A Strong.” Mergers & Acquisitions Report 26.8(2013): 23. Print.
Brennan, Andy. Lucky dog: Pet owners will invest in premium products as disposable income rises, 2014.
Cardeal, Nuno, and Nelson Antonio. “Valuable, rare, inimitable resources and organization (VRIO) resources or valuable, rare, inimitable resources (VRI) capabilities: What leads to competitive advantage?” African Journal of Business Management 6.37(2012): 10159-70. Print.
Company History Index: PETsMART, Inc. – Company Profile, Information, Business Description, History, Background Information on PETsMART, Inc. Reference for Business, 2014.
Creating a Smarter Pet Parent: PETsMART Inc. 2006 Annual Report. 2014. Web.
Dollinger, Mar. Entrepreneurship: Strategies and Resources. Web.
Dobbs, Michael. “Guidelines for applying Porter’s five forces framework: a set of industry analysis templates.” Competitiveness Review 24.1(2014): 32-45. Print.
Ferrara, Susan. “PETsMART Inc.” The Value Line Investment Survey (Part 3 – Ratings & Reports) 69.37(2014): 21-85. Print.
Global Pet Food Trends. Pathfinder Report 2010, 2012.
Jackson, Stuart. “Grow your business by offering less – and more “Grow your business by offering less – and more.” Journal of Business Strategy 29.5(2008): 47-49. Print.
Kotler, Philip, and Nancy Lee. Corporate Social Responsibility: Doing the Most Good for Your Company and Your Cause. 2014.
Kuczmarski, Thomas. “What is innovation? The art of welcoming risk”, Journal of Consumer Marketing 13.5(1996): 7-11. Print.
Knight, Molly. “Doggy docs and dorms.” Shopping Centers Today 29.7(2008): 17-18. Print.
Kortis, Bryan. Community TNR: Making an Impact on Free-roaming Cats.
La Monica, Paul. “Cashing In on the Consumer Rebound.” Money 42.2(2013): 47. Print.
Lee, Chung-Shing. “An analytical framework for evaluating e-commerce business models and strategies.” Internet Research 11.4(2001): 349-359. Print.
Mules, Rachel. “The Pet Industry and ‘Petrepreneurship.” BusiDate 22.1(2014): 5-7. Print.
Moloughney, Sean. “Pet Nutrition: Best in Show.” Nutraceuticals World 17.2(2014): 61-64. Print.
Oliveira, Sarah. Fresh Pet Food in North America, 2014. Web..
PETsMART Inc.: Old Dog, New Tricks. UBS Investment Research.
PETsMART: Promotions Opportunity Analysis.
Rego, Lopo, Neil Morgan, and Claes Fornell. “Reexamining the Market Share-Customer Satisfaction Relationship.” Journal of Marketing 77.5(2013): 1-20. Print.
Rothaermel, Frank. Strategic Management: Concepts, Georgia: McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2012. Print.
Stokes, David, and Wendy Lomax. Marketing, A Brief Introduction.
Sweeney, Daniel. “Improving the Profitability of Retail Merchandising Decisions.” Journal of Marketing 37.1(1973): 60-68. Print.
Wong, Bernard, and David Tein. Critical Success Factors for ERP Projects.
Yokoyama, Keiko. The Perspective of Social Business for CSR Strategy. 2014. Web.