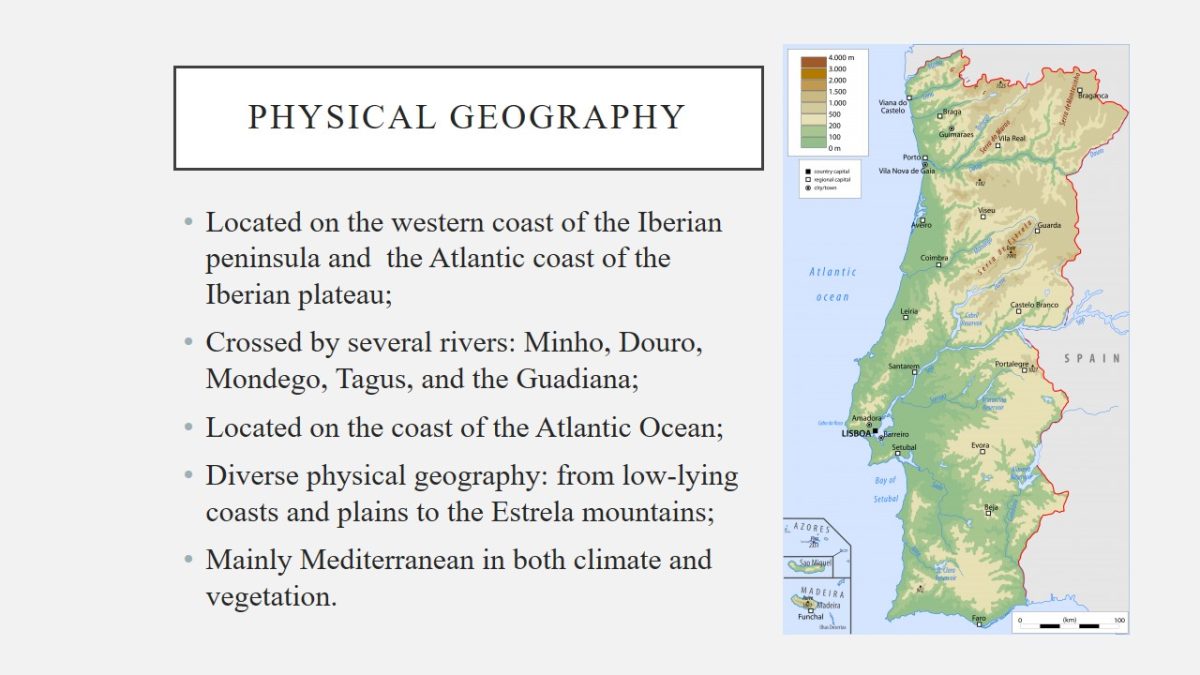
Physical geography
- Located on the western coast of the Iberian peninsula and the Atlantic coast of the Iberian plateau;
- Crossed by several rivers: Minho, Douro, Mondego, Tagus, and the Guadiana;
- Located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean;
- Diverse physical geography: from low-lying coasts and plains to the Estrela mountains;
- Mainly Mediterranean in both climate and vegetation.
Portugal is a European country located on the western coast of the Iberian peninsula and the Atlantic coast of the Iberian plateau. It is crossed by several rivers, such as Minho, Douro, Mondego, Tagus, and the Guadiana. The country is located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean. It has diverse physical geography: from low-lying coasts and plains to the Estrela mountains. In terms of the climate, Portugal is mainly Mediterranean in both climate and vegetation.
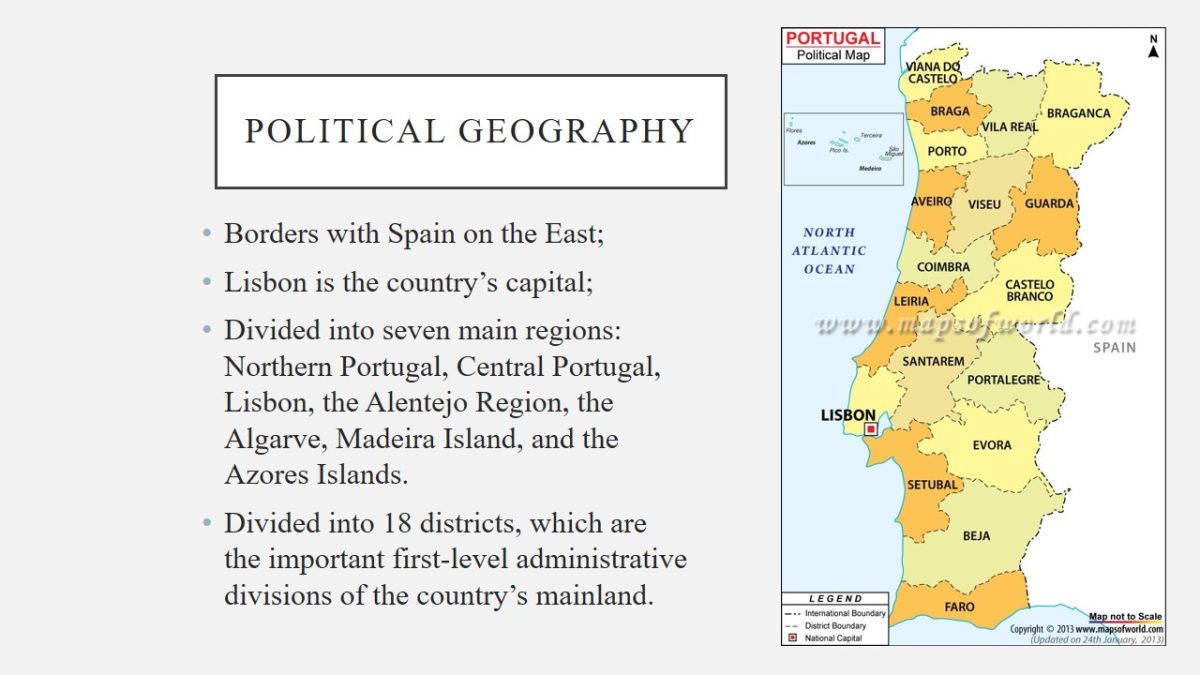
Political geography
- Borders with Spain on the East;
- Lisbon is the country’s capital;
- Divided into seven main regions: Northern Portugal, Central Portugal, Lisbon, the Alentejo Region, the Algarve, Madeira Island, and the Azores Islands.
- Divided into 18 districts, which are the important first-level administrative divisions of the country’s mainland.
Portugal borders with Spain on the East of the country. Lisbon is the country’s capital. The country is divided into seven main regions, which include Northern Portugal, Central Portugal, Lisbon, the Alentejo Region, the Algarve, Madeira Island, and the Azores Islands. It is also divided into 18 districts, which are the important first-level administrative divisions of the country’s mainland.
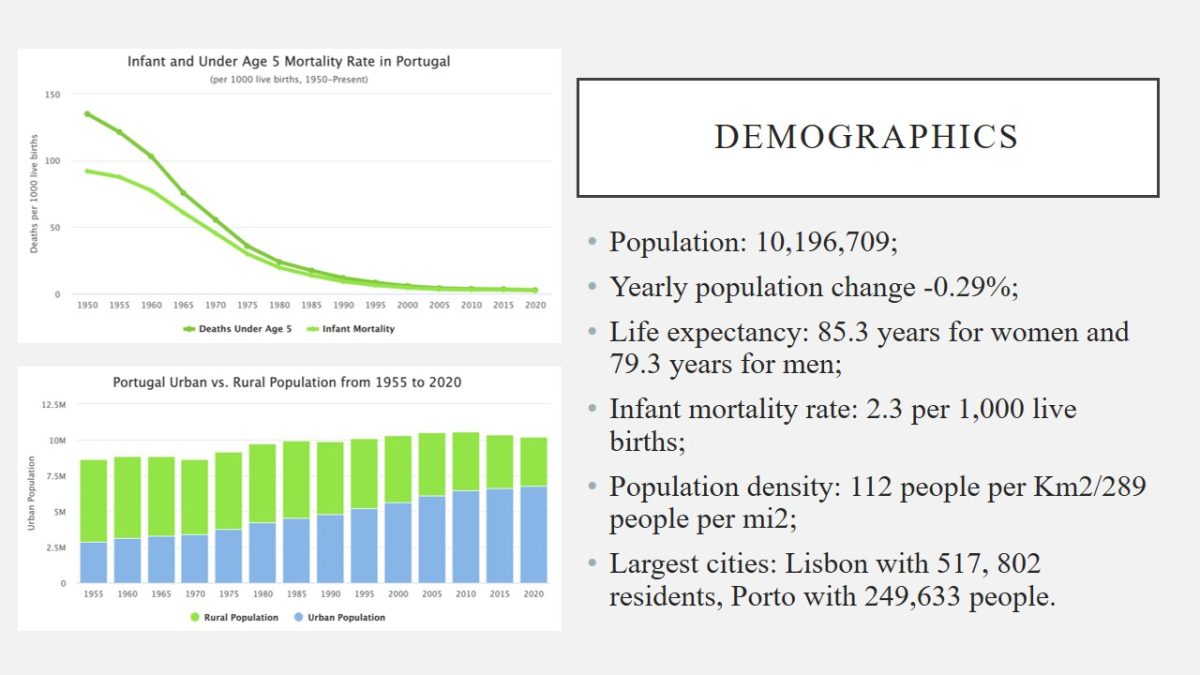
Demographics
- Population: 10,196,709;
- Yearly population change -0.29%;
- Life expectancy: 85.3 years for women and 79.3 years for men;
- Infant mortality rate: 2.3 per 1,000 live births;
- Population density: 112 people per Km2/289 people per mi2;
- Largest cities: Lisbon with 517, 802 residents, Porto with 249,633 people.
The population of Portugal is 10,196,709 people, with its yearly population change equal to -0.29%. The life expectancy of the country’s citizens is 85.3 years for women and 79.3 years for men. The infant mortality rate is 2.3 per 1,000 live births. The population density is 112 people per Km2, which is equal to 289 people per mi2. The largest cities are Lisbon with 517, 802 residents, and Porto with 249,633 residents.
Environmental Issues
- Water pollution in the country’s urban centers;
- Main pollutants include carbon emissions, sulfur dioxides, and nitrous oxide;
- The water supply is at risk from pollutants from cellulose and oil industries;
- The wildlife and agricultural activities are threatened by land desertification and erosion;
- The endangered species of mammals, birds, and mammals that exist in the country.
There are several environmental challenges that should be mentioned. The country is challenged by water pollution in its urban centers. Primary pollutants include carbon emissions, sulfur dioxides, and nitrous oxide. Because of this, the water supply is at risk from contaminants from cellulose and oil industries. Poor water quality affects wildlife and agricultural activities, which are threatened by land desertification and erosion. Also, it should be mentioned that there are endangered species of mammals, birds, and plants that exist in the country.

Challenges
- The nation is challenged by the quality of justice in the country;
- Bureaucracy is a concerning issue because it affects the way in which business is being carried out in the country;
- Challenges associated with the foreign policy, such as Brexit, the situation in Spain, and the inflow of refugees from another countries;
- Need to accelerate the digitalization of public institutions to streamline processes that still rely on traditional means;
- Portuguese citizens remain one of the oldest populations in the world with a shrinking labor force and low productivity.
There are several challenges that should be noted. First, Portugal is challenged by the quality of justice in the country. Second, bureaucracy remains a concerning issue because it affects the way in which business is being carried out in the country. Third, there are external issues associated with foreign policy, such as Brexit, the situation in Spain, and the inflow of refugees from other countries. The younger population has indicated a need to accelerate the digitalization of public institutions to streamline processes that still rely on traditional means. Finally, Portuguese citizens remain one of the oldest populations in the world, with a shrinking labor force and low productivity.

Snapshot Into the Future
- Brexit leads to Portugal receiving 7% less funds for 2021-2027.
- The country will be battling with disparities between regions, which limit social and economic productivity;
- There is a potential for facilitating industrial innovation;
- Portugal will be working toward having a greener approach to energy, circular economy, and climate change adaptations;
- Regional mobility will be the goal for creating a more connected Europe through the exchange of experiences and innovation.
