Principles of Business Excellence
Business excellence is not a new phenomenon in the business world. The concept is not unique to businesses. Business excellence is an aspect of the operations of many organizations. It stems from the desire to stand out from crowded marketplaces and the need to meet stakeholder expectations. Several excellence models exist in the modern world. This paper examines the excellence model used by the Prime Healthcare Organization. In particular, the paper examines the impact of the Dubai Quality Award to the operations of Prime Healthcare Group.
The first section of the paper contains an overview of Prime Healthcare Group. The section looks at its scope of operations, and the excellence awards attained by the company. The second section examines the Dubai Quality Award. This section deals with the content of the model, its processes, and its management. The third section of the paper deals with a critical examination of the excellence model. This section focuses on the evaluation of the perceived strengths and weaknesses of the model. The last section deals with the benefits of the model for the organization. In particular, the section looks at the benefits of the model to the business processes, service delivery, profitability, and brand recognition of the organization.
Overview of the Prime Healthcare Group
The Prime Healthcare Group is one of the largest healthcare providers in the UAE. Prime Healthcare Group prides itself in the provision of high quality healthcare for UAE residents. The company has over 650 staff members across all cadres (Prime Healthcare Group 2013). The organization also attracts patients from other countries who are seeking for medical attention in the UAE.
Medical Centres
The Prime Healthcare Group has several medical facilities located in different parts of the UAE. The locations of the health centres operated by the organization are in the table below.
Table 1: Locations of health centres operated by the Prime Healthcare Group.
Services
The operational model of the Prime Healthcare Group consists of five main service outlets. First, the organization plans to start operating the Prime Hospital. The Prime Hospital is an inpatient facility due to open soon. The Prime Hospital will have ultramodern health services in line with the vision of the UAE to become an international healthcare destination (The Oxford Business Group 2008). The second aspect of the organization is Medical Centres. The organization currently operates eight medical centres spread throughout the UAE. The medical centres are the main service delivery points for the organization. These medical centres provide a wide range of inpatient and outpatient services for patients.
Thirdly, the organization runs a diagnostic centre dedicated to the management of medical diagnosis. The centre operates independently. It handles clients referred from the health centres owned by the Prime Healthcare Group, and clients referred by other health facilities. The diagnostics centre offers a wide range of diagnostic services. These services include ultrasound, CT scans, and mammography, among others (Premier Diagnostic Centre 2013). The centre boasts of the best diagnostic services on the Diera side of Dubai (Premier Diagnostic Centre 2013). The centre hopes to attract patients who previously went to India, Thailand, and Europe for diagnostic services.
The Prime Healthcare Group also offers pharmaceutical services in the UAE. The group currently operates six pharmacies in various parts of the UAE. The pharmacies are located in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, and Sharjah. The pharmacies operated by the Prime Healthcare Group have relations with almost all medical insurance companies in the UAE (Prime Healthcare Group 2013). This means that patients with health insurance in the UAE can fill their prescriptions at any of these pharmacies. In addition to the provision of drugs, the pharmacies also provide first aid kits to many universities and corporate organizations.
The Prime Healthcare Group also offers a unique set of healthcare services to corporate clients. These services include the following. First, the company runs up to twenty on site clinics for major clients. On-site clinics are temporary healthcare access points for companies that are running large projects in off site locations. For instance, the construction of a sky crapper means that many people work in a small area fraught with risks. Such companies approach the Prime Healthcare Group and work out the modalities of setting up an on-site clinic. Another variation of this is the operation of corporate clinics. Corporate clinics are set up to serve the employees of a specific organization.
This means that the employees of those organizations do not need to spend time travelling to hospital. The clinics offer them outpatient services. This reduces the time spent on sick off, and increases the productivity of the companies. The current list of companies housing corporate clinics operated by the Prime Healthcare Group include Intercontinental Hotel, Al Futtain Group, and Emiril Dubai, among others.
Awards
The Prime Healthcare Group boasts of several awards and recognitions. The most notable among them are the Dubai Quality Appreciation Award of 2007 and 2012, Sharjar Economic excellence Award of 2010, and the ISO 15189 & ISO 9001-2008 certifications. These awards and recognitions show that the Dubai Healthcare Group is a reputable company, and is a good case study about the principles of Business Excellence.
Model Content Structure as Applied by the Organization
The main interest of this project is the application of the Dubai Quality Award to the operations of Prime Healthcare Group. This section deals with the content, processes, and management of the model.
Description of the Model
The Department of Economic Development is the custodian of the Dubai Quality Award. This award is the culmination of a quality management process that seeks to identify deserving organizations in Dubai. This award aims at promoting excellence in business as a means of boosting the overall economic development of the country. The Dubai Quality Award provides all the entrants with a road map for achieving excellence in their operations. The goal of the awards is to encourage all entrants to use high standards in their business. In this regard, all the entrants do not just stand a chance of winning the overall awards, but they also find a roadmap towards achieving business excellence in their operations.
An import aspect of the Dubai Quality Award is that it is not a targeted process, or a specific model. The Dubai Quality Award brings together many excellence initiatives. In this regard, any excellence model that shares the quality aspirations of the Dubai Quality Award can find space and inclusion in the Dubai Quality Award. In other words, the Dubai Quality Award is essentially a quality framework, rather than a specific model of business excellence. It is also important to note that the Dubai Quality Award uses the Excellence Model of the European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) (Government of Dubai 2012).
Content of the model
The content of the Dubai Quality Award is similar to the content of EFQM. Therefore, an in-depth examination of EFQM will give a good indication of the content of the Dubai Quality Award. EFQM has a set of three integrated components (EFQM 2013). The three components are “The Fundamental Concepts of Excellence, the Criteria, and the RADAR” (EFQM 2013).
EFQM has eight Fundamental Concepts of Excellence as outlined below in Table 2:
Table 2: EFQM Fundamental Concepts of Excellence (EFQM 2013).
The second component of EFQM is “The Criteria” (EFQM 2013). The EFQM model divides criteria into two main parts. The first part covers the enablers of excellence. The specific elements that constitute the “enablers” in the EFQM model are organizational leadership, people, strategy, partnerships & resources, and processes, products & services (EFQM 2013). The second part consists of “results” (EFQM 2013). In this regard, an excellent company should produce outstanding people results, customer results, society results, and business results. Figure 1 below provides a summary of EFQM’s Criteria.
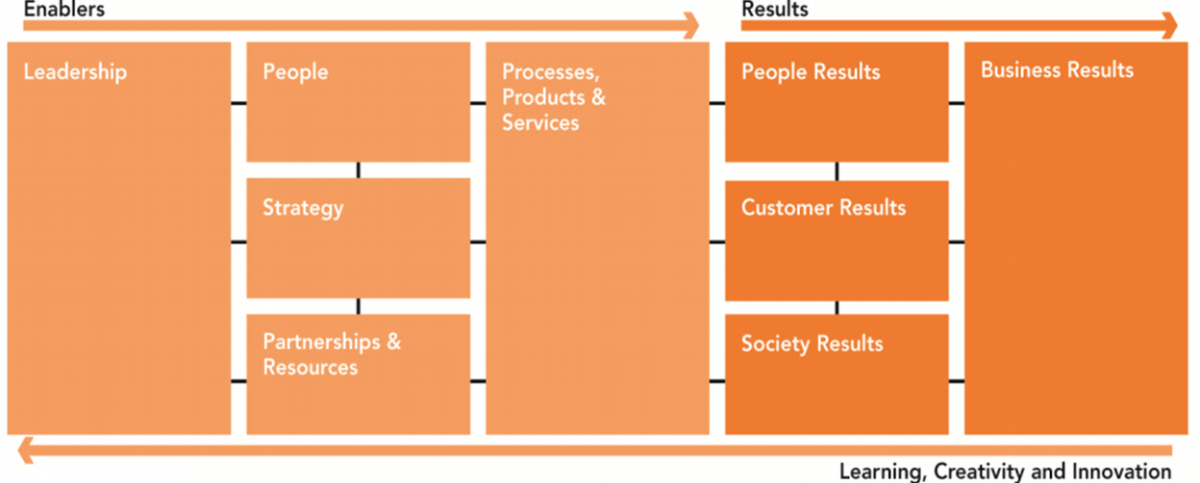
The third main component of EFQM’s model is the RADAR. RADAR is an acronym that covers the critical areas of evaluation for companies seeking recognition for business excellence as shown in the table below.
Table 4: RADAR.
Structure of the Model
In the context of the Dubai Quality Award, the main processes used in its management are as follows. The Ministry of Economic Development administers the award. Companies that intend to win the award, send in their application to the organizers. The organisers then select the companies that stand a chance to win the award after evaluations the applications. This means that the initial step towards the winning of the Dubai Quality Award is filling the application form.
After the initial assessment of the forms filled by the applicants, the organisers send assessors to all companies shortlisted after the scrutiny of the applications. The assessors visit each form to check how well the company is applying the EFQM model in their operations. The assessors look at management practice, financial performance, and consumers’ satisfaction.
After the assessment of the companies, the assessors hand in their reports to the Dubai Quality Award Supreme Council. The supreme council evaluates all entries and then picks the winner of the award. The decision of the Supreme Council is final in all matter relating to the Dubai Quality Award
Critical Examination of the Excellence Model
While this paper focuses on the Dubai Quality Award, it is impossible to carry out a critical evaluation of the award without reviewing EFQM, which is its base model. The criticisms given in this section do not distinguish between the two models. In all fairness, there is a large amount of support and criticism for excellence awards. This section will analyse the perceived strengths and weakness of the Dubai Quality Award
Strengths of the Dubai Quality Award
The Dubai Quality Award model has five main strengths. First, the Dubai Quality Award is encouraging businesses in the region to adopt a culture of excellence. The high profile nature of the award makes it attractive for businesses based on the visibility the award gives a winning business. Also, the application process forces managers to think about excellence in their business practices. In this regard, the motivating factor for companies seeking recognition in the Dubai Quality Award may not be a desire to become an excellent company but to get publicity for its efforts (Porter & Tanner 2012).
However, since the business must meet the high standards set by the award management team, they still end up having excellent practices. This means that the Dubai Quality Award is achieving its goal of improving business excellence but may not be changing the attitudes towards excellence directly. The Ministry of Economic Development will need to sustain the award for some time to come until business excellence becomes a norm in Dubai.
The second strength of the Dubai Quality Award is its reliance on EFQM. EFQM is a well-known excellence model across the world. This gives the Dubai Quality Award the international stature befitting a country that is working to become an investment destination. The reliance on EFQM as a quality model is good for the Dubai Quality Award because of its impact on the brand strength of the Dubai Quality Award. Investors can trust that a company winning the Dubai Quality Award is playing in the same league as the European companies with awards from EFQM. On the other hand, the Dubai Quality Award is at risk of losing its reputation should something go wrong in EFQM. This means that the Dubai Quality Award can experience all the risks associated with EFQM.
The third strength of the Dubai Quality Award is that the process is very rigorous. The first part of the process is a self-assessment of the company, by filling in forms designed to show the quality standards used in the company. The self-assessment forms form the basis for qualification for the next round. This round involves examinations of the business practices of the company by assessors. The assessors re-examine the assertions made by each company, and then use their findings to recommend winners of the Award. The rigour in the process ensures that only deserving companies win the award.
The Supreme Council also plays a part in the final decision on which company should win the final award. Critiques of the award point out that some elements of the award do not measure quality (Kanji 2012). In this sense, the rigour culminates in wasted efforts because the quality elements in each of the metrics used in the award are few. In this regard, the model is weaker than Total Quality Management (TQM), as a quality improvement program. There is some merit in this assertion because the Dubai Quality Award seems aimed at the processes, in addition to results. In this case, the results may not reflect the quality standards of an organization, but can reflect the operational efficiency of the organization. Further thought on this matter reveals that there is a need for a strict definition of quality in regards to the Dubai Quality Award.
The fourth benefit of the Dubai Quality Award is that it is increasing the stature of Dubai as a business destination. The decision to base the award on EFQM gives the Dubai Quality Award an international stature. This means that it is easy for an investor to know what to expect from a company that won the Dubai Quality Award. In a certain sense, an investor already familiar with EFQM does not need to reacquaint himself with the Dubai Quality Award. In this regard, the Dubai Quality Award is very beneficial to Dubai.
On the other hand, there is a need for the Dubai Quality Award to pursue a closer working relationship with EFQM to further increase the confidence of investors. A keen investor will still ask whether the holder of the European Quality Award is equivalent to the Winner of the Dubai Quality Award. The European Quality Award is the highest and most prestigious award issued by EFQM (Verweire & Berghe 2004).
The final benefit presented in this work regarding the Dubai Quality Award is that the process gives benefits to the participating companies, regardless of whether they win the award. The companies must fill in a self-assessment form for deliberation by assessors. In the process, the companies establish an internal mechanism for self-assessment leading to the identification of opportunities for improving their operations. When the assessors visit the company for evaluation, they also provide further insights into how the company can improve on its operations. This shows that the companies that apply for the Dubai Quality Award still benefit from the process regardless of whether they emerge as winners.
However, such companies must have an inherent desire to improve the quality of their operations to benefit from the process. This means that some companies do not benefit from the process at all. Quality improvements start with a commitment to the process (ISO 2012).
Flaws of the Model
As expected, the Dubai Quality Award has certain shortcomings. The first flaw is that EFQM lacks a means of quantifying improvement. This leads to a lack of precision in the outcomes of the EFQM model (Hansen 2010). This flaw is common in excellence model that address business processes rather than business outcomes. This does not mean that goal-oriented models are better. It also does not mean that process oriented models are not useful. However, the lack of a means to quantify quality is a major weakness. It can lead to perceived bias among the participants because there is no means of measuring improvement. This problem is significant for companies applying the model for the first time. It may be impossible for them to know how to rate certain aspects of their performance.
The second flaw associated with the Dubai Quality Award is its application across sectors. The quality award attempts to rate all companies based on the same standard. However, the use of a similar standard across different industries can lead to false categorization. The nature of businesses means that industries in certain industries have minor differences. For instance, the banking industry operates in highly regulated environments.
Other sectors such as the food and beverage industry have different presentations, evidenced by the famous star rating system used by hotels. Therefore, banks have an inherent bias when it comes to achieving the award simply because of the high degree of standardization in the sector. Also, mature industries tend to be better streamlined that young industries. The mining sector for instance has better quality standards compared to the IT sector simply because quality controls in the mining sector have evolved over many years. This means that the Dubai Quality Award cannot use the same standard for all industries.
The third limitation of the Dubai Quality Award is that it is difficult to quantify its overall economic benefits. A study done in the US showed that excellence awards did not lead to better performance on a state-by-state basis (Porter & Tanner 2012). It is extremely difficult to isolate the actual benefits in economic terms of the Dubai Quality Award to the country. Companies that win excellence awards indeed tend to outperform their peers in the years following the date of receiving of the award. However, the overall impact of such companies is insignificant at macro-economic level. This means that apart from the benefits accruing to the specific companies, the benefits that accrue to the overall economy may not justify the annual process of evaluating companies for the award.
The Dubai Quality Award also suffers from a misapplication. This means that the reasons for participating in the process vary from company to company. Some of the companies participate in the process for the wrong reasons. One example of this is that the award encourages competition among companies for the top prize. This is not inherently wrong except that it can lead to negative consequences. For instance, if a company makes winning the award its sole objective, it may not improve on excellence. This can create unbalanced companies working hard to win the quality award. The second challenge related to misapplication is that a company may try to improve all aspects of its operations at once (McCabe 2008). This is not good at the strategic level. Strategic management principles call for incremental changes rather than sudden system-wide adjustments (Cole 2003). In this regard, the Dubai Quality Award can harm a company rather than steer it towards excellence.
The final limitation of the Dubai Quality Award is its administrative structure. The current administrative structure has a supreme council largely composed of political and business leaders. While the supreme council can serve as an appellate body, it should not be the one making the final decisions in regards to the winners of the Dubai Quality Award. The assessors can make the decision on which companies deserve the award.
Benefits of the Model to the Organization
The excellence models are beneficial to organizations. Literature review showed that the contention is whether the benefits have economic significance at the macro-economic level. This section explores the benefits of the Dubai Quality Award to the Prime Healthcare Group. The benefits fall into four main categories. These categories include people results, customer results, society results, and business results. These result areas accrue from the EFQM model.
People Results
People results about the Dubai Quality Model refer to the human resource element of the organization. The model requires the organizations to develop performance indicators for all its employees to ensure that all the employees have clear goals. The continued participation of the company in the Dubai Quality Award means that all its employees have clear descriptions of the work.
The second people result accruing from the Dubai Quality Award for the company is that all its employees have clear goals related to the outcomes required from them. These outcomes arise from the needs of the patients and other stakeholders that benefit from the service offered by the company. The stakeholders of the company are sure about what to expect from the company. The company has a clear quality statement in regards to all its key services.
The third people result that the company enjoys is that is has a clear picture of the value created by each of its departments and strategic business units. This means that the company knows how well each of its departments is performing. This makes it easy to distribute resources to improve the performance of poorly performing department.
As part of the process towards the issuance of the Dubai Quality Award, the company must measure and document the performance of each member of staff. The benefit associated with this process is that promotion decisions are easy to make. Since the company can account for the performance of each member of staff, it can tell who deserves a promotion.
The company is also able to explain the trends affecting its human resource. This means that the company can explain the factors leading to attrition, and how best to retain top talent. Talent retention is one of the most challenging aspects of work in the modern economy. The demand for top talent is very high. Therefore, every company must do its best to retain its best talent. In this regard, the Dubai Healthcare Group has an upper hand in making staff retention decision.
Finally, the company has a clear picture of how its human resource compares that of other companies. This requirement means that the company not only knows how it is performing in regards to human resource management, but it can also rank itself based on the performance of its competitors.
Customer Results
Customer results refer to the outcomes the Dubai Healthcare Group should post in regards to caring for its customers. In this case, customers refer to the patients and medical personnel who use the services offered by the company. The key benefits of the Dubai Quality Award to the company’s customers are as follows.
First, the company now understands the needs of its customers. This partly explains why the company is planning to open two more health centres in Dubai. At the same time, it explains the decision by the company to operate corporate clinics for its major clients. The company realised that it can serve large clients better if it has a presence near the business premises of the corporate clients.
The second customer result that the Dubai Healthcare Group is currently enjoying because of participating in the Dubai Quality Award is that it has a clear set of objectives emanating from the needs of its clients. These objectives come from the understanding that clarity is essential when it comes to consumer needs (Porter 1991). This is enabling the company to develop its
The third benefit arising from the participation of the company in the Dubai Quality Award is increased confidence in the company. Customers now know that the company is committed to quality. This will make the company attractive to the quality conscious clients.
The final benefit accruing from the Dubai Quality Award in regards to customer results is that the company now has a long-term view of the needs of its customers. This means that the company is preparing to handle the strategic needs of existing customers and potential customers (Sahu 2009). The Dubai Healthcare group is planning to take advantage of the development of the Dubai Healthcare City by becoming one of the influential healthcare providers in the UAE.
Society Results
Every business must show commitment to sustainable business practices (Zokaei et al. 2013). In this regard, the Dubai Healthcare Group is benefiting from its participation in the Dubai Quality Award in the following ways.
First, the company has very clear goals related to sustainable business practices. It uses equipment that consumes the least electricity and generally seeks facility designs that conserve energy (Prime Healthcare Group 2013).
The second benefit of the Dubai Quality Award in regards to sustainability is that the company has clear objectives on sustainable business practices. The Dubai Quality Award requires companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable business. The main issues in Dubai of interest in sustainability are water and energy conservation. Every business with an interest in sustainable business practices must show its commitment towards the conservations of water and energy.
In the same vein, the company can now quantify its efforts in regards to sustainable business practices. This benefit goes beyond the award because sustainable business practices also lead to financial savings for every organization (Patzelt & Shepherd 2011). This means that if the Dubai Healthcare Group lives up to its sustainable business goals, then it will have a healthier bottom line.
Finally, the Dubai Healthcare Group now has a clear understanding of how sustainable business practices affect its operations. The benefits of sustainable business span the entire breadth of business activities. The company now knows the current, and the strategic benefits that will accrue from sustainable business practices.
Business Results
The final set of benefits that the Dubai Healthcare group enjoys because of participating in the Dubai Healthcare Group relates to the results of its business activities. The benefits accruing to the company are as follows.
First, the benefit that the Dubai Healthcare Group enjoys about business results is good publicity. The Dubai Healthcare Group won the award in 2012 (Prime Healthcare Group 2013). This gave the company international recognition and increased its profile. In this regard, the company’s brand name appreciated in the marketplace.
The second business result accruing to the company is that company has set very clear performance targets. This is one of the requirements of the Dubai Quality Award. Clear performance targets at every business level make it possible for the organization to determine whether it is performing well. Lack of clear performance targets is one of the main reasons why companies perform poorly (Porter 1998).
The third benefit is that the company now has very clear ideas about its sources of competitive advantage. Competitive advantages enable business to stay ahead of their competitors (Pearce 2005). Failure to know a business’s competitive advantages reduces the possibility of performing well in business. The participation of the company in the Dubai Quality Award made it possible for the company to know its strengths in the marketplace.
The fourth business result that company posted because it participated in the Dubai Quality Award is that it identified the key issues it needs to address to become an international player. Since the Dubai Quality Award is an offset of EFQM, the company can compare itself to any European company. This means that the award increased its profile. Potentially, this will have an impact on the source markets of the company’s customers.
The final benefit accruing to the Dubai Healthcare Group based on its participation in the Dubai Quality Award is that the company has a better understanding of the healthcare market (Bryman & Bell 2011). This means that the company can deploy better business strategies to meet its business objectives. One of the benefits of excellence models is that they give participating companies the opportunities to benchmark their performance with companies from other jurisdictions (Davies & Davies 2011). The benchmarking process makes it easy for the company to develop better business goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, excellence awards are good for businesses. However, there is need to find out whether they have any impact at the macro-economic level. It is also important for every business to clarify its reasons for participating in the excellence award. Having the wrong reasons can lead to very poor results.
Reference List
Bryman, A & Bell, E 2011, Business Research Methods, 3rd edn, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Cole, GA 2003, Strategic Management, Cengage Learning, Mason, OH.
Davies, RH & Davies, AJ 2011, Value Management: Translating Aspirations Into Performance, Gower Publishing, Surrey.
EFQM 2013, Model Criteria. Web.
Government of Dubai 2012, About DQA. Web.
Hansen, EG 2010, Responsible Leadership Systems: An Empirical Analysis of Integrating Corporate Responsibility into Leadership Systems, Springer, Berlin.
ISO 2012, Quality Management Principles, ISO Central Secretariat, Geneva.
Kanji, GK 2012, Measuring Business Excellence, Routledge, New York.
McCabe, S 2008, Benchmarking in Construction, John Wiley & Sons, London.
Patzelt, H & Shepherd, DA 2011, ‘Recognizing Opportunities for Sustainable Development’, Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, vol 10, no. 11, pp. 631-652.
Pearce, JA 2005, Strategic Management: Formulation, Implementation, and Control, McGraw-Hill , New York.
Porter, ME 1991, ‘Competitive Advantage’, in CA Montgomery, ME Porter (eds.), Strategy: Seeking and Securing Competitive Advantage, Harvard Business School Publishing Division, Boston, MA.
Porter, ME 1998, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance, Simon and Schuster, New York.
Porter, L & Tanner, S 2012, Assessing Business Excellence, Routledge, New York.
Premier Diagnostic Centre 2013, Overview. Web.
Prime Healthcare Group 2013, About Us. Web.
Sahu, RK 2009, Performance Management System, Excel Books, New Delhi.
The Oxford Business Group 2008, The Report: Dubai 2008, Oxford Business Group, Dubai.
Verweire, K & Berghe, L 2004, Integrated Performance Management: A Guide to Strategy Implementation, Sage, London.
Zokaei, KA, Lovins, HL, Wood, A & Hines, P 2013, Creating a Lean and Green Business System: Techniques for Improving Profits and Sustainability, Productivity Press, Parkway NW.